
Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 3 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes Jo Blackburn Richland College,Dallas,TX Dallas County Community College District ©2006,Prentice Hall
Chapter 3 Structure and Stereochemistry of Alkanes Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr. Jo Blackburn Richland College, Dallas, TX Dallas County Community College District © 2006, Prentice Hall
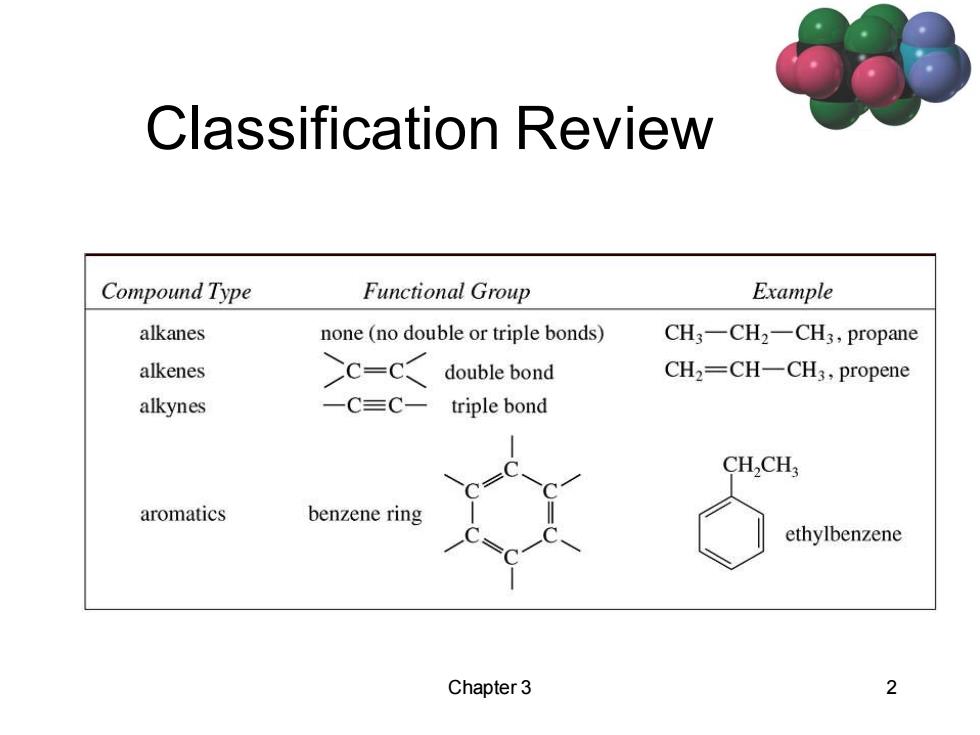
Classification Review Compound Type Functional Group Example alkanes none (no double or triple bonds) CH3一CH2-CH3,propane alkenes >c-c< double bond CH2=CH-CH3,propene alkynes 一C三C一 triple bond CHCH aromatics benzene ring ethylbenzene Chapter 3 2
Chapter 3 2 Classification Review
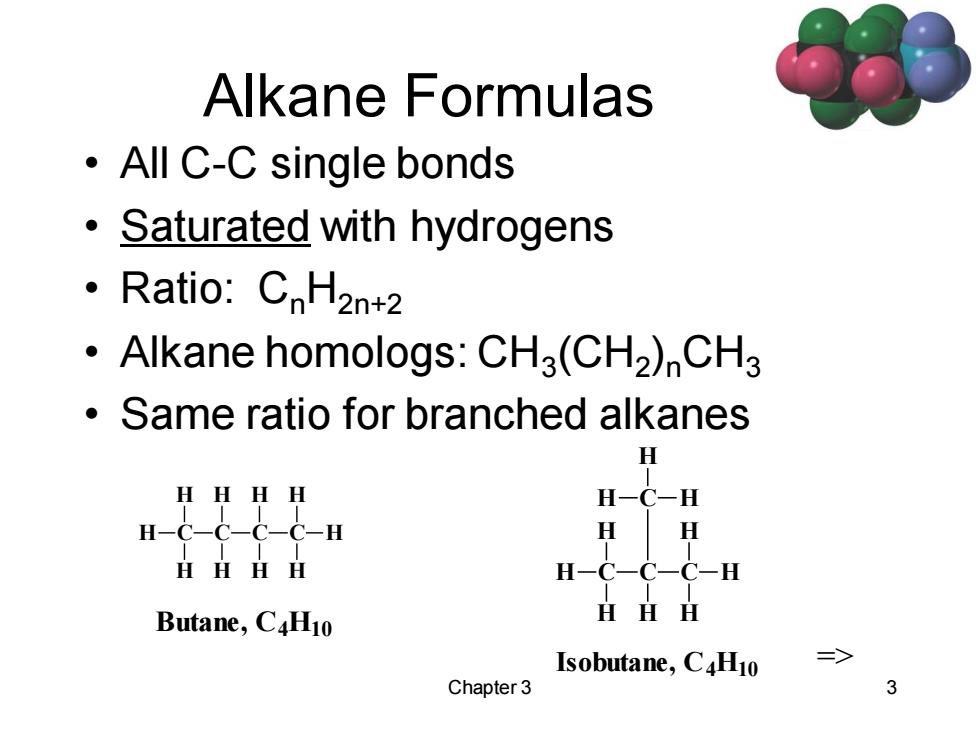
Alkane Formulas ·AllC-C single bonds Saturated with hydrogens 。Ratio::CnH2nt2 Alkane homologs:CH3(CH2)CH3 Same ratio for branched alkanes H HHHH H-C-H H-c-c-c-C-H H H HHHH H-C-C-C-H Butane,C4H10 HHH Isobutane,C4H10 => Chapter 3 3
