
病理学子 胰岛疾病 (Lesions of Islet of Langerhans Gland) 赵亮教授,副主任医师 南方医科大学基础医学院病理学系 南方医科大学南方医院病理科
南方医科大学基础医学院病理学系 南方医科大学南方医院病理科 胰岛疾病 (Lesions of Islet of Langerhans Gland) 赵亮 教授,副主任医师
糖尿病(Diabetes mellitus) 胰岛病变 胰岛细胞瘤(Islet cell tumor)
胰岛病变 糖尿病 (Diabetes mellitus) 胰岛细胞瘤 (Islet cell tumor)
IVC Left Splenic a. Hepatic a. adrenal gland Spleen Common bile duct Right adrenal gland Kidney Duodenum Tail of pancreas Head of pancreas Kidney Uncinate process IVC Aorta ©D Klemm'98
2024/7/6 3
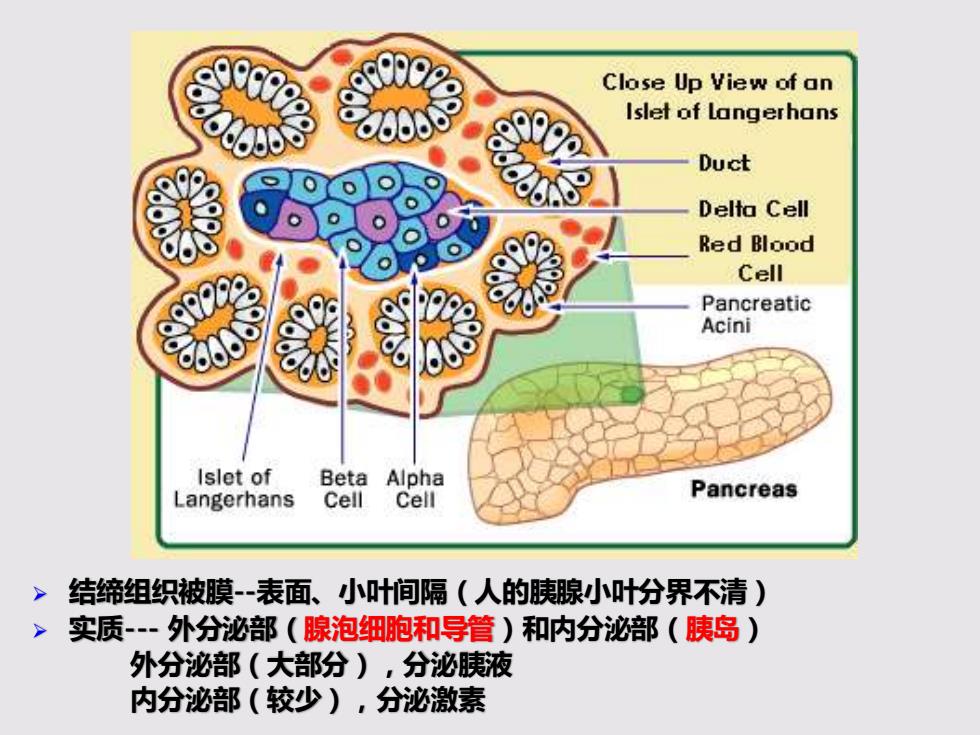
Close Up View of an Islet of Langerhans Duct Delta Cell Red Blood Cell Pancreatic Acini Islet of Beta Alpha Langerhans Cell Cell Pancreas 结缔组织被膜-表面、小叶间隔(人的胰腺小叶分界不清) > 实质-一外分泌部(腺泡细胞和导管)和内分泌部(胰岛) 外分泌部(大部分),分泌胰液 内分泌部(较少),分泌激素
