
生理学精品散案 Chapter 9 sense organs 案例:某虹膜炎患者,医生给予阿托品滴眼等治疗施。用药后患者出现疃孔扩大,视物不清,畏光,疑病情加重,第二天再次复诊。问 ①阿托品为什么会引起瞳孔扩大? ②患者是香一定是病情加重? I Receptors 1.Dentification Receptor a part of neuron or a specialized cell Sense organ Receptor non-neural cells 2.Classifications location: exteroceptor interoceptor type of stimlus: mechanoreceptor thermoreceptor nociceptor electromagnetic receptor ecepto (1)differential sensitivity adequate stimulus sensory threshold (2)Transduction *receptor potential *generator potentia
生理学精品教案 Chapter 9 sense organs 案例:某虹膜炎患者,医生给予阿托品滴眼等治疗措施。用药后患者出现瞳孔扩大,视物不清,畏光,疑病情加重,第二天再次复诊。问 ①阿托品为什么会引起瞳孔扩大? ②患者是否一定是病情加重? I Receptors 1.Dentification Receptor a part of neuron or a specialized cell Sense organ Receptor + non-neural cells 2.Classifications location: exteroceptor interoceptor type of stimulus: mechanoreceptor thermoreceptor nociceptor electromagnetic receptor chemoreceptor 3.Characteristics of receptor (1)differential sensitivity * adequate stimulus * sensory threshold (2)Transduction *receptor potential *generator potential