Chapter 3 3 Alkane Formulas • All C-C single bonds • Saturated with hydrogens • Ratio: CnH2n+2 • Alkane homologs: CH3 (CH2 )nCH3 • Same ratio for branched alkanes => C H C H H H C H H H C H H H Isobutane, C4H10 C H C H H H C C H H H H H H Butane, C4H10

Common Names 。Isobutane,“isomer of butane” Isopentane,isohexane,etc.,methyl branch on next-to-last carbon in chain. Neopentane,most highly branched Five possible isomers of hexane, 18 isomers of octane and 75 for decane! Chapter 3 4
Chapter 3 4 Common Names • Isobutane, “isomer of butane” • Isopentane, isohexane, etc., methyl branch on next-to-last carbon in chain. • Neopentane, most highly branched • Five possible isomers of hexane, 18 isomers of octane and 75 for decane! =>
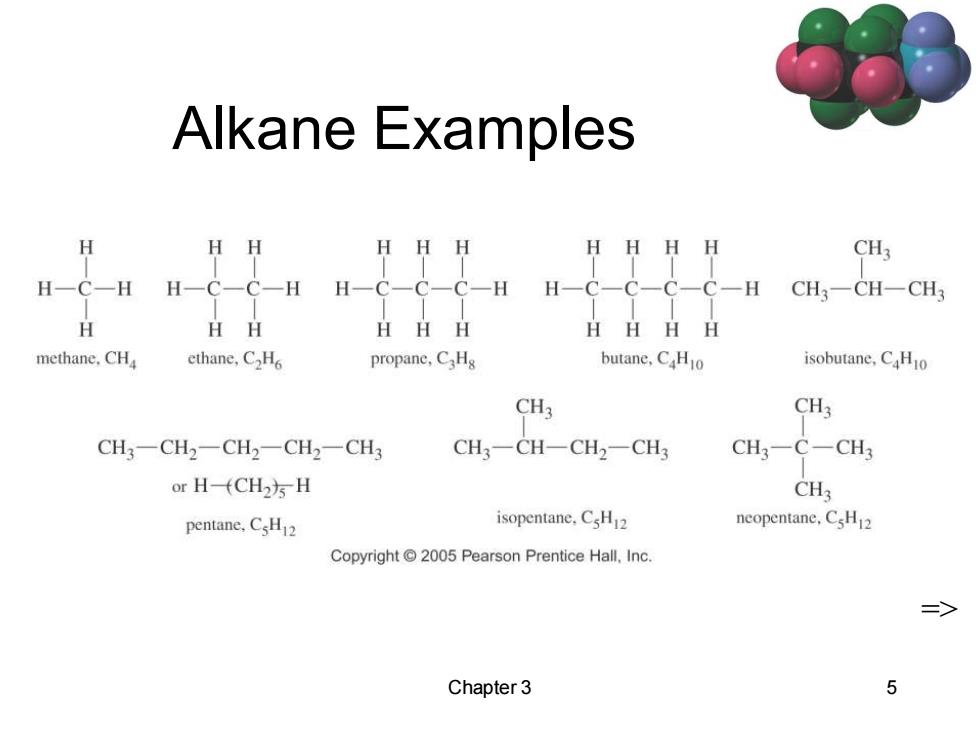
