
Clinical Pharmacokinetics Sun Wu-Yi Institute of Clinical Pharmacology, ∥EDICAL UNIVERSTT 125 Anhui Medical University
Clinical Pharmacokinetics Sun Wu-Yi Institute of Clinical Pharmacology, Anhui Medical University
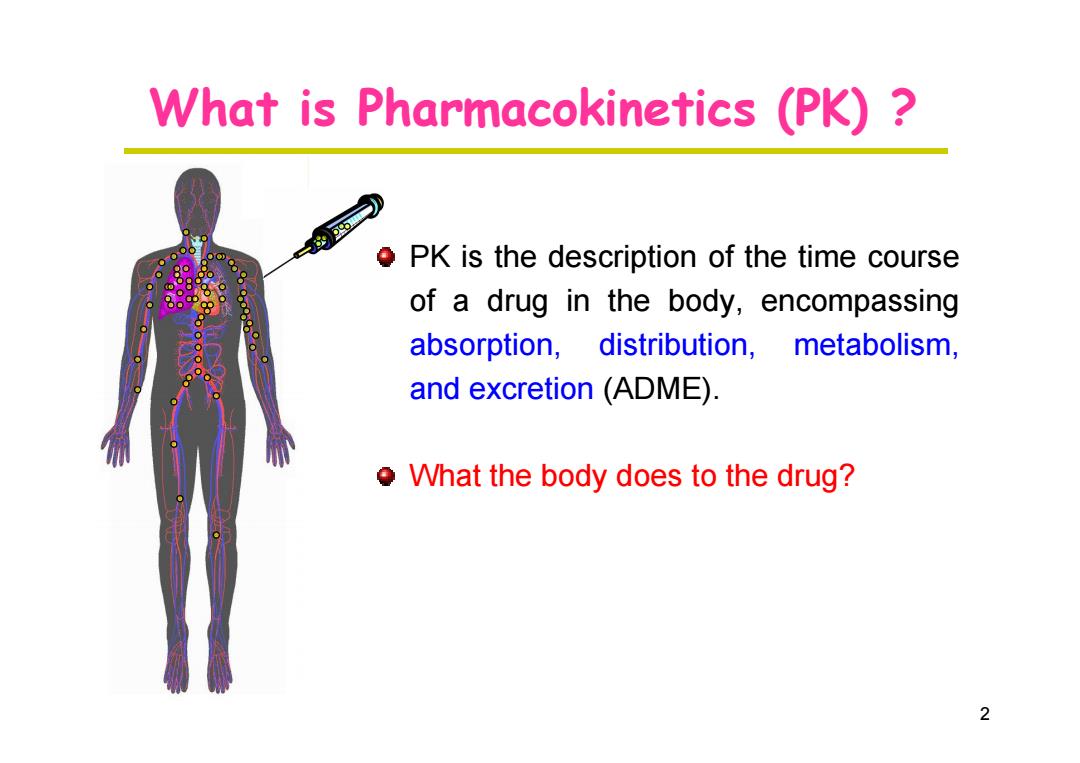
What is Pharmacokinetics (PK)? 295 PK is the description of the time course of a drug in the body,encompassing absorption,distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) o What the body does to the drug? 2
What is Pharmacokinetics (PK) ? PK is the description of the time course of a drug in the body, encompassing absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME). 2 What the body does to the drug?
