
第11卷第3期 智能系统学报 Vol.11 No.3 2016年6月 CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems Jun.2016 D0I:10.11992.tis.201603045 网络出版地址:http://www.enki..net/kcms/detail/23.1538.TP.20160513.0923.022.html 基于稠密子图的社区发现算法 郑文萍12,张浩杰,王杰12 (1.山西大学计算机与信息技术学院,山西太原030006;2.山西大学计算智能与中文信息处理教育部重点实验室, 山西太原030006) 摘要:基于密度的图聚类算法在社区发现中得到了广泛应用,然而由于其通过搜索网络中局部稠密子图来识别社 区,使得大量结点因不能构成稠密子图而未被聚类。针对此问题,给出了一种基于稠密子图的软聚类算法(comu- nity detection based dense subgraphs,BDSG)。首先给出一种中心社区发现方法;进而定义了一种结点的社区归属度, 并给出中心社区扩展策略;最终得到聚类结果。通过与CPM(clique percolation method),k-dense算法在空手道俱乐 部,海豚社交网络、大学生足球网络、电子邮件网络和合作网络等数据进行比较,表明BDSG算法在模块性指标与时 间效率方面体现了良好性能,同时中心社区扩展策略能在一定程度上提高CPM、k-dense等基于密度算法的聚类有 效性。 关键词:复杂网络:社区发现;图聚类;软聚类:密度:中心扩展策略;点介数:模块性 中图分类号:TP18文献标志码:A文章编号:1673-4785(2016)03-0426-07. 中文引用格式:郑文萍,张浩杰,王杰.基于稠密子图的社区发现算法[J].智能系统学报,2016,11(3):426432. 英文引用格式:ZHENG Wenping,ZHANG Haojie,WANG Jie.Community detection algorithm based on dense subgraphs[J]. CAAI transactions on intelligent systems,2016,11(3):426-432. Community detection algorithm based on dense subgraphs ZHENG Wenping'2,ZHANG Haojie',WANG Jie2 (1.School of Computer and Information Technology,Shanxi University,Taiyuan 030006,China;2.Key Laboratory of Computation In- telligence and Chinese Information Processing,Ministry of Education,Shanxi University,Taiyuan 030006,China) Abstract:The density-based graph clustering algorithm has been widely used in community detection.However, because it identifies a community by searching a partially dense subgraph in the network,many nodes do not consti- tute a dense subgraph and are therefore difficult to cluster.In this paper,we present a soft clustering algorithm based on dense subgraphs(BDSG)for detecting communities in complex networks.First,we propose a method for detecting the central communities.Next,we define the degree of community attribution of a node,and put forward a core community extended strategy.Finally,we obtain the clustering results of a network.Compared with the clique percolation method(CPM),k-dense algorithms from Zachary's Karate Club,the dolphin social network, the American college football network,the email network,and the collaboration network,BDSG shows considerably better performance with respect to modularity and time efficiency.In addition,the proposed core community extend- ed strategy may improve the effectiveness of the clustering-methods-based density,such as that in CPM,k-dense algorithms,and others. Keywords:complex network;community detection;graph clustering;soft clustering;density;core extended strat- egy;vertex betweenness;modularity 收稿日期:2016-03-19.网络出版日期:2016-05-13. 近年来,对各种复杂网络的研究是许多领域的 基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目(61572005,61272004),山西省煤基 研究热点之一[d),如生物网络、社交网络、电子邮 重点科技攻关项目(M02014-09). 通信作者:郑文萍.E-mail:wpzheng(@sxu.edu.cm 件网络、引文网络等已成为众多学者的主要研究对
第 11 卷第 3 期 智 能 系 统 学 报 Vol.11 №.3 2016 年 6 月 CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems Jun. 2016 DOI:10.11992.tis.201603045 网络出版地址:http: / / www.cnki.net / kcms/ detail / 23.1538.TP.20160513.0923.022.html 基于稠密子图的社区发现算法 郑文萍1,2 ,张浩杰1 ,王杰1,2 (1.山西大学 计算机与信息技术学院,山西 太原 030006; 2.山西大学 计算智能与中文信息处理教育部重点实验室, 山西 太原 030006) 摘 要:基于密度的图聚类算法在社区发现中得到了广泛应用,然而由于其通过搜索网络中局部稠密子图来识别社 区,使得大量结点因不能构成稠密子图而未被聚类。 针对此问题,给出了一种基于稠密子图的软聚类算法( commu⁃ nity detection based dense subgraphs,BDSG)。 首先给出一种中心社区发现方法;进而定义了一种结点的社区归属度, 并给出中心社区扩展策略;最终得到聚类结果。 通过与 CPM( clique percolation method)、k⁃dense 算法在空手道俱乐 部、海豚社交网络、大学生足球网络、电子邮件网络和合作网络等数据进行比较,表明 BDSG 算法在模块性指标与时 间效率方面体现了良好性能, 同时中心社区扩展策略能在一定程度上提高 CPM、k⁃dense 等基于密度算法的聚类有 效性。 关键词:复杂网络;社区发现;图聚类;软聚类;密度;中心扩展策略;点介数;模块性 中图分类号:TP18 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1673⁃4785(2016)03⁃0426⁃07. 中文引用格式:郑文萍,张浩杰,王杰.基于稠密子图的社区发现算法[J]. 智能系统学报, 2016, 11(3): 426⁃432. 