
●●● ●●●● ●●●● Microwave and RF Design of ●●●● ●●●●0 ●●●0 ●●●● ● ● Wireless Systems Chapter 10 Receiver Design 接收机设计 Dr.Xian Qi Lin 1
Microwave and RF Design of Wireless Systems Chapter 10 Receiver Design 接收机设计 Dr. Xian Qi Lin 1

●●● ●●●● ●●● ●●● The purpose of receiver:recovering the desired ●●● ●●0 ●●●● signal from a wide spectrum of transmitting sources,interference,and noise. 接收机的目的:从发射信号、干扰和噪声中恢复所需的信号。 §l0.1 Receiver Architectures接收机的结构 §10.2 Dynamic Range动态范围 §10.3 Selection of IF Frequency中频选择 2
The purpose of receiver: recovering the desired signal from a wide spectrum of transmitting sources, interference, and noise. 接收机的目的:从发射信号、干扰和噪声中恢复所需的信号。 §10.1 Receiver Architectures 接收机的结构 §10.2 Dynamic Range 动态范围 §10.3 Selection of IF Frequency 中频选择 2

●●●】 ●●●● ●●●● S 10.1 Receiver Architectures ●●●● ●●●● ●●●● ●●●● ●● 1.Receiver Requirements 接收机需求 2.Tuned Radio Frequency Receiver 射频调谐接收机 3.Direct Conversion Receiver 直接变换接收机 4.Superheterodyne Receiver 超外差接收机 5.Deplexing双t 3
§10.1 Receiver Architectures 1. Receiver Requirements 接收机需求 2. Tuned Radio Frequency Receiver 射频调谐接收机 3. Direct Conversion Receiver 直接变换接收机 4. Superheterodyne Receiver 超外差接收机 5. Deplexing 双工 3

●●● ●●●● ●●●●心 1.Receiver Requirements ●●●● ●●●● ●●●● ①High gain高增益(~l00dB): ●●●● ●● Spread over the RF,IF and baseband stages to avoid instability or oscillation. 在射频、中频和基带级分配增益,避免不稳定或自激 Avoid more than 50~60dB of gain at any one frequency. 避免在任何一个频率上增益超过50~60dB。 ②Selectivity选择性:it is more effective to use a sharp cutoff BPF at IF stage to select only the desired frequency band. 在中频级采用具有陡峭截止特性的带通滤波器选出需要的频率。 ③Down-conversion.下变频 ④Detection.检测 ⑤Isolation.隔离Duplexing filter双工滤波 4
