
放射卫生学 公共卫生学院放射医学系 2020.03.06
放 射 卫生 学 公共卫生学院放射医学系 2020.03.06

补充部分 核物理基础 Basic knowledge of nuclear physics
核物理基础 Basic knowledge of nuclear physics 补充部分

本章节内容 。电磁辐射 。原子核及其稳定性 (原子核的结构、衰变、核反应) 。射线与物质的相互作用 。射线的生物学作用
本章节内容 ⚫ 电磁辐射 ⚫ 原子核及其稳定性 (原子核的结构、衰变、核反应) ⚫ 射线与物质的相互作用 ⚫ 射线的生物学作用
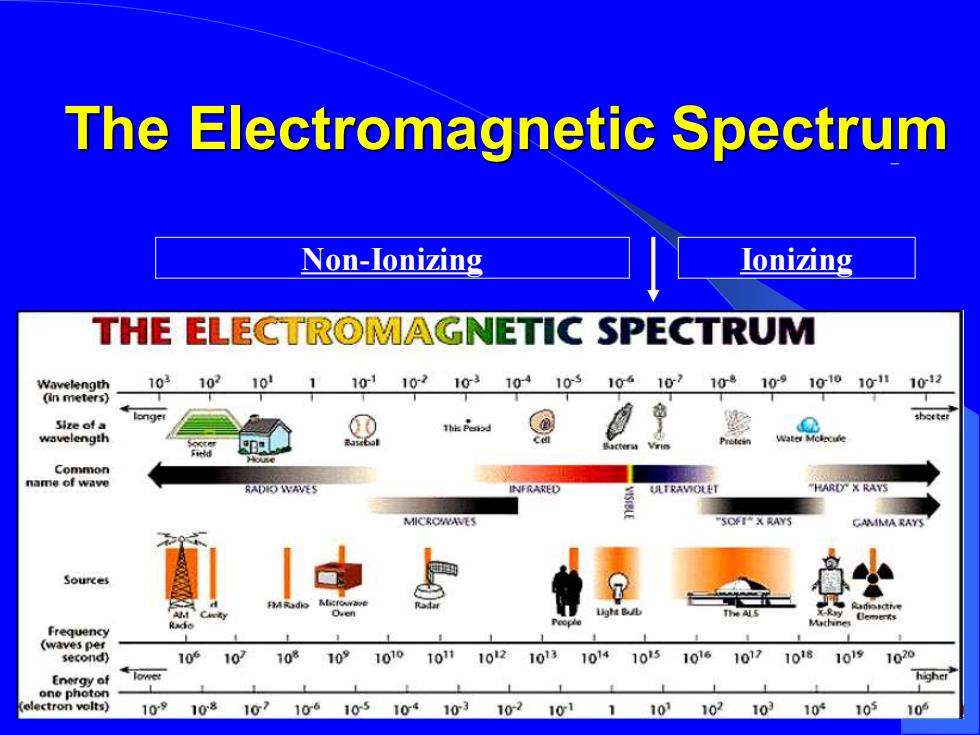
The Electromagnetic Spectrum Non-lonizing Ioni☑ing THE ELECTROMAGNETIC SPECTRUM 103 102101110110210310410310610210%1091g101011012 e。fa wavelength Common name of wave RADIO WAVES ULTRAMOLET HARD X RAYS MICROWAVES SOFI X RAYS CAMMA RAYS Sources 电 Frequency (waves pe second) 10 10 108 10 1010 1012 1013 1014 10151016 10171018 1019 1020 higher 109 108 10106103104103102101 1103102103102105 109
The Electromagnetic Spectrum Non-Ionizing Ionizing

辐 射 辐射 radiation 电磁辐射 electromagnetic radiation ·粒子辐射 grainy radiation ● 电离辐射 ionization radiation 。非电离辐射 non-ionization radiatio
辐 射 ⚫ 辐射 radiation ⚫ 电磁辐射 electromagnetic radiation ⚫ 粒子辐射 grainy radiation ⚫ 电离辐射 ionization radiation ⚫ 非电离辐射 non-ionization radiatio

原子核结构的设想、修正和证实 卢瑟福的试验(1903年于蒙特利尔的麦吉尔大学): 以a源照射1/3m厚云母片,片后置一硫化锌闪烁屏,发现 1.绝大部分仍集中于屏中央一一中空 2.极少部分偏转,不规则一一有带正电、质量和电量都较大 的未知物(粒子) 1909年和德国科学家盖革和18岁助手马斯登实验: 上述实验用0.06m金箔,侧加铅板、移动闪烁屏观察 1.发现反射a粒子一一遇质量比a还大的粒子
原子核结构的设想、修正和证实 卢瑟福的试验(1903年于蒙特利尔的麦吉尔大学): 以α源照射1/3mm厚云母片,片后置一硫化锌闪烁屏,发现 1.绝大部分仍集中于屏中央--中空 2.极少部分偏转,不规则--有带正电、质量和电量都较大 的未知物(粒子) 1909年和德国科学家盖革和18岁助手马斯登实验: 上述实验用0.06mm金箔,侧加铅板、移动闪烁屏观察 1.发现反射α粒子--遇质量比α还大的粒子

