
人工智能基础 吉建民 USTC jianminOustc.edu.cn 2022年2月20日 口卡4三4色进分QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 人工智能基础 吉建民 USTC jianmin@ustc.edu.cn 2022 年 2 月 20 日

Used Materials Disclaimer:本课件采用了S.Russell and P.Norvig's Artificial Intelligence-A modern approach slides,徐林莉老师课件和其他网 络课程课件,也采用了GitHub中开源代码,以及部分网络博客 内容 4口◆4⊙t1三1=,¥9QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Used Materials Disclaimer: 本课件采用了 S. Russell and P. Norvig’s Artificial Intelligence –A modern approach slides, 徐林莉老师课件和其他网 络课程课件,也采用了 GitHub 中开源代码,以及部分网络博客 内容

Table of Contents Course overview What is Al7 A brief history The state of the art 口卡4回三4色,进分QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Table of Contents Course overview What is AI? A brief history The state of the art

Different people think of Al differently "The automation of]activities that we "The study of mental faculties through associate with human thinking,activ- the use of computational models" ities such as decision-making.problem (Charniak+MeDermott,1985) solving.learning..."(Bellman.1978) "The study of how to make computers "The branch of computer science that do things at which,at the moment.peo- is concerned with the automation of in- ple are better"(Rich+Knight,1991) telligent behavior"(Luger+Stubblefield. 1993) Views of Al fall into four categories: Thinking humanly Thinking rationally Acting humanly Acting rationally The textbook advocates“acting rationally(理性的)
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Different people think of AI differently The textbook advocates “acting rationally (理性的)
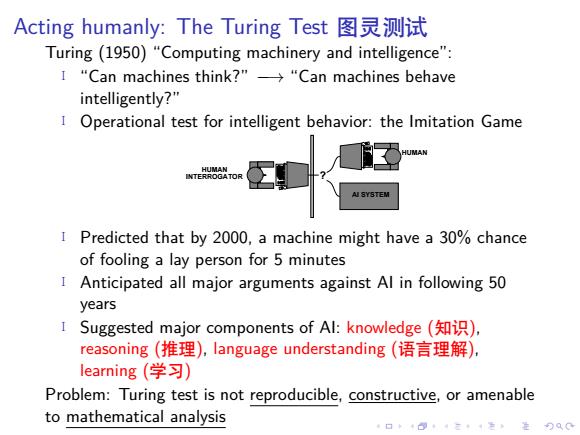
Acting humanly::The Turing Test图灵测试 Turing(1950)"Computing machinery and intelligence": 1"Can machines think?”→“Can machines behave intelligently?" I Operational test for intelligent behavior:the Imitation Game MAN A SYSTEM I Predicted that by 2000,a machine might have a 30%chance of fooling a lay person for 5 minutes Anticipated all major arguments against Al in following 50 years Suggested major components of Al:knowledge(知识), reasoning(推理),language understanding(语言理解), learning(学习) Problem:Turing test is not reproducible,constructive,or amenable to mathematical analysis
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Acting humanly: The Turing Test 图灵测试 Turing (1950) “Computing machinery and intelligence”: ▶ “Can machines think?” −→ “Can machines behave intelligently?” ▶ Operational test for intelligent behavior: the Imitation Game AI SYSTEM HUMAN ? HUMAN INTERROGATOR ▶ Predicted that by 2000, a machine might have a 30% chance of fooling a lay person for 5 minutes ▶ Anticipated all major arguments against AI in following 50 years ▶ Suggested major components of AI: knowledge (知识), reasoning (推理), language understanding (语言理解), learning (学习) Problem: Turing test is not reproducible, constructive, or amenable to mathematical analysis

Thinking humanly:Cognitive Science(认知科学) I 1960s "cognitive revolution":information-processing psychology replaced prevailing orthodoxy of behaviorism I Requires scientific theories of internal activities of the brain -What level of abstraction?“Knowledge”or“circuits"? How to validate?Requires Predicting and testing behavior of human subjects (top-down),or Direct identification from neurological data(bottom-up) I Both approaches (roughly,Cognitive Science and Cognitive Neuroscience)are now distinct from Al 4口◆4⊙t1三1=,¥9QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Thinking humanly: Cognitive Science (认知科学) ▶ 1960s “cognitive revolution”: information-processing psychology replaced prevailing orthodoxy of behaviorism ▶ Requires scientific theories of internal activities of the brain ▶ What level of abstraction? “Knowledge” or “circuits”? ▶ How to validate? Requires ▶ Predicting and testing behavior of human subjects (top-down), or ▶ Direct identification from neurological data (bottom-up) ▶ Both approaches (roughly, Cognitive Science and Cognitive Neuroscience) are now distinct from AI