英文引用格式:ZHENG Wenping, ZHANG Haojie, WANG Jie. Community detection algorithm based on dense subgraphs[ J]. CAAI transactions on intelligent systems, 2016,11(3): 426⁃432. Community detection algorithm based on dense subgraphs ZHENG Wenping 1,2 , ZHANG Haojie 1 , WANG Jie 1,2 (1. School of Computer and Information Technology, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China; 2. Key Laboratory of Computation In⁃ telligence and Chinese Information Processing, Ministry of Education, Shanxi University, Taiyuan 030006, China) Abstract:The density-based graph clustering algorithm has been widely used in community detection. However, because it identifies a community by searching a partially dense subgraph in the network, many nodes do not consti⁃ tute a dense subgraph and are therefore difficult to cluster. In this paper, we present a soft clustering algorithm based on dense subgraphs (BDSG) for detecting communities in complex networks. First, we propose a method for detecting the central communities. Next, we define the degree of community attribution of a node, and put forward a core community extended strategy. Finally, we obtain the clustering results of a network. Compared with the clique percolation method (CPM), k-dense algorithms from Zachary's Karate Club, the dolphin social network, the American college football network, the email network, and the collaboration network, BDSG shows considerably better performance with respect to modularity and time efficiency. In addition, the proposed core community extend⁃ ed strategy may improve the effectiveness of the clustering-methods-based density, such as that in CPM, k-dense algorithms, and others. Keywords:complex network; community detection; graph clustering; soft clustering; density; core extended strat⁃ egy; vertex betweenness; modularity 收稿日期:2016⁃03⁃19. 网络出版日期:2016⁃05⁃13. 基金项目:国家自然科学基金项目( 61572005,61272004),山西省煤基 重点科技攻关项目(MQ2014⁃09). 通信作者:郑文萍. E⁃mail: wpzheng@ sxu.edu.cn. 近年来,对各种复杂网络的研究是许多领域的 研究热点之一[1⁃3] ,如生物网络、社交网络、电子邮 件网络、引文网络等已成为众多学者的主要研究对

第3期 郑文萍,等:基于稠密子图的社区发现算法 ·427. 象。大量研究表明,复杂网络中存在着一种普遍特 面的性能表现。基于归属度的中心社区扩展策略也 征—社区结构。复杂网络中社区发现)不仅 将应用在CPM、k-dense等基于密度的图聚类算法 有助于深入研究整个网络的拓扑结构、功能模块以 中,对未聚类结点进一步处理,以提高聚类有效性。 及动力学特性,同时在生物蛋白质的性能与互作用 的分析6、社会组织结构的网络分析)、搜索引 1背景知识 擎[]及推荐系统[)等方面均有广泛的应用前景,因 通常,一个复杂网络可以表示为图G=(V,E), 此具有十分重要的理论意义和应用价值。 其中顶点集V={1,2,…,vn},n=V;边集E中每 目前,社区发现算法的研究主要分为基于图划 条边e,对应V中一对顶点(:,心)之间的连接关系, 分的聚类算法[1o)、基于谱分析的聚类算法[2]、基 m=IEI。顶点v的邻域Nc()={u|(v,u)∈E}, 于层次的聚类算法[)]和基于密度的聚类算法[) 表示图G中与顶点v相邻的顶点集合,简记为V,。 等。其中基于密度的聚类算法通过搜索网络中稠密 结点:的度记为k,。除非特别指明,以下仅考虑简 子图1能较好地发现网络中的功能模块,因此在社 区发现中得到了广泛应用。2005年,Palla等161提 单无向图,因此k.=NI。令UCV(G),用[U]G表 出派系过滤算法(clique percolation method,CPM), 示G的结点子集U的导出子图,在不发生混淆时, 首先挖掘网络中结点数大于k的所有派系(完全 记为[U]。记顶点子集[U]在G中的邻域为 图),然后将重叠结点大于k-1的派系合并得到k Nc(U)={ulu∈Nc(x)Ax∈U}o 派系社区。2006年,Saito等[]提出k-dense子图结 在复杂网络中,图G的密度[20]记为De= 构,通过寻找网络中的k-dense结构进行社区检测。 m 2009年,Sun等18以CPM为基础,通过改进寻找派 n(n-1)2。可以看出,D。∈【0,],当D。越趋近于 系的方法提高算法效率,提出迭代派系过滤算法 1,图G中的边数越多;当Dc=1时,图G为完全图。 iterative-clique percolation method,ICPM)2010 结点的点介数2B()可以用来度量结点 年,Liu等I]提出基于极大团的聚类算法(cluste- 在网络G中的重要性。如果一对结点(:,)间共 ring-based on maximal cliques,CMC),通过搜索网络 有L条不同的最短路径,其中有L()条经过 中的所有极大团,并依据相互连接度合并重叠率较 结点4,那么结点对结点对(:,)的贡献为 高的极大团得到网络的社区结构。由于这些算法要 搜索网络中的相对稠密子图来进行聚类,当网络中 L)/L0定义结点的点介数B(): 存在包含大量结点的稀疏子图时,这些结点可能最 B(u)= L两 (1)》 终成为未聚类结点,造成了聚类结果的不完全覆盖。 这些未聚类结点构成的稀疏子图可能具有某种功 通常一个结点的点介数越大,则该结点对网络 能,或者与某些稠密子图共同行使功能,因此需要对 结构的影响越大。点介数是网络中结点重要性度量 网络中的部分未聚类结点进行进一步分析,判断其 指标之一。 是否属于某一社区或形成新的社区。 针对基于密度算法中大量未聚类结点问题,提 2结点对社区的归属度定义 出一种基于稠密子图的社区发现算法(community 基于密度的图聚类算法中可能存在大量不属于 detection based on dense subgraphs,BDSG)。首先通 任何已有社区的未聚类结点,为了将这些结点聚类 过搜索网络中的相对稠密子图得到中心社区:对于 到合适的社区,需要定义未聚类结点和社区的关联 未聚类结点,定义了结点v对社区C的归属度b(, 强度,称为结点v对于社区C的归属度b(v,C)。归 C)来度量结点和社区的连接倾向程度:基于归属 属度的定义对聚类结果的影响至关重要,结点,对 度,给出一种中心社区扩展策略(core community ex- 于社区C的归属度越大,则结点属于社区C的可 tended strateg罗,CE),对未聚类结点进一步处理。 BDSG算法中,一个结点可能属于多个社区,是一种 能性越大。 软聚类方法。通过在空手道俱乐部、海豚社交网络、 Cui等2基于结点v与社区C关联边数定义了 大学生足球网络、电子邮件网络和合作网络5个真 结点对于社区C的归属度6,(,C)=N,nC,其 实网络上与CPM、k-dense算法进行比较,评估和分 k 析BDSG算法在未聚类结点分配和社区模块性等方 中N,∩C={ul(u,u)∈E,u∈C}表示结点v在社区
象。 大量研究表明,复杂网络中存在着一种普遍特 征———社区结构[4] 。 复杂网络中社区发现[5] 不仅 有助于深入研究整个网络的拓扑结构、功能模块以 及动力学特性,同时在生物蛋白质的性能与互作用 的分析[6] 、社会组织结构的网络分析[7] 、 搜索引 擎[8]及推荐系统[9]等方面均有广泛的应用前景,因 此具有十分重要的理论意义和应用价值。 目前,社区发现算法的研究主要分为基于图划 分的聚类算法[10⁃11] 、基于谱分析的聚类算法[12] 、基 于层次的聚类算法[13] 和基于密度的聚类算法[14] 等。 其中基于密度的聚类算法通过搜索网络中稠密 子图[15]能较好地发现网络中的功能模块,因此在社 区发现中得到了广泛应用。 2005 年,Palla 等[16] 提 出派系过滤算法( clique percolation method,CPM), 首先挖掘网络中结点数大于 k 的所有派系(完全 图),然后将重叠结点大于 k-1 的派系合并得到 k 派系社区。 2006 年,Saito 等[17] 提出 k⁃dense 子图结 构,通过寻找网络中的 k⁃dense 结构进行社区检测。 2009 年,Sun 等[18]以 CPM 为基础,通过改进寻找派 系的方法提高算法效率,提出迭代派系过滤算法 ( iterative⁃clique percolation method, ICPM )。 2010 年,Liu 等[19] 提出基于极大团的聚类算法( cluste⁃ ring⁃based on maximal cliques,CMC),通过搜索网络 中的所有极大团,并依据相互连接度合并重叠率较 高的极大团得到网络的社区结构。 由于这些算法要 搜索网络中的相对稠密子图来进行聚类,当网络中 存在包含大量结点的稀疏子图时,这些结点可能最 终成为未聚类结点,造成了聚类结果的不完全覆盖。 这些未聚类结点构成的稀疏子图可能具有某种功 能,或者与某些稠密子图共同行使功能,因此需要对 网络中的部分未聚类结点进行进一步分析,判断其 是否属于某一社区或形成新的社区。 