玻尔理论解释了原子光谱分立性和原子的稳定性 The Nobel Prize in Physics (922 for his services in the investigation of the structure of atoms and of the N.Bohr (1885-1962) radiation emanating from them
玻尔理论解释了原子光谱分立性和原子的稳定性 The Nobel Prize in Physics 1922 for his services in the investigation of the structure of atoms and of the radiation emanating from them N. Bohr (1885-1962)
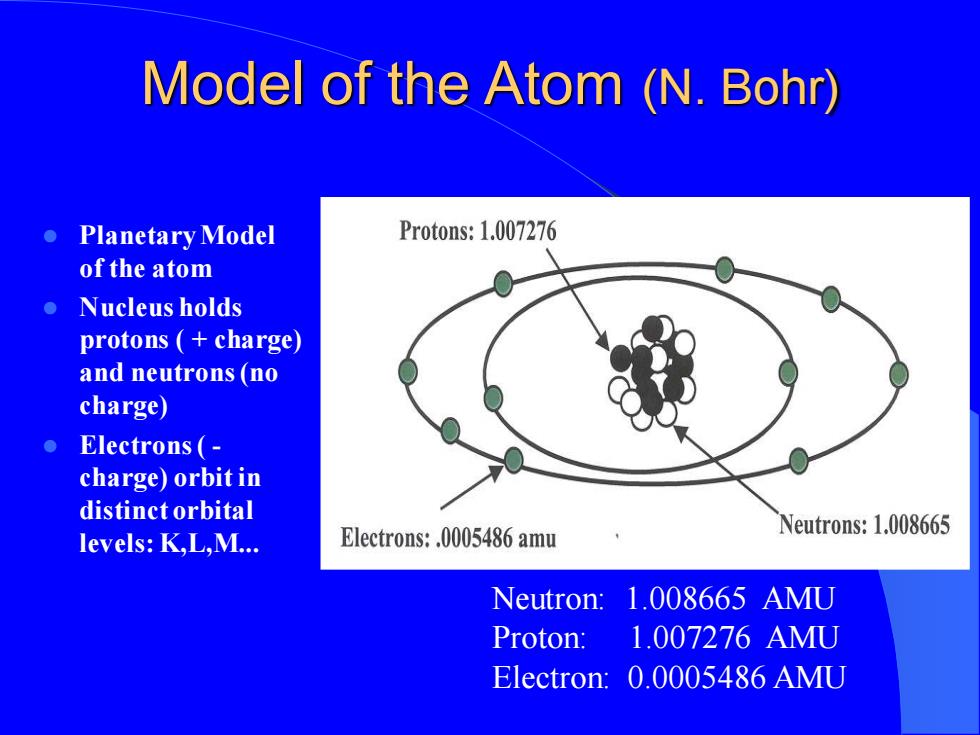
Model of the Atom (N.Bohr) ● Planetary Model Protons:1.007276 of the atom ● Nucleus holds protons charge) and neutrons(no charge) Electrons(- charge)orbit in distinct orbital levels:K,L,M. Electrons:.0005486 amu Neutrons:1.008665 Neutron: 1.008665AMU Proton: 1.007276AMU Electron:0.0005486 AMU
Model of the Atom (N. Bohr) ⚫ Planetary Model of the atom ⚫ Nucleus holds protons ( + charge) and neutrons (no charge) ⚫ Electrons ( - charge) orbit in distinct orbital levels: K,L,M. Neutron: 1.008665 AMU Proton: 1.007276 AMU Electron: 0.0005486 AMU

原子和原子核 ·核外电子 荷电量:1.602×109C 运行轨道、数目、能量及其变化规律 原子和原子核 表示法:Xm 构成:中子、质子 特点:质量大、密度高、稳定性在一定条件下改变
原子和原子核 ⚫ 核外电子 荷电量:1.602×10-9C 运行轨道、数目、能量及其变化规律 ⚫ 原子和原子核 表示法:Z AXm 构成:中子、质子 特点:质量大、密度高、稳定性在一定条件下改变

几个定义 元素:原子核内具有相同电荷数的同一类原子。 核素:原子核内质子数、中子数和能态完全相同 的一类原子。 同位素:原子核内质子数相同、中子数不同的多种 核素。 同质异能素:中子数和质子数都相同而仅仅是能量 状态不同的两种核素
几个定义 元素:原子核内具有相同电荷数的同一类原子。 核素:原子核内质子数、中子数和能态完全相同 的一类原子。 同位素:原子核内质子数相同、中子数不同的多种 核素。 同质异能素:中子数和质子数都相同而仅仅是能量 状态不同的两种核素