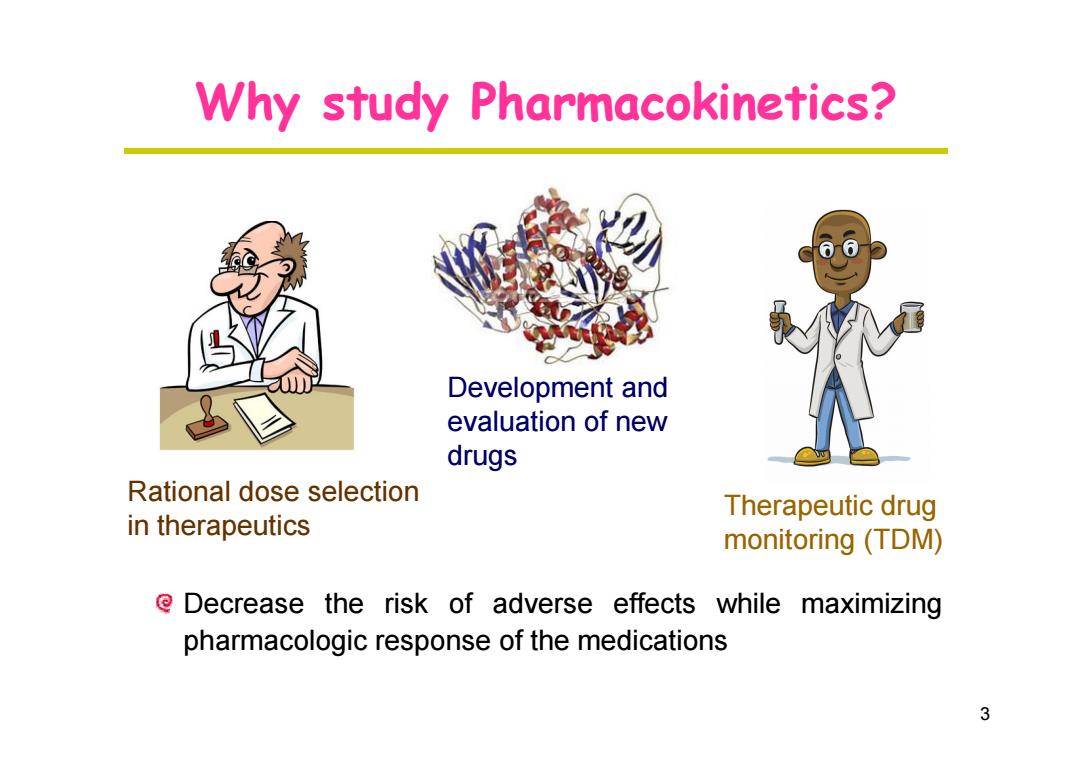
Why study Pharmacokinetics? Development and evaluation of new drugs Rational dose selection Therapeutic drug in therapeutics monitoring (TDM) e Decrease the risk of adverse effects while maximizing pharmacologic response of the medications 3
Why study Pharmacokinetics? Development and 3 Rational dose selection in therapeutics evaluation of new drugs Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) Decrease the risk of adverse effects while maximizing pharmacologic response of the medications

Outline ADME factors Review of Basic Pharmacokinetic Parameters Mathematical Basis of Clinical Pharmacokinetics Applications of Clinical Pharmacokinetics Factors affecting selection of the drug Clinical Pharmacokinetics in Drug Development Study questions 4
