
第十一章 植物的逆境生理 Stress Physiology 芦苇
第十一章 植物的逆境生理 Stress Physiology 芦苇

第一节 抗性生理通论 第十一章 植物的逆境生理 第二节 植物的抗寒性 第三节 植物的抗旱性 第四节 植物的抗盐性
第一节 抗性生理通论 第十一章 植物的逆境生理 第二节 植物的抗寒性 第三节 植物的抗旱性 第四节 植物的抗盐性

重点 1.植物在逆境下形态结构与生理生化代谢变化 2.高低温对植物伤害及抗寒,耐热机理及途径 3.干旱,湿涝,盐碱对植物伤害及抗旱,抗涝,抗盐碱机理及途径 4.大气污染的种类及对植物伤害特点 5. 抗逆生理与农业生产关系, 掌握提高作物抗逆性途径
重点 1.植物在逆境下形态结构与生理生化代谢变化 2.高低温对植物伤害及抗寒,耐热机理及途径 3.干旱,湿涝,盐碱对植物伤害及抗旱,抗涝,抗盐碱机理及途径 4.大气污染的种类及对植物伤害特点 5. 抗逆生理与农业生产关系, 掌握提高作物抗逆性途径

所有对植物生命活动不利的环境条件统称为逆境(Stress) 第一节 抗性生理通论 1、逆境、胁迫(强)与胁变 逆境种类 物理的,如旱、涝、冷、热等; 化学的,如盐、碱、空气污染等; 生物的,如病、虫害等。 逆境生理(Stress physiology): 研究逆境对植物伤害以及植物对 逆境的适应与抵抗能力的科学。 一. 逆境及植物的抗逆性 沙枣
所有对植物生命活动不利的环境条件统称为逆境(Stress) 第一节 抗性生理通论 1、逆境、胁迫(强)与胁变 逆境种类 物理的,如旱、涝、冷、热等; 化学的,如盐、碱、空气污染等; 生物的,如病、虫害等。 逆境生理(Stress physiology): 研究逆境对植物伤害以及植物对 逆境的适应与抵抗能力的科学。 一. 逆境及植物的抗逆性 沙枣

胁迫(强)与胁变 随胁迫强度不同,胁变程度有差异 弹性胁变:程度轻, 解除胁迫以后又能恢复的胁变称弹性胁变; 塑性胁变:程度重, 解除胁迫以后不能恢复的胁变称塑性胁变。 塑性胁变严重时会成为永久性伤害,甚至导致死亡。 胁迫(强) 借助物理学上概念,任何一种使 植物体产生有害变化的环境因子 称为胁迫(Stress),如温度胁 迫、水分胁迫、盐分胁迫等。 在胁迫下植物体发生的 生理生化变化称为胁变 (Strain)。 胁变
胁迫(强)与胁变 随胁迫强度不同,胁变程度有差异 弹性胁变:程度轻, 解除胁迫以后又能恢复的胁变称弹性胁变; 塑性胁变:程度重, 解除胁迫以后不能恢复的胁变称塑性胁变。 塑性胁变严重时会成为永久性伤害,甚至导致死亡。 胁迫(强) 借助物理学上概念,任何一种使 植物体产生有害变化的环境因子 称为胁迫(Stress),如温度胁 迫、水分胁迫、盐分胁迫等。 在胁迫下植物体发生的 生理生化变化称为胁变 (Strain)。 胁变

Figure 22.23 A flooded maize field. Flooding in the US Midwest in 1993 resulted in an estimated 33% reduction in yield compared with 1992
Figure 22.23 A flooded maize field. Flooding in the US Midwest in 1993 resulted in an estimated 33% reduction in yield compared with 1992
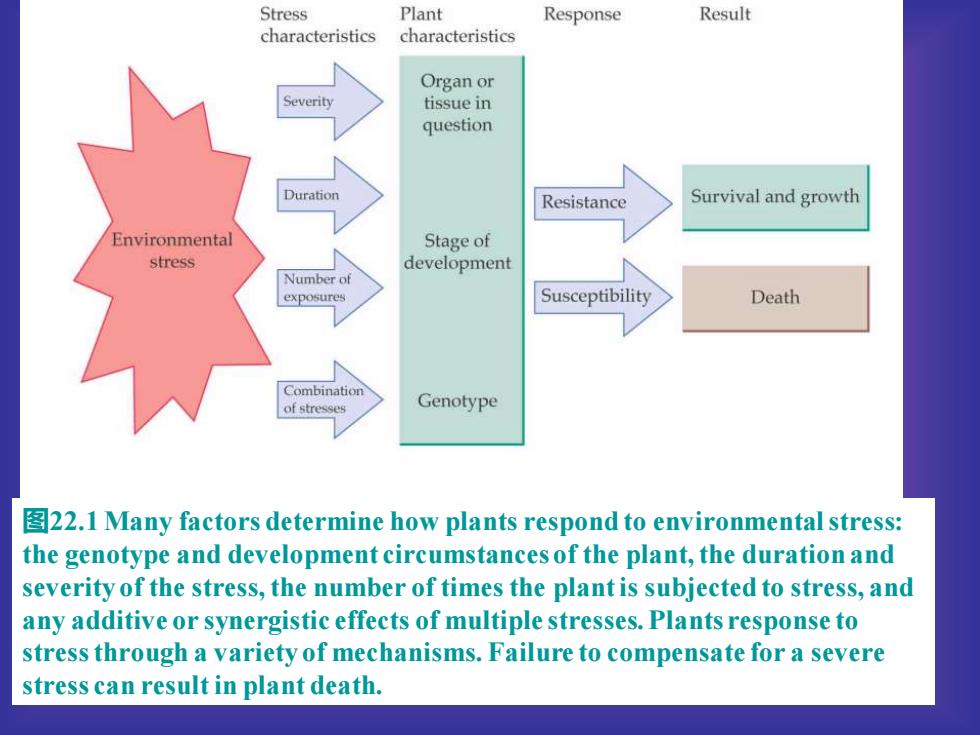
图22.1 Many factors determine how plants respond to environmental stress: the genotype and development circumstances of the plant, the duration and severity of the stress, the number of times the plant is subjected to stress, and any additive or synergistic effects of multiple stresses. Plants response to stress through a variety of mechanisms. Failure to compensate for a severe stress can result in plant death
图22.1 Many factors determine how plants respond to environmental stress: the genotype and development circumstances of the plant, the duration and severity of the stress, the number of times the plant is subjected to stress, and any additive or synergistic effects of multiple stresses. Plants response to stress through a variety of mechanisms. Failure to compensate for a severe stress can result in plant death

