
Financial Econometrics Chapter 10.Propensity Score Matching Jin Ling School of Finance,Zhongnan University of Economics and Law
Financial Econometrics Chapter 10. Propensity Score Matching Jin Ling School of Finance, Zhongnan University of Economics and Law 1

Outline The Matching Methodology for Causal Inference The Propensity Score Matching The Application for Propensity Score Matching 2
• The Matching Methodology for Causal Inference • The Propensity Score Matching • The Application for Propensity Score Matching 2 Outline
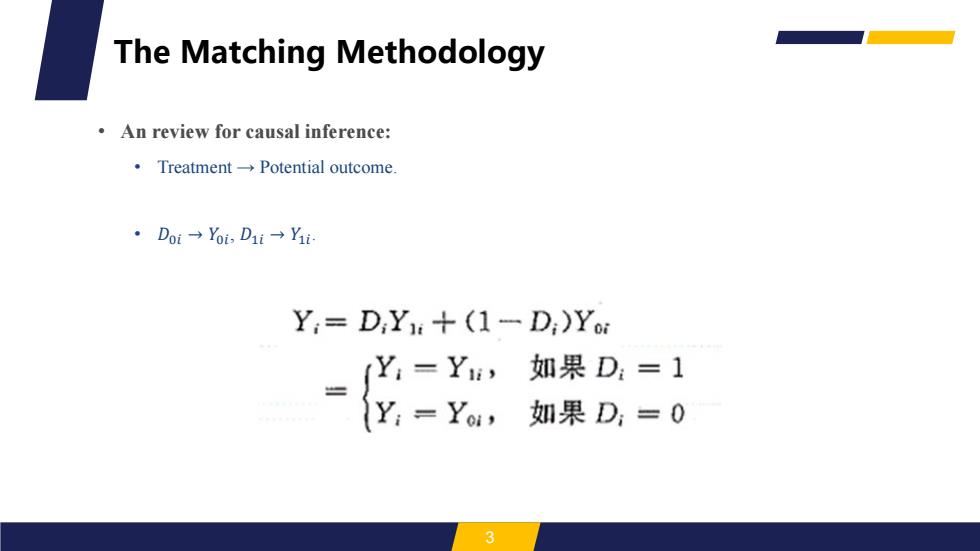
The Matching Methodology An review for causal inference: 。Treatment→Potential outcome. ·Doi→YoiD1i→Yi Yi=D;Y+(1-D:)Yo (Y:=Yi,如果D:=1 {Y:=Yu,如果D,=0 3
• An review for causal inference: • Treatment → Potential outcome. • 𝐷0𝑖 → 𝑌0𝑖 , 𝐷1𝑖 → 𝑌1𝑖 . 3 The Matching Methodology
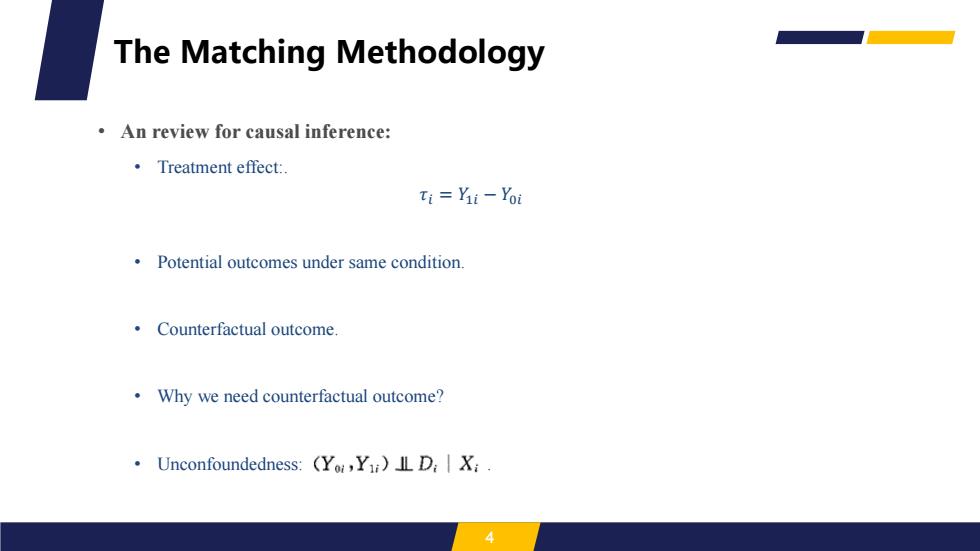
The Matching Methodology An review for causal inference: ·Treatment effect:. Ti=Yi-Yoi Potential outcomes under same condition. Counterfactual outcome. Why we need counterfactual outcome? Unconfoundedness:(Yoi,Y1)IL D:X;
• An review for causal inference: • Treatment effect:. 𝜏𝑖 = 𝑌1𝑖 − 𝑌0𝑖 • Potential outcomes under same condition. • Counterfactual outcome. • Why we need counterfactual outcome? • Unconfoundedness: . 4 The Matching Methodology

