
电子科学与工程学院 95 1.2典型辐射问题的解析方法 从显
1.2典型辐射问题的解析方法

一、天线的基本原理及参数
一、天线的基本原理及参数

What is an antenna? The IEEE Standard Definitions of Terms (IEEE Std 145-1983): ●“A means for radiating or receiving radio waves” "An antenna is any device that converts electronic signals to electromagnetic waves (and vice versa)"effectively with minimum loss of signals,as shown in Fig.1. EM Waves Portion of radio wave intercepted by receiving antenna Transmitting Receiving antenna antenna Transmission Transmission line line Transmitter Receiver Electronic Electronic Figure 1.Wireless communication system
What is an antenna? The IEEE Standard Definitions of Terms (IEEE Std 145-1983): “A means for radiating or receiving radio waves” “An antenna is any device that converts electronic signals to electromagnetic waves (and vice versa)” effectively with minimum loss of signals, as shown in Fig.1. Figure 1. Wireless communication system

1.Radiation Mechanism(辐射机理 "to create radiation,there must be a time-varying current or an acceleration(or deceleration)of charge" 1.Single wire If a charge is not moving,current is not created and there is no radiation. If charge is moving with a uniform velocity: a.There is no radiation if the wire is straight,and infinite in extent. b.There is radiation if the wire is curved,bent,discontinuous,terminated,or truncated If charge is oscillating in a time-motion,it radiates even if the wire is straight. 乡 (c)Discontinuous 纱 (a)Curved 乡 (d)Terminated Ground (b)Bent 奇 乡 (e)Truncated
1. Radiation Mechanism(辐射机理) “to create radiation, there must be a time-varying current or an acceleration (or deceleration) of charge” If a charge is not moving, current is not created and there is no radiation. If