Alkane Examples HH HHHH CH3 H一C-H H-C-C-H H-C-C-C-H H-C- -C- CH3一CH-CH H HH HHH HHHH methane,CHa ethane,C2H6 propane,CHg butane,CHo isobutane,CHo CH3 CH3 CH3-CH2-CH2一CH2一CH3 CH3一CH-CH2-CH3 CH3-C-CH3 or H-fCH2)s H CH3 pentane.CsH2 isopentane.CsH2 neopentane,CsH2 Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. 二> Chapter 3
Chapter 3 5 Alkane Examples =>

IUPAC Names 0 Find the longest continuous carbon chain. Number the carbons,starting closest to the first branch. Name the groups attached to the chain, using the carbon number as the locator. Alphabetize substituents. Use di-,tri-,etc.,for multiples of same substituent. > Chapter 3 6
Chapter 3 6 IUPAC Names • Find the longest continuous carbon chain. • Number the carbons, starting closest to the first branch. • Name the groups attached to the chain, using the carbon number as the locator. • Alphabetize substituents. • Use di-, tri-, etc., for multiples of same substituent. =>
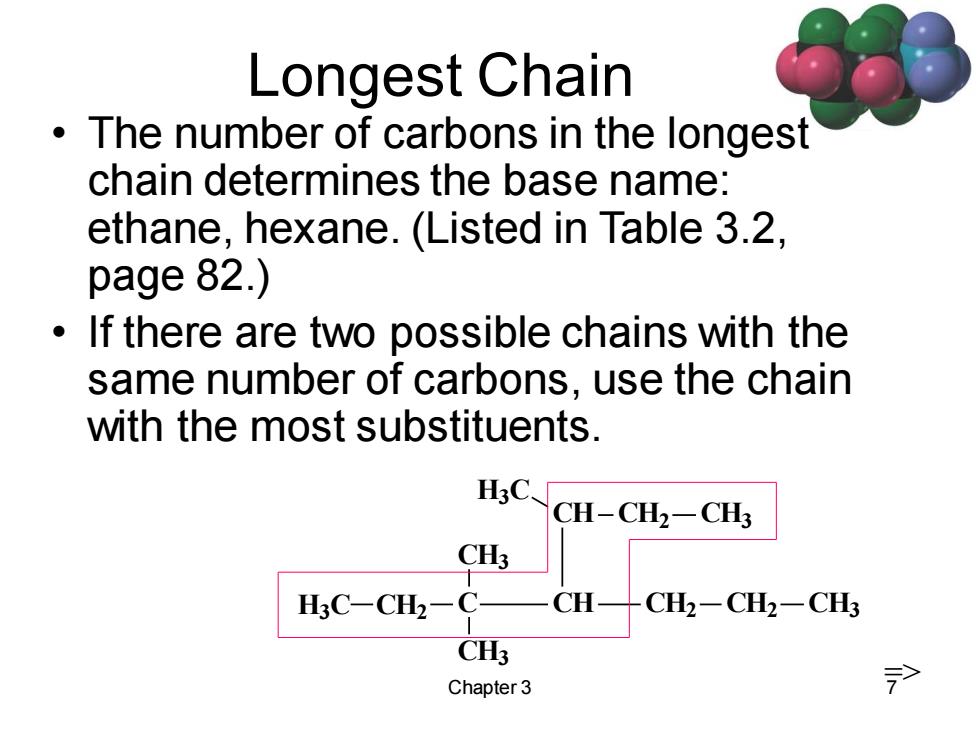
