
●●● ●●●● To conclude -1 ●●●●● ●●●0 Lossless ●●●●0 Y=(R+j@L)(G+j@C) joLC=a+j ●●●0 §2.1 Transmission line ●●●0 > R+joL ●● Vc 红0 e自 edu,力 NG+joC 2π 2π 1 0 = (.) GA: B√C LC fLC I(-0 Z气+2g1 V(-) Z+jZotgBI V VSWR= max 1+=S 1-r Zo:B 0 =R+R4x+X可 R+joL G+j@C §2.2The,Smith.Chart 不。 B>0 容性 感性 T= le/-w Z-1 B=05 B=1 G=0. G=1 (0,0) (1,0 (0,∞) Ta 1+r (0,0) (1,0) 匹配点 短路点 匹配点 开路点 S 1- 开路点 短路点 B=- 电压波刊 电压波腹 1+ 电流波节 电流波腹 Rmin-K Rmax-S Gmin-K B=-0. Gmax-S <0容性 1-r B<ol 感性 1
To conclude - 1 §2.1 Transmission line §2.2 The Smith Chart 1 0 R j ωL L Z G j ωC C Lossless ( )( ) R j L G j C j LC j 0 R jL L Z G jC C 22 1 LC f LC 1 p v LC max min 1 1 V VSWR S V L 0 0 0 ( ) ( ) in L V l Z jZ tg l Z Z I l Z jZ tg l 2 2 2 1 2 ( )( ) in l g in g in g R P V RR X X 1 4 1 L j l L Z e Z 1 1 S 1 1 Z
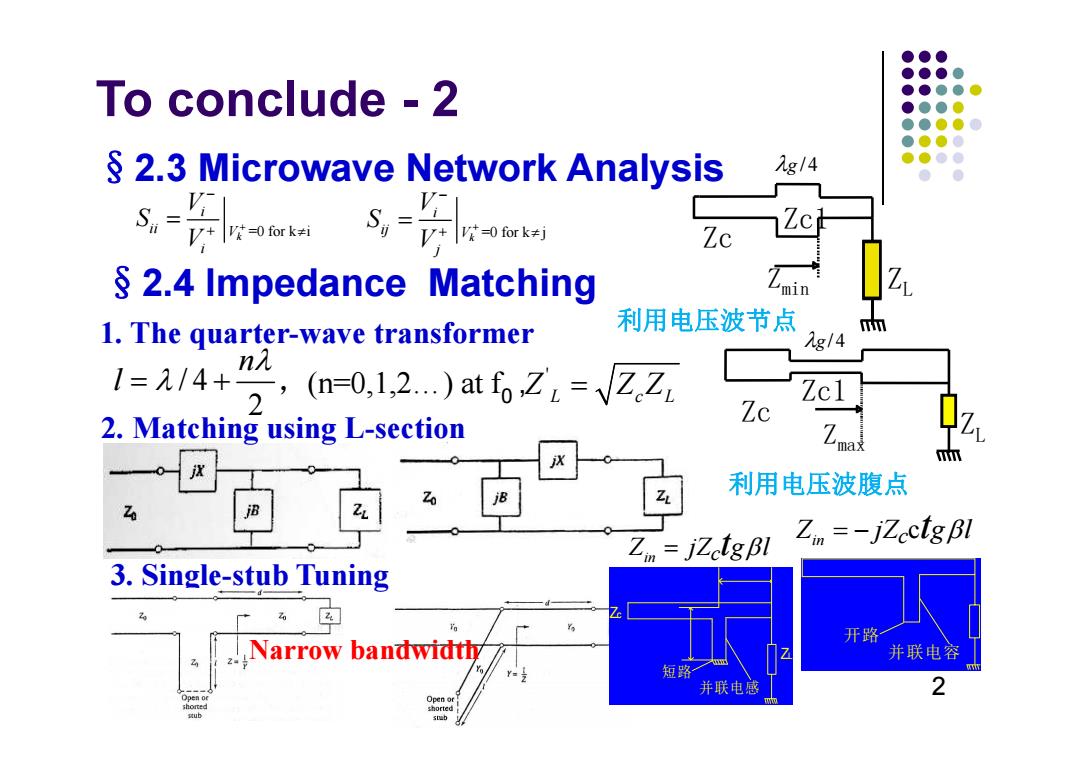
●●● ●●●● To conclude -2 ●●●● ●●●● ●●●●0 ●●●● S 2.3 Microwave Network Analysis 2g/4 ●●●● ● Zc S 2.4 Impedance Matching min 1.The quarter-wave transformer 利用电压波节点 g/4 1=A/4+2,a-012)t6Z.=2☑ n Zcl 2.Matching using L-section Zc 流 利用电压波腹点 Zin jZctgBl Zin =-jZectg Bl 3.Single-stub Tuning 肉 Narrow bandwidtly 开路 并联电容 短路 并联电感 2 Open o shorted
To conclude - 2 3. Single-stub Tuning / 4 2 n l ' , Z L Z Zc L (n=0,1,2…) at f0 , Narrow bandwidth 2. Matching using L-section 1. The quarter-wave transformer §2.4 Impedance Matching 2 §2.3 Microwave Network Analysis 利用电压波节点 g / 4 Zc Zmin Z L Zc1 利用电压波腹点 Zmax Z L Zc1 Zc g /4 开路 并联电容 短路 并联电感 Zc ZL =0 for k i k i ii V i V S V =0 for k j k i ij V j V S V c Zin c j Z tg l Zin c jZ g l t