针对基于密度算法中大量未聚类结点问题,提 出一种基于稠密子图的社区发现算法( community detection based on dense subgraphs,BDSG)。 首先通 过搜索网络中的相对稠密子图得到中心社区;对于 未聚类结点,定义了结点 v 对社区 C 的归属度 b(v, C)来度量结点和社区的连接倾向程度;基于归属 度,给出一种中心社区扩展策略(core community ex⁃ tended strategy, CE),对未聚类结点进一步处理。 BDSG 算法中,一个结点可能属于多个社区,是一种 软聚类方法。 通过在空手道俱乐部、海豚社交网络、 大学生足球网络、电子邮件网络和合作网络 5 个真 实网络上与 CPM、k⁃dense 算法进行比较,评估和分 析 BDSG 算法在未聚类结点分配和社区模块性等方 面的性能表现。 基于归属度的中心社区扩展策略也 将应用在 CPM、k⁃dense 等基于密度的图聚类算法 中,对未聚类结点进一步处理,以提高聚类有效性。 1 背景知识 通常,一个复杂网络可以表示为图 G = (V,E) , 其中顶点集 V = v1 ,v2 ,…,vn { } ,n = V ;边集 E 中每 条边 ei,j对应 V 中一对顶点(vi,vj)之间的连接关系, m = | E | 。 顶点 v 的邻域 NG (v) = {u | (v,u) ∈ E} , 表示图 G 中与顶点 v 相邻的顶点集合,简记为 Nv。 结点 v 的度记为 kv。 除非特别指明,以下仅考虑简 单无向图,因此 kv =| Nv | 。 令 U⊆V(G) ,用 [U] G 表 示 G 的结点子集 U 的导出子图,在不发生混淆时, 记为 [U] 。 记 顶 点 子 集 [U] 在 G 中 的 邻 域 为 NG(U)= {u | u∈NG (x) ∧x∈U}。 在复 杂 网 络 中, 图 G 的 密 度[20] 记 为 DG = m n(n-1) / 2 。 可以看出,DG∈ [0,1] ,当 DG 越趋近于 1,图 G 中的边数越多;当 DG = 1 时,图 G 为完全图。 结点 vk 的点介数[21]B vk ( ) 可以用来度量结点 vk 在网络 G 中的重要性。 如果一对结点( vi,vj ) 间共 有 Lvi ,vj条不同的最短路径,其中有 Lvi ,vj vk ( ) 条经过 结点 vk,那么结点 vk 对结点对 ( vi, vj ) 的贡献为 Lvi ,vj vk ( ) / Lvi ,vj 。 定义结点 vk 的点介数 B vk ( ) : B vk ( ) = ∑ n i = 1 ∑ n j = i+1 Lvi ,vj vk ( ) Lvi ,vj (1) 通常一个结点的点介数越大,则该结点对网络 结构的影响越大。 点介数是网络中结点重要性度量 指标之一。 2 结点对社区的归属度定义 基于密度的图聚类算法中可能存在大量不属于 任何已有社区的未聚类结点,为了将这些结点聚类 到合适的社区,需要定义未聚类结点和社区的关联 强度,称为结点 v 对于社区 C 的归属度 b(v,C)。 归 属度的定义对聚类结果的影响至关重要,结点 v 对 于社区 C 的归属度越大,则结点 v 属于社区 C 的可 能性越大。 Cui 等[22]基于结点 v 与社区 C 关联边数定义了 结点 v 对于社区 C 的归属度 bp(v,C)= Nv∩C kv ,其 中 Nv∩C = {u | (v,u) ∈E,u∈C} 表示结点 v 在社区 第 3 期 郑文萍,等:基于稠密子图的社区发现算法 ·427·
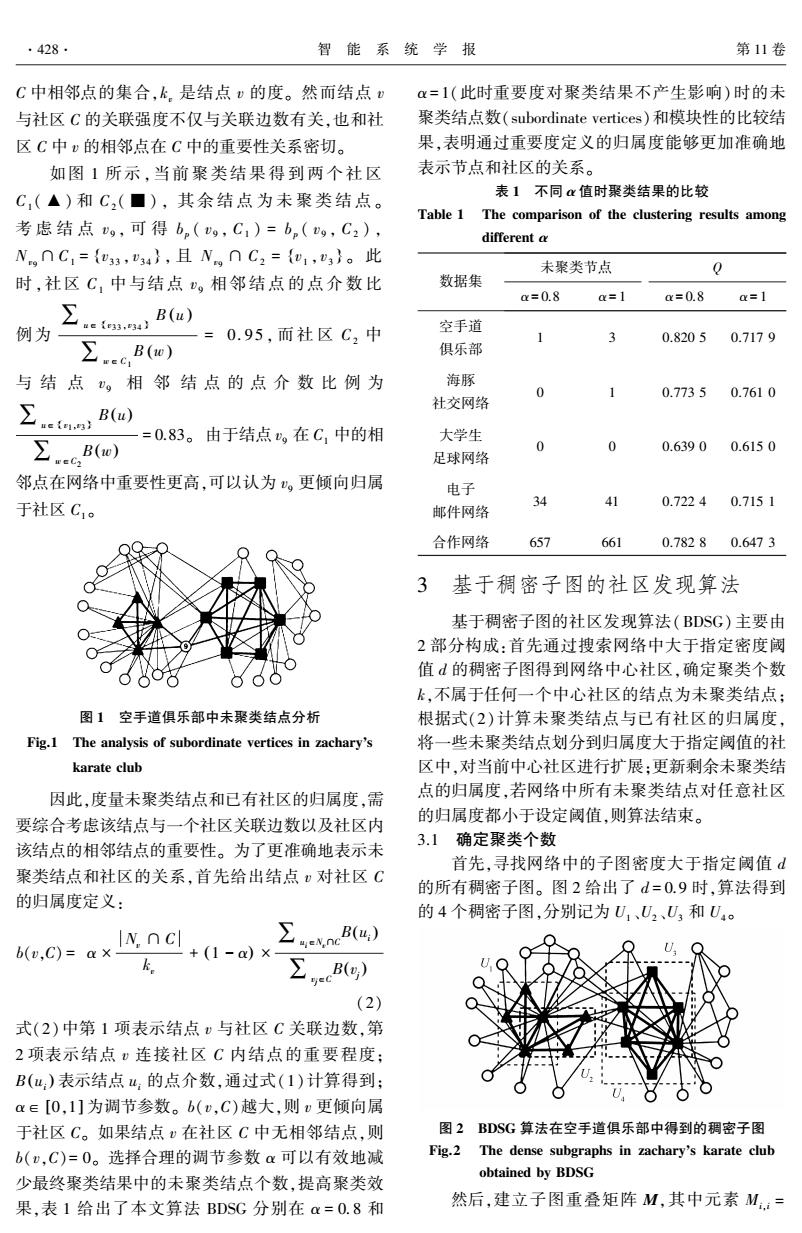
.428 智能系统学报 第11卷 C中相邻点的集合,k,是结点的度。然而结点 α=1(此时重要度对聚类结果不产生影响)时的未 与社区C的关联强度不仅与关联边数有关,也和社 聚类结点数(subordinate vertices)和模块性的比较结 区C中v的相邻点在C中的重要性关系密切。 果,表明通过重要度定义的归属度能够更加准确地 如图1所示,当前聚类结果得到两个社区 表示节点和社区的关系。 C,(▲)和C2(■),其余结点为未聚类结点。 表1不同x值时聚类结果的比较 Table 1 The comparison of the clustering results among 考虑结点g,可得b(g,C1)=bn(g,C2), different a N,nC,={u33,34},且Ng∩C2={w1,3}。此 未聚类节点 0 时,社区C,中与结点。相邻结点的点介数比 数据集 a=0.8 a=1 ax=0.8 a=1 ∑ 、B(u) 例为 e{e33,34} -=0.95,而社区C2中 空手道 3 0.8205 0.7179 ∑.c,B(o) 俱乐部 与结点,相邻结点的点介数比例为 海豚 0 0.77350.7610 社交网络 =0.83。由于结点,在C,中的相 大学生 ∑.ecBo) 0 0 0.6390 0.6150 足球网络 邻点在网络中重要性更高,可以认为,更倾向归属 电子 于社区C1 34 41 0.72240.7151 邮件网络 合作网络 657 661 0.78280.6473 3基于稠密子图的社区发现算法 基于稠密子图的社区发现算法(BDSG)主要由 2部分构成:首先通过搜索网络中大于指定密度阈 值d的稠密子图得到网络中心社区,确定聚类个数 k,不属于任何一个中心社区的结点为未聚类结点; 图1空手道俱乐部中未聚类结点分析 根据式(2)计算未聚类结点与已有社区的归属度, Fig.1 The analysis of subordinate vertices in zachary's 将一些未聚类结点划分到归属度大于指定阈值的社 karate club 区中,对当前中心社区进行扩展:更新剩余未聚类结 因此,度量未聚类结点和已有社区的归属度,需 点的归属度,若网络中所有未聚类结点对任意社区 要综合考虑该结点与一个社区关联边数以及社区内 的归属度都小于设定阈值,则算法结束。 该结点的相邻结点的重要性。为了更准确地表示未 3.1确定聚类个数 首先,寻找网络中的子图密度大于指定阈值d 聚类结点和社区的关系,首先给出结点,对社区C 的所有稠密子图。图2给出了d=0.9时,算法得到 的归属度定义: 的4个稠密子图,分别记为U1、U2、U3和U40 b(v.c)=ax Iyncl nB(u) +(1-a)× ke ∑,2B) (2) 式(2)中第1项表示结点与社区C关联边数,第 2项表示结点:连接社区C内结点的重要程度: B(u:)表示结点u,的点介数,通过式(1)计算得到; a∈[0,1]为调节参数。b(,C)越大,则u更倾向属 于社区C。如果结点在社区C中无相邻结点,则 图2BDSG算法在空手道俱乐部中得到的稠密子图 b(,C)=0。选择合理的调节参数α可以有效地减 Fig.2 The dense subgraphs in zachary's karate club obtained by BDSG 少最终聚类结果中的未聚类结点个数,提高聚类效 果,表1给出了本文算法BDSG分别在=0.8和 然后,建立子图重叠矩阵M,其中元素M.:=
C 中相邻点的集合,kv 是结点 v 的度。 然而结点 v 与社区 C 的关联强度不仅与关联边数有关,也和社 区 C 中 v 的相邻点在 C 中的重要性关系密切。 如图 1 所示,当前 聚 类 结 果 得 到 两 个 社 区 C1 ( ▲) 和 C2 ( ■ ) , 其 余 结 点 为 未 聚 类 结 点。 考 虑 结 点 v 9 , 可 得 bp ( v 9 , C1 ) = bp ( v 9 , C2 ) , Nv9∩C1 = v 33 , v 34 { } , 且 Nv9 ∩ C2 = v 1 , v 3 { } 。 此 时,社区 C1 中与结 点 v 9 相 邻 结 点 的 点 介 数 比 例为 ∑u∈ v33 ,v { 34 } B (u ) ∑w∈C1 B (w ) = 0 . 95 , 而 社 区 C2 中 与 结 点 v 9 相 邻 结 点 的 点 介 数 比 例 为 ∑u∈ v1 ,v { 3 } B(u) ∑w∈C2 B(w) = 0.83。 由于结点 v9 在 C1 中的相 邻点在网络中重要性更高,可以认为 v9 更倾向归属 于社区 C1 。 图 1 空手道俱乐部中未聚类结点分析 Fig.1 The analysis of subordinate vertices in zacharys karate club 因此,度量未聚类结点和已有社区的归属度,需 要综合考虑该结点与一个社区关联边数以及社区内 该结点的相邻结点的重要性。 为了更准确地表示未 聚类结点和社区的关系,首先给出结点 v 对社区 C 的归属度定义: b(v,C) = α × Nv ∩ C kv + (1 - α) × ∑ui∈Nv∩C B ui ( ) ∑vj∈C B vj ( ) (2) 式(2)中第 1 项表示结点 v 与社区 C 关联边数,第 2 项表示结点 v 连接社区 C 内结点的重要程度; B ui ( ) 表示结点 ui 的点介数,通过式(1)计算得到; α∈ [0,1] 为调节参数。 b(v,C)越大,则 v 更倾向属 于社区 C。 如果结点 v 在社区 C 中无相邻结点,则 b(v,C)= 0。 选择合理的调节参数 α 可以有效地减 少最终聚类结果中的未聚类结点个数,提高聚类效 果,表 1 给出了本文算法 BDSG 分别在 α = 0. 8 和 α= 1(此时重要度对聚类结果不产生影响) 时的未 聚类结点数(subordinate vertices)和模块性的比较结 果,表明通过重要度定义的归属度能够更加准确地 表示节点和社区的关系。 表 1 不同 α 值时聚类结果的比较 Table 1 The comparison of the clustering results among different α 数据集 未聚类节点 Q α= 0.8 α= 1 α= 0.8 α= 1 空手道 俱乐部 1 3 0.820 5 0.717 9 海豚 社交网络 0 1 0.773 5 0.761 0 大学生 足球网络 0 0 0.639 0 0.615 0 电子 邮件网络 34 41 0.722 4 0.715 1 合作网络 657 661 0.782 8 0.647 3 3 基于稠密子图的社区发现算法 基于稠密子图的社区发现算法(BDSG)主要由 2 部分构成:首先通过搜索网络中大于指定密度阈 值 d 的稠密子图得到网络中心社区,确定聚类个数 k,不属于任何一个中心社区的结点为未聚类结点; 根据式(2)计算未聚类结点与已有社区的归属度, 将一些未聚类结点划分到归属度大于指定阈值的社 区中,对当前中心社区进行扩展;更新剩余未聚类结 点的归属度,若网络中所有未聚类结点对任意社区 的归属度都小于设定阈值,则算法结束。 3.1 确定聚类个数 首先,寻找网络中的子图密度大于指定阈值 d 的所有稠密子图。 图 2 给出了 d = 0.9 时,算法得到 的 4 个稠密子图,分别记为 U1 、U2 、U3 和 U4 。 图 2 BDSG 算法在空手道俱乐部中得到的稠密子图 Fig.2 The dense subgraphs in zacharys karate club obtained by BDSG 然后,建立子图重叠矩阵 M,其中元素 Mi,i = ·428· 智 能 系 统 学 报 第 11 卷