Outline ADME factors Review of Basic Pharmacokinetic Parameters Mathematical Basis of Clinical Pharmacokinetics 4 Applications of Clinical Pharmacokinetics Study questions • Factors affecting selection of the drug • Clinical Pharmacokinetics in Drug Development

ADME Factors
ADME Factors
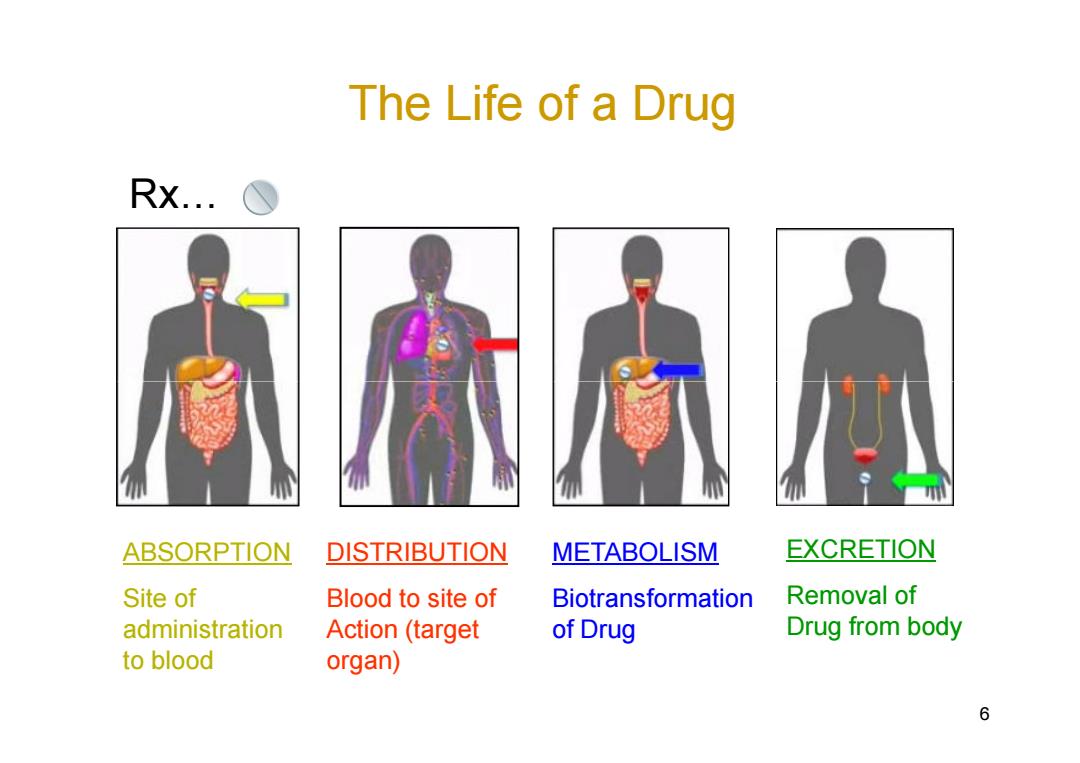
The Life of a drug Rx... ABSORPTION DISTRIBUTION METABOLISM EXCRETION Site of Blood to site of Biotransformation Removal of administration Action(target of Drug Drug from body to blood organ) 6
The Life of a Drug Rx6 6 ABSORPTION Site of administration to blood DISTRIBUTION Blood to site of Action (target organ) METABOLISM Biotransformation of Drug EXCRETION Removal of Drug from body
