
CORPOR∫E FINANCIA小D MANAGEMEN」 PART III CAPITAL INVESTMENT DECISION (chapter 8-11) 州经怡贸易大号 UNW原s方C等NTE3风制U方男0G0Cs
CORPORATE FINANCIAL CORPORATE FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT MANAGEMENT PART III CAPITAL INVESTMENT DECISION (chapter 8-11)

Chapter 11 The Cost of Capital 渊补经价货多方居 YO年NEB证事00003
Chapter 11 Chapter 11 The Cost of Capital

Introduction 1.Weighted Average Cost of Capital 2.Component Costs 3.Marginal Cost of Capital 渊补经价货多方居 YO年NEB证事00003
Introduction Introduction 1. Weighted Average Cost of Capital 2. Component Costs 3. Marginal Cost of Capital

1.Weighted Average Cost of Capital ●Cost of capital What the firm must pay for capital The return required by investors Minimum rate of return required on new investments Determined in the capital markets Depends on the risk associated with the firm's activities Equal to the equilibrium rate of return demanded by investors in the capital markets for securities of that degree of risk 渊外校价贫量方是 老YO年NE证事0EO0h3
4 1. Weighted Average Cost of Capital zCost of capital – What the firm must pay for capital – The return required by investors – Minimum rate of return required on new investments – Determined in the capital markets – Depends on the risk associated with the firm’s activities Equal to the equilibrium rate of return demanded by investors in the capital markets for securities of that degree of risk

Continued... Weighted Average Cost of Capital:k Discount rate used when computing the NPV of a project of average risk Hurdle rate used in conjunction with the IRR Based on the after-tax cost of capital Obtained from the weighted costs of the individual components Weights equal to the proportion of each of the components in the target capital structure 渊外校价贫多方号 YO年NEB证事0000
5 Continued Continued… zWeighted Average Cost of Capital: ka – Discount rate used when computing the NPV of a project of average risk – Hurdle rate used in conjunction with the IRR – Based on the after-tax cost of capital – Obtained from the weighted costs of the individual components – Weights equal to the proportion of each of the components in the target capital structure
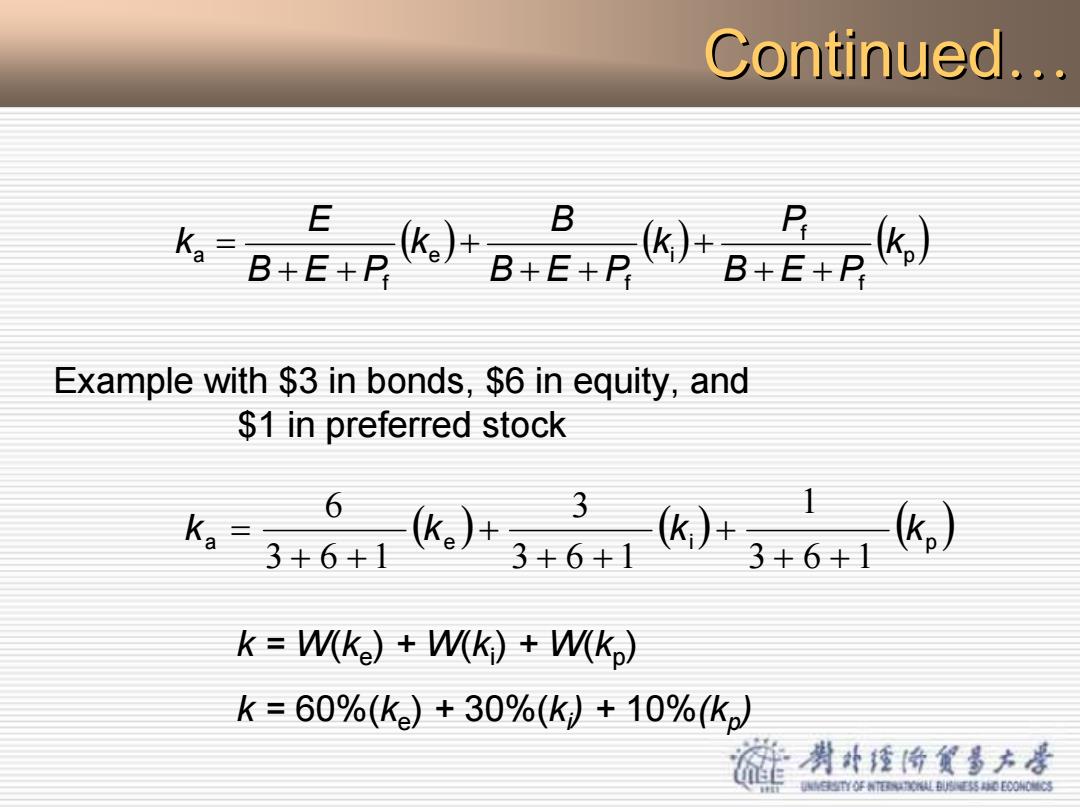
Continued... B k2 B+E+P k。+ B+E+P Example with $3 in bonds,$6 in equity,and $1 in preferred stock 6 3+6+1 3+6+1 3+6+1 k=W(ke)W(k)+W(kp) k=60%(ke)+30%(k)+10%(k。 渊外楂价货多方是 YO年N0事0E000
Continued Continued… ( ) ( ) ( ) p f f i f e f a k B E P P k B E P B k B E P E k + + + + + + + + = Example with $3 in bonds, $6 in equity, and $1 in preferred stock ( ) ( ) ( ) ka ke ki kp 3 6 1 1 3 6 1 3 3 6 1 6 + + + + + + + + = k = W(ke) + W(ki) + W(kp) k = 60%(ke) + 30%(ki) + 10%(kp)