charge is moving with a uniform velocity: a. There is no radiation if the wire is straight, and infinite in extent. b. There is radiation if the wire is curved, bent, discontinuous, terminated, or truncated If charge is oscillating in a time-motion, it radiates even if the wire is straight. 1. Single wire
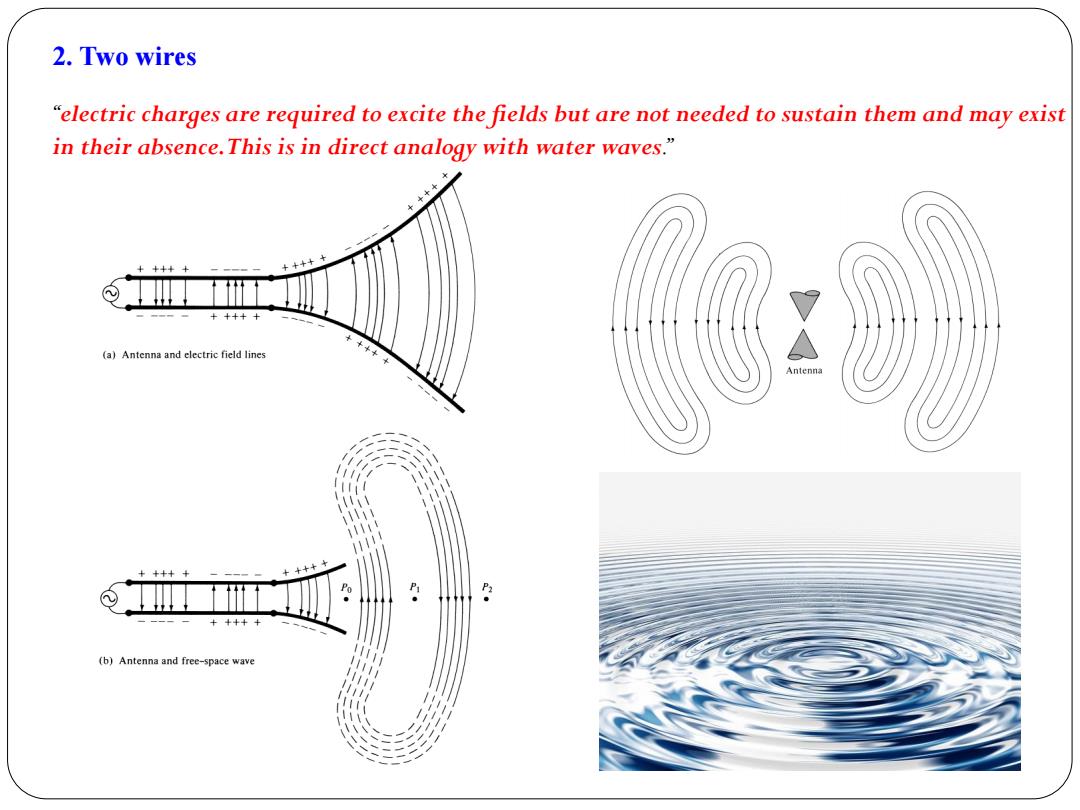
2.Two wires "electric charges are required to excite the fields but are not needed to sustain them and may exist in their absence.This is in direct analogy with water waves." +++++ +++++ (a)Antenna and electric field lines Antenna +++++ ++++ P ● +++++ (b)Antenna and free-space wave
2. Two wires “electric charges are required to excite the fields but are not needed to sustain them and may exist in their absence. This is in direct analogy with water waves

+中 (a)【=T/4(T=period) (b)t=T/2 (T=period) /2 (c)t=T/2 (T=period)
