
首先了解样品的性质 一般性质:试样的体积、酶(蛋白质)和 杂质的量、试样的pH及离子强度 酶的物化特性:大小、pI、S(solubility)、 亲水性、化学性质 酶的生化特性:稳定性、辅助因子 第六节 酶纯化步骤的设计
首先了解样品的性质 一般性质:试样的体积、酶(蛋白质)和 杂质的量、试样的pH及离子强度 酶的物化特性:大小、pI、S(solubility)、 亲水性、化学性质 酶的生化特性:稳定性、辅助因子 第六节 酶纯化步骤的设计

考虑相容性 A.开始阶段 样品体积、数量大 首先考虑高容量capacity,其次高分辨率resolution 处理量小时则反之 B.盐析后盐浓度高,影响离子交换色谱和电泳, 需先进行透析或凝胶过滤脱盐。 1.分离方法的顺序
考虑相容性 A.开始阶段 样品体积、数量大 首先考虑高容量capacity,其次高分辨率resolution 处理量小时则反之 B.盐析后盐浓度高,影响离子交换色谱和电泳, 需先进行透析或凝胶过滤脱盐。 1.分离方法的顺序

C 分离的每个步骤选择不同性质的分 离方法 D 最后分离条件注重复原性、快速, 因为蛋白质越纯稳定性下降越快
C 分离的每个步骤选择不同性质的分 离方法 D 最后分离条件注重复原性、快速, 因为蛋白质越纯稳定性下降越快

2.初步纯化 一般注意点: A. 温度 B.避免极端I,pH C.有机溶剂 D.蛋白质的浓度(高稳定,因为蛋白质带 负电,排斥力大) E.避免泡沫和膜的形成 F.酶的活性
2.初步纯化 一般注意点: A. 温度 B.避免极端I,pH C.有机溶剂 D.蛋白质的浓度(高稳定,因为蛋白质带 负电,排斥力大) E.避免泡沫和膜的形成 F.酶的活性

6.纯化步骤的定量评价 3.选择性的纯化步骤 色谱法 4.检查纯化的进展情况 常用电泳(PAGE, SDS-PAGE, IEF) 5.进一步纯化 根据4结果,若分子大小差异— —GEC 若电荷差异——离子交换色谱
6.纯化步骤的定量评价 3.选择性的纯化步骤 色谱法 4.检查纯化的进展情况 常用电泳(PAGE, SDS-PAGE, IEF) 5.进一步纯化 根据4结果,若分子大小差异— —GEC 若电荷差异——离子交换色谱

7.在纯化过程中酶活力的损失 主要原因:蛋白质变性 避免方法:改变温度和pH 其他原因:辅助因子被去除
7.在纯化过程中酶活力的损失 主要原因:蛋白质变性 避免方法:改变温度和pH 其他原因:辅助因子被去除
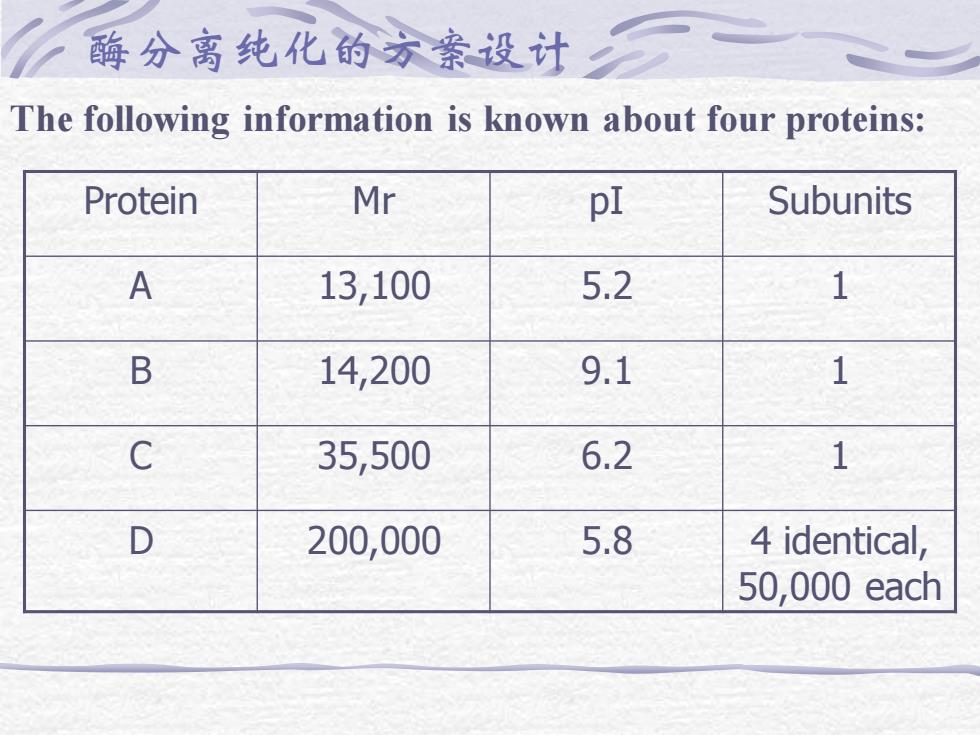
酶分离纯化的方案设计 The following information is known about four proteins: Protein Mr pI Subunits A 13,100 5.2 1 B 14,200 9.1 1 C 35,500 6.2 1 D 200,000 5.8 4 identical, 50,000 each
酶分离纯化的方案设计 The following information is known about four proteins: Protein Mr pI Subunits A 13,100 5.2 1 B 14,200 9.1 1 C 35,500 6.2 1 D 200,000 5.8 4 identical, 50,000 each

a. Sketch the elution profile expected if this mixture is run on a Sephadex G-100 gel filtration column run in 50 mM phosphate buffer, pH 6. Label the peaks. b. Sketch the gel obtained from running these proteins on an SDS polyacrylamide electrophoresis gel at pH 8.0, (after staining and destaining). c. What predictions can you make about the results of a native PAGE at pH 7.6 ( state any assumptions you might need to make about the % acrylamide in the gel )
a. Sketch the elution profile expected if this mixture is run on a Sephadex G-100 gel filtration column run in 50 mM phosphate buffer, pH 6. Label the peaks. b. Sketch the gel obtained from running these proteins on an SDS polyacrylamide electrophoresis gel at pH 8.0, (after staining and destaining). c. What predictions can you make about the results of a native PAGE at pH 7.6 ( state any assumptions you might need to make about the % acrylamide in the gel )

d. Sketch the elution profile of these proteins from a carboxymethyl cellulose ion exchange chromatography column, run at pH 6.25 (with a salt gradient, if necessary). Label the peaks
d. Sketch the elution profile of these proteins from a carboxymethyl cellulose ion exchange chromatography column, run at pH 6.25 (with a salt gradient, if necessary). Label the peaks

第七节 蛋白质浓度的测定 凯氏定氮法 双缩脲法 福林(Folin)-酚试剂法 考马斯蓝染色法 紫外光吸收法
第七节 蛋白质浓度的测定 凯氏定氮法 双缩脲法 福林(Folin)-酚试剂法 考马斯蓝染色法 紫外光吸收法