① High gain高增益(~100 dB): Spread over the RF, IF and baseband stages to avoid instability or oscillation. 在射频、中频和基带级分配增益,避免不稳定或自激 Avoid more than 50~60dB of gain at any one frequency. 避免在任何一个频率上增益超过50~60dB。 ② Selectivity选择性: it is more effective to use a sharp cutoff BPF at IF stage to select only the desired frequency band. 在中频级采用具有陡峭截止特性的带通滤波器选出需要的频率。 ③ Down-conversion.下变频 ④ Detection.检测 ⑤ Isolation.隔离Duplexing filter双工滤波 1.Receiver Requirements 4
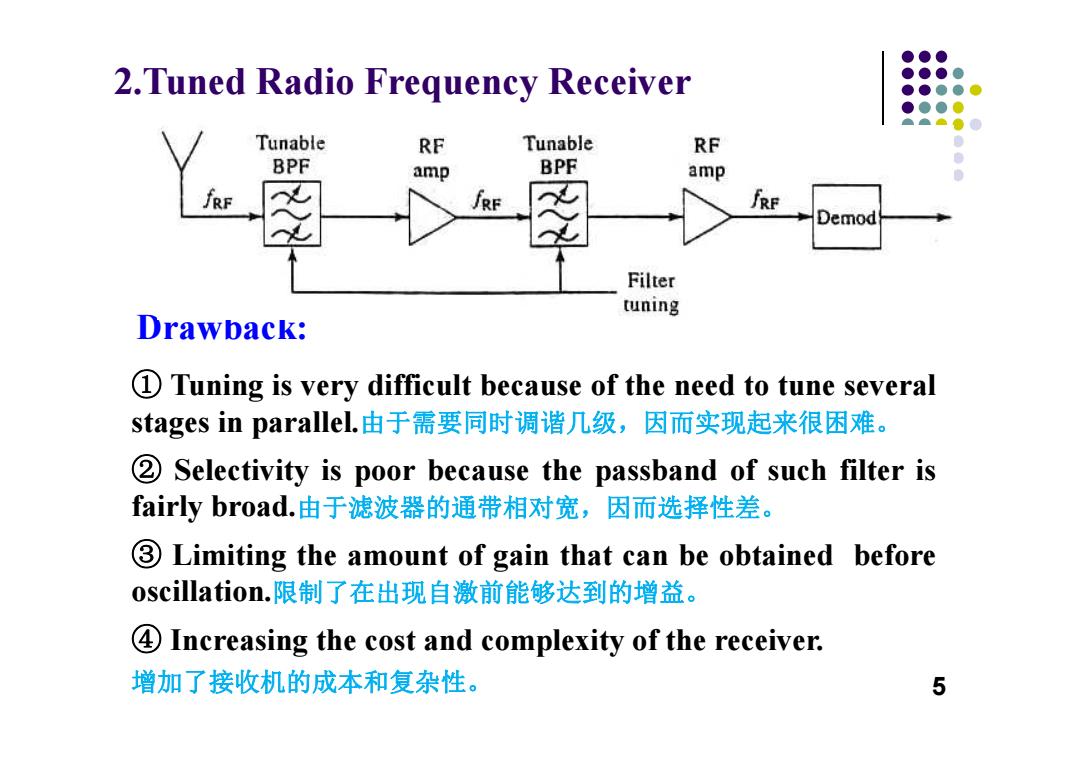
●●● 2.Tuned Radio Frequency Receiver ●●●● ●●●● ●●●● Tunable RF Tunable RF BPF amp BPF amp ● fRF Demod Filter tuning Drawback: 1 Tuning is very difficult because of the need to tune several stages in parallel..由于需要同时调谐几级,因而实现起来很困难。 2 Selectivity is poor because the passband of such filter is fairly broad.由于滤波器的通带相对宽,因而选择性差。 3 Limiting the amount of gain that can be obtained before oscillation.限制了在出现自激前能够达到的增益。 4 Increasing the cost and complexity of the receiver. 增加了接收机的成本和复杂性。 5
① Tuning is very difficult because of the need to tune several stages in parallel.由于需要同时调谐几级,因而实现起来很困难。 ② Selectivity is poor because the passband of such filter is fairly broad.由于滤波器的通带相对宽,因而选择性差。 ③ Limiting the amount of gain that can be obtained before oscillation.限制了在出现自激前能够达到的增益。 ④ Increasing the cost and complexity of the receiver. 增加了接收机的成本和复杂性。 2.Tuned Radio Frequency Receiver Drawback: 5