An Mechanism stimulus mechanically-gated ion channel permeability个 receptor-G protein-second messenger membrane potential↓ Characteristics stimulus个 +magnitude个 Non-all or none electrotonic propagation Summation「spatial Temporal (3)Encoding To transform the information from stimulus into a train of nerve impulses The quality (modality)of sensation specific part of the brain of activated receptor (Adaptation when a maintained stimulus of constant strength is applied to a receptor,the frequency of the AP in its sensory nerve declines ever time
Mechanism Characteristics (3)Encoding To transform the information from stimulus into a train of nerve impulses The quality (modality) of sensation specific part of the brain The quantity (intensity) of sensation Frequency of AP Number of activated receptor (4) Adaptation when a maintained stimulus of constant strength is applied to a receptor, the frequency of the AP in its sensory nerve declines ever time
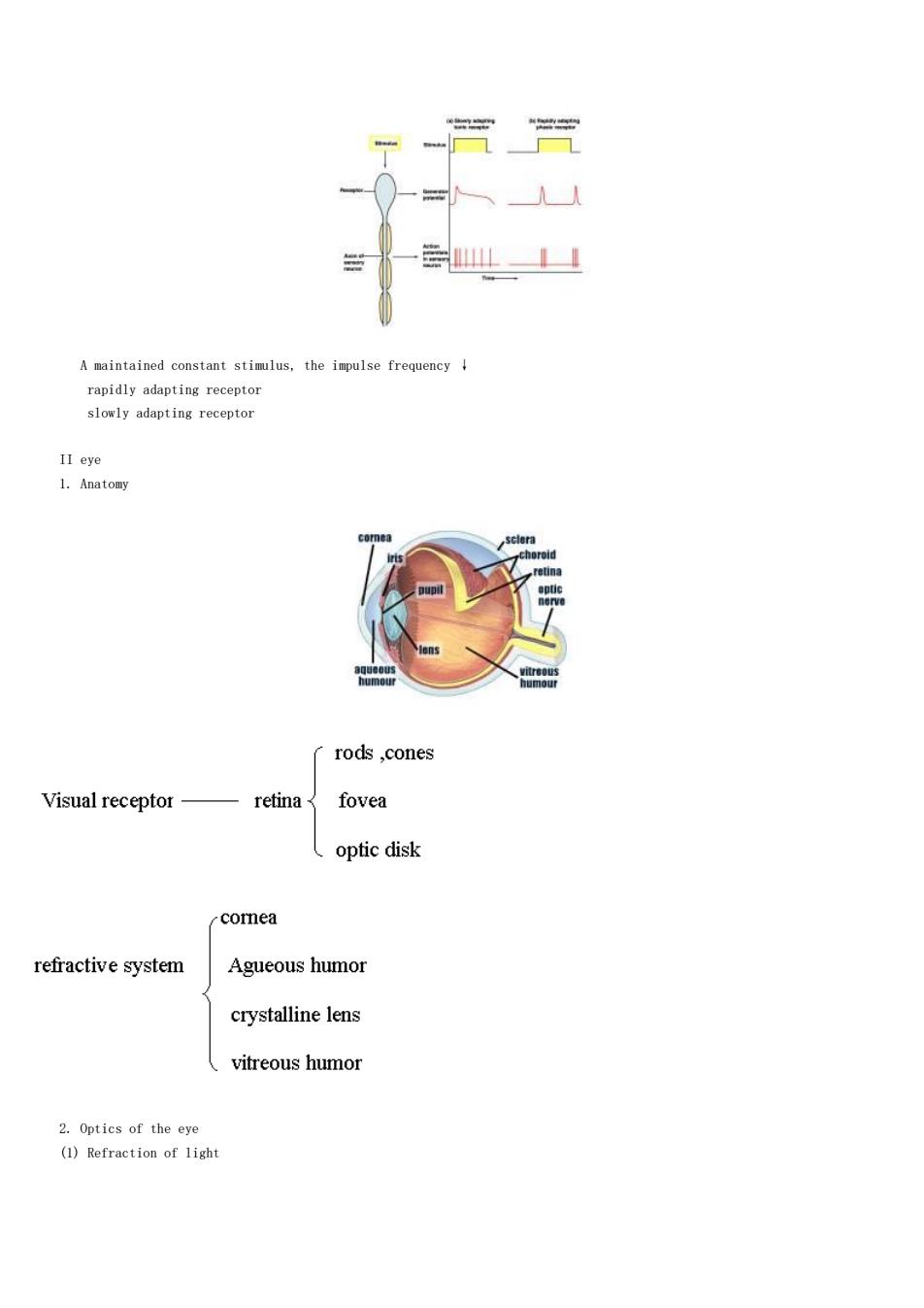
A maintained constant stimlus,the impulse frequency rapidly adapting receptor slowly adapting receptor rods,cones Visual receptor retina〈 fovea optic disk comea refractive system Agueous humor crystalline lens vitreous humor 2.Optics of the eye (1)Refraction of light
