
Chapter2 Chapter 2 Outlines Materials and Structural systems 2.1 Materials used in tall building structures for Tall Buildings 2.2 Design Principles 2.3 Lateral Load-resisting system 2.4 Diaphragm Systems 2.5 Foundations Tong University.2015 2.1 Confined Concrete 2.2 Design principle 2.2.1 Design requirements 2.2.1 Design requirements Architectural requirements Construction requirements Construction safety Green Design,or LEED LeedershpnEnergynd EenaDesn 本课件版权归作者所有,仅供个人学习使用,请勿转载。 1
1 Chapter 2 Materials and Structural systems for Tall Buildings Xiong Haibei, Tongji University, 2015 Chapter 2 Outlines 2.1 Materials used in tall building structures 2.2 Design Principles 2.3 Lateral Load-resisting system 2.4 Diaphragm Systems 2.5 Foundations 2.1 Confined Concrete Why Confined Concrete should be used? How to confine the concrete? Source:Bungale S. Taranath, Reinforced Concrete Design of Tall Buildings, CRC Press, 2010 2.2 Design principle 2.2.1 Design requirements Architectural requirements Environment Occupancy Comfort Structural safety requirements Strength capability Deformation tolerance Durability 2.2.1 Design requirements Construction requirements Feasibility New techniques application Construction safety Cost economic requirements Green Design, or LEED Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design 本课件版权归作者所有,仅供个人学习使用,请勿转载

2.2.2 Structural Design Requirements 2.2.3 Design Principles 2 and elmn High performance materials. Non-structural elements sign. Structural Characteristics 2.3 Lateral Load-resisting system oTall 233Tb 2.3.4 Frame with wall system Wcoreominant omn 23.7 cramne w houhbefortdoen 23.8 Mega system 2.3 Lateral Load-resisting system 2.3 Lateral Load 本课件版权归作者所有,仅供个人学习使用,请勿转载。 2
2 1. Favorable site 2. Enough capability of foundation, avoid unexpected settlements 3. Regularity in plan, avoid large torsion, and avoid weak story and soft story in building 4. Set some separation (gaps) : temperature joint, settlement joint and seismic joint 5. More earthquake resistant systems, avoiding progressive collapse. 2.2.2 Structural Design Requirements 6. Clear load path and reasonable schematics of tall building structures, 7. Ductility of structures and elements, 8. Integration of structure, 9. High performance materials, 10. Non-structural elements design. 2.2.3 Design Principles Structural Characteristics Tall The lateral forces are dominantly control the tall buildings’ performance. Under a uniform wind load the overturning moment at the base varies in proportion to the height of the building, while the lateral drift varies as the third power. Wind loads and earthquake action are dominant comparing with the vertical loads. Fire resistant time should be longer. Progressive collapse failure mode should be forbidden. 