5 ● To conclude -3 ● 56.0 ● Impedance Matching ● ● g/4 Z C1 g/4 R>Z 电路结构 Z Zer R g14 RZe R.<Zc 3
To conclude - 3 Wide bandwidth Impedance Matching 3

●●● Microwave and RF ●●●● ●●●● ●●●● ●●●● ●●●● Design of Wireless ●●●● ● Systems Chapter 3 Noise and Distortion in Microwave system 微波系统中的噪声和失真 Dr.Xian Qi Lin 5
Microwave and RF Design of Wireless Systems Noise and Distortion in Microwave System 微波系统中的噪声和失真 Chapter 3 Dr. Xian Qi Lin 5

●●● ●●●● ●●●● ●●●● ●●●● Noise determines the threshold for the minimum ●●●0 ●●● signal level that can be reliably detected by a receiver. 噪声决定了一个接收机中能够被检测的最小信号电平 Source来源: 1.Generated internally by the receiver circuitry, such as thermal noise.来自于接收机内部电路,比如热噪声 2.From external environment,such as atmosphere, interstellar,man-nade interference..来自于外部,比如大气、星 际和人为的干扰。 ●Noise is a random process..噪声是一个随机过程 6
Noise determines the threshold for the minimum signal level that can be reliably detected by a receiver. 噪声决定了一个接收机中能够被检测的最小信号电平 Source来源: 1. Generated internally by the receiver circuitry, such as thermal noise.来自于接收机内部电路,比如热噪声 2. From external environment, such as atmosphere, interstellar, man-made interference.来自于外部,比如大气、星 际和人为的干扰。 Noise is a random process.噪声是一个随机过程 6

●●● ●●●● S 3.1 Review of Random Processes ●●●● ●●●● ●●●● 随机过程回顾 ●●●● ●●●● §3.2 Thermal Noise热噪声 §3.3 Noise in Linear System线性系统中的噪声 §3.4 Basic Threshold Detection基本的门限检测 3.5 Noise Temperature and Noise Figure 噪声温度和噪声系数 3.6 Noise Figure of Passive Networks 无源网络的噪声系数 3.7 Dynamic Range and Intermodulation Distortion 动态范围和交调失真 7
§3.1 Review of Random Processes 随机过程回顾 §3.2 Thermal Noise 热噪声 §3.3 Noise in Linear System 线性系统中的噪声 §3.4 Basic Threshold Detection 基本的门限检测 §3.5 Noise Temperature and Noise Figure 噪声温度和噪声系数 §3.6 Noise Figure of Passive Networks 无源网络的噪声系数 §3.7 Dynamic Range and Intermodulation Distortion 动态范围和交调失真 7

