
Maintenance of textural integrity in frozen, shredded vegetables Li Ni, PhD Danny Lin, M.S. Diane Barrett, PhD Food Science & Technology University of California, Davis
Maintenance of textural integrity in frozen, shredded vegetables Li Ni, PhD Danny Lin, M.S. Diane Barrett, PhD Food Science & Technology University of California, Davis

Outline ◼ Background ◼ Texture measurement of vegetables ◼ Optimization of LTLT pretreatment ◼ Optimization of exogenous CaCl2 concentration ◼ Color improvement of green vegetables
Outline ◼ Background ◼ Texture measurement of vegetables ◼ Optimization of LTLT pretreatment ◼ Optimization of exogenous CaCl2 concentration ◼ Color improvement of green vegetables

Textural integrity of frozen vegetables ◼ Structure and condition of the raw vegetable ◼ Maturity at harvest ◼ Blanching, freezing, thawing and cooking conditions used for preparation ◼ Interaction of the structural components at cell walls and cell membranes
Textural integrity of frozen vegetables ◼ Structure and condition of the raw vegetable ◼ Maturity at harvest ◼ Blanching, freezing, thawing and cooking conditions used for preparation ◼ Interaction of the structural components at cell walls and cell membranes
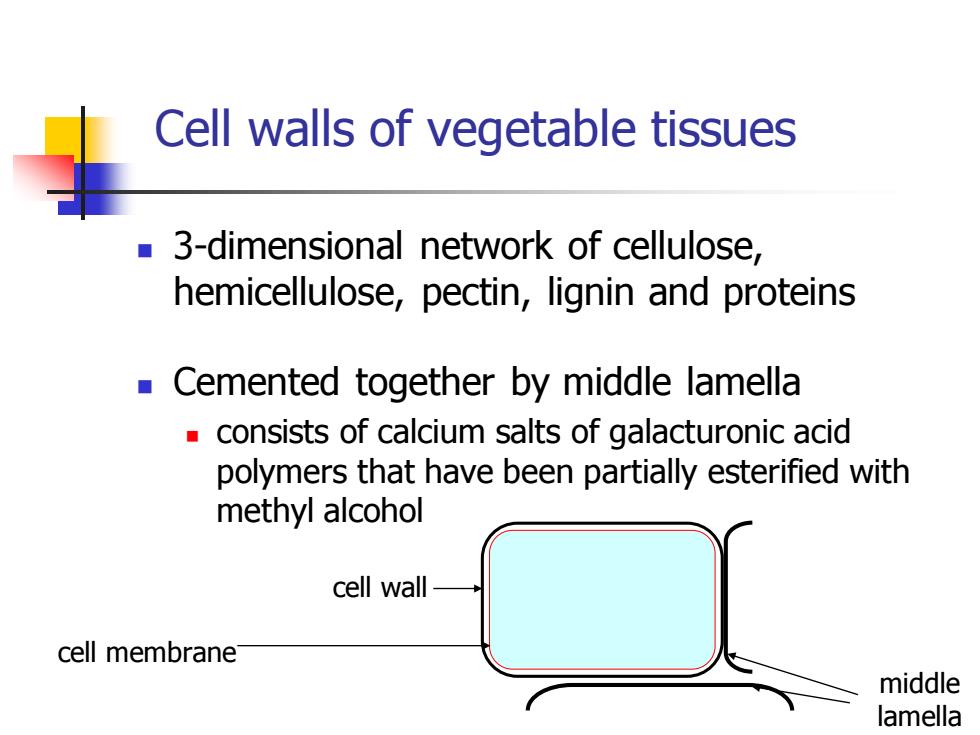
Cell walls of vegetable tissues ◼ 3-dimensional network of cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin, lignin and proteins ◼ Cemented together by middle lamella ◼ consists of calcium salts of galacturonic acid polymers that have been partially esterified with methyl alcohol cell wall cell membrane middle lamella
Cell walls of vegetable tissues ◼ 3-dimensional network of cellulose, hemicellulose, pectin, lignin and proteins ◼ Cemented together by middle lamella ◼ consists of calcium salts of galacturonic acid polymers that have been partially esterified with methyl alcohol cell wall cell membrane middle lamella