2.3 Lateral Load-resisting system 2.3.1 Frame system 2.3.2 Wall system 2.3.3 Tube system 2.3.4 Frame with wall system 2.3.5 Frame supporting wall system 2.3.6 Frame with tube system 2.3.7 Combined tube system 2.3.8 Mega system 2.3 Lateral Load-resisting system 引自:Bungale S. Taranath, Reinforced Concrete Design of Tall Buildings, CRC Press, 2010 2.3 Lateral Load-resisting system 引自:reading material:Mir M.Ali, Structural Development inTallBuildings, Steel Concrete 本课件版权归作者所有,仅供个人学习使用,请勿转载
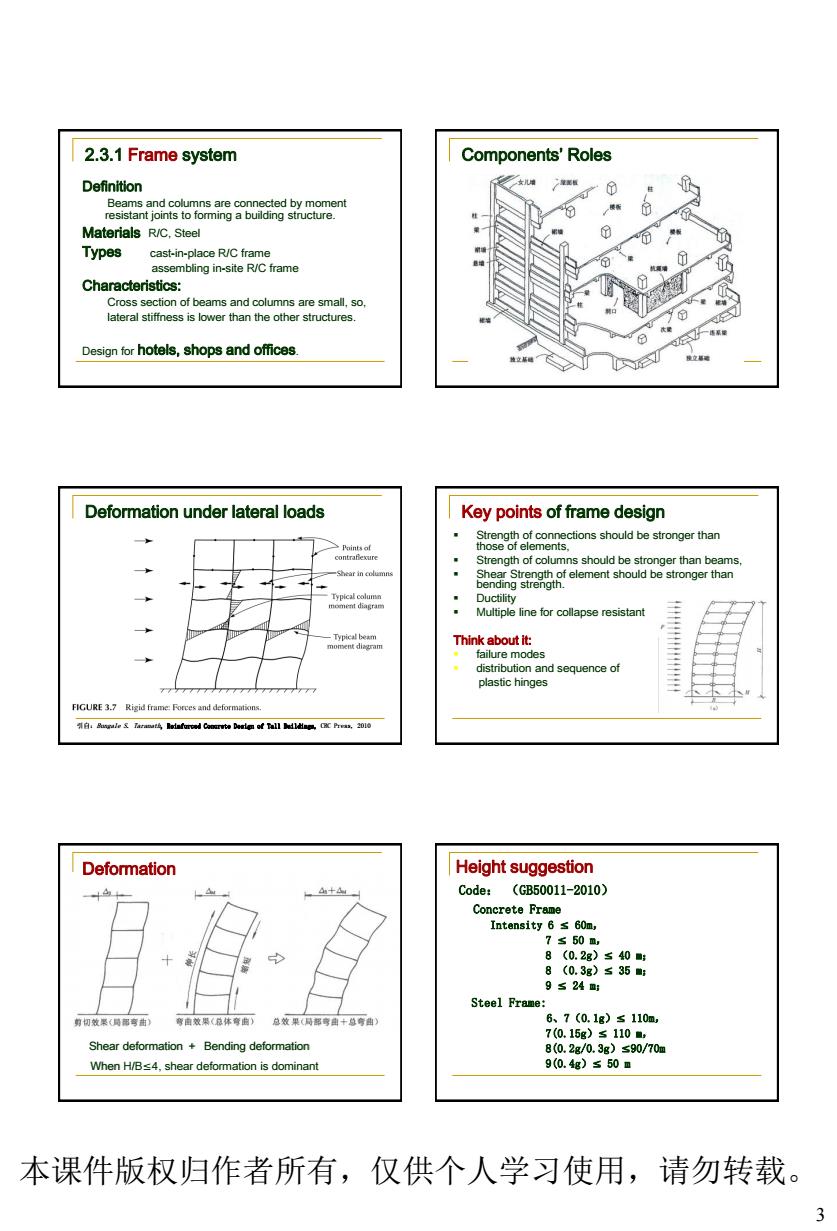
2.3.1 Frame system Components'Roles Definition t onure Materials RC.Stee Characteristics: esinfor hotels,shops and offices. Deformation under lateral loads Key points of frame design ions should be stronger than ne or c stant Think about it: plastic hinges Deformation Height suggestion Code:(GB50011-2010) 150 Steel Frame: 6、7(0.1g)≤110m Shear deformation Bending deformation When H/Bs4,shear deformation is dominant 本课件版权归作者所有,仅供个人学习使用,请勿转载。 3
3 2.3.1 Frame system Definition Beams and columns are connected by moment resistant joints to forming a building structure. Materials R/C, Steel Types cast-in-place R/C frame assembling in-site R/C frame Characteristics: Cross section of beams and columns are small, so, lateral stiffness is lower than the other structures. Design for hotels, shops and offices. Components’ Roles Deformation under lateral loads 引自:Bungale S. Taranath, Reinforced Concrete Design of Tall Buildings, CRC Press, 2010 Key points of frame design Strength of connections should be stronger than those of elements, Strength of columns should be stronger than beams, Shear Strength of element should be stronger than bending strength. Ductility Multiple line for collapse resistant Think about it: failure modes distribution and sequence of plastic hinges Shear deformation + Bending deformation When H/B4, shear deformation is dominant Deformation Code: (GB50011-2010) Concrete Frame Intensity 6 60m, 7 50 m, 8 (0.2g) 40 m; 8 (0.3g) 35 m; 9 24 m; Steel Frame: 6、7(0.1g) 110m, 7(0.15g) 110 m, 8(0.2g/0.3g)90/70m 9(0.4g) 50 m Height suggestion 本课件版权归作者所有,仅供个人学习使用,请勿转载

Drifts limitation Concrete frame Pasti-aic50 ??? 本课件版权归作者所有,仅供个人学习使用,请勿转载
4 Drifts limitation Concrete frame Elastic drifts 1/550 Plastic-elastic drifts1/50 Steel frame Elastic drifts 1/250 Plastic-elastic drifts1/50 ??? 本课件版权归作者所有,仅供个人学习使用,请勿转载