●● 3.1 Review of Random Processes ●● ●●● ●●● 概率与随 ●●●● (I)Probability and Random Variables机变量 -∞<Xo<+∞,PX=X}=0;0≤PX≤X}≤1; (2)The Cumulative Distribution Function 累积分布函数 Fx(X)=PX≤x;P{X1≤X≤x2}=Fx(X2)-Fx(K1)i (3)The Probability Density Function概率密度函数 fx=dFx()/dx;px<X≤x,}=∫f(w)d∫f.(dx=l (4)Some Important Probability Density Functions Uniform distribution:(x)= ,for a≤x≤b均匀分布 b-a Gaussian distribution: f(x)= e-(x-mi12o,for -0≤X≤+0 Rayleigh distribution: V2πo2 高斯分布 r 瑞利分布 (x)=京e "for 0≤x≤+0 8
2 2 ( ) /2 2 1 ( )= , 2 x m x f x e for x 1 ( )= , b-a x f x for a x b §3.1 Review of Random Processes (1) Probability and Random Variables -∞<x 0<+ ∞ , P{X=x 0}=0; 0 ≤ P{X≤x 0} ≤1; (2)The Cumulative Distribution Function F X(x)=P{X ≤ x}; P{x1 ≤ X ≤x2 }=F X(x 2)-F X(x 1); (3)The Probability Density Function fX(x)=dF X(x)/dx; (4) Some Important Probability Density Functions Uniform distribution: Gaussian distribution: Rayleigh distribution: 2 1 x + 1 2 x P{x <X x }= ( ) ; ( ) 1 x x f x dx f x dx 2 2 /2 2 r ( )= , 0 r x f x e for x 8 概率与随 机变量 累积分布函数 概率密度函数 均匀分布 高斯分布 瑞利分布

●●● ●●●● ●●●●● (5)Expected Values ●●●● 期望值 ●●●● ●●●● =EX)=[xf(x)dx,EfeX)=cE(X).E(X+Y)=E(X)+E(Y) ●●●● Variance,o2=E{(x-x))=(x-x)f (x)dx 自相关及功率谱密度 (6)Autocorrelation and Power Spectral Density Deterministic Signal:R()=x(t)x(t+dt;R(0)2R(),R()=R() Random Signal:R()=E{x (t)x(t+)} Power Spetral Density:S(@)=R()ed--Fourier transform of R() R)=2a」s(eede ac时Rmer月-7-r20-&0-2 .(eo V2(t) Z 9
2 2 { } ( ) , { } { }, { } { } { } , {( )} ( ) ( ) x x x E X xf x dx E cX cE X E X Y E X E Y Variance E x x x x f x dx * * Deterministic Signal: ( ) ( ) ( ) ; (0) ( ), ( ) ( ) Random Signal: ( ) { ( ) ( )} R x t x t dt R R R R R E x t xt 2 2 Power Spetral Density: ( ) ( ) Fourier transform of ( ) 1 () ( ) ; 2 ( ) ( ( )) 1 (0) Received Power: ( ) 2 j j V j L V LL LL S Re d R R S ed V t EV t R P S ed ZZZZ (5)Expected Values (6)Autocorrelation and Power Spectral Density 9 期望值 自相关及功率谱密度