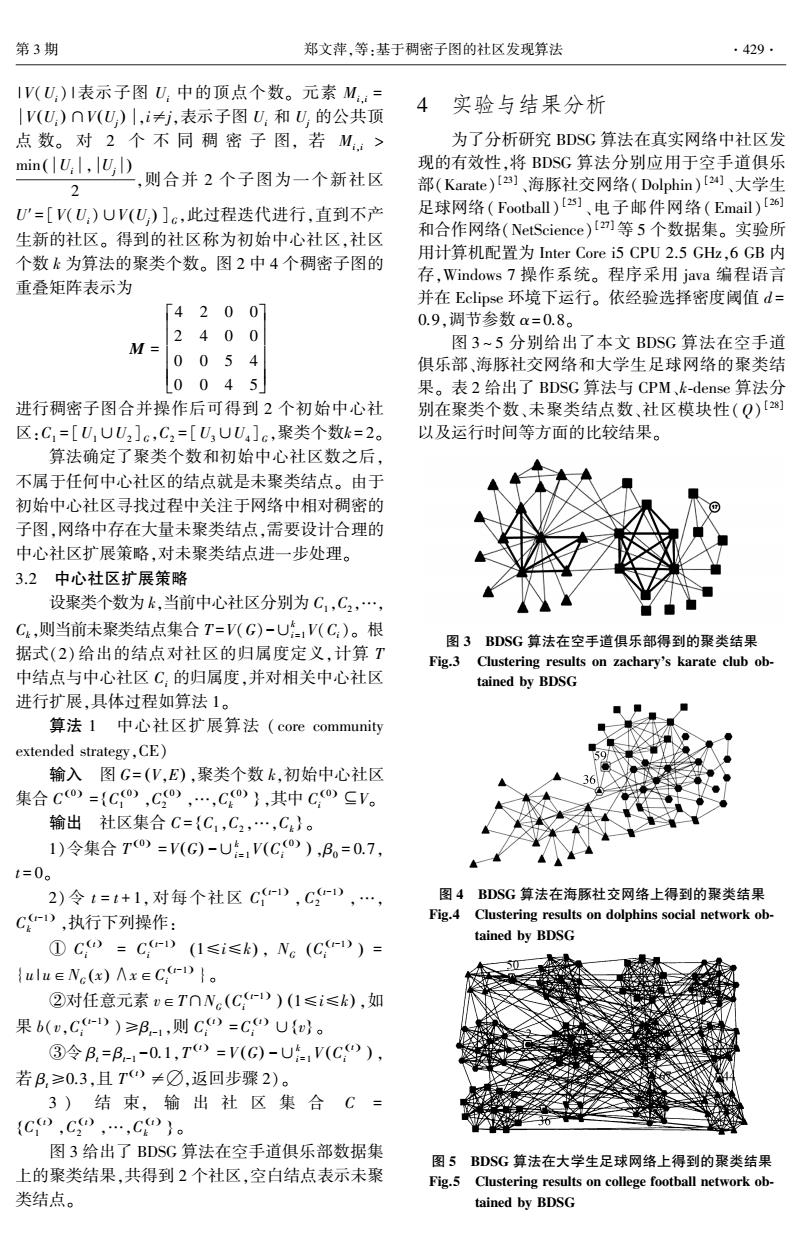
第3期 郑文萍,等:基于稠密子图的社区发现算法 ·429. 1V(U:)1表示子图U:中的顶点个数。元素M:= |V(U)nV(U)|,i≠j,表示子图U,和U,的公共顶 4实验与结果分析 点数。对2个不同稠密子图,若M:> 为了分析研究BDSG算法在真实网络中社区发 min(U:l,U) 现的有效性,将BDSG算法分别应用于空手道俱乐 则合并2个子图为一个新社区 部(Karate)[]、海豚社交网络(Dolphin)[24]、大学生 U'=[V(U)UV(U)]c,此过程迭代进行,直到不产 足球网络(Football)[2]、电子邮件网络(Email)[] 生新的社区。得到的社区称为初始中心社区,社区 和合作网络(NetScience)I]等5个数据集。实验所 个数k为算法的聚类个数。图2中4个稠密子图的 用计算机配置为Inter Core i5CPU2.5GHz,6GB内 存,Windows7操作系统。程序采用java编程语言 重叠矩阵表示为 并在Eclipse环境下运行。依经验选择密度阈值d= [42007 0.9,调节参数a=0.8。 240 0 M= 图3~5分别给出了本文BDSG算法在空手道 0054 俱乐部、海豚社交网络和大学生足球网络的聚类结 L0045 果。表2给出了BDSG算法与CPM、k-dense算法分 进行稠密子图合并操作后可得到2个初始中心社 别在聚类个数、未聚类结点数、社区模块性(Q)【测 区:C,=[UUU2]c,C2=[U3UU]c,聚类个数k=2。 以及运行时间等方面的比较结果。 算法确定了聚类个数和初始中心社区数之后, 不属于任何中心社区的结点就是未聚类结点。由于 初始中心社区寻找过程中关注于网络中相对稠密的 子图,网络中存在大量未聚类结点,需要设计合理的 中心社区扩展策略,对未聚类结点进一步处理。 3.2中心社区扩展策略 设聚类个数为k,当前中心社区分别为C1,C2,…, Ck,则当前未聚类结点集合T=V(G)-U,V(C:)。根 图3BDSG算法在空手道俱乐部得到的聚类结果 据式(2)给出的结点对社区的归属度定义,计算T Fig.3 Clustering results on zachary's karate club ob- 中结点与中心社区C:的归属度,并对相关中心社区 tained by BDSG 进行扩展,具体过程如算法1。 算法1中心社区扩展算法(core community extended strategy,CE) 输入图G=(V,E),聚类个数k,初始中心社区 集合Co)={Co),C),…,C)},其中CoSV。 输出社区集合C={C,C2,…,C4}。 1)令集合To=V(G)-UV(Co),B。=0.7, t=0。 2)令t=t+1,对每个社区C),C-),…, 图4BDSG算法在海豚社交网络上得到的聚类结果 CD,执行下列操作: Fig.4 Clustering results on dolphins social network ob- tained by BDSG ①Co=C-)(1≤i≤k),Ne(C,)= {ulu∈Ne(x)Ax∈C,-D}。 ②对任意元素vETONc(C)(1≤i≤k),如 果b(u,C-))≥B1,则C0=C0U{}。 ③令B.=B--0.1,T=V(G)-U(C), 若B,≥0.3,且T≠☑,返回步骤2)。 3)结束,输出社区集合C= {C0,C,…,C}。 图3给出了BDSG算法在空手道俱乐部数据集 图5BDSG算法在大学生足球网络上得到的聚类结果 上的聚类结果,共得到2个社区,空白结,点表示未聚 Fig.5 Clustering results on college football network ob- 类结点。 tained by BDSG
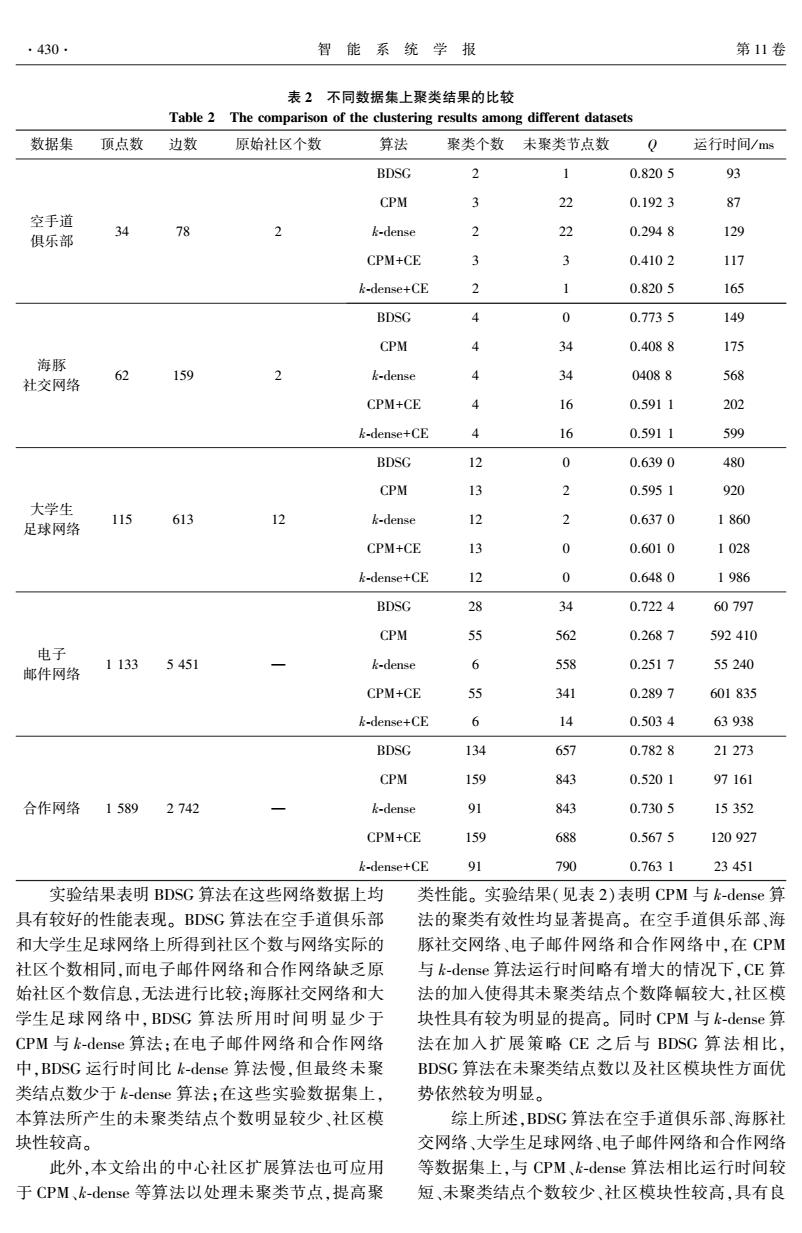
| V(Ui) |表示子图 Ui 中的顶点个数。 元素 Mi,i = V Ui ( ) ∩V Uj ( ) ,i≠j,表示子图 Ui 和 Uj 的公共顶 点 数。 对 2 个 不 同 稠 密 子 图, 若 Mi,i > min Ui , Uj ( ) 2 ,则合并 2 个子图为一个新社区 U′= [V(Ui)∪V Uj ( ) ] G ,此过程迭代进行,直到不产 生新的社区。 得到的社区称为初始中心社区,社区 个数 k 为算法的聚类个数。 图 2 中 4 个稠密子图的 重叠矩阵表示为 M = 4 2 0 0 2 4 0 0 0 0 5 4 0 0 4 5 é ë ê ê ê ê ê ù û ú ú ú ú ú 进行稠密子图合并操作后可得到 2 个初始中心社 区:C1 = [U1∪U2 ] G ,C2 = [U3∪U4 ] G ,聚类个数k = 2。 算法确定了聚类个数和初始中心社区数之后, 不属于任何中心社区的结点就是未聚类结点。 由于 初始中心社区寻找过程中关注于网络中相对稠密的 子图,网络中存在大量未聚类结点,需要设计合理的 中心社区扩展策略,对未聚类结点进一步处理。 3.2 中心社区扩展策略 设聚类个数为 k,当前中心社区分别为 C1,C2,…, Ck,则当前未聚类结点集合 T =V(G)-∪k i=1V(Ci)。 根 据式(2) 给出的结点对社区的归属度定义,计算 T 中结点与中心社区 Ci 的归属度,并对相关中心社区 进行扩展,具体过程如算法 1。 算法 1 中心社区扩展算法 ( core community extended strategy,CE) 输入 图 G= (V,E) ,聚类个数 k,初始中心社区 集合 C (0 ) = C (0 ) 1 ,C (0 ) 2 ,…,C (0 ) k { } ,其中 C (0 ) i ⊆V。 输出 社区集合 C = C1 ,C2 ,…,Ck { } 。 1)令集合 T (0 ) = V(G) -∪k i = 1V C (0 ) i ( ) ,β0 = 0.7, t = 0。 2) 令 t = t + 1,对每个社区 C (t-1 ) 1 ,C (t-1 ) 2 ,…, C (t-1 ) k ,执行下列操作: ① C (t) i = C (t-1 ) i (1≤i≤k) , NG C (t-1 ) i ( ) = {u | u∈NG (x) ∧x∈C (t-1 ) i }。 ②对任意元素 v∈T∩NG C (t-1 ) i ( ) (1≤i≤k) ,如 果 b(v,C (t-1 ) i )≥βt-1 ,则 C (t) i =C (t) i ∪{v} 。 ③令 βt = βt-1 -0.1,T (t) = V (G) -∪k i = 1V C (t) i ( ) , 若 βt≥0.3,且 T (t) ≠∅,返回步骤 2)。 3 ) 结 束, 输 出 社 区 集 合 C = C (t) 1 ,C (t) 2 ,…,C (t) k { } 。 图 3 给出了 BDSG 算法在空手道俱乐部数据集 上的聚类结果,共得到 2 个社区,空白结点表示未聚 类结点。 4 实验与结果分析 为了分析研究 BDSG 算法在真实网络中社区发 现的有效性,将 BDSG 算法分别应用于空手道俱乐 部(Karate) [23] 、海豚社交网络(Dolphin) [24] 、大学生 足球网络( Football) [25] 、电子邮件网络( Email) [26] 和合作网络(NetScience) [27]等 5 个数据集。 实验所 用计算机配置为 Inter Core i5 CPU 2.5 GHz,6 GB 内 存,Windows 7 操作系统。 程序采用 java 编程语言 并在 Eclipse 环境下运行。 依经验选择密度阈值 d = 0.9,调节参数 α= 0.8。 图 3 ~ 5 分别给出了本文 BDSG 算法在空手道 俱乐部、海豚社交网络和大学生足球网络的聚类结 果。 表 2 给出了 BDSG 算法与 CPM、k⁃dense 算法分 别在聚类个数、未聚类结点数、社区模块性(Q) [28] 以及运行时间等方面的比较结果。 图 3 BDSG 算法在空手道俱乐部得到的聚类结果 Fig.3 Clustering results on zacharys karate club ob⁃ tained by BDSG 图 4 BDSG 算法在海豚社交网络上得到的聚类结果 Fig.4 Clustering results on dolphins social network ob⁃ tained by BDSG 图 5 BDSG 算法在大学生足球网络上得到的聚类结果 Fig.5 Clustering results on college football network ob⁃ tained by BDSG 第 3 期 郑文萍,等:基于稠密子图的社区发现算法 ·429·