The Matching Methodology How to satisfy unconfoundedness: ·Control variable. Difference-in-difference model. Instrumental variable. 5
• How to satisfy unconfoundedness: • Control variable. • Difference-in-difference model. • Instrumental variable. 5 The Matching Methodology

The Matching Methodology The matching methodology to satisfy unconfoundedness: Confounding bias and sample selection bias. The covariate affects both treatment probability and potential outcome. The treatment status is not driven by the covariates:DID and IV. Control for the covariates. What if the treatment probability is same for treatment group and non-treatment group? Replication to eliminate the disturbance from confounding factors. 6
• The matching methodology to satisfy unconfoundedness: • Confounding bias and sample selection bias . • The covariate affects both treatment probability and potential outcome. • The treatment status is not driven by the covariates: DID and IV. • Control for the covariates. • What if the treatment probability is same for treatment group and non-treatment group? • Replication to eliminate the disturbance from confounding factors. 6 The Matching Methodology
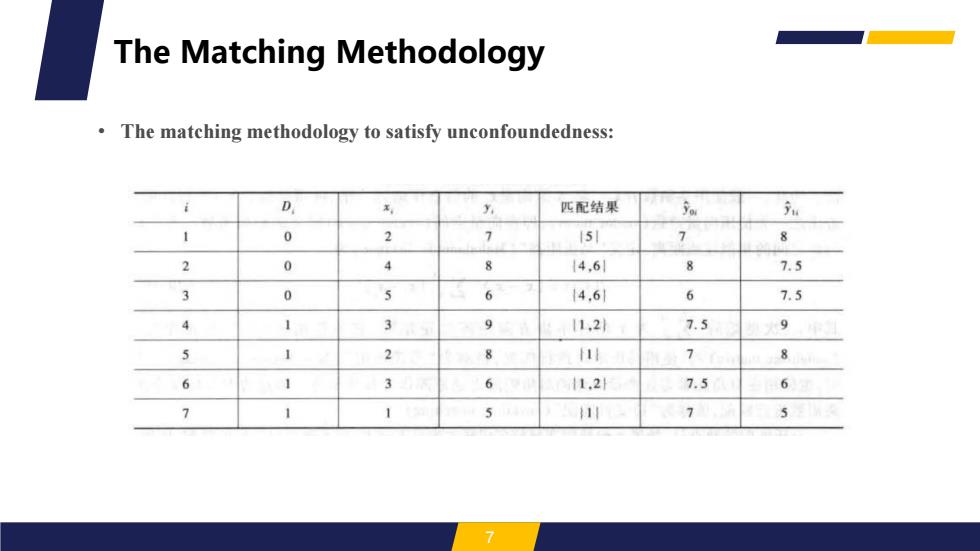
The Matching Methodology 。 The matching methodology to satisfy unconfoundedness: D 匹配结果 Yor 1 0 2 151 7 8 2 0 4 8 14,61 8 7.5 3 0 5 6 14.61 6 7.5 4 1 3 9 11,21 7.5 9 5 1 2 8 114 1 6 1 3 6 11.21 7.5 6 7 1 1 5 111 7 5 7
• The matching methodology to satisfy unconfoundedness: 7 The Matching Methodology

Outline The Matching Methodology for Causal Inference The Propensity Score Matching The Application for Propensity Score Matching 8
• The Matching Methodology for Causal Inference • The Propensity Score Matching • The Application for Propensity Score Matching 8 Outline

The Propensity Score Matching The covariate determines the treatment probability: 。A set of covariates. How to match treatment and control groups using a set of covariates? Can we ensure that all covariates are same for treatment and control groups? 9
• The covariate determines the treatment probability: • A set of covariates. • How to match treatment and control groups using a set of covariates? • Can we ensure that all covariates are same for treatment and control groups? 9 The Propensity Score Matching

The Propensity Score Matching Dimension reduction: ·A set of covariates→A function. The methodology to develop a function. The difference between treatment and control groups under a set of covariates. ·The distance function in vector space:Mahalanobis distance(马氏距离) Dy(,y)=V(-y)TE-1(-y) The limitation when using Mahalanobis distance:relative distance and absolute distance. 10
• Dimension reduction: • A set of covariates→A function. • The methodology to develop a function. • The difference between treatment and control groups under a set of covariates. • The distance function in vector space: Mahalanobis distance (马氏距离) • The limitation when using Mahalanobis distance: relative distance and absolute distance. 10 The Propensity Score Matching