
个 Diabetes Mellitus 南方医科大学珠江医院内分泌科杨力副主任医师副教授 Department of Endocrinology Second Clinical Medical College of Southern Medical University
1 南方医科大学珠江医院内分泌科 杨力 副主任医师 副教授 Department of Endocrinology Second Clinical Medical College of Southern Medical University Diabetes Mellitus
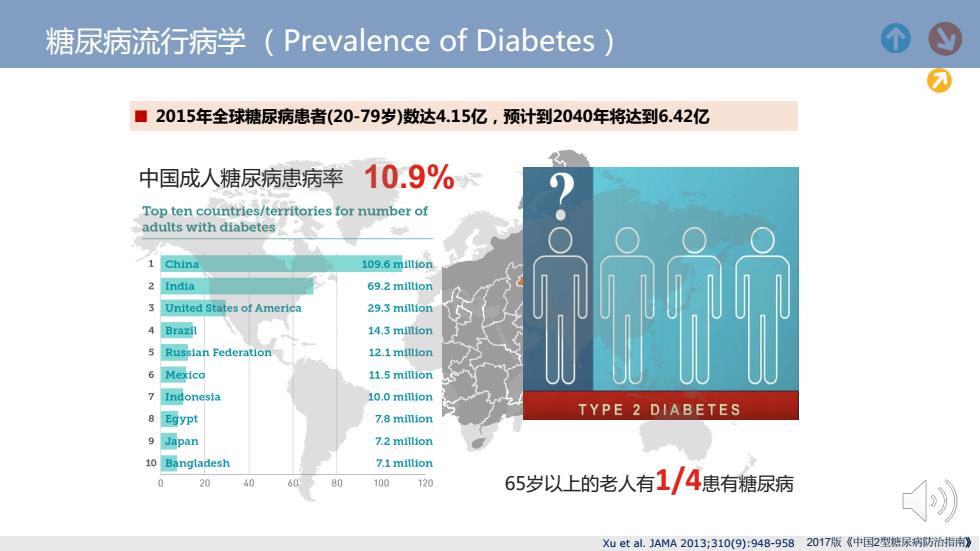
糖尿病流行病学(Prevalence of Diabetes) 个 ■2015年全球糖尿病患者(20-79岁)数达4.15亿,预计到2040年将达到6.42亿 中国成人糖尿病患病率10.9% Top ten countries/territories for number of adults with diabetes 1 China 109.6m1l1on 2 India 69.2 million 3 United States of America 29.3 million 4 Brazil 14.3 miltion 5 Russian Federation 12.1mlllion 6 Mexico 11.5 million 7 Indonesia 10.0 million 8 Egypt TYPE 2 DIABETES 7.8 million 9 Japan 7.2 million 10 Bangladesh 7.1million 0 20 40 80 100 120 65岁以上的老人有1/4患有糖尿病 Xu et al..JAMA2013;310(9):948-9582017版《中国2型糖尿病防治指南》
糖尿病流行病学 (Prevalence of Diabetes) Xu et al. JAMA 2013;310(9):948-958 中国成人糖尿病患病率 10.9% 2017版《中国2型糖尿病防治指南》 ■ 2015年全球糖尿病患者(20-79岁)数达4.15亿,预计到2040年将达到6.42亿 65岁以上的老人有1/4患有糖尿病
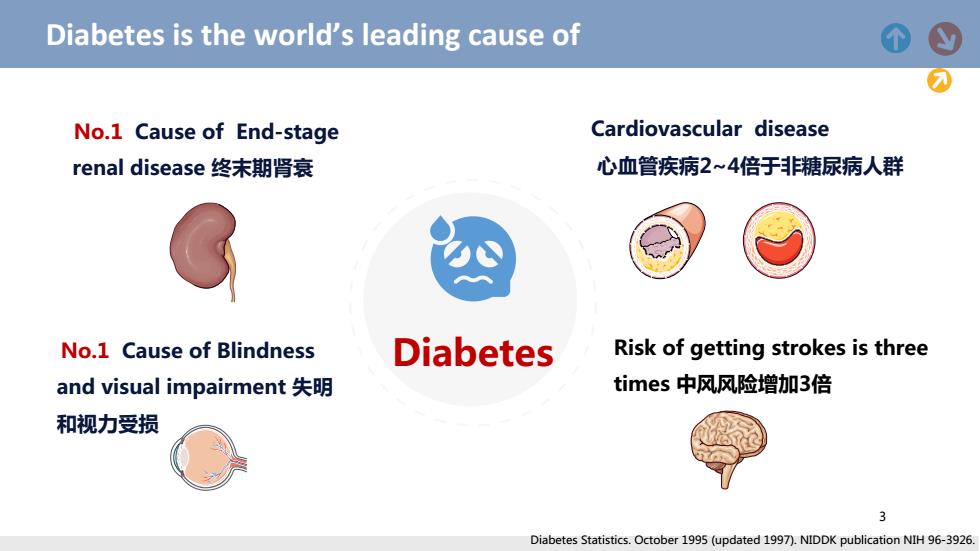
Diabetes is the world's leading cause of No.1 Cause of End-stage Cardiovascular disease renal disease终末期肾衰 心血管疾病2~4倍于非糖尿病人群 No.1 Cause of Blindness Diabetes Risk of getting strokes is three and visual impairment失明 times中风风险增加3倍 和视力受损 3 Diabetes Statistics.October 1995(updated 1997).NIDDK publication NIH 96-3926
3 Diabetes Diabetes Statistics. October 1995 (updated 1997). NIDDK publication NIH 96-3926. 3 Diabetes is the world’s leading cause of No.1 Cause of End-stage renal disease 终末期肾衰 No.1 Cause of Blindness and visual impairment 失明 和视力受损 Cardiovascular disease 心血管疾病2~4倍于非糖尿病人群 Risk of getting strokes is three times 中风风险增加3倍
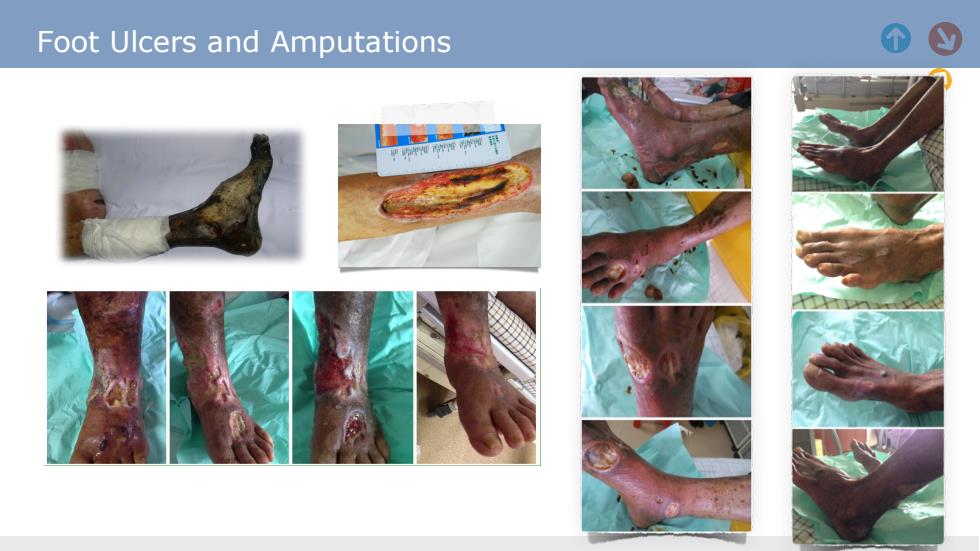
Foot Ulcers and Amputations 个
Foot Ulcers and Amputations