·430 智能系统学报 第11卷 表2不同数据集上聚类结果的比较 Table 2 The comparison of the clustering results among different datasets 数据集 顶点数 边数 原始社区个数 算法 聚类个数 未聚类节点数 Q 运行时间/ms BDSG 2 0.8205 93 CPM 3 22 0.1923 87 空手道 俱乐部 304 78 k-dense 2 22 0.2948 129 CPM+CE 3 3 0.4102 117 k-dense+CE 0.8205 165 BDSG 0 0.7735 149 CPM 4 34 0.4088 175 海豚 社交网络 159 k-dense 4 34 04088 568 CPM+CE 4 16 0.5911 202 k-dense+CE 16 0.5911 599 BDSG 12 0 0.6390 480 CPM 13 2 0.5951 920 大学生 115 613 k-dense 12 2 0.6370 足球网络 1860 CPM+CE 13 0 0.6010 1028 k-dense+CE 12 0 0.6480 1986 BDSG 28 34 0.7224 60797 CPM 55 562 0.2687 592410 电子 邮件网络 11335451 k-dense 6 558 0.2517 55240 CPM+CE 55 341 0.2897 601835 k-dense+CE 6 14 0.5034 63938 BDSG 134 657 0.7828 21273 CPM 159 843 0.5201 97161 合作网络 1589 2742 k-dense 91 843 0.7305 15352 CPM+CE 159 688 0.5675 120927 A-dense+CE 91 790 0.7631 23451 实验结果表明BDSG算法在这些网络数据上均 类性能。实验结果(见表2)表明CPM与k-dense算 具有较好的性能表现。BDSG算法在空手道俱乐部 法的聚类有效性均显著提高。在空手道俱乐部、海 和大学生足球网络上所得到社区个数与网络实际的 豚社交网络、电子邮件网络和合作网络中,在CPM 社区个数相同,而电子邮件网络和合作网络缺乏原 与k-dense算法运行时间略有增大的情况下,CE算 始社区个数信息,无法进行比较:海豚社交网络和大 法的加入使得其未聚类结点个数降幅较大,社区模 学生足球网络中,BDSG算法所用时间明显少于 块性具有较为明显的提高。同时CPM与k-dense算 CPM与k-dense算法:在电子邮件网络和合作网络 法在加入扩展策略CE之后与BDSG算法相比, 中,BDSG运行时间比k-dense算法慢,但最终未聚 BDSG算法在未聚类结点数以及社区模块性方面优 类结点数少于k-dense算法:在这些实验数据集上, 势依然较为明显。 本算法所产生的未聚类结点个数明显较少、社区模 综上所述,BDSG算法在空手道俱乐部、海豚社 块性较高。 交网络、大学生足球网络、电子邮件网络和合作网络 此外,本文给出的中心社区扩展算法也可应用 等数据集上,与CPM、k-dense算法相比运行时间较 于CPM、k-dense等算法以处理未聚类节点,提高聚 短、未聚类结点个数较少、社区模块性较高,具有良
表 2 不同数据集上聚类结果的比较 Table 2 The comparison of the clustering results among different datasets 数据集 顶点数 边数 原始社区个数 算法 聚类个数 未聚类节点数 Q 运行时间/ ms 空手道 俱乐部 34 78 2 BDSG 2 1 0.820 5 93 CPM 3 22 0.192 3 87 k⁃dense 2 22 0.294 8 129 CPM+CE 3 3 0.410 2 117 k⁃dense+CE 2 1 0.820 5 165 海豚 社交网络 62 159 2 BDSG 4 0 0.773 5 149 CPM 4 34 0.408 8 175 k⁃dense 4 34 0408 8 568 CPM+CE 4 16 0.591 1 202 k⁃dense+CE 4 16 0.591 1 599 大学生 足球网络 115 613 12 BDSG 12 0 0.639 0 480 CPM 13 2 0.595 1 920 k⁃dense 12 2 0.637 0 1 860 CPM+CE 13 0 0.601 0 1 028 k⁃dense+CE 12 0 0.648 0 1 986 电子 邮件网络 1 133 5 451 — BDSG 28 34 0.722 4 60 797 CPM 55 562 0.268 7 592 410 k⁃dense 6 558 0.251 7 55 240 CPM+CE 55 341 0.289 7 601 835 k⁃dense+CE 6 14 0.503 4 63 938 合作网络 1 589 2 742 — BDSG 134 657 0.782 8 21 273 CPM 159 843 0.520 1 97 161 k⁃dense 91 843 0.730 5 15 352 CPM+CE 159 688 0.567 5 120 927 k⁃dense+CE 91 790 0.763 1 23 451 实验结果表明 BDSG 算法在这些网络数据上均 具有较好的性能表现。 BDSG 算法在空手道俱乐部 和大学生足球网络上所得到社区个数与网络实际的 社区个数相同,而电子邮件网络和合作网络缺乏原 始社区个数信息,无法进行比较;海豚社交网络和大 学生足球网络中,BDSG 算法所用时间明显少于 CPM 与 k⁃dense 算法;在电子邮件网络和合作网络 中,BDSG 运行时间比 k⁃dense 算法慢,但最终未聚 类结点数少于 k⁃dense 算法;在这些实验数据集上, 本算法所产生的未聚类结点个数明显较少、社区模 块性较高。 此外,本文给出的中心社区扩展算法也可应用 于 CPM、k⁃dense 等算法以处理未聚类节点,提高聚 类性能。 实验结果(见表 2)表明 CPM 与 k⁃dense 算 法的聚类有效性均显著提高。 在空手道俱乐部、海 豚社交网络、电子邮件网络和合作网络中,在 CPM 与 k⁃dense 算法运行时间略有增大的情况下,CE 算 法的加入使得其未聚类结点个数降幅较大,社区模 块性具有较为明显的提高。 同时 CPM 与 k⁃dense 算 法在加入扩展策略 CE 之后与 BDSG 算法相比, BDSG 算法在未聚类结点数以及社区模块性方面优 势依然较为明显。 综上所述,BDSG 算法在空手道俱乐部、海豚社 交网络、大学生足球网络、电子邮件网络和合作网络 等数据集上,与 CPM、k⁃dense 算法相比运行时间较 短、未聚类结点个数较少、社区模块性较高,具有良 ·430· 智 能 系 统 学 报 第 11 卷

第3期 郑文萍,等:基于稠密子图的社区发现算法 ·431. 好的聚类性能。同时,中心社区扩展算法可以有效 CHEN Kehan,HAN Panpan,WU Jian.User clustering 地提高CPM、k-dense算法的聚类性能,该算法也可 based social network recommendation[]].Chinese journal of 用于其他非结点完全覆盖算法。 computers,.2013,36(2):349-359. [10]FREY B J,DUECK D.Clustering by passing messages be- 5结束语 tween data points[J].Science,2007,315(5814):972- 976. 本文提出一种基于稠密子图的图聚类算法 [11]NEWMAN M E J.Community detection and graph partitio- BDSG,解决了基于密度算法中大量未聚类结点问 ning[]Europhysics letters,2013,103(2):28003. 题。通过搜索网络中的相对稠密子图得到中心社 [12]NEWMAN M E J.Spectral methods for community detec- 区:通过定义结点对社区的归属度来度量结点和社 tion and graph partitioning[J].Physical review E,2013, 区连接倾向性,进而给出一种中心社区扩展策略对 88(4):042822. 中心社区外结点进行聚类。通过与CPM、k-dense算 [13]LIN Chuncheng,KANG Jiarong,CHEN J Y.An integer 法在5个真实网络数据集上进行分析比较,结果表 programming approach and visual analysis for detecting hi- 明,BDSG算法在未聚类结点个数、模块性及运行时 erarchical community structures in social networks[J].In- 间方面均表现出较好的性能。同时中心社区扩展策 formation sciences,2015,299:296-311. 略与其他算法相结合,对提高CPM、k-dense等算法 [14]REN Jun,WANG Jianxin,LI Min,et al.Identifying pro- tein complexes based on density and modularity in protein- 的聚类性能具有一定的适用性。 