➢ 结缔组织被膜--表面、小叶间隔(人的胰腺小叶分界不清) ➢ 实质--- 外分泌部(腺泡细胞和导管)和内分泌部(胰岛) 外分泌部(大部分),分泌胰液 内分泌部(较少),分泌激素
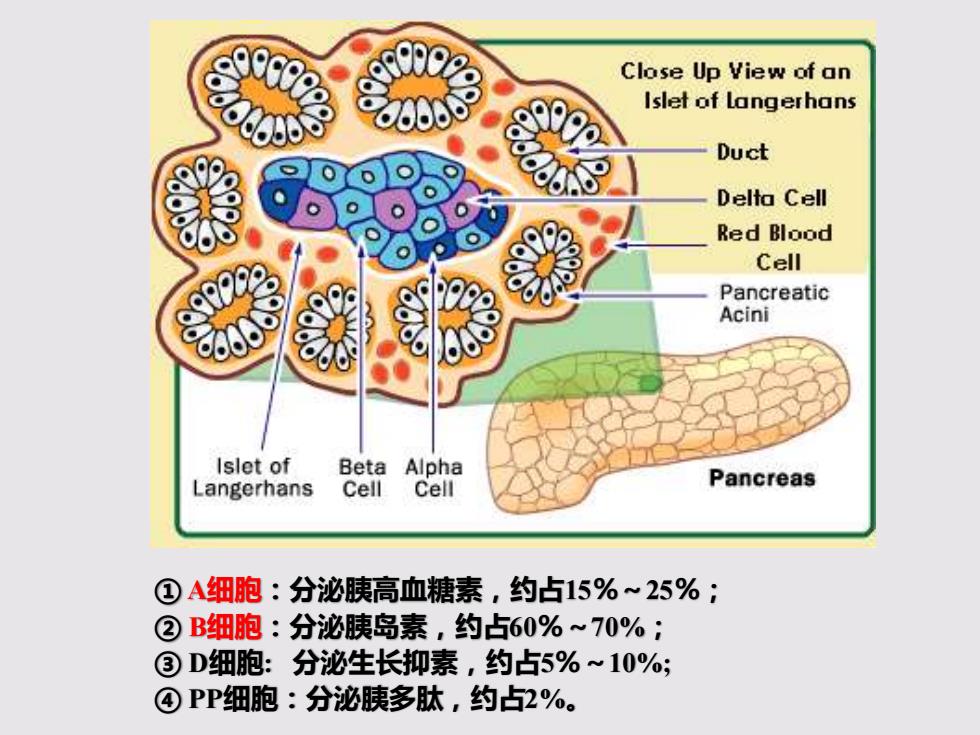
Close Up View of an Islet of Langerhans Duct Delta Cell Red Blood Cell Pancreatic Acini Islet of Beta Alpha Langerhans Cell Cell Pancreas ①A细胞:分泌胰高血糖素,约占15%~25%; ②B细胞:分泌胰岛素,约占60%~70%; ③D细胞:分泌生长抑素,约占5%~10%; ④PP细胞:分泌胰多肽,约占2%
① A细胞:分泌胰高血糖素,约占15%~25%; ② B细胞:分泌胰岛素,约占60%~70%; ③ D细胞: 分泌生长抑素,约占5%~10%; ④ PP细胞:分泌胰多肽,约占2%

A normal pancreatic islet of Langerhans surrounded by exocrine pancreatic acinar tissue
A normal pancreatic islet of Langerhans surrounded by exocrine pancreatic acinar tissue