Softening of vegetables by thermal processing ◼ Resistance to deforming forces ◼ Turgor ◼ Cell wall rigidity ◼ Breakage of cell walls accompanied by release of vacuolar contents ◼ Separation of one cell from another - failure at the adhesive layer between the cells
Softening of vegetables by thermal processing ◼ Resistance to deforming forces ◼ Turgor ◼ Cell wall rigidity ◼ Breakage of cell walls accompanied by release of vacuolar contents ◼ Separation of one cell from another - failure at the adhesive layer between the cells
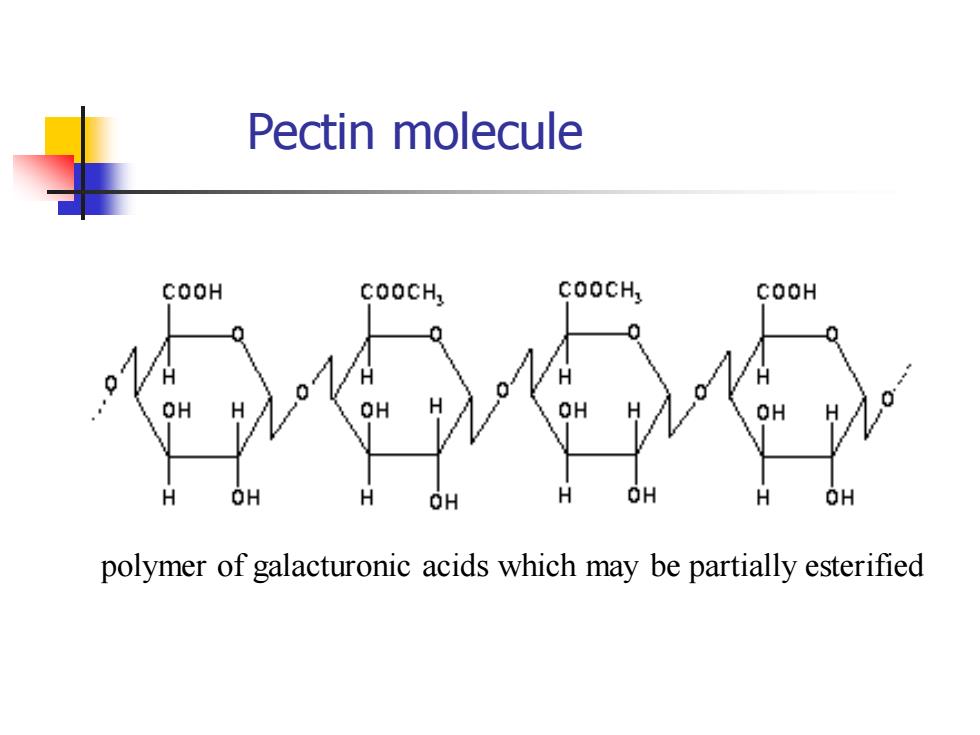
Pectin molecule polymer of galacturonic acids which may be partially esterified
Pectin molecule polymer of galacturonic acids which may be partially esterified
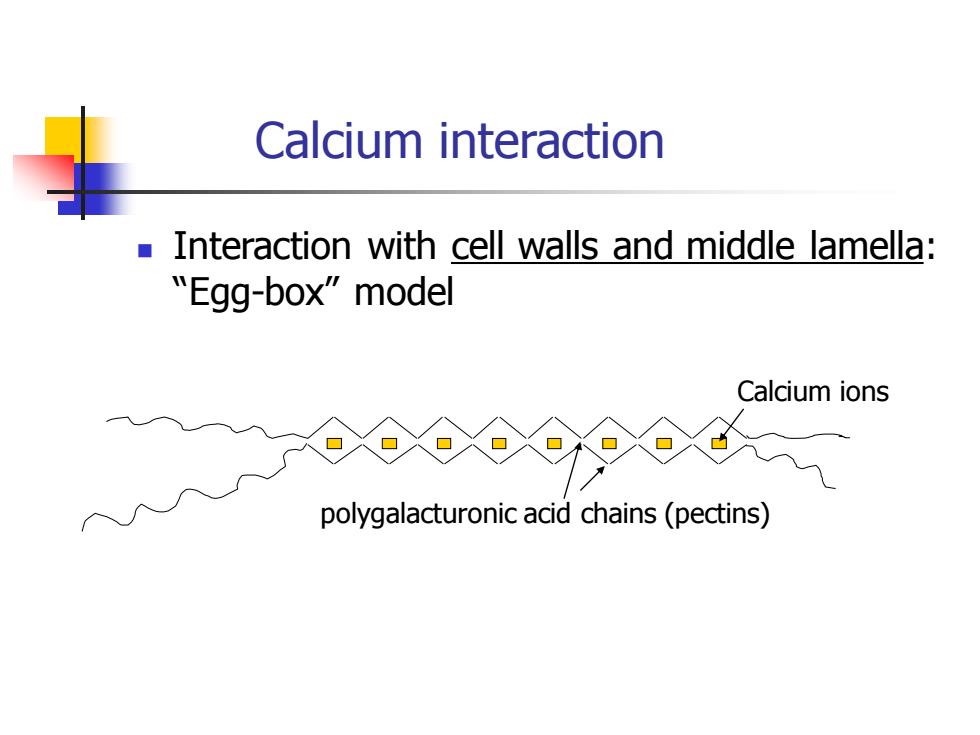
Calcium interaction ◼ Interaction with cell walls and middle lamella: “Egg-box” model Calcium ions polygalacturonic acid chains (pectins)
Calcium interaction ◼ Interaction with cell walls and middle lamella: “Egg-box” model Calcium ions polygalacturonic acid chains (pectins)
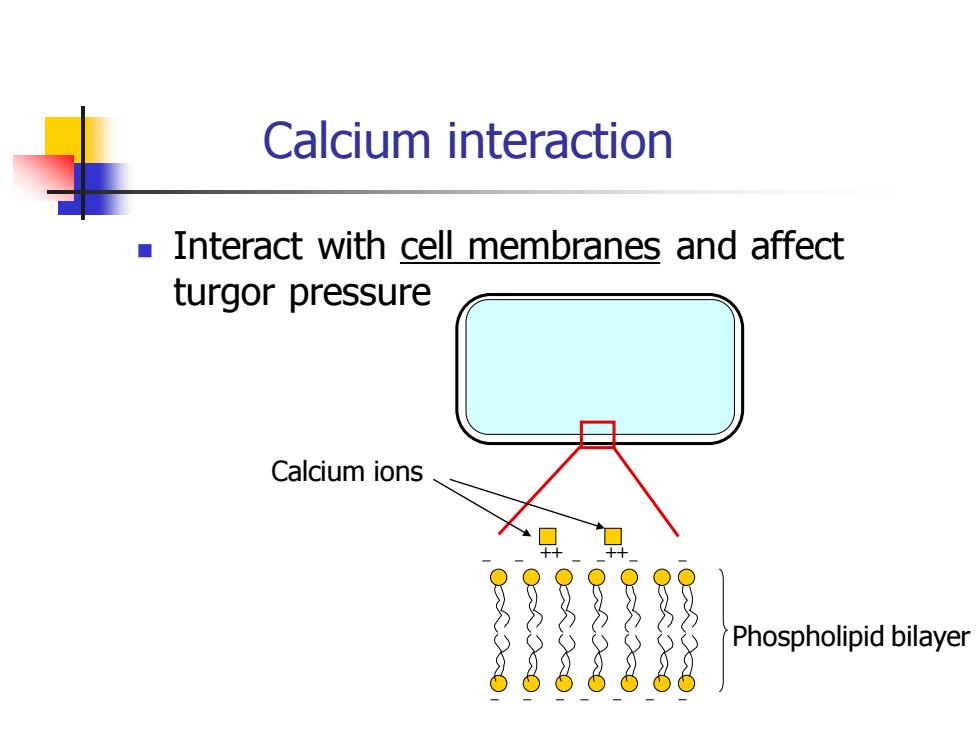
Calcium interaction ◼ Interact with cell membranes and affect turgor pressure ++ ++ Phospholipid bilayer Calcium ions
Calcium interaction ◼ Interact with cell membranes and affect turgor pressure ++ ++ Phospholipid bilayer Calcium ions