鲁台教动 重点难点 熟悉 糖尿病基本概念和分型 掌握 糖尿病的临床表现和常见并发症;诊断方法和诊断标准; 综合治疗原则 熟悉 口服降糖药的分类、作用机理和副作用,胰岛素的使用原则; 糖尿病酮症酸中毒的诊断依据和治疗原则 0
重点难点 熟悉 熟悉 掌握 糖尿病的临床表现和常见并发症;诊断方法和诊断标准; 综合治疗原则 口服降糖药的分类、作用机理和副作用,胰岛素的使用原则; 糖尿病酮症酸中毒的诊断依据和治疗原则 糖尿病基本概念和分型

Learning Objectives 个 Know the main types of diabetes Understand the causes of diabetes Know the symptoms and complications of diabetes Understand the diagnostic criteria for diabetes Describe the management and common emergencies of diabetes
Learning Objectives Describe the management and common emergencies of diabetes Understand the diagnostic criteria for diabetes Know the symptoms and complications of diabetes Understand the causes of diabetes Know the main types of diabetes 6

The three steps of diagnosis of diabetes 个 Can be diagnosed as Diabetes? 。血糖的相关检测 B What type of Diabetes? ·分型的相关检测 What diabetic complications? 。 糖尿病急性并发症 糖尿病慢性并发症
• 血糖的相关检测 • Can be diagnosed as Diabetes? • 分型的相关检测 What type of Diabetes? The three steps of diagnosis of diabetes • 糖尿病急性并发症 • 糖尿病慢性并发症 What diabetic complications?

个 STEP One 01 Can be Diagnosed as Diabetes ·临床表现(典型表现与非典型表现) ·血糖的相关检测(空腹血糖、餐后血糖、糖化血红蛋白) ·糖尿病诊断标准
STEP One Can be Diagnosed as Diabetes 01 • 临床表现(典型表现与非典型表现) • 血糖的相关检测(空腹血糖、餐后血糖、糖化血红蛋白) • 糖尿病诊断标准

What is Diabetes? 个 American diabetes association(ADA).1997 Diabetes is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycaemia resulting from defects in insulin secretion(胰岛素缺乏),resistance to insulin action( 胰岛素抵抗)or a combination of both. The chronic diabetic hyperglyceamia is associated with long-term damage,dysfunction and failure of various organs
Diabetes is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by hyperglycaemia (高血糖) resulting from defects in insulin secretion(胰岛素缺乏), resistance to insulin action( 胰岛素抵抗) or a combination of both. What is Diabetes? The chronic diabetic hyperglyceamia is associated with long-term damage, dysfunction and failure of various organs. American diabetes association (ADA) . 1997

Normal Glycometabolism Cycle Process Food Digestion Absorption catabolism glycolysis(糖酵解) H2O,CO2,ATP anabolism The action of Insulin: Glycogen .Decreased blood glucose (糖原) Activation of glucose transporter molecules(葡萄糖转运子) Glyconeogenesis (糖异生) ·Increased glycolysis(糖酵解) ,Decreased glyconeogenesis(糖异生) Storage of glucose in liver and muscles Amino acids、Glycerol as glycogen(糖原)
Normal Glycometabolism Cycle Process Food Glycogen (糖原) Amino acids 、Glycerol H2O,CO2,ATP catabolism anabolism Digestion Absorption Glyconeogenesis (糖异生) glycolysis (糖酵解) Glucose The action of Insulin: •Decreased blood glucose •Activation of glucose transporter molecules(葡萄糖转运⼦) •Increased glycolysis(糖酵解) •Decreased glyconeogenesis(糖异⽣) •Storage of glucose in liver and muscles as glycogen(糖原)