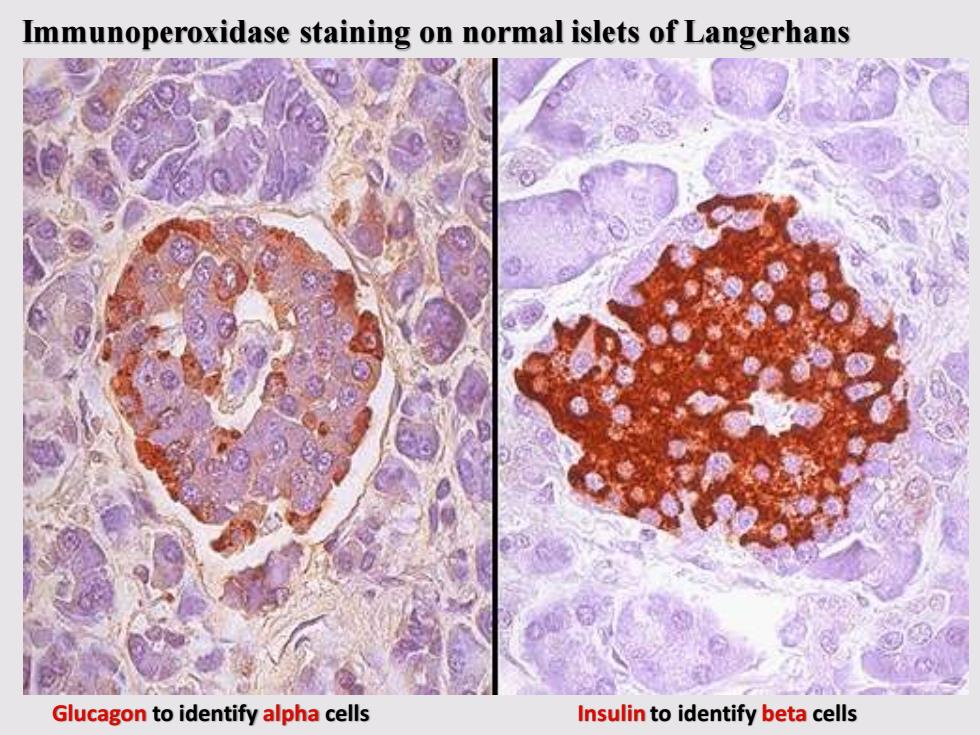
Immunoperoxidase staining on normal islets of Langerhans Glucagon to identify alpha cells Insulin to identify beta cells
Glucagon to identify alpha cells Insulin to identify beta cells Immunoperoxidase staining on normal islets of Langerhans
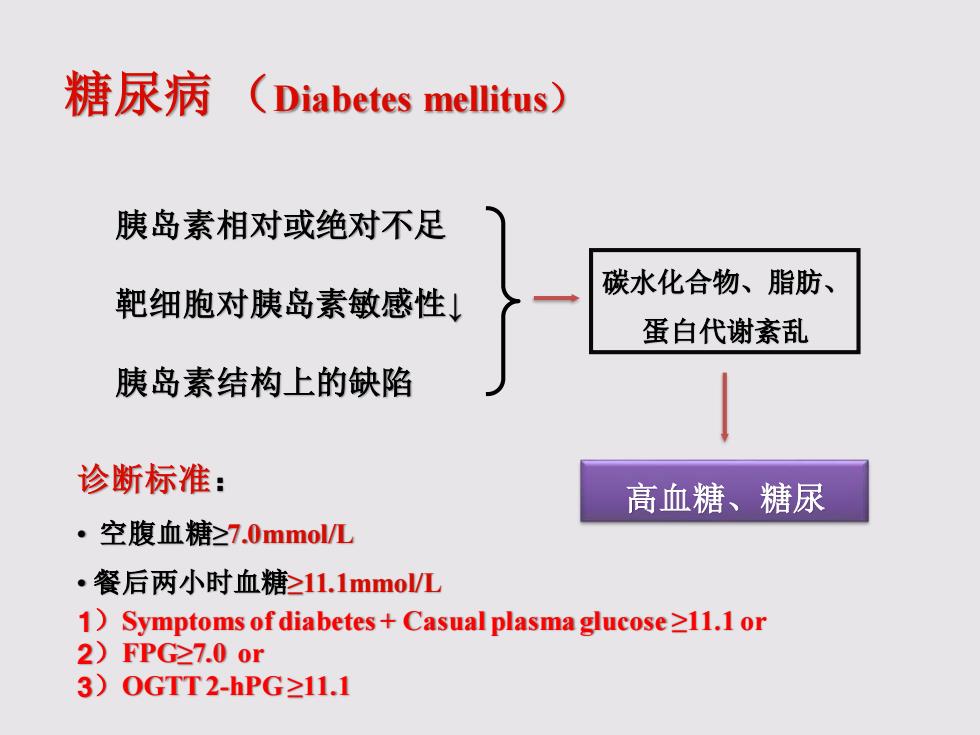
糖尿病(Diabetes mellitus) 胰岛素相对或绝对不足 碳水化合物、脂肪、 靶细胞对胰岛素敏感性↓ 蛋白代谢紊乱 胰岛素结构上的缺陷 诊断标准: 高血糖、糖尿 。空腹血糖≥7.0mmol/L ·餐后两小时血糖≥11.1mmol/L 1)Symptoms of diabetes+Casual plasma glucose 211.1 or 2)FPG≥7.0or 3)0GTT2-hPG≥11.1
糖尿病 (Diabetes mellitus) 胰岛素相对或绝对不足 靶细胞对胰岛素敏感性↓ 胰岛素结构上的缺陷 碳水化合物、脂肪、 蛋白代谢紊乱 高血糖、糖尿 诊断标准: • 空腹血糖≥7.0mmol/L • 餐后两小时血糖≥11.1mmol/L 1)Symptoms of diabetes + Casual plasma glucose ≥11.1 or 2)FPG≥7.0 or 3)OGTT 2-hPG ≥11.1