++++-----+
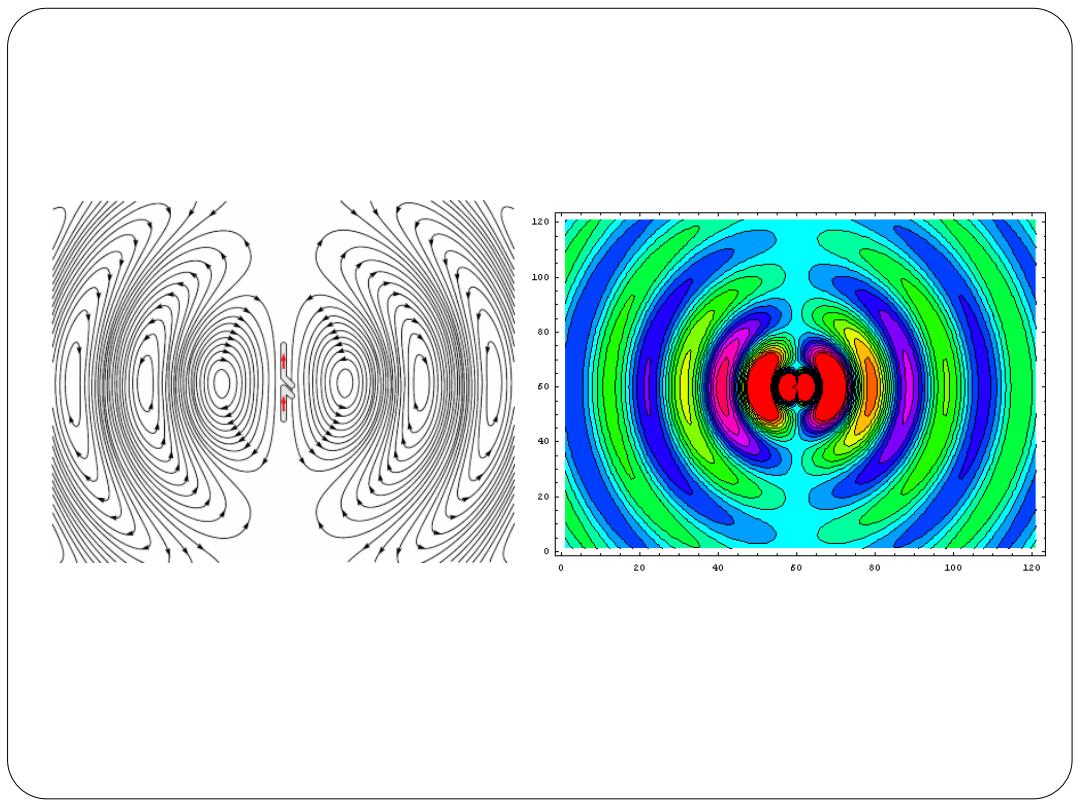
120 2>> 100 80 60 20 0 20 40 60 80 100 120
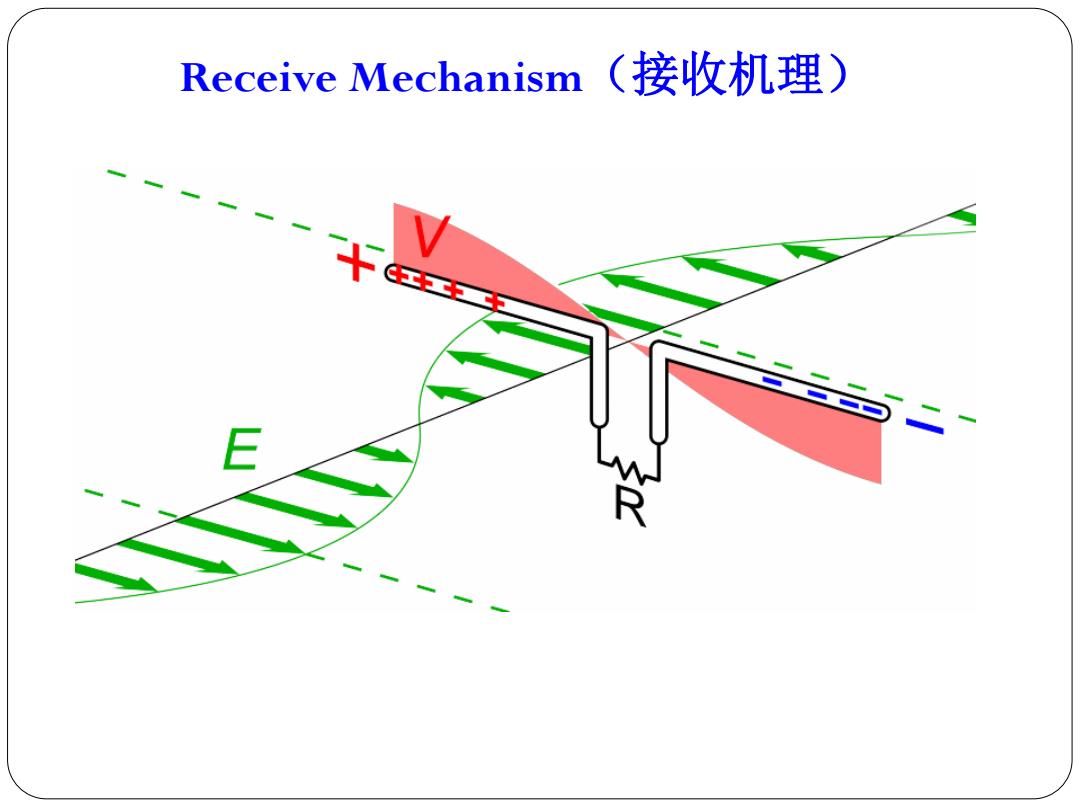
Receive Mechanism(接收机理 C工C王 R
Receive Mechanism(接收机理)

2.天线分类 1.按工作性质分类可分为发射天线、接收天线和收发共用天线。 2.按用途分类 有通信天线、广播天线、电视天线、雷达天线、导航天线、测向天线等。 3.按天线特性分类 ■ 从方向性分:有强方向性天线、弱方向性天线、定向天线、全向天线、 针状波束天线、扇形波束天线等。 ■从极化特性分:有线极化天线、圆极化天线和椭圆极化天线。线极化天 线又分为垂直极化和水平极化天线。 ■从频带特性分:有窄频带天线、宽频带天线和超宽频带天线。 4.按天线上电流分布分类有行波天线、驻波天线。 5.按使用波段分类 有长波、超长波天线、中波天线、短波天线、超短波天线和微波天线。 6.按载体分 有车载天线、机载天线、星载天线,弹载天线等。 7.按天线外形分类 有鞭状天线、T形天线、Γ形天线、V形天线、菱形天线、环天线、螺旋天 线、波导口天线、波导缝隙天线、喇叭天线、反射面天线等
2. 天线分类
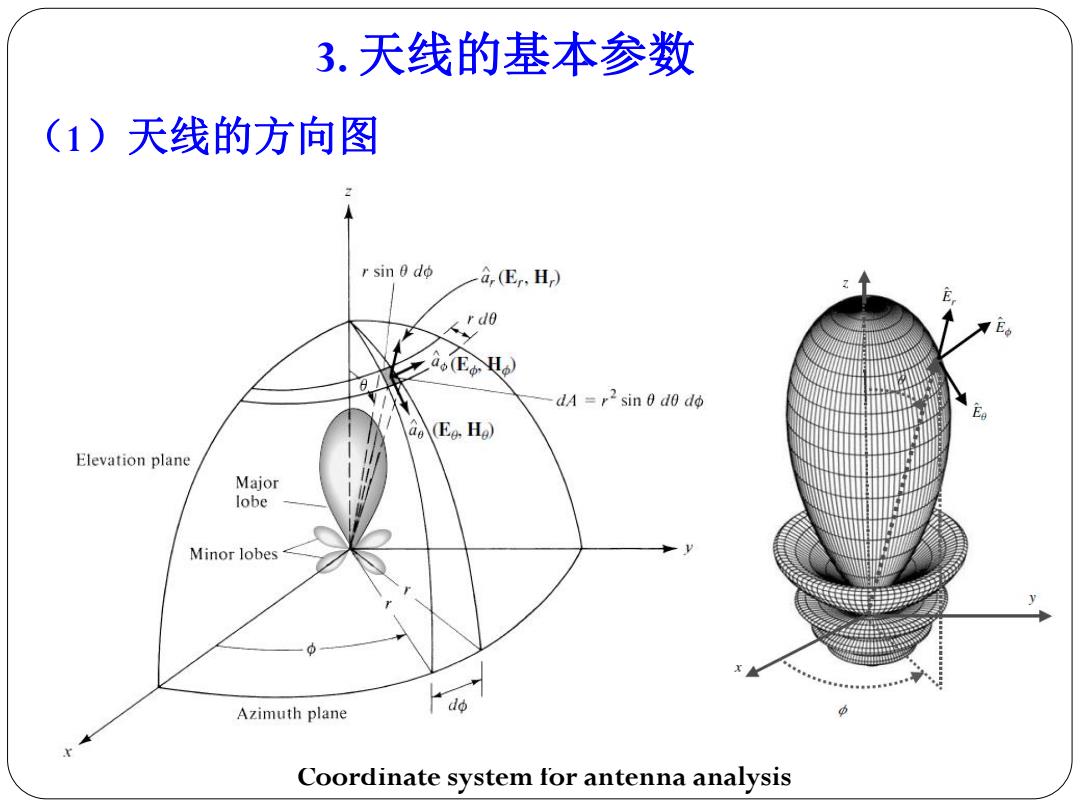
3.天线的基本参数 (1)天线的方向图 r sin 0 do a,Er.H) E rdo aoE H) dA =r2 sin 0 do do (E.H) Elevation plane Major lobe Minor lobes Azimuth plane do Coordinate system for antenna analysis
3. 天线的基本参数 Coordinate system for antenna analysis (1)天线的方向图