Outline Overview of web search Next generation search engines CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, 2 June25-27,2010
Outline • Overview of web search • Next generation search engines 2 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010
Characteristics of Web Information "Infinite"size (Surface vs.deep Web) Surface static HTML pages Deep=dynamically generated HTML pages(DB) ·Semi-structured -Structured HTML tags,hyperlinks,etc Unstructured Text Different format (pdf,word,ps,...) 。Multi--media(Textual,,audio,images,…) High variances in quality(Many junks) "Universal"coverage(can be about any content) CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June25-27,2010
Characteristics of Web Information • “Infinite” size (Surface vs. deep Web) – Surface = static HTML pages – Deep = dynamically generated HTML pages (DB) • Semi-structured – Structured = HTML tags, hyperlinks, etc – Unstructured = Text • Different format (pdf, word, ps, …) • Multi-media (Textual, audio, images, …) • High variances in quality (Many junks) • “Universal” coverage (can be about any content) 3 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010

General Challenges in Web Information Management Handling the size of the Web How to ensure completeness of coverage? Efficiency issues Dealing with or tolerating errors and low quality information Addressing the dynamics of the Web Some pages may disappear permanently New pages are constantly created CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, 4 June25-27,2010
General Challenges in Web Information Management • Handling the size of the Web – How to ensure completeness of coverage? – Efficiency issues • Dealing with or tolerating errors and low quality information • Addressing the dynamics of the Web – Some pages may disappear permanently – New pages are constantly created 4 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010

“Free text'"vs.“Structured text" So far,we've assumed "free text" Document word sequence -Query word sequence Collection a set of documents -Minimal structure .. But,we may have structures on text(e.g.,title, hyperlinks) Can we exploit the structures in retrieval? CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June25-27,2010
