
Key points in crystallography Miller indices,Bravis-Miller indices for hexagonal structure Lattice spacing calculation Reciprocal lattice <-real lattice Know how to read a crystal structure Table 1.4 Crystallographic data for FeC,iron carbide or cementite,which exists in equilibrium with a-Fe in most steels Pearson Structure symbol a,b,c x,B,7 Point Phase type space group (nm) ) Atoms set X Occ CFe3 CFe3 oP16 Pnma 0.50890 C 4c 890250450 100 0.67433 Fe1 4c 036250852 100 0.45235 Fe2 8d 186063328100
Key points in crystallography • Miller indices, Bravis-Miller indices for hexagonal structure • Lattice spacing calculation • Reciprocal lattice real lattice • Know how to read a crystal structure

Physics of X-ray radiation
Physics of X-ray radiation

Physics of X-ray radiation ·Vavelength of X-ray ·X-ray absorption ·X-ray generators ·Safety issues Wilhelm Conrad Rontgen and the first human X-ray photo
Physics of X-ray radiation • Wavelength of X-ray • X-ray absorption • X-ray generators • Safety issues Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen and the first human X-ray photo
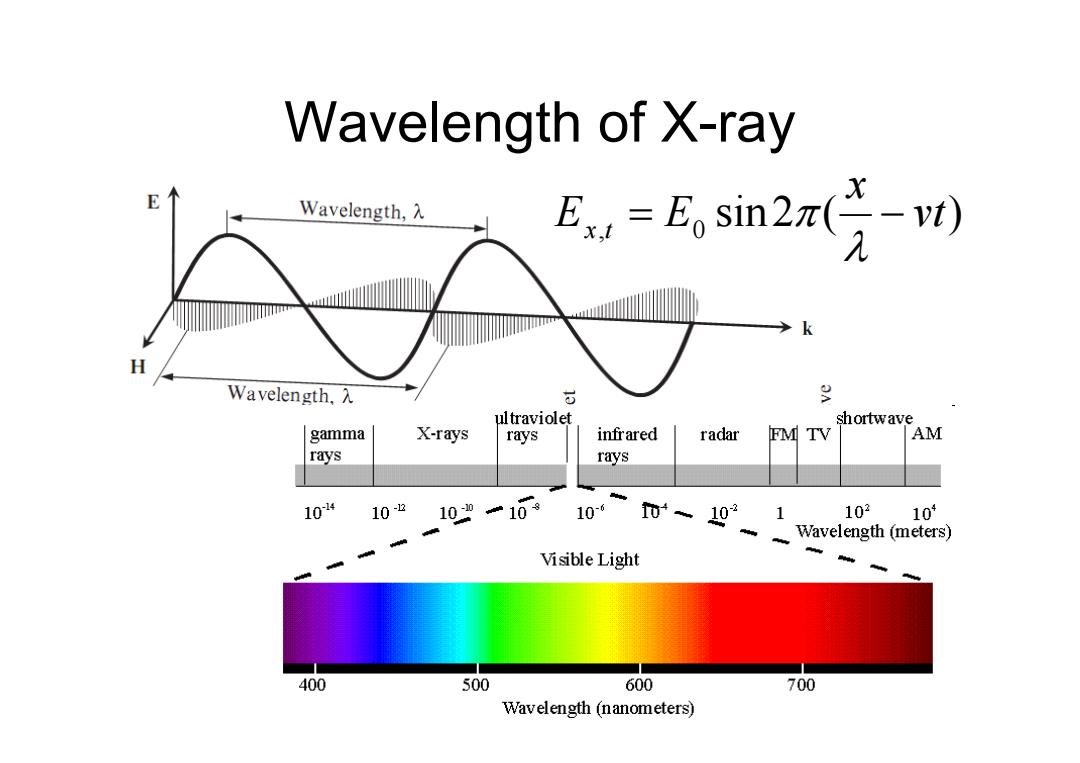
Wavelength of X-ray E Wavelength,入 E,=E,sin2x(经W k H Wavelength,入 5 g ultraviolet shortwave gamma X-rays rays infrared radar FMTV AM rays rays 10-4 10-2 10一109 10-6 0、021 102 104 Wavelength (meters) Visible Light 400 500 600 700 Wavelength(nanometers)
Wavelength of X-ray E E x t x,t 0 sin 2 H H x t x,t 0 sin 2 sin 2 ( ) , 0 vt x E x t E
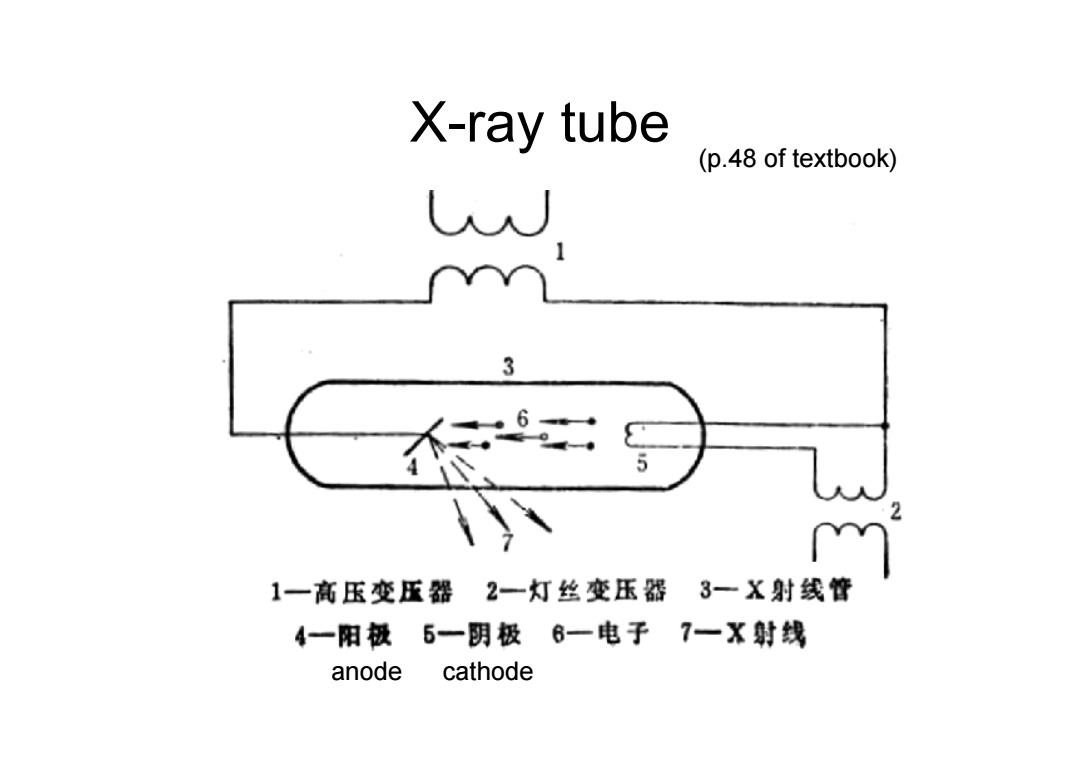
X-ray tube (p.48 of textbook) U 3 1一高压变压器 2一灯丝变压器3一X射线管 4一阳极5一阴极6一电子7一X射线 anode cathode
X-ray tube (p.48 of textbook) anode cathode
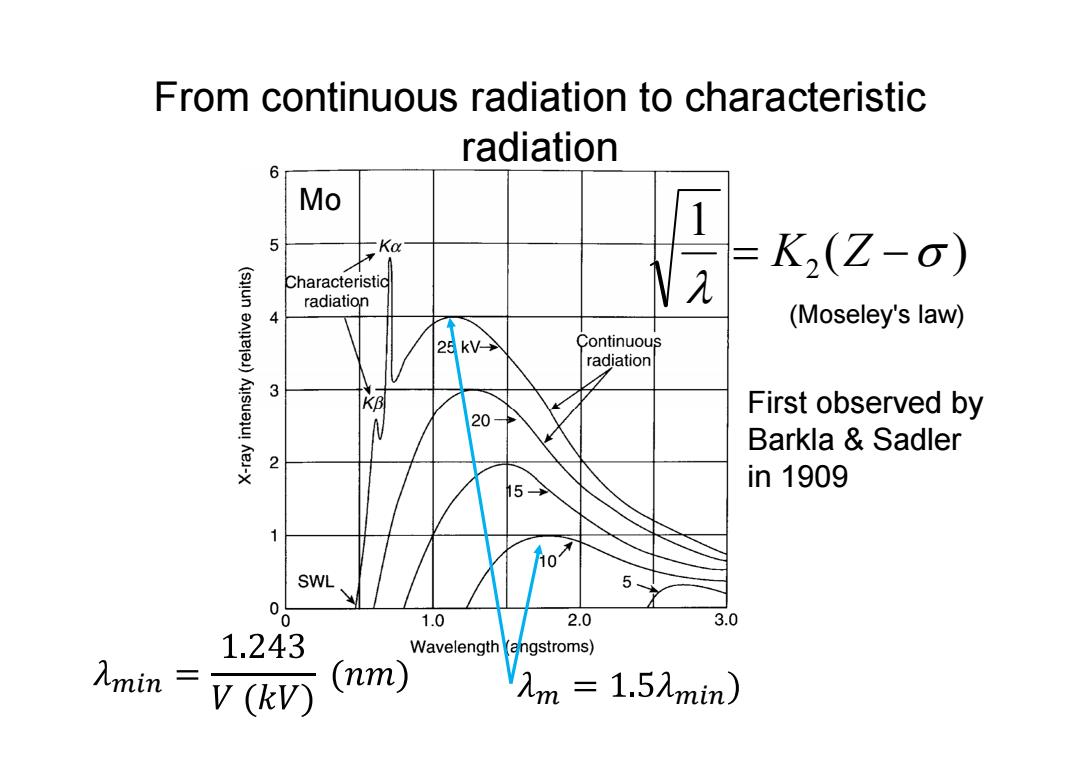
From continuous radiation to characteristic radiation Mo 1 5 -Ka K2(Z-0) Characteristid radiation (Moseley's law) 25kV→ Continuous radiation 3 KB First observed by N 20→ Barkla Sadler h5> in1909 1 SWL 5 0 1.0 2.0 3.0 1.243 Wavelength (angstroms) V(kV) (nm) Vm=1.5mim)