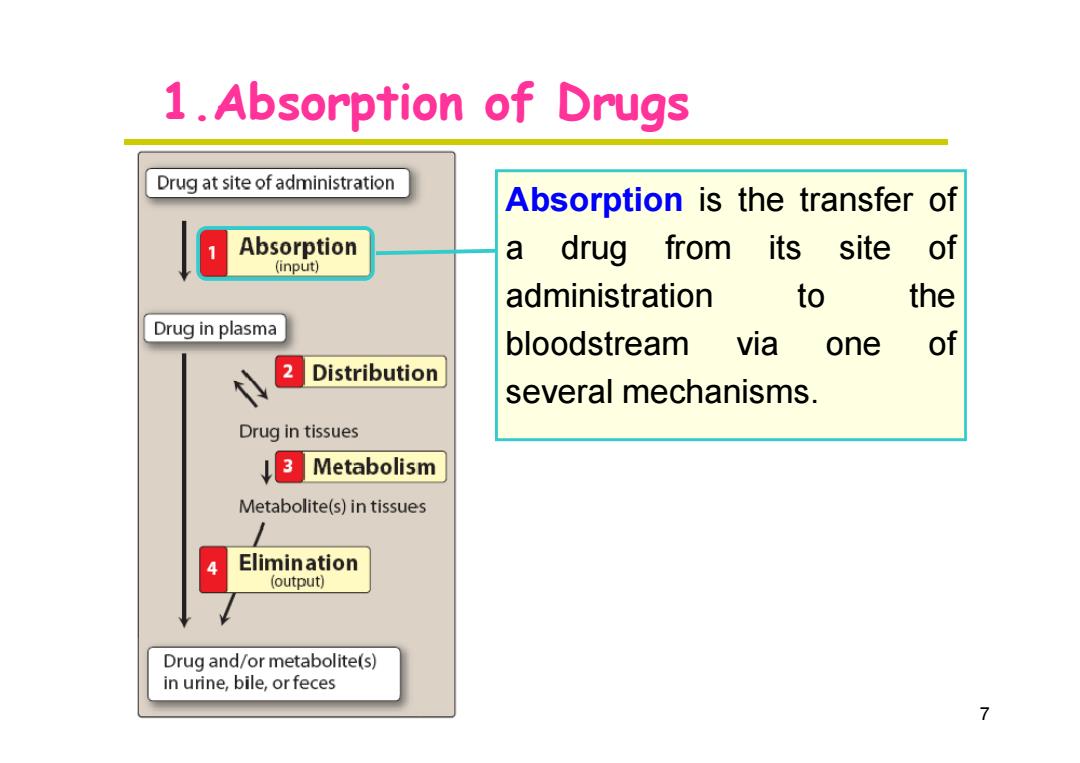
1.Absorption of Drugs Drug at site of administration Absorption is the transfer of Absorption a drug from its site of (input) administration to the Drug in plasma bloodstream via one of 2 Distribution several mechanisms. Drug in tissues 3 Metabolism Metabolite(s)in tissues 4 Elimination (output) Drug and/or metabolite(s) in urine,bile,or feces 7
1.Absorption of Drugs Absorption is the transfer of a drug from its site of administration to the bloodstream via one of several mechanisms. 7
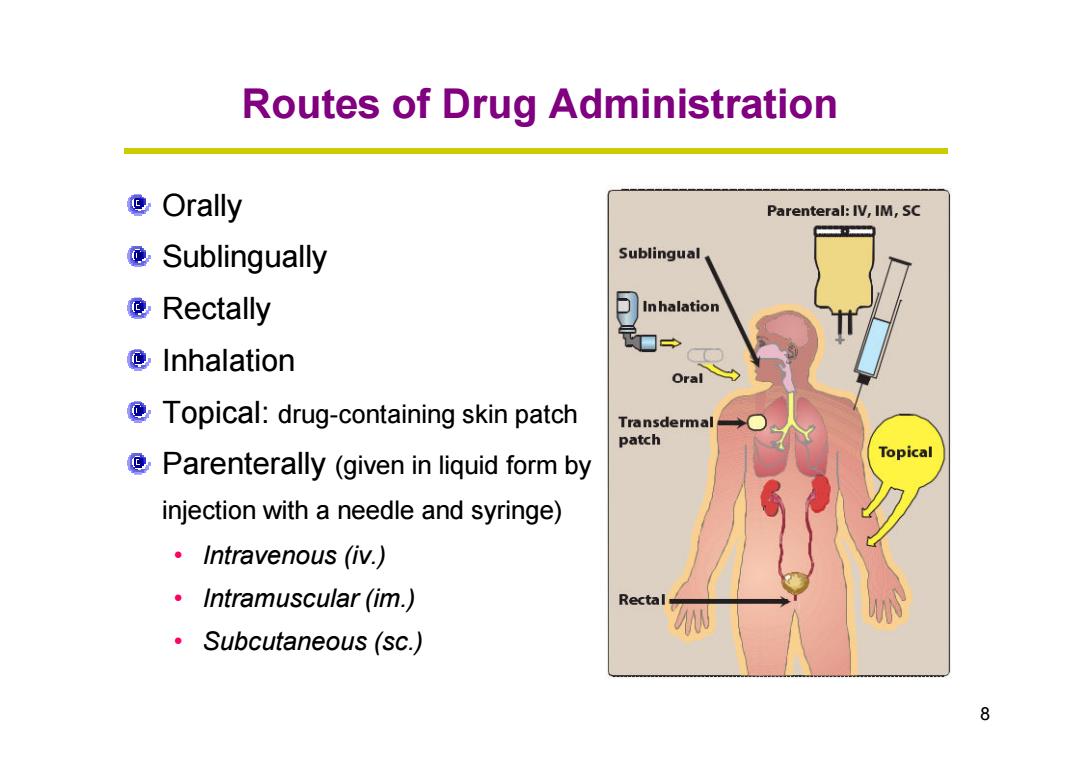
Routes of Drug Administration Orally Parenteral:IV,IM,SC @Sublingually Sublingual Rectally □Inhalation Inhalation Oral Topical:drug-containing skin patch Transdermal