●●● ●●● §3.2 Thermal Noise ●●●● ●●●● ●●●● ●●●● 1Thermal noise is caused by the random motion of charge carriers.噪声由电荷的随机运动产生 2Other sources of noise include shot noise,flicker noise,plasma noise,,and quantum noise..噪声的其它来源 包括散弹噪声、闪烁噪声、等离子噪声和量子噪声 3Although these types of noise differ from thermal noise in terms of their origin,their characteristics are similar.尽管这些噪声的来源不同于热噪声,它们的特点相同。 10
§3.2 Thermal Noise ①Thermal noise is caused by the random motion of charge carriers. 噪声由电荷的随机运动产生 ②Other sources of noise include shot noise, flicker noise, plasma noise, and quantum noise.噪声的其它来源 包括散弹噪声、闪烁噪声、等离子噪声和量子噪声 ③Although these types of noise differ from thermal noise in terms of their origin, their characteristics are similar.尽管这些噪声的来源不同于热噪声,它们的特点相同。 10
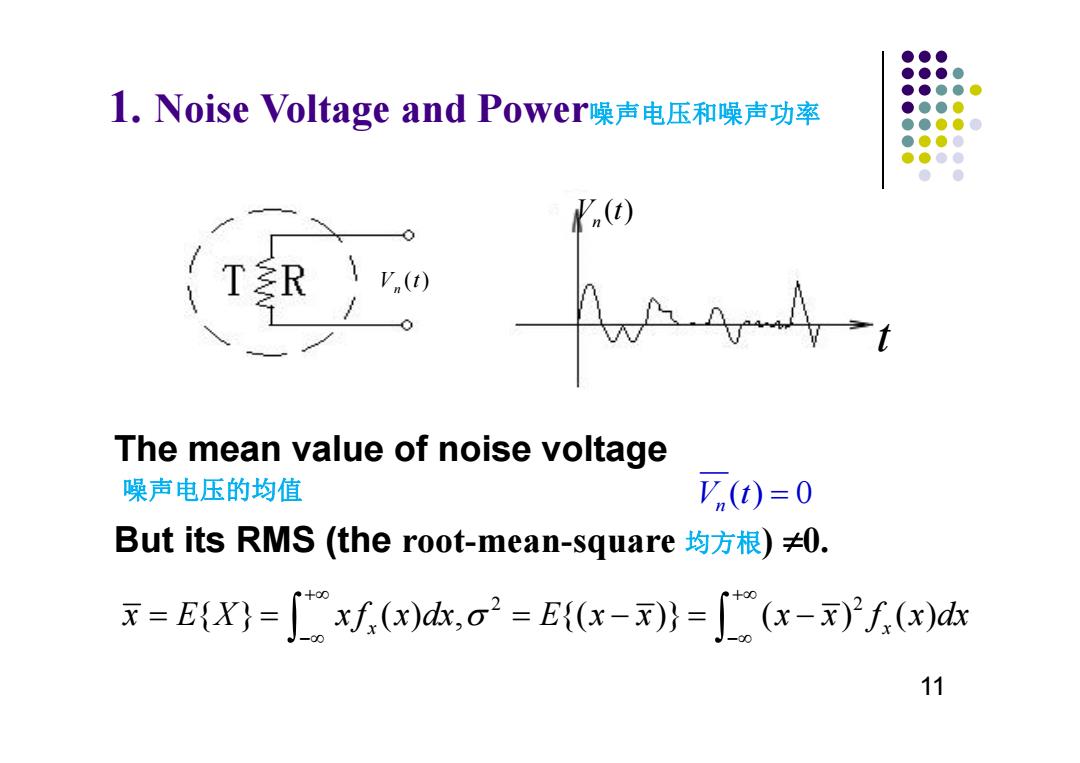
●●● ●●●● ●●●●● l.Noise Voltage and Poweri噪声电压和噪声功率 ●●●0 ●●●●0 ●●●0 ●●●● ●● The mean value of noise voltage 噪声电压的均值 ()=0 But its RMS(the root-mean-square均方根)≠0. =E)=xf(x)dx,o2=E((x-x))=(x-x)f(x)dx 11
1. Noise Voltage and Power噪声电压和噪声功率 The mean value of noise voltage 噪声电压的均值 () 0 V t n ( ) V t n ( ) V t n t 2 2 { } ( ) , {( )} ( ) ( ) x x x E X x f x dx E x x x x f x dx But its RMS (the root-mean-square 均方根) 0. 11