From continuous radiation to characteristic radiation Mo ( ) 1 2 K Z First observed by Barkla & Sadler in 1909 (Moseley's law)
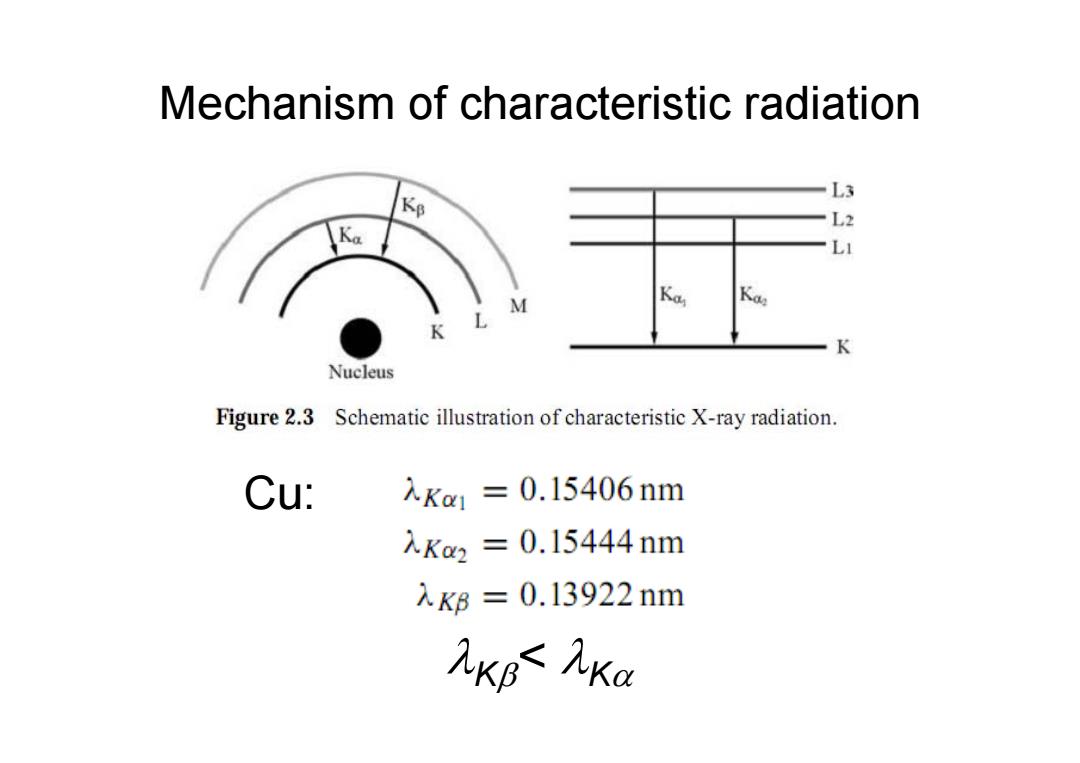
Mechanism of characteristic radiation Kp L3 L2 LI K L M K Nucleus Figure 2.3 Schematic illustration of characteristic X-ray radiation. Cu: 入Ka1=0.15406nm 入Ka2=0.15444nm 入KB=0.13922nm XKB AKa
Cu: K< K Mechanism of characteristic radiation
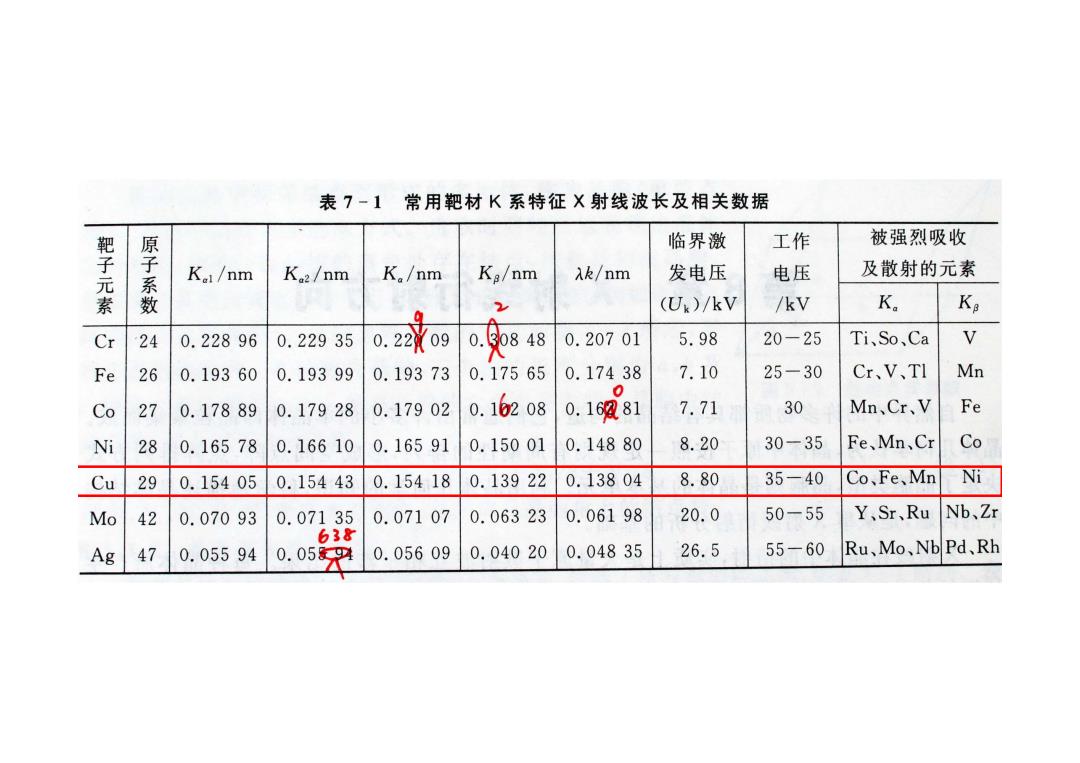
表7-1常用靶材K系特征X射线波长及相关数据 临界激 工作 被强烈吸收 靶子元素 原子系数 Kal/nm K2/nm K。/nm Ka/nm Ak/nm 发电压 电压 及散射的元素 2 (Ux)/kV /kV K。 Ke Cr 24 0.22896 0.22935 0.22o9 o.o 48 0.20701 5.98 20-25 Ti、So、Ca V Fe 26 0.19360 0.19399 0.19373 0.17565 0.17438 7.10 25-30 Cr、V、TI Mn C 0 27 0.17889 0.17928 0.17902 0.16208 0.16881 7.71 30 Mn、Cr、V Fe Ni 28 0.16578 0.16610 0.16591 0.15001 0.14880 8.20 30-35 