Continued... O Risk vs.required return trade-off:Required return rf Risk premium rf risk-free rate o Real rate of return determined by supply and demand o Plus a premium for the effects of inflation Components of the risk premium Business risk -associated with the amount of operating leverage O Financial risk -associated with the use of financial leverage o Marketability risk -refers to the ability to quickly buy and sell O Interest rate risk -arising from changes in interest rates o Seniority risk -due to the priority of a security's claim on assets 渊外经价货多方是 超直O年N0l8药0000习
Continued Continued… z Risk vs. required return trade-off : Required return = rf + Risk premium – rf = risk-free rate o Real rate of return determined by supply and demand o Plus a premium for the effects of inflation – Components of the risk premium o Business risk -associated with the amount of operating leverage o Financial risk -associated with the use of financial leverage o Marketability risk -refers to the ability to quickly buy and sell o Interest rate risk -arising from changes in interest rates o Seniority risk -due to the priority of a security’s claim on assets
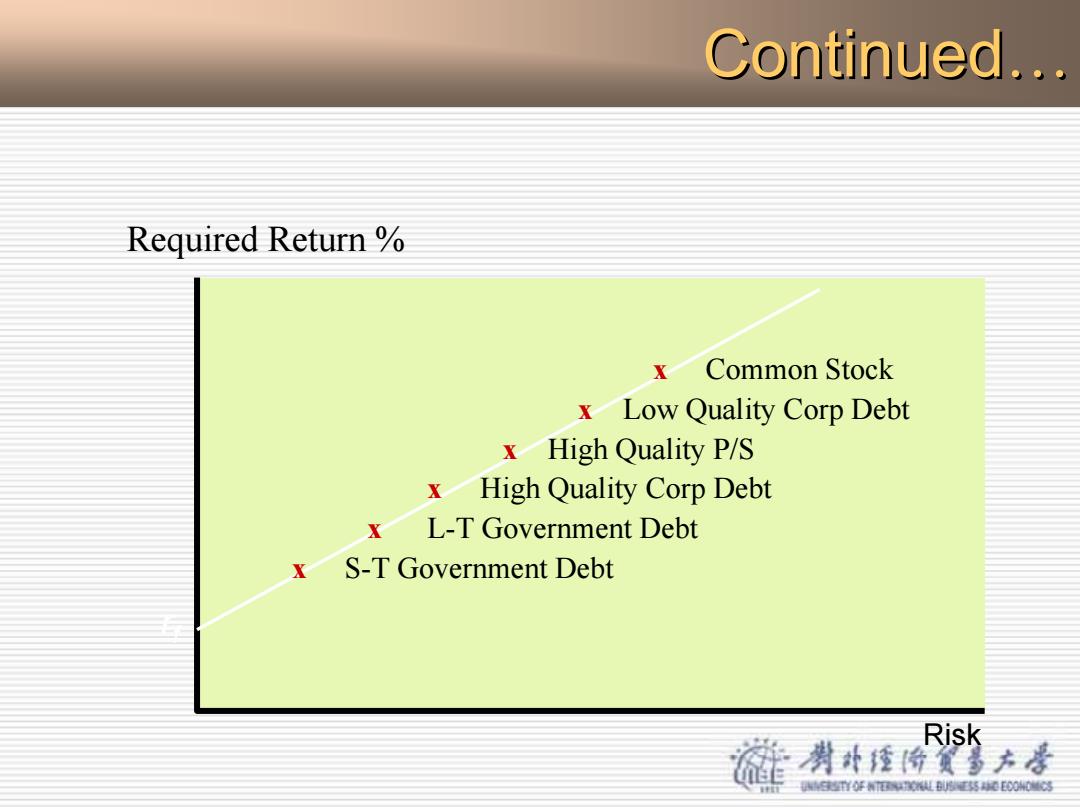
Continued... Required Return x Common Stock x Low Quality Corp Debt x High Quality P/S x High Quality Corp Debt L-T Government Debt x S-T Government Debt Risk 州升佳份兴方是 YO年N0事0E0003
rf Risk Required Return % x Common Stock x Low Quality Corp Debt x High Quality P/S x High Quality Corp Debt x L-T Government Debt x S-T Government Debt Continued Continued…

2.Component Costs Cost of Debt ki=kd (1-T) Interest is tax deductible OCost of Preferred Stock kp=Dy/Pnet Dividends are not tax deductible Pnet:Net of issuance costs 剥外校价贫多方号 YO年N0事0E0003
2.Component Costs zCost of Debt ki = kd (1 – T) Interest is tax deductible zCost of Preferred Stock kp = D p /Pnet Dividends are not tax deductible Pnet : Net of issuance costs

Continued... O Cost of internal equity capital k。=D/Po+8 Cost of R/E using constant dividend g k。=r+B0m-r分 CAPM Risk premium on debt approach Add Cost of external equity ke=DilPnet+g Pnet=Po(1-) 剥外经价贫多方居 YO年N0事0E0003
Continued Continued… zCost of internal equity capital – ke = D1/P0 + g Cost of R/E using constant dividend g – ke = rf + βj(rm – rf) CAPM – Risk premium on debt approach Add % zCost of external equity k′e = D1/Pnet + g Pnet = P0(1 – f)