patch Parenterally (given in liquid form by Topical injection with a needle and syringe) ·Intravenous(m.) ·Intramuscular(im.) Rectal ·Subcutaneous(sc.) 8
Routes of Drug Administration Orally Sublingually Rectally Inhalation 8 Topical: drug-containing skin patch Parenterally (given in liquid form by injection with a needle and syringe) • Intravenous (iv.) • Intramuscular (im.) • Subcutaneous (sc.)
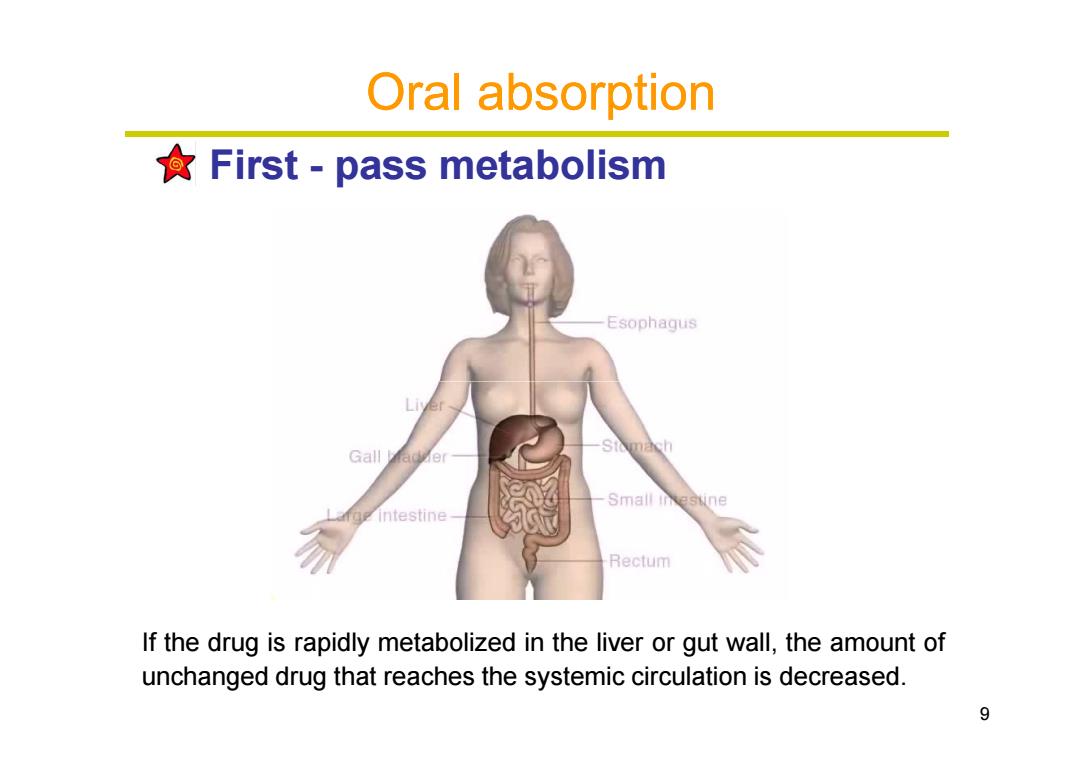
Oral absorption First-pass metabolism Esophaqus Gall Small inesune Rectum If the drug is rapidly metabolized in the liver or gut wall,the amount of unchanged drug that reaches the systemic circulation is decreased. 9
Oral absorption First - pass metabolism 9 If the drug is rapidly metabolized in the liver or gut wall, the amount of unchanged drug that reaches the systemic circulation is decreased