A maintained constant stimulus, the impulse frequency ↓ rapidly adapting receptor slowly adapting receptor II eye 1. Anatomy 2. Optics of the eye (1) Refraction of light
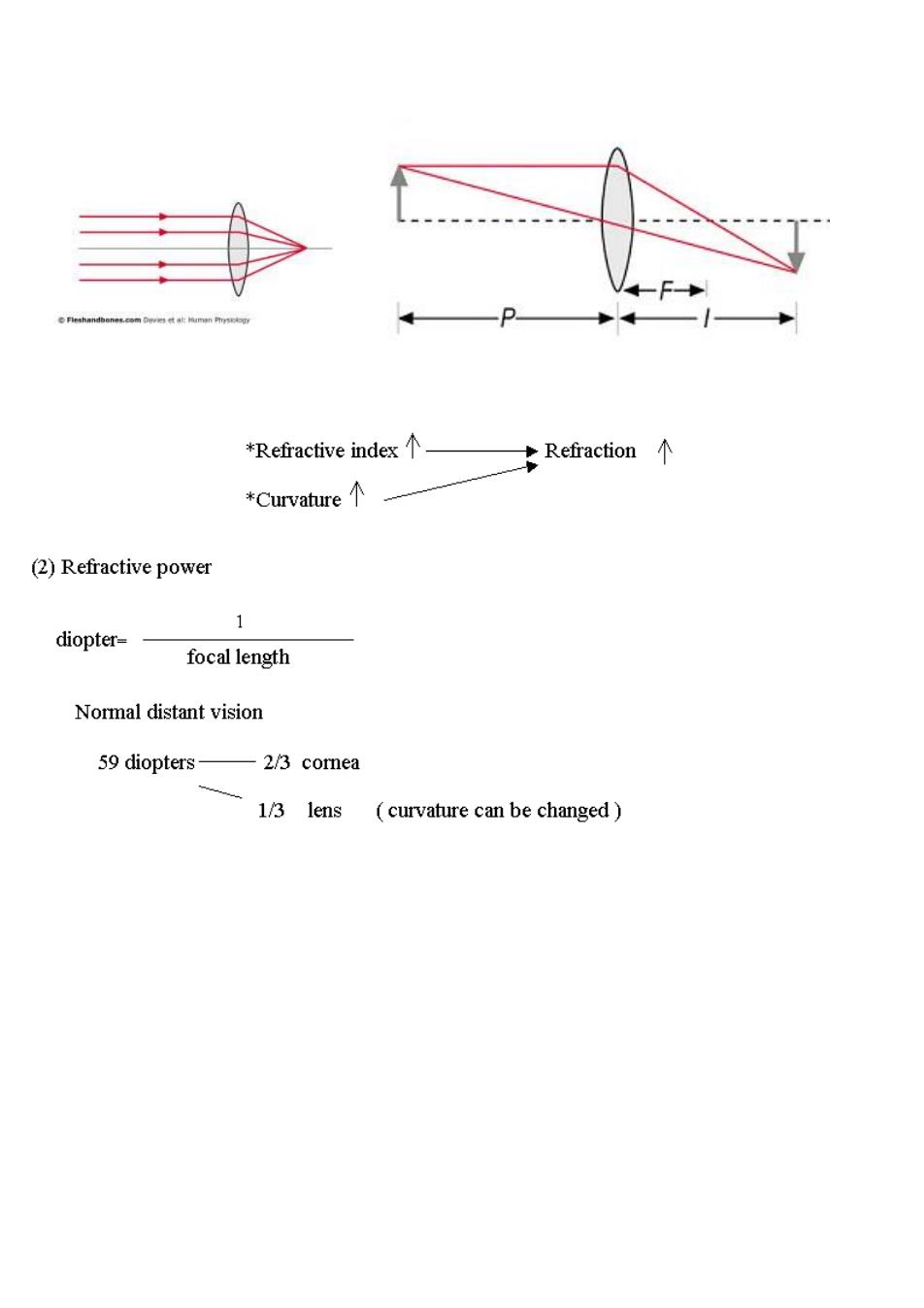
*Refractive index个 Refraction个 *Curvature个 (2)Refractive power 1 diopter- focal length Normal distant vision 59 diopters- -2/3 cornea 1/3 lens (curvature can be changed)
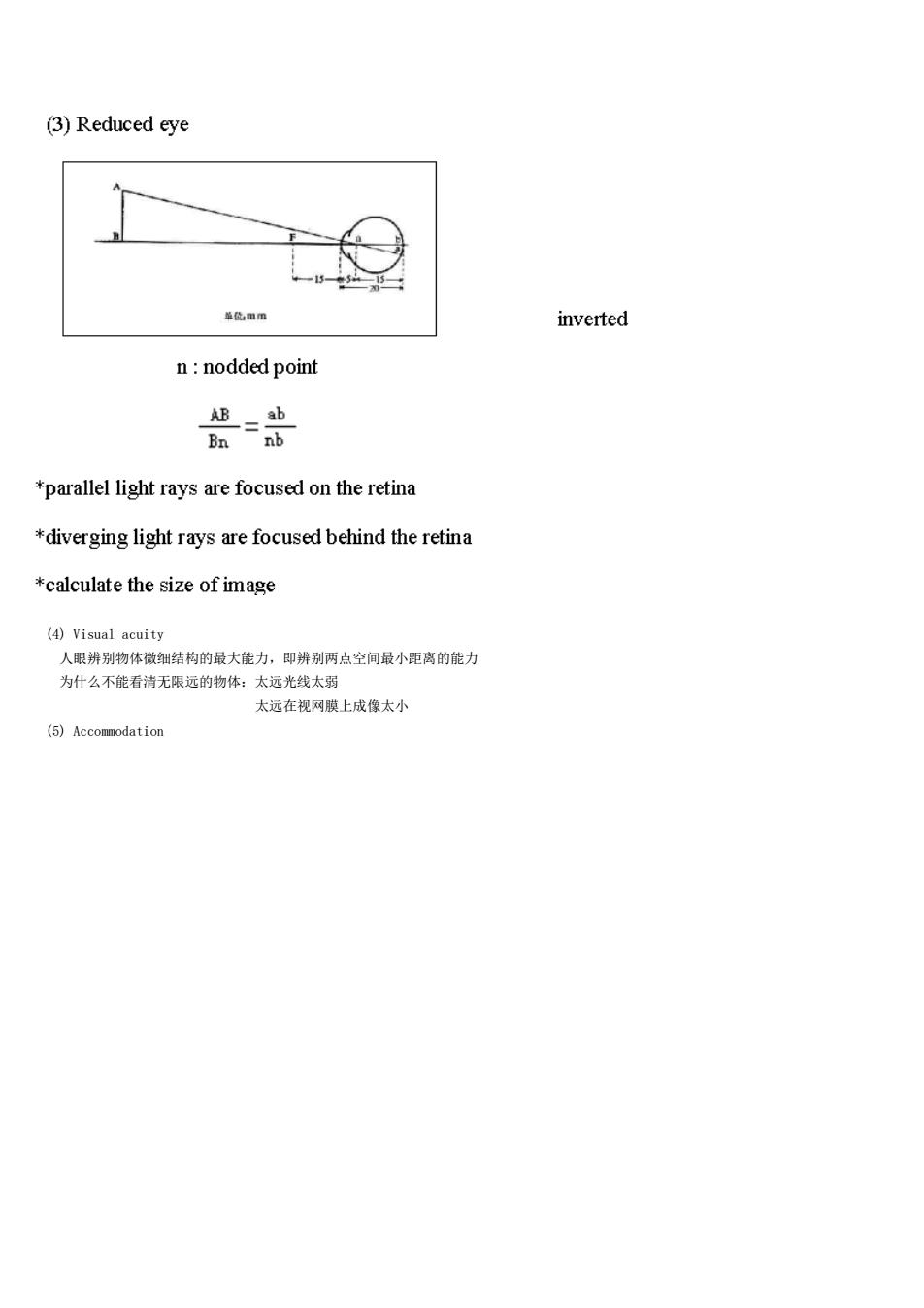
(3)Reduced eye inverted n:nodded point *parallel light rays are focused on the retina *diverging light rays are focused behind the retina *calculate the size of image (④Visual acuity 人眼辨别物体微细结构的最大能力,即辨别两点空间最小距离的能力 为什么不能看消无限运的物体:太远光线太 太运远在视网膜上成像太小 ()⑤Accomodation
(4) Visual acuity 人眼辨别物体微细结构的最大能力,即辨别两点空间最小距离的能力 为什么不能看清无限远的物体:太远光线太弱 太远在视网膜上成像太小 (5) Accommodation
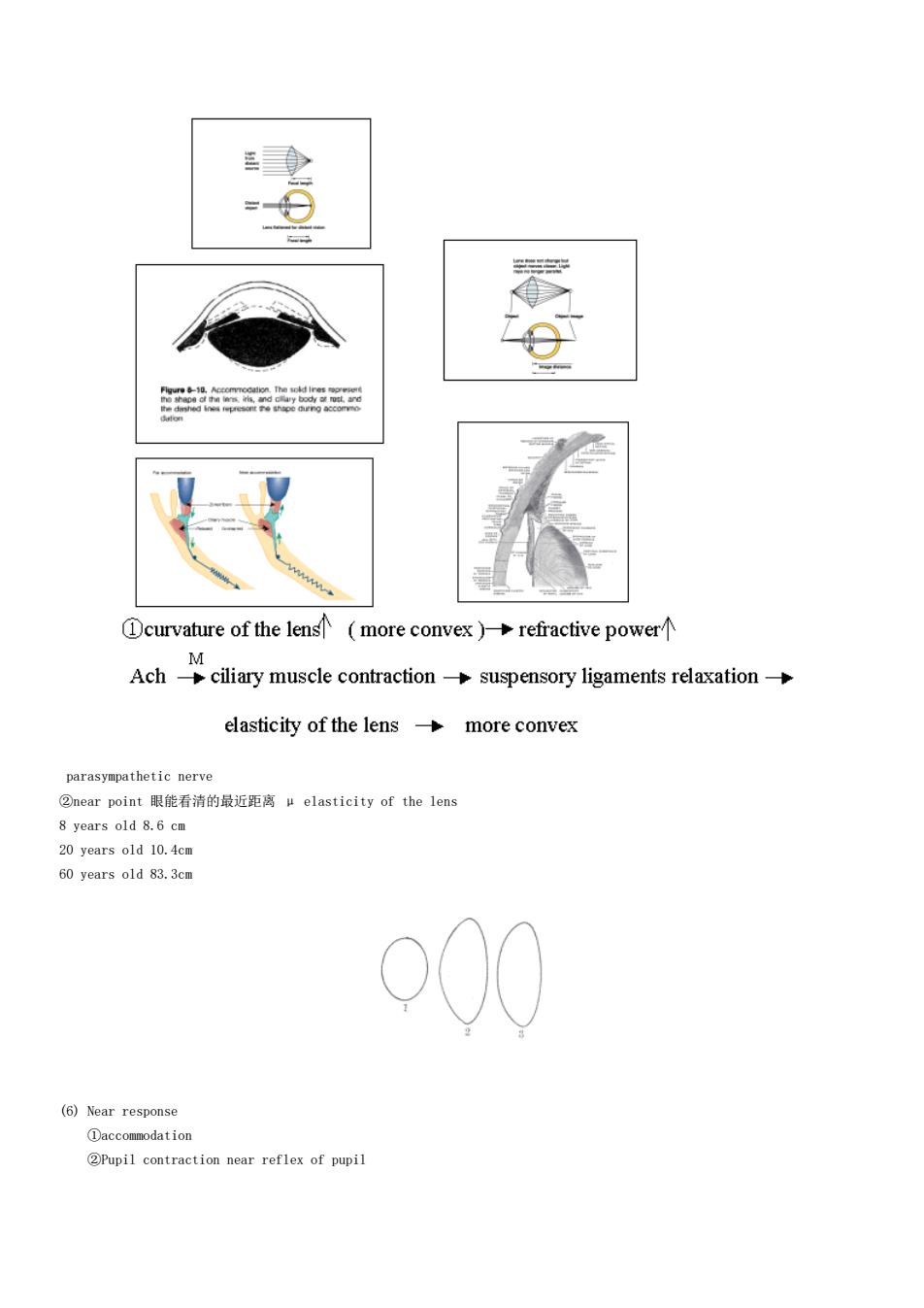