To conclude-1 ●●● ●●●● ●●●●● Effect of Rayleigh Fading on Bit Error Rats ●●●● ●●●●0 Rayleigh PDF:f(r)=re-/a2 P(r)lsy.PSK=[1-/1+)]/2 P.(r)lSyn.ASK=[1-VT/(4+T)]/2 P-(r)lsyn.FSK=[1-/(2+T)]/2 Pe(r)INonc.FSK=1/(2+r) 10° 10 T= 2a2Ep Nonfaded case: no 10-2 Faded 2a2=1T=E6/n0 10-3 104 Nonfaded △EXAMPLE 10-3 -Coherent PSK ---Noncoherent FSK 9.4,page.323. 106 107 -10 0 10 20 30 40 r=2a2E,/no(dB) 6
6 Nonfaded case: Effect of Rayleigh Fading on Bit Error Rats To conclude-1 Syn.PSK ( ) | [1 / (1 )] / 2 P r e Syn.FSK ( ) | [1 / (2 )] / 2 P r e Syn.ASK ( )| [1 / (4 )] / 2 P r e Nonc.FSK ( ) | 1/ (2 ) P r e 2 0 2 Eb n 2 2 /2 2 Rayleigh PDF: ( ) / r rf r re 2 0 21 / Eb = n Δ EXAMPLE 9.4, page. 323

To conclude-2 ●●● ●●●● ●●●●● ●●●0 M-ary Digital Modulation ●●●●0 ●●●0 ●●●● M=25 T6=1/R n=5 =M=32 distinct symbols; S1 S1 t Symbol rate:Rs;Bit rate:Rp=5 Rs S2 Bandwidth efficiency:n bps/Hz T,=1/R,=5/R M=2",bitnary:n=1,M=2symbols(0,1) R LPF ◆QPSK Binary Store cos wot data(NRZ) two bits 50) Rp bits/s (serial to parallel) sino R,= symbols/s p=p0= erfc( E 2n0 LPF P(s)=1-(1-P()(1-p)2P()=erfc(E,/2n) ed-P.byrsk E,=2E。 Bandwidth efficiency is 2 bps/Hz. 7
7 To conclude-2 M-ary Digital Modulation n=5 => M=32 distinct symbols; Symbol rate: Rs; Bit rate: Rb=5 Rs Bandwidth efficiency: n bps/Hz 1/ 5/ TR R ss b 1/ T R b b 1s 2s 2s 2s 1s t M=25 2 , : 1, 2 (0,1) n M bitnary n M symbols QPSK () ( ) 0 1 ( ) 2 2 I Q s e e E P P erfc n () () ( ) () 0 1 (1 )(1 ) 2 ( / 2 ) s I QI Pe eee s P P P erfc E n ( ) 0 Syn.PSK 1 ( /) | 2 e P erfc E n P e be ( ) 0 1 () 2 2 2 e s e sb E P erfc E E n Bandwidth efficiency is 2 bps/Hz
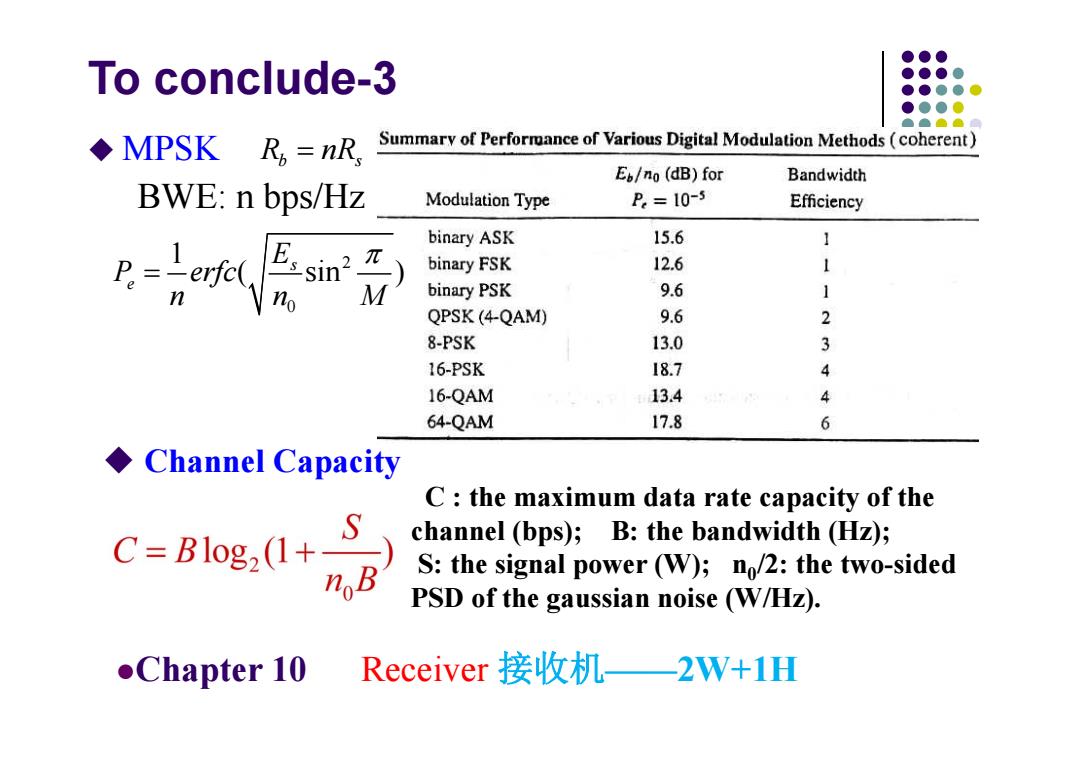