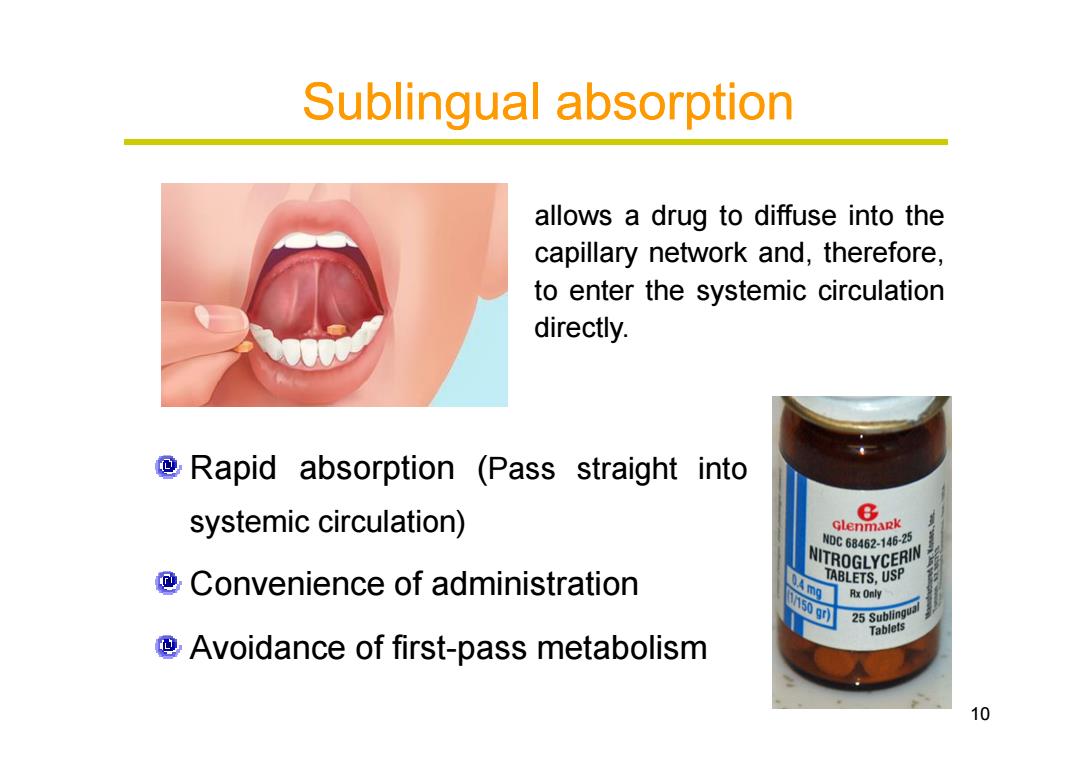
Sublingual absorption allows a drug to diffuse into the capillary network and,therefore, to enter the systemic circulation directly. @Rapid absorption (Pass straight into systemic circulation) 8 Glenmapk NM0C6B462-146-25 NITROGLYCERIN Convenience of administration TABLETS,USP Rx Only 25 Sublingua Tablets @Avoidance of first-pass metabolism 10
Sublingual Sublingual absorption absorption allows a drug to diffuse into the capillary network and, therefore, to enter the systemic circulation directly. 10 Rapid absorption (Pass straight into systemic circulation) Convenience of administration Avoidance of first-pass metabolism