1.Optical principles of light microscopy Seeing is believing 100μm
1. Optical principles of light microscopy Seeing is believing
Optical/light microscopy The most widely used and the most fundamental measure to check the microstructure. ·Applications Quality control in materials processing Failure analysis of a component during service -Structure-property relationship establishment 2
Optical/light microscopy • The most widely used and the most fundamental measure to check the microstructure. • Applications – Quality control in materials processing – Failure analysis of a component during service – Structure-property relationship establishment 2

Optical principles Image formation and resolution ·Instrumentation Objective lens (numerical aperture, aberration) CCD/CMOS digital imaging system 3
Optical principles • Image formation and resolution • Instrumentation • Objective lens (numerical aperture, aberration) • CCD/CMOS digital imaging system 3

Refraction(折射) n=1 n>1 n=1 Refractive index(折 射率) Vacuum 1 。Air 1.0003 Water 1.333 Incident wave Reflected ● Cytoplasm 1.35-1.38? wave 9 ●Glycerol 1.475 (anhydrous) Refractive index n,=1 ●Immersion oil 1.515 Speed =c ●Fused silica 1.46 Optical glasses 1.5-1.9 Refractive index na Speed c/n Refracted wave 。Diamond 2.417 2/n Depends on wavelength and temperature →Snel'slaw: Mirror law: n Sin(0)=n2 Sin(02) 8.=6 4
Refraction (折射 ) • Refractive index ( 折 射率 ) 4
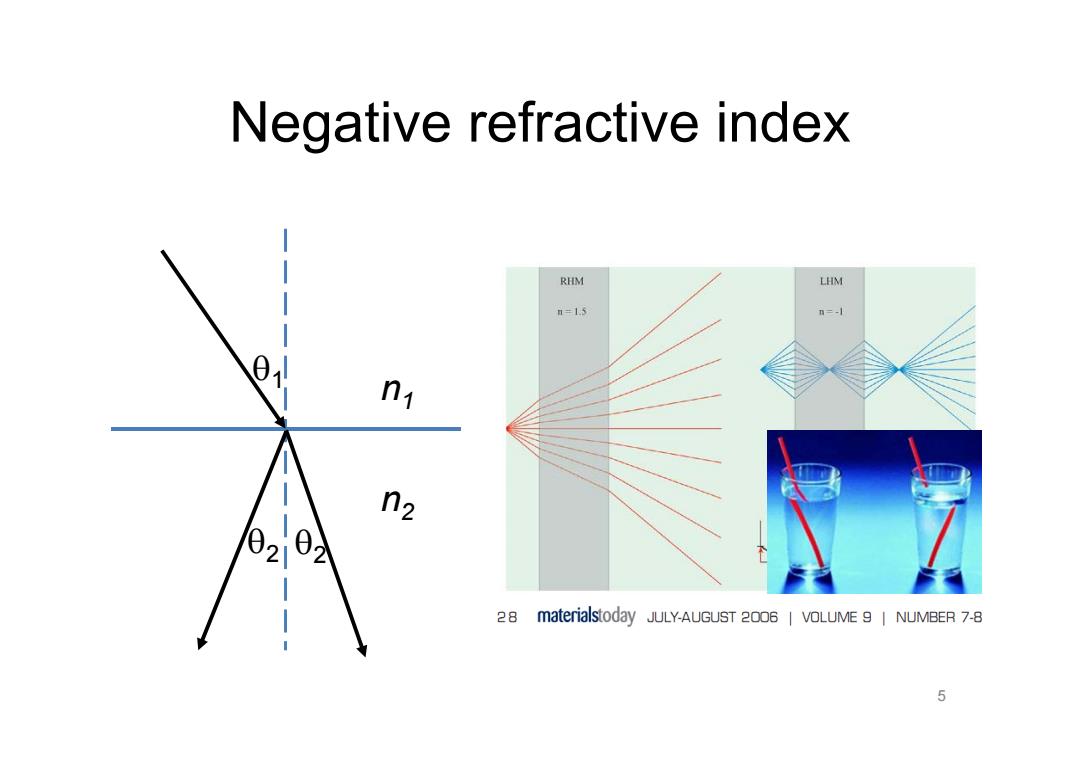
Negative refractive index RHM LHM =1.5 n=-1 n1 n2 28 materialstoday JULY-AUGUST 2006 VOLUME 9 NUMBER 7-8 5
Negative refractive index 5 2 1 2 n 1 n 2

Dispersion(色散) Refractive index n depends on wave length http://gallery.hd.org/_c/natural-science/prism-and- refraction-of-light-into-rainbow-AJHD.jpg.html 6
Dispersion (色散) • Refractive index n depends on wave length 6
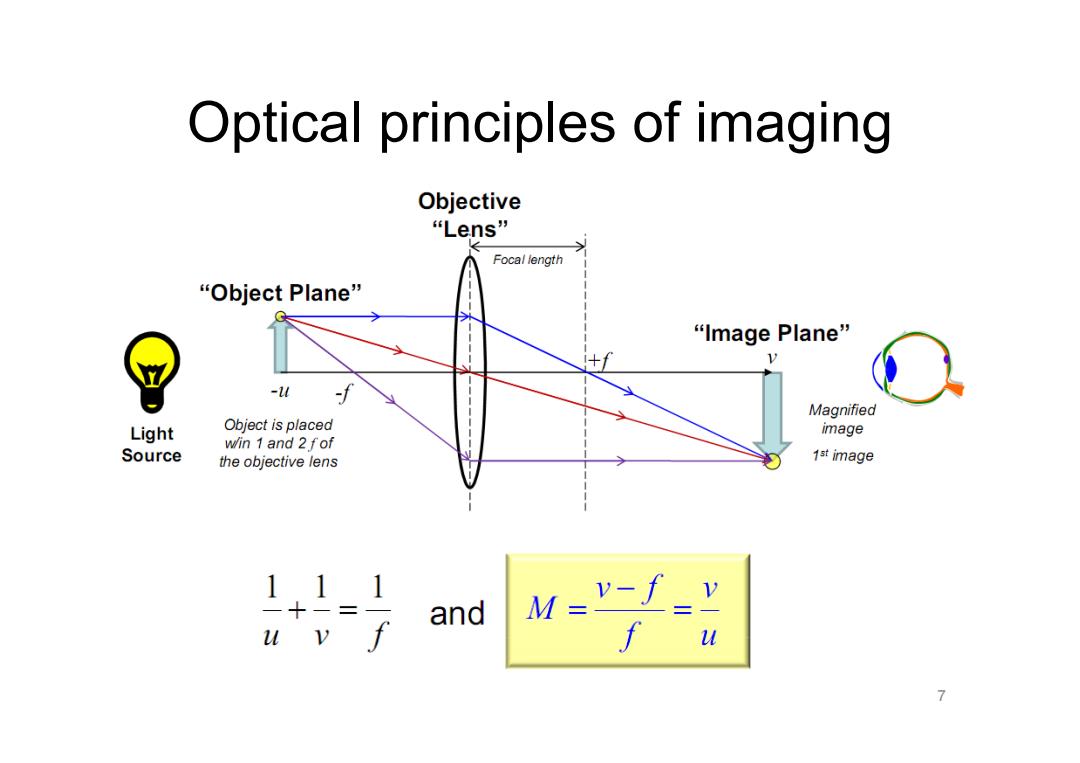
Optical principles of imaging Objective “Lens” Focal length “Object Plane” “Image Plane” D -u f Magnified Light Object is placed image win 1 and 2fof Source the objective lens 1st image 1,11 and M=v-I=Y u v f u