Fe、Mn、Cr Co Cu 29 0.15405 0.15443 0.15418 0.13922 0.13804 8.80 35-40 Co、Fe、Mn Ni Mo 42 0.07093 0.07135 0.07107 0.06323 0.06198 20.0 50-55 Y、Sr、Ru Nb、Zr 638 Ag 47 0.05594 0.059 0.05609 0.04020 0.04835 26.5 55-60 Ru、Mo、NbPd、Rh
2 H alkalai alkaline lanthanide actinide transition metals earths metals He hefurn 1.00g 4.003 4 atomic num元素 6 碳7 氢8 氧9 10 Li Be symbol other semi- non- halogens noble B metals metals metals gases N 0 F Ne ithium berytiun elemeet name boron earbon nrogen oxygen fluorine 8841 012 10.811 1201 14.007 16000 19.000 20.180 11 12 14 15 16 硫17 18氢 Na Mg Solid Liquid Gas Synthetic Al Si s CI Ar sodum :agn63m alurninum sacon phosphorus sulfur chlorine argon 22G90 24305 26982 28.066 30.974 32065 35453 39948 19 20 21 航22 23 釩24 路25 26媛27 站28 桌29 年30 31 32 绪33 砷34 雷35 36 K Ca Sc Ti Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr potassium c漱m scandum btanum vanadum chtomum manganesa ron cobalt