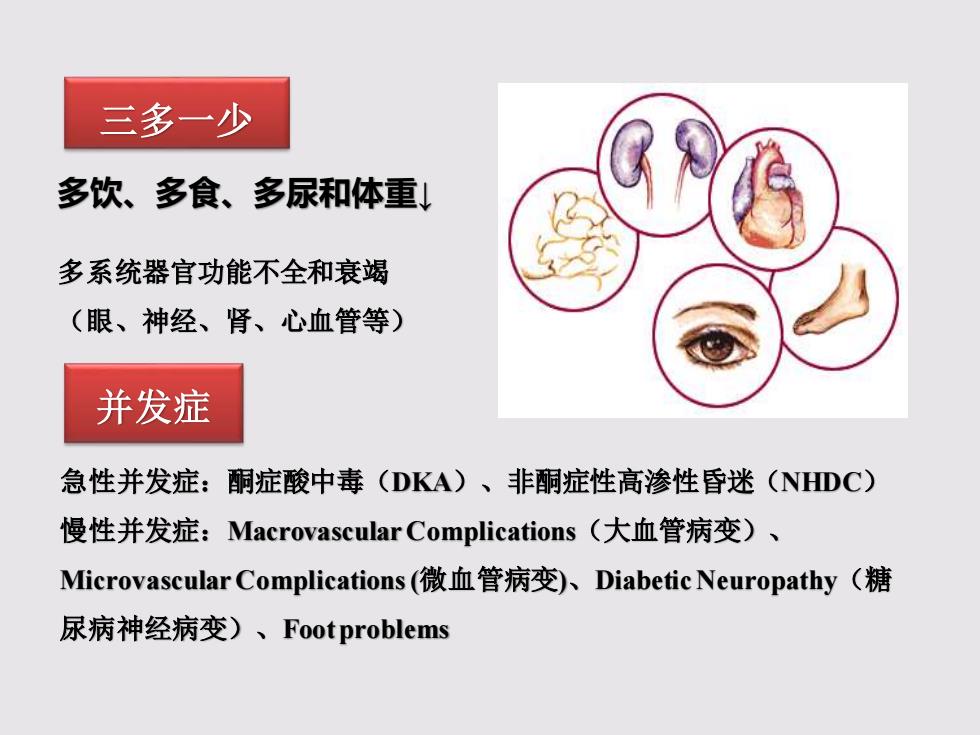
三多一少 多饮、多食、多尿和体重↓ 多系统器官功能不全和衰竭 (眼、神经、肾、心血管等) 并发症 急性并发症:酮症酸中毒(DKA)、非酮症性高渗性昏迷(NHDC) 慢性并发症:Macrovascular Complications(大血管病变)、 Microvascular Complications(微血管病变)、Diabetic Neuropathy(糖 尿病神经病变)、Foot problems
多饮、多食、多尿和体重↓ 三多一少 并发症 急性并发症:酮症酸中毒(DKA)、非酮症性高渗性昏迷(NHDC) 慢性并发症:Macrovascular Complications(大血管病变)、 Microvascular Complications (微血管病变)、Diabetic Neuropathy(糖 尿病神经病变)、Foot problems 多系统器官功能不全和衰竭 (眼、神经、肾、心血管等)
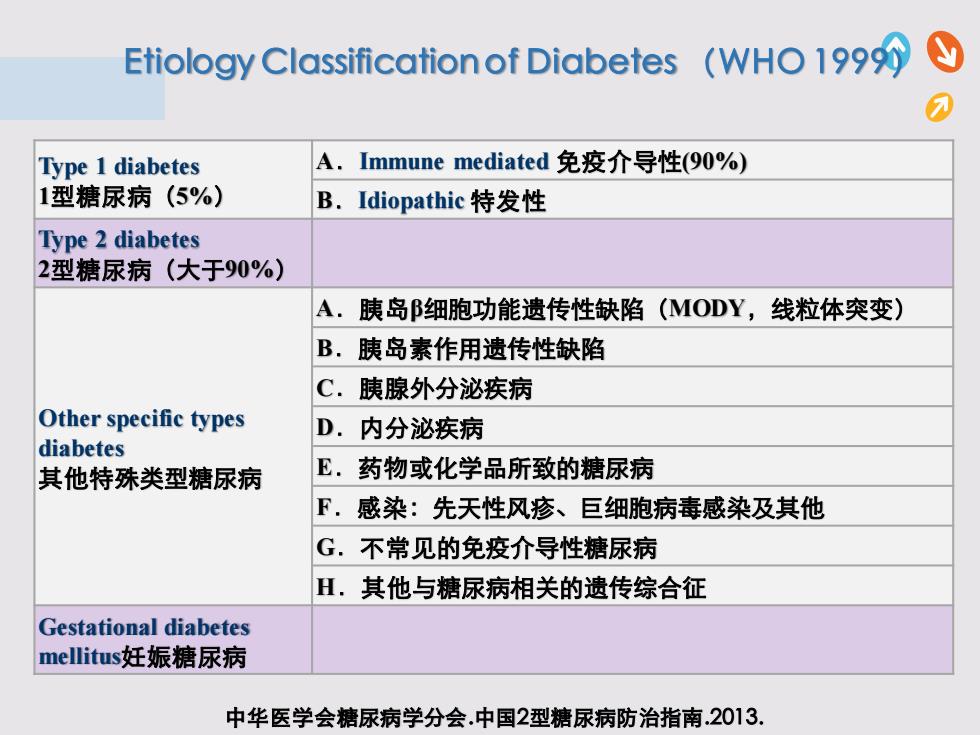
Etiology Classification of Diabetes (WHO199 Type 1 diabetes A.Immune mediated免疫介导性(90%) 1型糖尿病(5%) B.Idiopathic特发性 Type 2 diabetes 2型糖尿病(大于90%) A.胰岛细胞功能遗传性缺陷(MODY,线粒体突变) B,胰岛素作用遗传性缺陷 C.胰腺外分泌疾病 Other specific types D.内分泌疾病 diabetes 其他特殊类型糖尿病 E.药物或化学品所致的糖尿病 F.感染:先天性风疹、巨细胞病毒感染及其他 G.不常见的免疫介导性糖尿病 H.其他与糖尿病相关的遗传综合征 Gestational diabetes mellitus妊娠糖尿病 中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南.2013
中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南.2013. Type 1 diabetes 1型糖尿病(5%) A.Immune mediated 免疫介导性(90%) B.Idiopathic 特发性 Type 2 diabetes 2型糖尿病(大于90%) Other specific types diabetes 其他特殊类型糖尿病 A.胰岛β细胞功能遗传性缺陷(MODY,线粒体突变) B.胰岛素作用遗传性缺陷 C.胰腺外分泌疾病 D.内分泌疾病 E.药物或化学品所致的糖尿病 F.感染:先天性风疹、巨细胞病毒感染及其他 G.不常见的免疫介导性糖尿病 H.其他与糖尿病相关的遗传综合征 Gestational diabetes mellitus妊娠糖尿病 Etiology Classification of Diabetes (WHO 1999)