protein interaction network[J].BMC systems biology, 参考文献: 2013,7(S4):S12. [15]LI Xiaoli,FOO C S,NG S K.Discovering protein comple- [1]FORTUNATO S.Community detection in graphs[J].Phys- xes in dense reliable neighborhoods of protein interaction ics reports,2010,486(3/4/5):75-174. networks[C]//Proceedings of the computational systems [2]NEPUSZ T,YU Haiyuan,PACCANARO A.Detecting over- bioinformatics conference.San Diego,USA,2007,6: lapping protein complexes in protein-protein interaction net- 157-168. works[J.Nature methods,2012,9(5):471-472. [16]PALLA G,DEReNYI I,FARKAS I,et al.Uncovering the [3]DEYLAMI H A,ASADPOUR M.Link prediction in social overlapping community structure of complex networks in networks using hierarchical community detectionC//Pro- nature and society J.Nature,2005,435:814-818. ceedings of the 7th conference on information and knowledge [17]SAITO K,YAMADA T,KAZAMA K.Extracting commu- technology.Urmia,Iran,2015:1-5. nities from complex networks by the k-dense method[J]. [4]SCHAEFFER S E.Graph clustering[J].Computer science IEICE transactions on fundamentals of electronics,commu- review,2007,1(1):27-64. nications and computer sciences,2008,E91-A (11 ) [5]杨博,刘大有,U Jiming,等.复杂网络聚类方法[J]. 3304-3311. 软件学报,2009,20(1):54-66. [18]SUN Penggang,GAO Lin.Fast algorithms for detecting o- YANG Bo,LIU Dayou,LIU Jiming,et al.Complex network verlapping functional modules in protein-protein interaction clustering algorithms [J].Journal of software,2009,20 networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE computational in- (1):54-66. telligence in bioinformatics and computational biology. [6]冀俊忠,刘志军,刘红欣,等.蛋白质相互作用网络功 Nashville,TN,USA,2009:247-254. 能模块检测的研究综述[J].自动化学报,2014,40(4): [19]LIU Guimei,WONG L,CHUA H N.Complex discovery 577.593. from weighted PPI networks[J].Bioinformatics,2009,25 JI Junzhong,LIU Zhijun,LIU Hongxin,et al.An overview (15):1891-1897. of research on functional module detection for protein-protein [20]BADER G D,HOGUE C W V.An automated method for interaction networks J.Acta automatica sinica,2014,40 finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction (4):577-593 networks[.BMC bioinformatics,2003,4(1):2. [7]PALLA G,BARABASI A L,VICSEK T.Quantifying social [21]FREEMAN L C.A set of measures of centrality based on group evolution[J].Nature,2007,446(7136):664-667. betweenness[J].Sociometry,1977,40(1):35-41. [8]SIDIROPOULOS A,PALLIS G,KATSAROS D,et al.Pre- [22 CUI Yaizu,WANG Xingyuan,EUSTACE J.Detecting fetching in content distribution networks via web communi- community structure via the maximal sub-graphs and be- ties identification and outsourcing[J].World wide web, longing degrees in complex networks[J].Physica A:sta- 2008,11(1):39-70. tistical mechanics and its applications,2014,416:198- [9]陈克寒,韩盼盼,吴健.基于用户聚类的异构社交网络 207. 推荐算法[J].计算机学报,2013,36(2):349-359. [23]ZACHARY WW.An information flow model for conflict
好的聚类性能。 同时,中心社区扩展算法可以有效 地提高 CPM、k⁃dense 算法的聚类性能,该算法也可 用于其他非结点完全覆盖算法。 5 结束语 本文提出一种基于稠密子图的图聚类算法 BDSG,解决了基于密度算法中大量未聚类结点问 题。 通过搜索网络中的相对稠密子图得到中心社 区;通过定义结点对社区的归属度来度量结点和社 区连接倾向性,进而给出一种中心社区扩展策略对 中心社区外结点进行聚类。 通过与 CPM、k⁃dense 算 法在 5 个真实网络数据集上进行分析比较,结果表 明,BDSG 算法在未聚类结点个数、模块性及运行时 间方面均表现出较好的性能。 同时中心社区扩展策 略与其他算法相结合,对提高 CPM、k⁃dense 等算法 的聚类性能具有一定的适用性。 参考文献: [1]FORTUNATO S. Community detection in graphs[ J]. Phys⁃ ics reports, 2010, 486(3 / 4 / 5): 75⁃174. [2]NEPUSZ T, YU Haiyuan, PACCANARO A. Detecting over⁃ lapping protein complexes in protein⁃protein interaction net⁃ works[J]. Nature methods, 2012, 9(5): 471⁃472. [3]DEYLAMI H A, ASADPOUR M. Link prediction in social networks using hierarchical community detection[C] / / Pro⁃ ceedings of the 7th conference on information and knowledge technology. Urmia, Iran, 2015: 1⁃5. [4]SCHAEFFER S E. Graph clustering[ J]. Computer science review, 2007, 1(1): 27⁃64. [5]杨博, 刘大有, LIU Jiming, 等. 复杂网络聚类方法[ J]. 软件学报, 2009, 20(1): 54⁃66. YANG Bo, LIU Dayou, LIU Jiming, et al. Complex network clustering algorithms [ J ]. Journal of software, 2009, 20 (1): 54⁃66. [6]冀俊忠, 刘志军, 刘红欣, 等. 蛋白质相互作用网络功 能模块检测的研究综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(4): 577⁃593. JI Junzhong, LIU Zhijun, LIU Hongxin, et al. An overview of research on functional module detection for protein⁃protein interaction networks[J]. Acta automatica sinica, 2014, 40 (4): 577⁃593. [7]PALLA G, BARABáSI A L, VICSEK T. Quantifying social group evolution[J]. Nature, 2007, 446(7136): 664⁃667. [8]SIDIROPOULOS A, PALLIS G, KATSAROS D, et al. Pre⁃ fetching in content distribution networks via web communi⁃ ties identification and outsourcing [ J]. World wide web, 2008, 11(1): 39⁃70. [9]陈克寒, 韩盼盼, 吴健. 