nickel copper zine galium gemmaniumn arsanc seleeium bromine krypton 39098 40.078 44956 47867 60942 51.996 490g 55.845 59933 58.695 63546 8539 69.723 7281 74.922 7896 7904 8明80 3> 38 39 纪40结41 想42 钼4344钉45 能46 纪47 481 49 50 锡51 52 53 54 Rb Sr Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te Xe rubidiurn sbo也um ytrum zrtcrum riobiumn techneum 法m thodium palladium silver cadnim indum antmomy odine xenon 65468 87.62 89906 9124 92906 95.54 101.07 10291 10642 10787 11241 11480 118.71 12178 127.60 12690 13129 55 绝56 71 增72给73 74篇75婆76饿77 法78鉑79 80 81 8283 经84 釙85 86 Cs Ba Lu Hf Ta W Re os r Pt Au Hg TI Pb Bi Po At Rn cesiur barium ketiumn hum tartalum tungsten thenium osmium ind um piatinum gold mercury thalium 地sd bismuth polenium aaline radon 13291 13739 17497 17849 160.95 18384 16821 19023 19222 19508 18697 200.50 20438 2072 20899 20 210 122沟 87 防88 103赞104被105金杜106金喜克107金波108金黑109金麦110论 111 112 13 114 115 116 117 118 Fr Ra Lr Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt Ds Rg Uub Uut Uug Uup Uuh Uus Uuo 水um radium therfordum dubnim seaborgium behrium 特m 作m 电, ununbium uu时 【221 22 26 2611 262 26间 264 26期 26 28月 272 285的 281 2991 29向 32 n⊙ 129可 57.70 57 58 鈽59 60 敛61 62 63 64 465 腻66 67 头68 每69 链70 lanthanides La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Im Yb 鑭系元素 cenum Y. 13891 140.12 140.91 14424 14可 15038 16196 15725 15893 162.50 18493 167,26 16893 173.04 89-102 89 钢90 处91 候9293 单94 95 阔96 97 98 99 100错101 102钱 actinides Ac Th Pa Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No 鋼系元素 227 232.04 231.04 23803 237 1244个 24习 24 247 2511 252 25万 25周
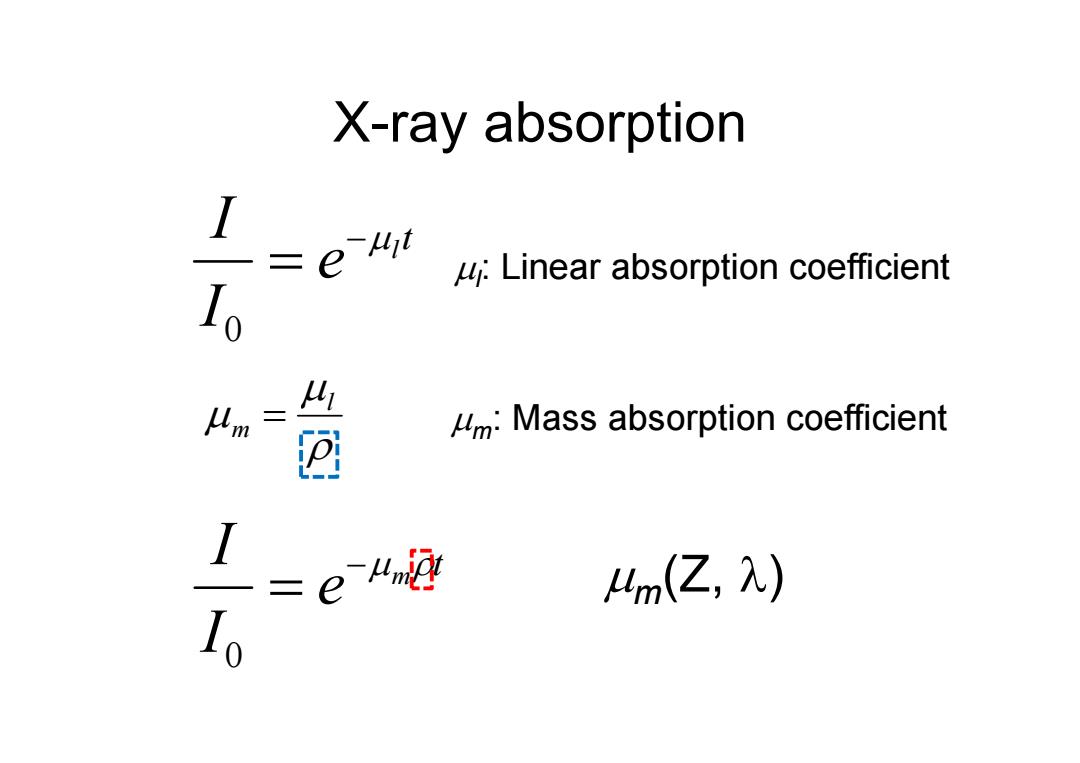
X-ray absorption I u:Linear absorption coefficient Io 凸 m:Mass absorption coefficient 4m(Z,入)
X-ray absorption t l e I I 0 m t e I I 0 l m l: Linear absorption coefficient m: Mass absorption coefficient m(Z, )