Longest Chain The number of carbons in the longest chain determines the base name: ethane,hexane.(Listed in Table 3.2, page 82.) If there are two possible chains with the same number of carbons,use the chain with the most substituents. HC、 CH-CH2-CH3 CH3 H3C-CH2-C- CH CH2-CH2-CH3 CH3 Chapter 3 >
Chapter 3 7 Longest Chain • The number of carbons in the longest chain determines the base name: ethane, hexane. (Listed in Table 3.2, page 82.) • If there are two possible chains with the same number of carbons, use the chain with the most substituents. C CH3 CH2 CH3 CH CH2 CH2 CH3 CH CH2 CH3 H3C H3C =>
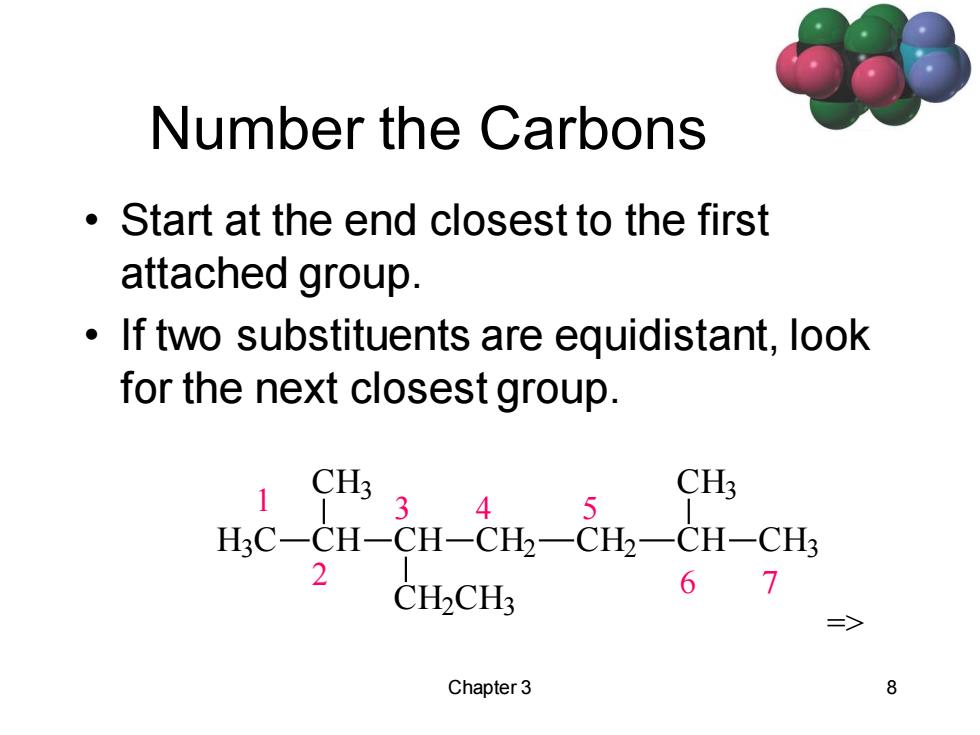
Number the Carbons Start at the end closest to the first attached group. If two substituents are equidistant,look for the next closest group. CH3 3 CH3 4 5 H3C-CH-CH-CH2一CH2一CH-CH 2 CH2CH: 67 Chapter 3 8