“Free text” vs. “Structured text” • So far, we’ve assumed “free text” – Document = word sequence – Query = word sequence – Collection = a set of documents – Minimal structure … • But, we may have structures on text (e.g., title, hyperlinks) – Can we exploit the structures in retrieval? 5 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010
Examples of Document Structures Intra-doc structures(=relations of components) Natural components:title,author,abstract, sections,references,.. Annotations:named entities,subtopics, markups,… Inter-doc structures (=relations between documents) Topic hierarchy Hyperlinks/citations (hypertext) CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June25-27,2010 6
Examples of Document Structures • Intra-doc structures (=relations of components) – Natural components: title, author, abstract, sections, references, … – Annotations: named entities, subtopics, markups, … • Inter-doc structures (=relations between documents) – Topic hierarchy – Hyperlinks/citations (hypertext) 6 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010
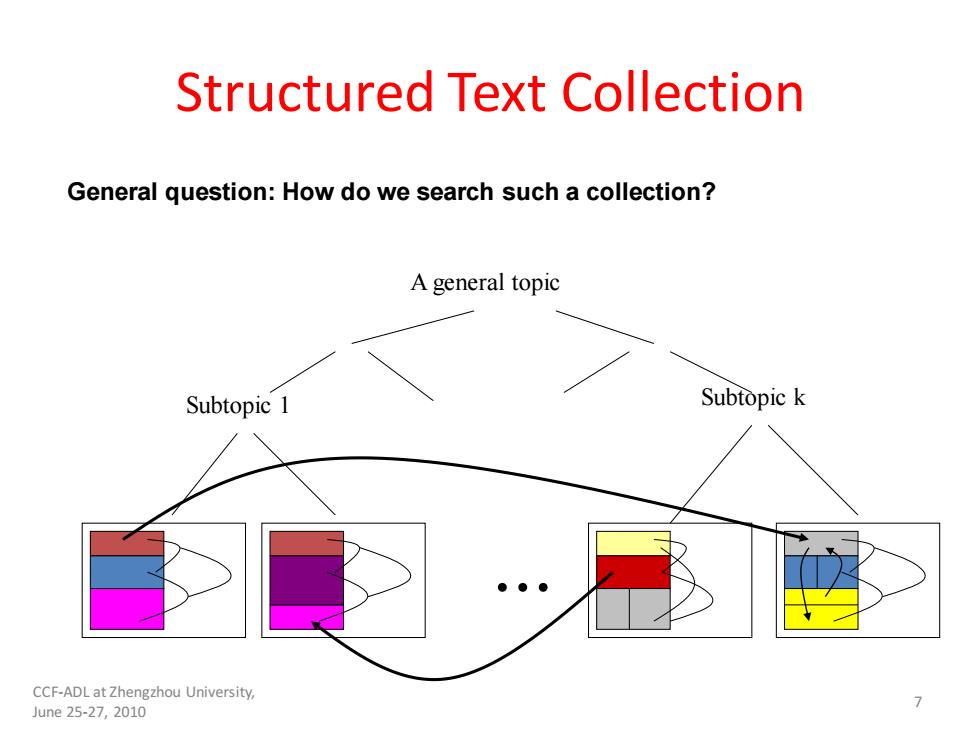
Structured Text Collection General question:How do we search such a collection? A general topic Subtopic 1 Subtopic k CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June25-27,2010
Structured Text Collection ... Subtopic 1 Subtopic k A general topic General question: How do we search such a collection? 7 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010
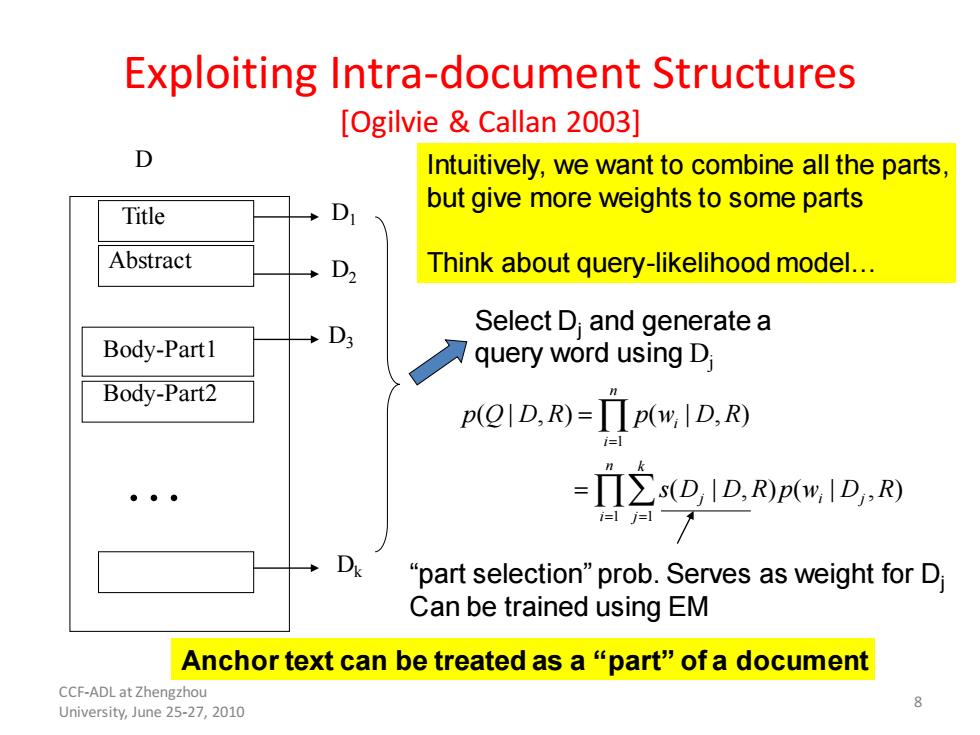
Exploiting Intra-document Structures [Ogilvie Callan 2003] D Intuitively,we want to combine all the parts. but give more weights to some parts Title D Abstract +D2 Think about query-likelihood model... Select D and generate a Body-Part1 +D3 query word using D; Body-Part2 p(QID.R)-TIp(w.ID.R) -TIEs(D,ID.R)pOID.R i=1j=1 D "part selection"prob.Serves as weight for D Can be trained using EM Anchor text can be treated as a "part"of a document CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University,June 25-27,2010
Exploiting Intra-document Structures [Ogilvie & Callan 2003] Title Abstract Body-Part1 Body-Part2 … D D1 D2 D3 Dk Intuitively, we want to combine all the parts, but give more weights to some parts Think about query-likelihood model… 1 1 1 ( | , ) ( | , ) ( | , ) ( | , ) n i i n k j i j i j p Q D R p w D R s D D R p w D R = = = = = “part selection” prob. Serves as weight for Dj Can be trained using EM Select Dj and generate a query word using Dj Anchor text can be treated as a “part” of a document 8 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010