= 零 Dcurvature of the lens more convex)-refractive power Achciary muscle contractionsupensory ligaments relaxation elasticity of the lens-more convex parasympathetic nerve ②near point眼能看清的最近距离elasticity of the lens 8 years old 8.6 cm 20 years old 10.4c 60 years old 83.3cm (6)Near response ①accommodation 2Pupil contraction near reflex of pupil
parasympathetic nerve ②near point 眼能看清的最近距离 μ elasticity of the lens 8 years old 8.6 cm 20 years old 10.4cm 60 years old 83.3cm (6) Near response ①accommodation ②Pupil contraction near reflex of pupil
Convergence convergence reflex (7)Errors of refraction *Emmetropia normal vision +Myopia Nearsightedness Characteristics:parallel light rays are focused in front of retina Causes too long eveball Tooch refractory power Correction concave lens *Hyperopia Farsightedness Characteristics:parallel light rays are focused behind retina Cause too shoot evehall too weak refractor powe Correction convex lens *Astigmatism Characteristics light rays are refracted to different focus Cause the currature of refractive system are not uniform Correction eylindrical lens *presbuopia Characteristics near point Cause elasticity of the lens Correction conves lens (8)visual field (9)binocular vision and stereopsis
③Convergence convergence reflex (7) Errors of refraction *Emmetropia normal vision *Myopia Nearsightedness Characteristics: parallel light rays are focused in front of retina Causes too long eyeball Too much refractory power Correction concave lens *Hyperopia : Farsightedness Characteristics: parallel light rays are focused behind retina Cause too shoot eyeball too weak refractory power Correction convex lens *Astigmatism Characteristics light rays are refracted to different focus Cause the currature of refractive system are not uniform Correction cylindrical lens *presbuopia Characteristics near point ↑ Cause elasticity of the lens ↓ Correction conves lens (8) visual field (9) binocular vision and stereopsis
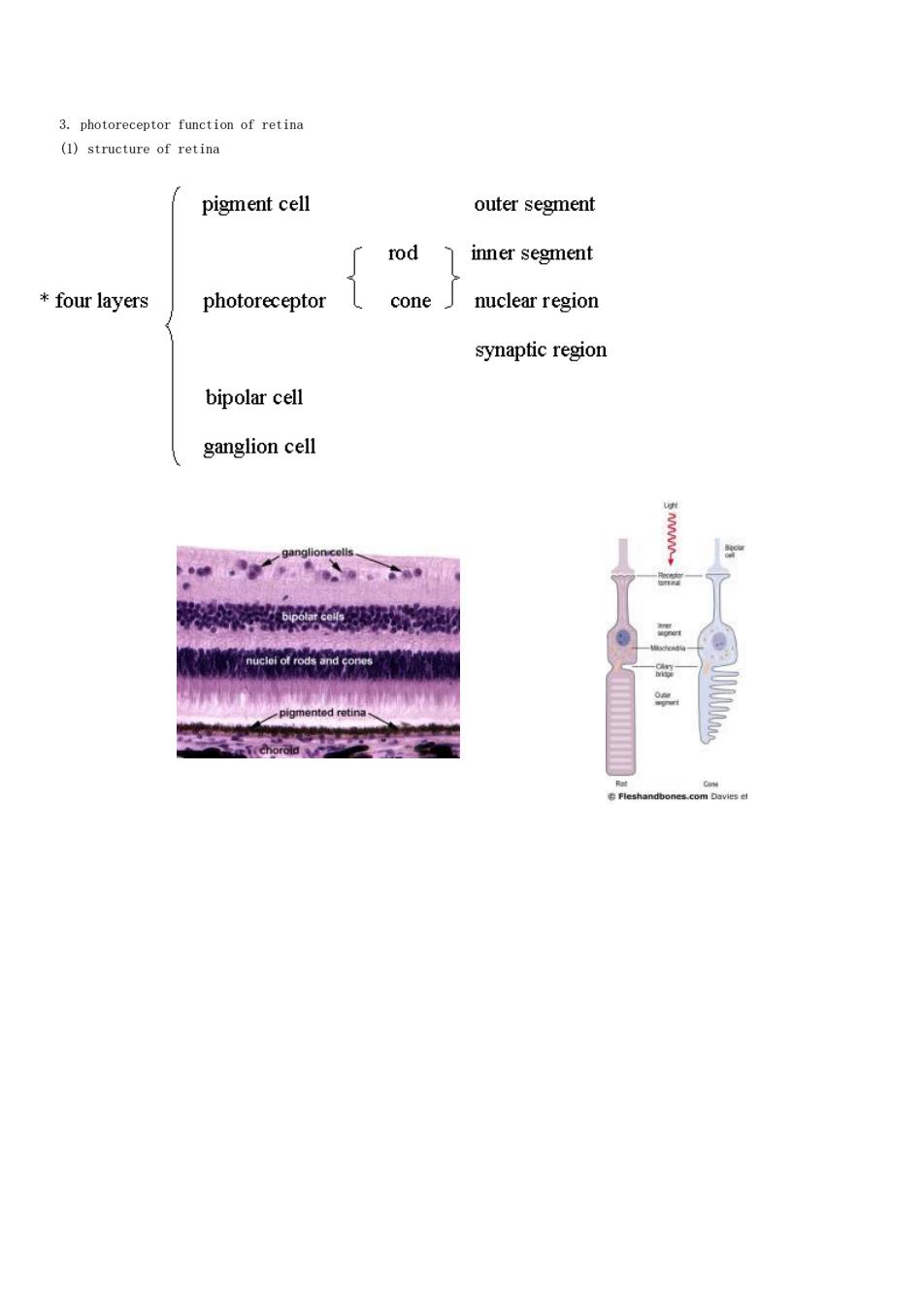
3.photoreceptor function of retina (1)structure of retina pigment cell outer segment rod inner segment four layers photoreceptor cone J nuclear region synaptic region bipolar cell ganglion cell
3. photoreceptor function of retina (1) structure of retina

Rod Bipolar cell-ganglion cell Cone *optic disc blind spot The Retina *Fovea almost only cone location sensitivity visual color photo acuity vision function chemi cals scotopic rod peripheal high 10 no rhodopsin vision cone central high cone photopic yes pigment vision (3)photochemical reaction of rhodopsin
(3) photochemical reaction of rhodopsin
opsin+all-trans-retinal all-trans etinol 1l-cis-retinal← (vitaminA) (4)photoreceptor potential- 一yperpolarization R.esting potential4 omv lisht→Na'channel close→RP个 (Nat channel open)depolarization) (hyperpolarization) 1 photon◆1mv light-rhodopsin decomposetransducin phosphodiesterase- cGMPNa'channel close Nat influx-hyperpolarization (5)dark adaptation and light adaptation ①dark adaptation ②light adaptation *level of photochemical pupilary light reflex sensitivity to light 500.0001000.000 times ③night blindness vitamine A↓ (6)color vision Trichromacy theory
(5) dark adaptation and light adaptation ①dark adaptation ②light adaptation *level of photochemical *pupilary light reflex sensitivity to light 500,000~1000,000 times ③night blindness vitamine A ↓ (6) color vision Trichromacy theory