Thinking rationally:Laws of Thought 1 Normative (or prescriptive)rather than descriptive I Aristotle(亚里士多德):what are correct arguments/,thought processes? Several Greek schools developed various forms of logic: notation and rules of derivation for thoughts;may or may not have proceeded to the idea of mechanization I Direct line through mathematics and philosophy to modern Al I Problems: Not all intelligent behavior is mediated by logical deliberation What is the purpose of thinking?What thoughts should I have? Logical systems tend to do the wrong thing in the presence of uncertainty ·部分学者观点,部分学者不同意 口卡4回三4色,进分QC
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Thinking rationally: Laws of Thought ▶ Normative (or prescriptive) rather than descriptive ▶ Aristotle (亚里士多德): what are correct arguments/thought processes? ▶ Several Greek schools developed various forms of logic: notation and rules of derivation for thoughts; may or may not have proceeded to the idea of mechanization ▶ Direct line through mathematics and philosophy to modern AI ▶ Problems: ▶ Not all intelligent behavior is mediated by logical deliberation ▶ What is the purpose of thinking? What thoughts should I have? ▶ Logical systems tend to do the wrong thing in the presence of uncertainty ▶ 部分学者观点,部分学者不同意

Acting rationally 1 Rational behavior:doing the right thing The right thing:that which is expected to maximize goal achievement,given the available information Doesn't necessarily involve thinking-e.g.,blinking reflex-but thinking should be in the service of rational action ~Aristotle(Nicomachean Ethics,亚里士多德所著《尼各马可伦 理学》) Every art and every inquiry,and similarly every action and pursuit,is thought to aim at some good I Entirely dependent on goals! I Irrational insane,irrationality is sub-optimal action I Rational successful Our focus here: Systems which make the best possible decisions given goals, evidence,and constraints In the real world,usually lots of uncertainty ..and lots of complexity Usually,we're just approximating rationality 461三1声,是90C
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Acting rationally ▶ Rational behavior: doing the right thing ▶ The right thing: that which is expected to maximize goal achievement, given the available information ▶ Doesn’t necessarily involve thinking—e.g., blinking reflex—but thinking should be in the service of rational action ▶ Aristotle (Nicomachean Ethics, 亚里士多德所著《尼各马可伦 理学》): Every art and every inquiry, and similarly every action and pursuit, is thought to aim at some good ▶ Entirely dependent on goals! ▶ Irrational ̸= insane, irrationality is sub-optimal action ▶ Rational ̸= successful ▶ Our focus here: ▶ Systems which make the best possible decisions given goals, evidence, and constraints ▶ In the real world, usually lots of uncertainty ▶ . . . and lots of complexity ▶ Usually, we’re just approximating rationality

Rational agents Maximize Your Expected Utility I An agent is an entity that perceives and acts I This course is about designing rational agents I Abstractly,an agent is a function from percept histories to actions: f:P*→A 1 For any given class of environments and tasks,we seek the agent(or class of agents)with the best performance 1 Caveat:computational limitations make perfect rationality unachievable->design best program for given machine resources 口卡+·三色,是分Q0
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Rational agents Maximize Your Expected Utility ▶ An agent is an entity that perceives and acts ▶ This course is about designing rational agents ▶ Abstractly, an agent is a function from percept histories to actions: f : P ∗ → A ▶ For any given class of environments and tasks, we seek the agent (or class of agents) with the best performance ▶ Caveat: computational limitations make perfect rationality unachievable → design best program for given machine resources

Self Driving Car Architecture SENSORS PERCEPTION PLANNING CONTROL DETECTION CAMERA ROUTE PLANNING PIO LANE DETECTION RADAR TRAFFIC LIGHT PREDICTION DETECTION CLASSIFICATION MPC TRAFFIC 5IGN DETECTION &CLASSIFICATION REHAVOR LIDAR PLANNING OBJECT DETECTION 表TRACKING TRAIECTORY OTHERS GPS PLANNING FREE SPACE DETECTION OTHERS LOCALIZATION MAP 日+4+4二1在)QG
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Self Driving Car Architecture