Exploiting Inter-document Structures Document collection has links (e.g.,Web, citations of literature) ·Query:text query Results:ranked list of documents Challenge:how to exploit links to improve ranking? CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, 9 June25-27,2010
Exploiting Inter-document Structures • Document collection has links (e.g., Web, citations of literature) • Query: text query • Results: ranked list of documents • Challenge: how to exploit links to improve ranking? 9 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010
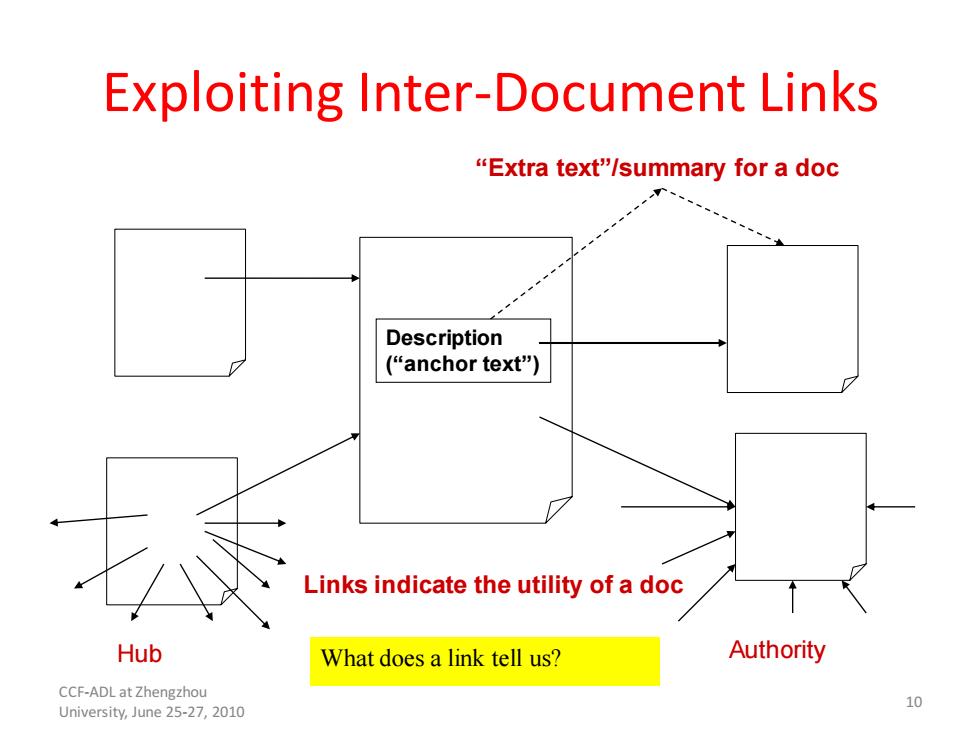
Exploiting Inter-Document Links "Extra text"/summary for a doc Description (“anchor text") Links indicate the utility of a doc Hub What does a link tell us? Authority CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University,June 25-27,2010 10
Exploiting Inter-Document Links Description (“anchor text”) Hub Authority “Extra text”/summary for a doc Links indicate the utility of a doc What does a link tell us? 10 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010

PageRank:Capturing Page "Popularity" [Page Brin 98] 。Intuitions Links are like citations in literature -A page that is cited often can be expected to be more useful in general ·PageRank is essentially“citation counting”,but improves over simple counting -Consider "indirect citations"(being cited by a highly cited paper counts a lot...) Smoothing of citations(every page is assumed to have a non-zero citation count) PageRank can also be interpreted as random surfing (thus capturing popularity) CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June25-27,2010
PageRank: Capturing Page “Popularity” [Page & Brin 98] • Intuitions – Links are like citations in literature – A page that is cited often can be expected to be more useful in general • PageRank is essentially “citation counting”, but improves over simple counting – Consider “indirect citations” (being cited by a highly cited paper counts a lot…) – Smoothing of citations (every page is assumed to have a non-zero citation count) • PageRank can also be interpreted as random surfing (thus capturing popularity) 11 CCF-ADL at Zhengzhou University, June 25-27, 2010