Chapter 3 8 Number the Carbons • Start at the end closest to the first attached group. • If two substituents are equidistant, look for the next closest group. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 H3 C CH CH3 CH CH2 CH3 CH2 CH2 CH CH3 CH3 =>
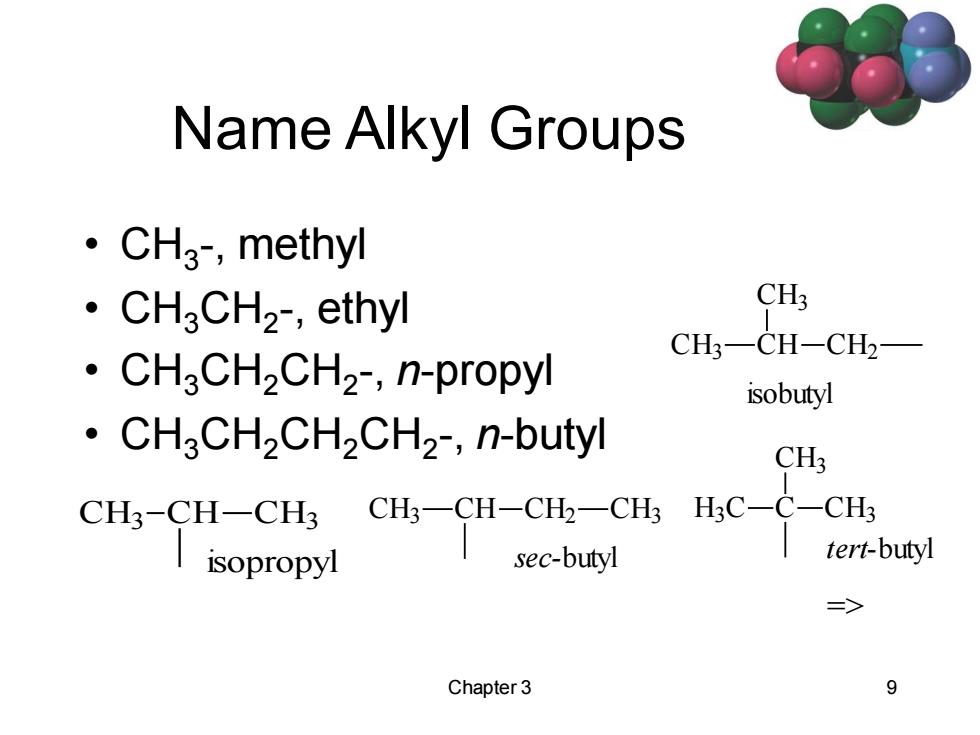
Name Alkyl Groups ·CH3,methyl ·CH3CH2,ethyl CH3 CH3一CH-CH2 ·CH3CH2CH2,n-propyl isobutyl CHaCH2CH2CH2-,n-butyl CH3 CH3-CH-CH3 CH3-CH-CH2-CH3 H;C-C-CH3 isopropyl sec-butyl tert-butyl => Chapter 3 9
Chapter 3 9 Name Alkyl Groups • CH3 -, methyl • CH3CH2 -, ethyl • CH3CH2CH2 -, n-propyl • CH3CH2CH2CH2 -, n-butyl CH3 CH CH2 CH3 sec-butyl CH3 CH CH3 CH2 isobutyl CH3 CH CH3 isopropyl H3 C C CH3 CH3 tert-butyl =>
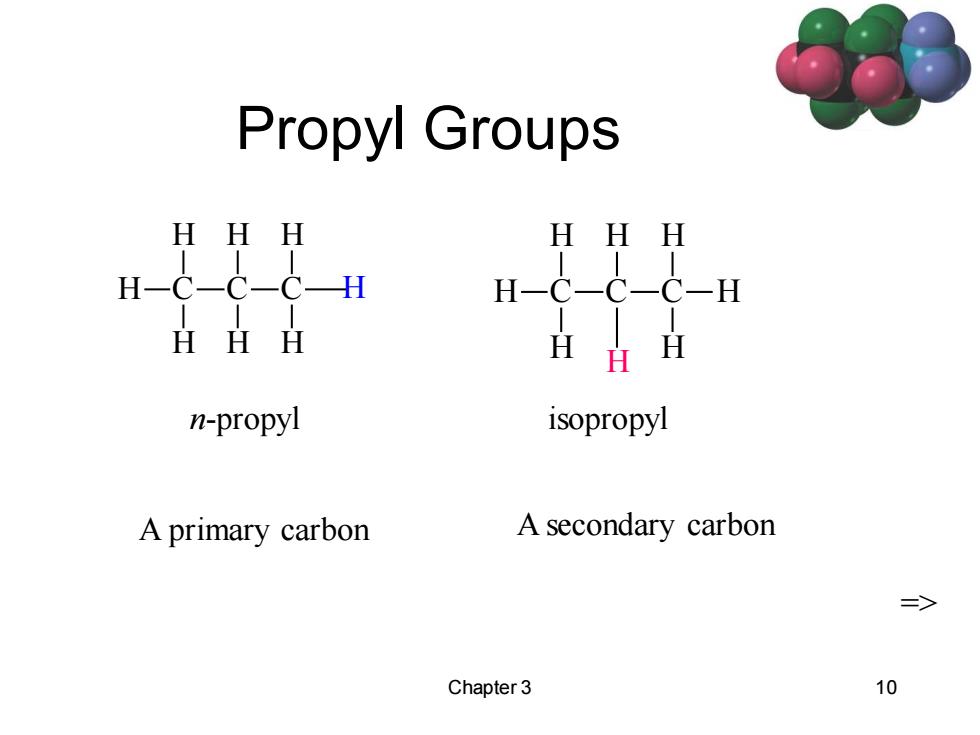
Propyl Groups HHH HHH HHH H n-propyl isopropyl A primary carbon A secondary carbon => Chapter 3 10
Chapter 3 10 Propyl Groups C H H H C H H C H H H n-propyl C H H H C H C H H H isopropyl H A primary carbon A secondary carbon =>