Pectinmethylesterase (PME) ◼ Hydrolyzes the methyl ester linkages in pectin molecules and releases methanol and free galacturonic acid moieties ◼ Free carboxyl groups then form Ca-bridges between pectin molecules ◼ Activity ◼ Inactive at temperatures 50C ◼ Activated 50C and reacts with cell wall pectins ◼ rapidly deactivated at 70C
Pectinmethylesterase (PME) ◼ Hydrolyzes the methyl ester linkages in pectin molecules and releases methanol and free galacturonic acid moieties ◼ Free carboxyl groups then form Ca-bridges between pectin molecules ◼ Activity ◼ Inactive at temperatures 50C ◼ Activated 50C and reacts with cell wall pectins ◼ rapidly deactivated at 70C

Objective ◼ Improve texture integrity and crispiness of frozen vegetables ◼ Activation of PME ◼ LTLT pretreatment ◼ Calcium binds free carboxyl groups ◼ Addition of Ca2+ ◼ Improve color of pretreated frozen vegetables ◼ 3-step-blanching ◼ Addition of Zn2+ ◼ Increased pH - calcium lactate
Objective ◼ Improve texture integrity and crispiness of frozen vegetables ◼ Activation of PME ◼ LTLT pretreatment ◼ Calcium binds free carboxyl groups ◼ Addition of Ca2+ ◼ Improve color of pretreated frozen vegetables ◼ 3-step-blanching ◼ Addition of Zn2+ ◼ Increased pH - calcium lactate