基于用户聚类的异构社交网络 推荐算法[J]. 计算机学报, 2013, 36(2): 349⁃359. CHEN Kehan, HAN Panpan, WU Jian. User clustering based social network recommendation[J]. Chinese journal of computers, 2013, 36(2): 349⁃359. [10]FREY B J, DUECK D. Clustering by passing messages be⁃ tween data points[ J]. Science, 2007, 315( 5814): 972⁃ 976. [11]NEWMAN M E J. Community detection and graph partitio⁃ ning[J]. Europhysics letters, 2013, 103(2): 28003. [12]NEWMAN M E J. Spectral methods for community detec⁃ tion and graph partitioning[ J]. Physical review E, 2013, 88(4): 042822. [13]LIN Chuncheng, KANG Jiarong, CHEN J Y. An integer programming approach and visual analysis for detecting hi⁃ erarchical community structures in social networks[ J]. In⁃ formation sciences, 2015, 299: 296⁃311. [14]REN Jun, WANG Jianxin, LI Min, et al. Identifying pro⁃ tein complexes based on density and modularity in protein⁃ protein interaction network [ J ]. BMC systems biology, 2013, 7(S4): S12. [15]LI Xiaoli, FOO C S, NG S K. Discovering protein comple⁃ xes in dense reliable neighborhoods of protein interaction networks[ C] / / Proceedings of the computational systems bioinformatics conference. San Diego, USA, 2007, 6: 157⁃168. [16]PALLA G, DERéNYI I, FARKAS I, et al. Uncovering the overlapping community structure of complex networks in nature and society[J]. Nature, 2005, 435: 814⁃818. [17]SAITO K, YAMADA T, KAZAMA K. Extracting commu⁃ nities from complex networks by the k⁃dense method[ J]. IEICE transactions on fundamentals of electronics, commu⁃ nications and computer sciences, 2008, E91⁃A ( 11 ): 3304⁃3311. [18]SUN Penggang, GAO Lin. Fast algorithms for detecting o⁃ verlapping functional modules in protein⁃protein interaction networks[C] / / Proceedings of the IEEE computational in⁃ telligence in bioinformatics and computational biology. Nashville, TN, USA, 2009: 247⁃254. [19] LIU Guimei, WONG L, CHUA H N. Complex discovery from weighted PPI networks[J]. Bioinformatics, 2009, 25 (15): 1891⁃1897. [20]BADER G D, HOGUE C W V. An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks[J]. BMC bioinformatics, 2003, 4(1): 2. [21]FREEMAN L C. A set of measures of centrality based on betweenness[J]. Sociometry, 1977, 40(1): 35⁃41. [22] CUI Yaizu, WANG Xingyuan, EUSTACE J. Detecting community structure via the maximal sub⁃graphs and be⁃ longing degrees in complex networks[J]. Physica A: sta⁃ tistical mechanics and its applications, 2014, 416: 198⁃ 207. [23] ZACHARY W W. An information flow model for conflict 第 3 期 郑文萍,等:基于稠密子图的社区发现算法 ·431·

.432. 智能系统学报 第11卷 and fission in small groups[J].Journal of anthropological 作者简介: research,1977,33(4):452-473. 郑文萍,1979年生,女,副教授,中 [24]LUSSEAU D,SCHNEIDER K,BOISSEAU O J,et al.The 国计算机学会会员,主要研究方向为图 bottlenose dolphin community of Doubtful Sound features a 论算法、生物信息学等。主持多项国家 large proportion of long-lasting associations:Can geograph- 级项目,发表学术论文多篇。 ic isolation explain this unique trait[].Behavioral ecology and sociobiology,2003,54(4):396-405. [25]NEWMAN M E J.Finding community structure in networks 张浩杰,1991年8月生,男,硕士研 using the eigenvectors of matrices[J].Physical review E, 究生,主要研究方向为数据挖掘、图聚 2006,74(3):036104. [26]GUIMERa R,DANON L,DiAZ-GUILERA A,et al.Self- 类等。 similar community structure in a network of human interac- tions[J].Physical review E,2003,68(6):065103. [27]NEWMAN M E J,GIRVAN M.Finding and evaluating community structure in networks[J].Physical review E, 2004,69(2):026113. 王杰,1988年8月生,男,博士研究 [28 ]SHEN Huawei,CHENG Xueqi,CAI Kai,et al.Detect o- 生,主要研究方向为数据挖掘,生物信 verlapping and hierarchical community structure in net- works[J].Physica A:statistical mechanics and its appli- 息学。 cations,2009.388(8):1706-1712. 2016年协同软件过程国际会议 International Track on Collaborative Software Processes Building complex and trustworthy software systems in the shortest time-to-market remains the challenging objective that competitive companies are facing constantly,and mastering the development process is a key issue towards this objective.Companies and software de- velopers need to be able to formalize their development processes in order to analyze them,to enact them,and to assess them for quality measurement and efficiency improvement.In the context of complex software and systems development,there are many actors involved in the development who use different tools and heterogeneous