Optical principles of imaging 7
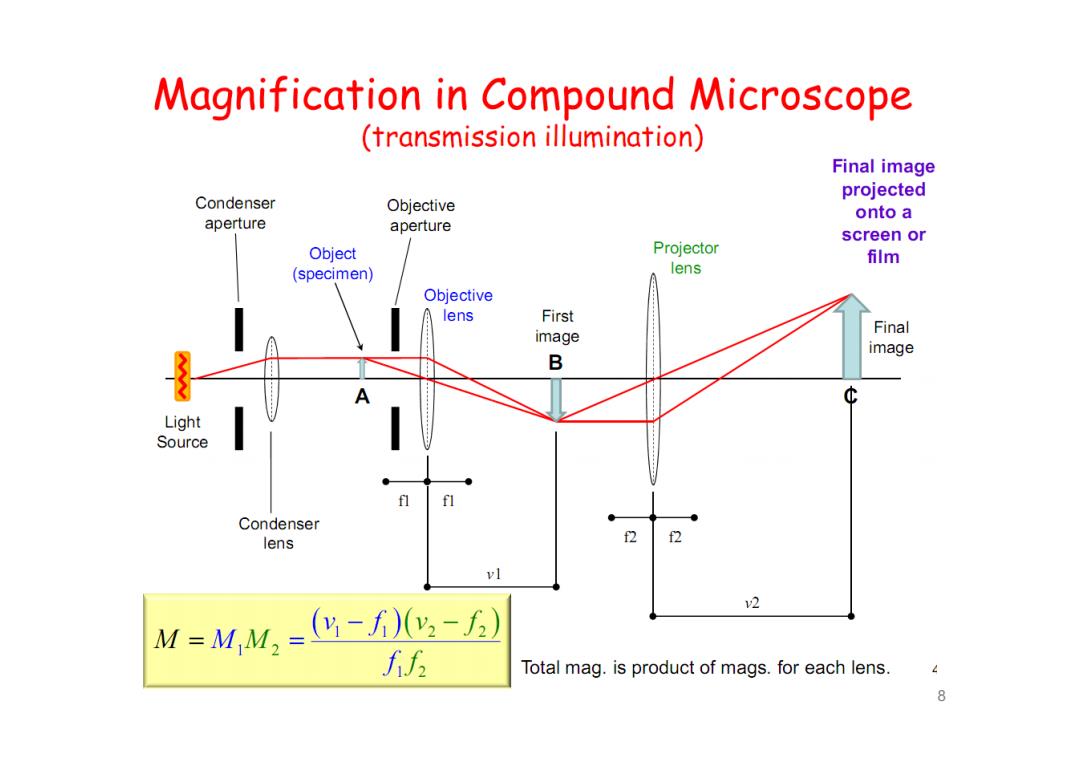
Magnification in Compound Microscope (transmission illumination) Final image projected Condenser Objective onto a aperture aperture screen or Object Projector film (specimen) lens Objective lens First image Final image B Light Source Condenser lens 2 vl v2 M=M,M,=--) f Total mag.is product of mags.for each lens. 8
8
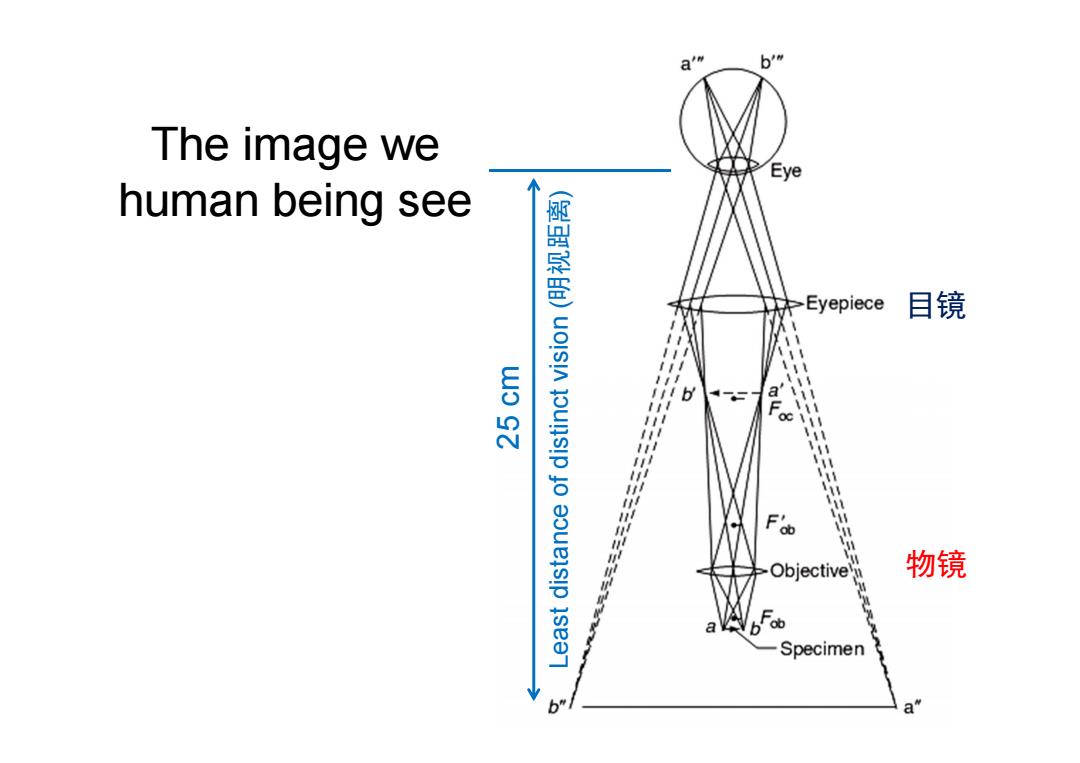
b' The image we Eye human being see Eyepiece 目镜 b a F'o Objective 物镜 Specimen 8. a
The image we human being see 9 25 cm 物镜 目镜 Least distance of distinct vision (明视距离)

Magnification vs.resolution ·Magnification -The ratio of image to object. -Calculated by linear optics. ·Resolution -The ability to distinguish two points. 。Limit? 10
Magnification vs. resolution • Magnification – The ratio of image to object. – Calculated by linear optics. • Resolution – The ability to distinguish two points. • Limit? 10