●●● To conclude-3 ●●●● ●●●● ●●●● ◆MPSK R,=nR, Summary of Performance of Various Digital Modulation Methods(coherent) E/no(dB)for Bandwidth BWE:n bps/Hz Modulation Type P.=10-5 Efficiency binary ASK 15.6 1 binary FSK 12.6 1 binary PSK 9.6 1 QPSK(4-QAM) 9.6 2 8-PSK 13.0 3 16-PSK 18.7 4 16-QAM 13.4 4 64-QAM 17.8 6 ◆Channel Capacity C:the maximum data rate capacity of the C=B1og2(1+ channel (bps);B:the bandwidth (Hz); noB S:the signal power (W);n/2:the two-sided PSD of the gaussian noise (W/Hz). Chapter 10 Receiver接收机—2W+1H
To conclude-3 BWE: n bps/Hz MPSK Channel Capacity C : the maximum data rate capacity of the channel (bps); B: the bandwidth (Hz); S: the signal power (W); n0/2: the two-sided PSD of the gaussian noise (W/Hz). Rb s nR 2 0 1 ( sin ) s e E P erfc n nM Chapter 10 Receiver 接收机——2W+1H

To continue ●●● ●●●● ●●●●● ●●●0 ●●●●0 ●●●0 ●●●● ●● ●Chapter 10 Receiver Design接收机设计 9
To continue 9 Chapter 10 Receiver Design 接收机设计
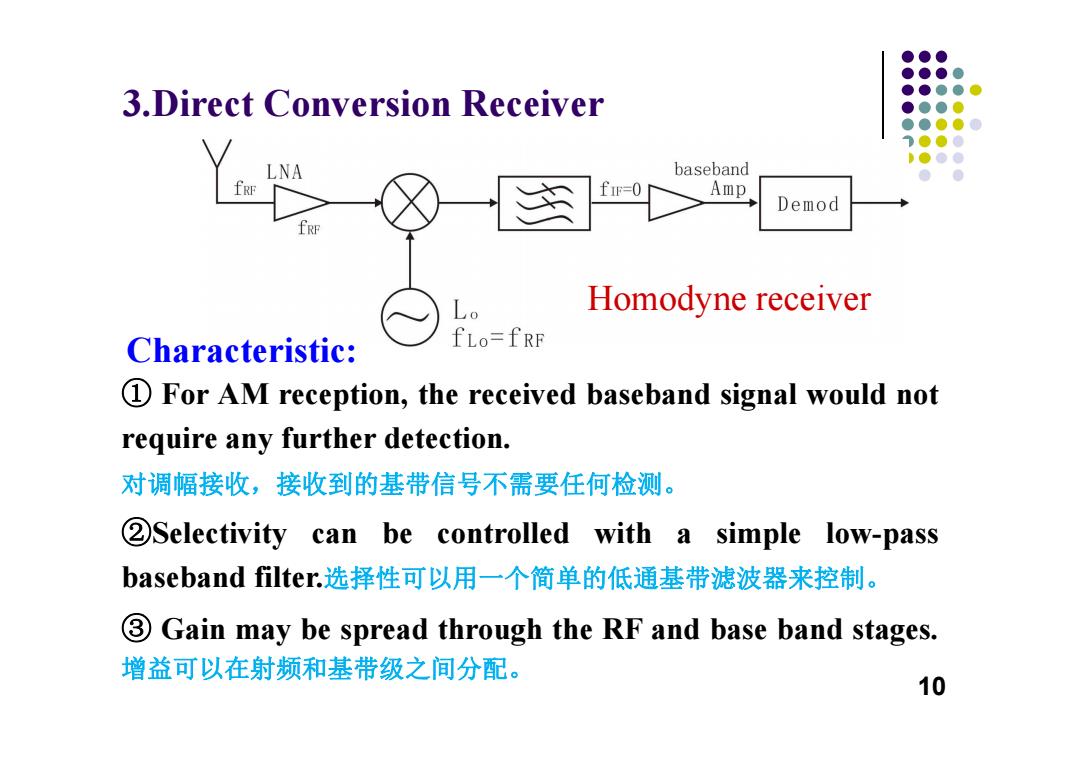
●●● ●●●● ●●●● 3.Direct Conversion Receiver ●●● ●●●●● 1●●● ●●色 LNA baseband ● fRF fIF=0 Amp Demod fRF Lo Homodyne receiver Characteristic: fLo=fRF 1 For AM reception,the received baseband signal would not require any further detection. 对调幅接收,接收到的基带信号不需要任何检测。 2Selectivity can be controlled with a simple low-pass baseband filter.选择性可以用一个简单的低通基带滤波器来控制。 3 Gain may be spread through the RF and base band stages. 增益可以在射频和基带级之间分配。 10
3.Direct Conversion Receiver ① For AM reception, the received baseband signal would not require any further detection. 对调幅接收,接收到的基带信号不需要任何检测。 ②Selectivity can be controlled with a simple low-pass baseband filter.选择性可以用一个简单的低通基带滤波器来控制。 ③ Gain may be spread through the RF and base band stages. 增益可以在射频和基带级之间分配。 Characteristic: Homodyne receiver 10