modeling languages.So we can say that resulting processes are highly collabora- tive and must be described and enacted as such. Most published papers propose innovative technical and human approaches to expand collaboration support,often backed up by theo- ry brought from various disciplines including,management science,design science,cognitive sciences and social sciences.The track CSP2016 mainly seeks papers with theory,models,design principles,methodologies,and case studies that contribute to better under- stand the complex interrelations between collaboration and technology for software and systems development processes.Considering the heterogeneity of research in collaboration and technology,researchers may address the validation of their work through multiple approaches including laboratory experiments,fieldwork,analytic evaluations,case studies,prototyping,and empirical tests. The aim of this track is to gather researchers and industrial practitioners working in the field of Collaborative Process Support for Software Development.It will provide an opportunity for the community to exchange ideas and to present emerging new technologies and understanding in the field. Website:https://www.irit.fr/CSP2016/
and fission in small groups[ J]. Journal of anthropological research, 1977, 33(4): 452⁃473. [24]LUSSEAU D, SCHNEIDER K, BOISSEAU O J, et al. The bottlenose dolphin community of Doubtful Sound features a large proportion of long⁃lasting associations: Can geograph⁃ ic isolation explain this unique trait[J]. Behavioral ecology and sociobiology, 2003, 54(4): 396⁃405. [25]NEWMAN M E J. Finding community structure in networks using the eigenvectors of matrices[ J]. Physical review E, 2006, 74(3): 036104. [26]GUIMERà R, DANON L, DíAZ⁃GUILERA A, et al. Self⁃ similar community structure in a network of human interac⁃ tions[J]. Physical review E, 2003, 68(6): 065103. [27] NEWMAN M E J, GIRVAN M. Finding and evaluating community structure in networks[ J]. Physical review E, 2004, 69(2): 026113. [28]SHEN Huawei, CHENG Xueqi, CAI Kai, et al. Detect o⁃ verlapping and hierarchical community structure in net⁃ works[J]. Physica A: statistical mechanics and its appli⁃ cations, 2009, 388(8): 1706⁃1712. 作者简介: 郑文萍,1979 年生,女,副教授,中 国计算机学会会员,主要研究方向为图 论算法、生物信息学等。 主持多项国家 级项目,发表学术论文多篇。 张浩杰,1991 年 8 月生,男,硕士研 究生,主要研究方向为数据挖掘、图聚 类等。 王杰,1988 年 8 月生,男,博士研究 生,主要研究方向为数据挖掘,生物信 息学。 2016 年协同软件过程国际会议 International Track on Collaborative Software Processes Building complex and trustworthy software systems in the shortest time⁃to⁃market remains the challenging objective that competitive companies are facing constantly, and mastering the development process is a key issue towards this objective. Companies and software de⁃ velopers need to be able to formalize their development processes in order to analyze them, to enact them, and to assess them for quality measurement and efficiency improvement. In the context of complex software and systems development, there are many actors involved in the development who use different tools and heterogeneous modeling languages. So we can say that resulting processes are highly collabora⁃ tive and must be described and enacted as such. Most published papers propose innovative technical and human approaches to expand collaboration support, often backed up by theo⁃ ry brought from various disciplines including, management science, design science, cognitive sciences and social sciences. The track CSP’2016 mainly seeks papers with theory, models, design principles, methodologies, and case studies that contribute to better under⁃ stand the complex interrelations between collaboration and technology for software and systems development processes. Considering the heterogeneity of research in collaboration and technology, researchers may address the validation of their work through multiple approaches including laboratory experiments, fieldwork, analytic evaluations, case studies, prototyping, and empirical tests. The aim of this track is to gather researchers and industrial practitioners working in the field of Collaborative Process Support for Software Development. It will provide an opportunity for the community to exchange ideas and to present emerging new technologies and understanding in the field. Website: https:/ / www.irit.fr/ CSP2016/ ·432· 智 能 系 统 学 报 第 11 卷