2. 逆境伤害性质 1) 直接伤害(direct stress injury) 2) 间接伤害(indirect stress injury) 严重的逆境,短时间作用产生的对植物生命结构 (蛋白质、膜、核酸等)的不可逆伤害。 这时植物还来不及发生代谢上的改变。 如高温烫伤、冰冻等。 较弱的逆境,长时间作用,可以把原来的弹 性胁变转化为塑性胁变,造成伤害。 主要是代谢紊乱
2. 逆境伤害性质 1) 直接伤害(direct stress injury) 2) 间接伤害(indirect stress injury) 严重的逆境,短时间作用产生的对植物生命结构 (蛋白质、膜、核酸等)的不可逆伤害。 这时植物还来不及发生代谢上的改变。 如高温烫伤、冰冻等。 较弱的逆境,长时间作用,可以把原来的弹 性胁变转化为塑性胁变,造成伤害。 主要是代谢紊乱
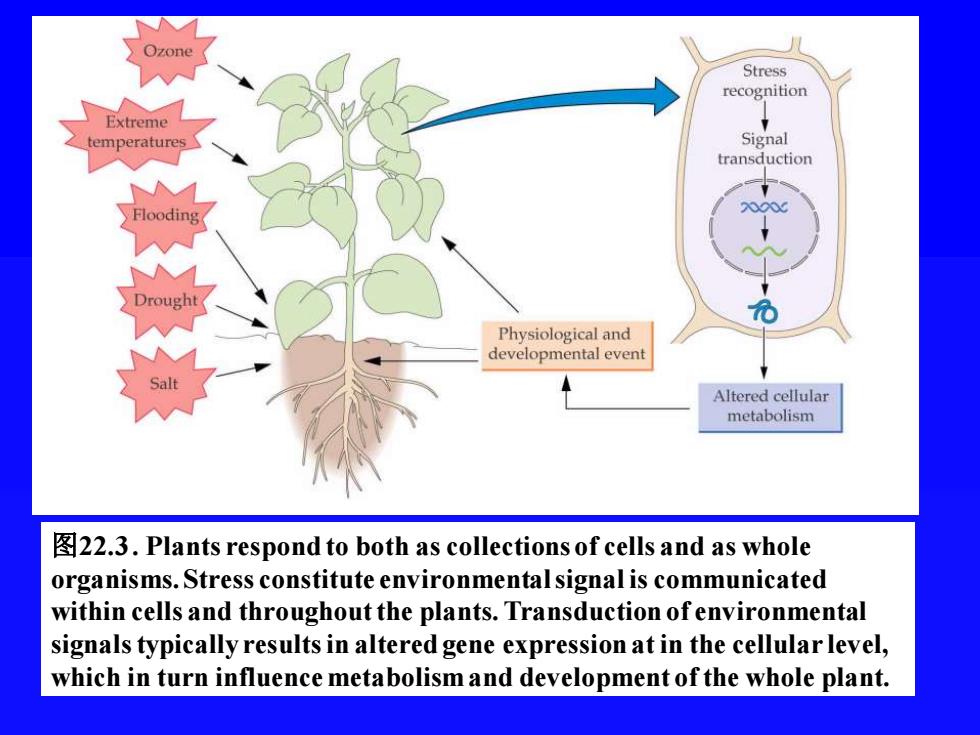
图22.3 . Plants respond to both as collections of cells and as whole organisms. Stress constitute environmental signal is communicated within cells and throughout the plants. Transduction of environmental signals typically results in altered gene expression at in the cellular level, which in turn influence metabolism and development of the whole plant
图22.3 . Plants respond to both as collections of cells and as whole organisms. Stress constitute environmental signal is communicated within cells and throughout the plants. Transduction of environmental signals typically results in altered gene expression at in the cellular level, which in turn influence metabolism and development of the whole plant

3. 植物对逆境的适应与抵抗 抗性=胁强 / 胁变 植物对逆境的适应与抵抗能力,称为抗逆性(hardiness) 植物抗逆性 强弱取决于 遗传潜力 抗逆锻炼 指植物在逆境下,逐渐形成了对逆境的适 应与抵抗能力。这一过程称为抗逆锻炼。 胡杨
3. 植物对逆境的适应与抵抗 抗性=胁强 / 胁变 植物对逆境的适应与抵抗能力,称为抗逆性(hardiness) 植物抗逆性 强弱取决于 遗传潜力 抗逆锻炼 指植物在逆境下,逐渐形成了对逆境的适 应与抵抗能力。这一过程称为抗逆锻炼。 胡杨