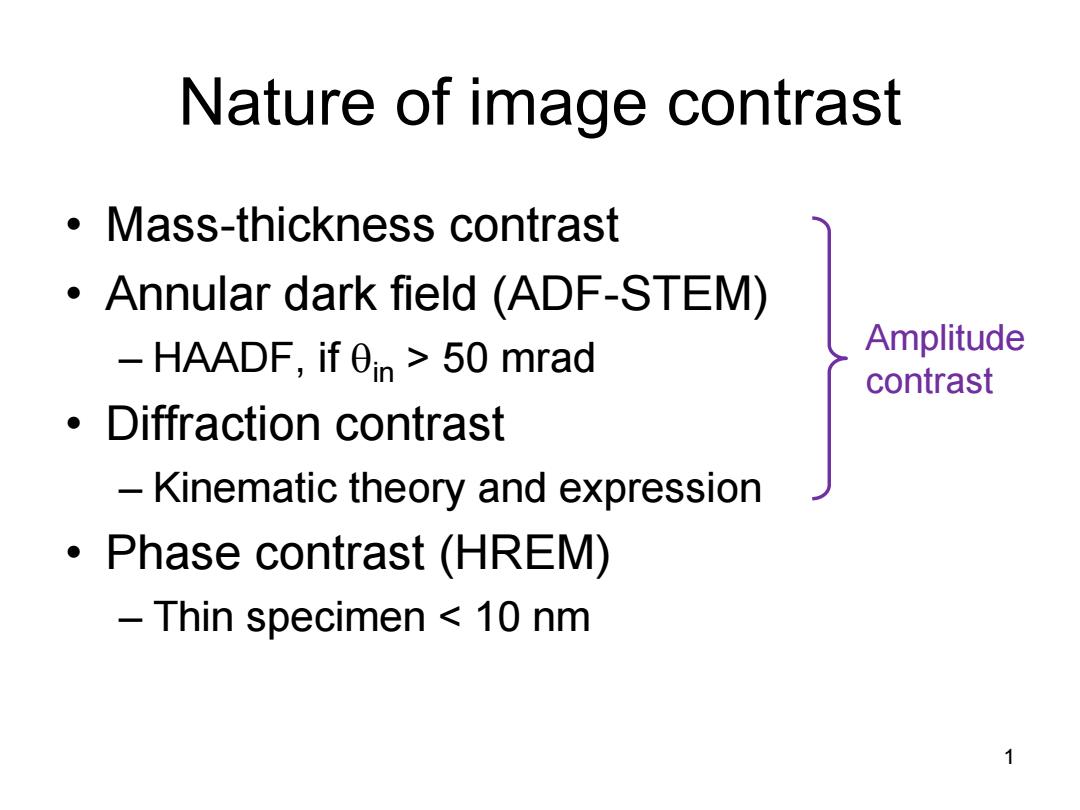
Nature of image contrast Mass-thickness contrast Annular dark field (ADF-STEM) HAADF,if 0in>50 mrad Amplitude contrast Diffraction contrast Kinematic theory and expression Phase contrast (HREM) Thin specimen 10 nm 1
Nature of image contrast • Mass-thickness contrast • Annular dark field (ADF-STEM) – HAADF, if in > 50 mrad • Diffraction contrast – Kinematic theory and expression • Phase contrast (HREM) – Thin specimen < 10 nm 1 Amplitude contrast
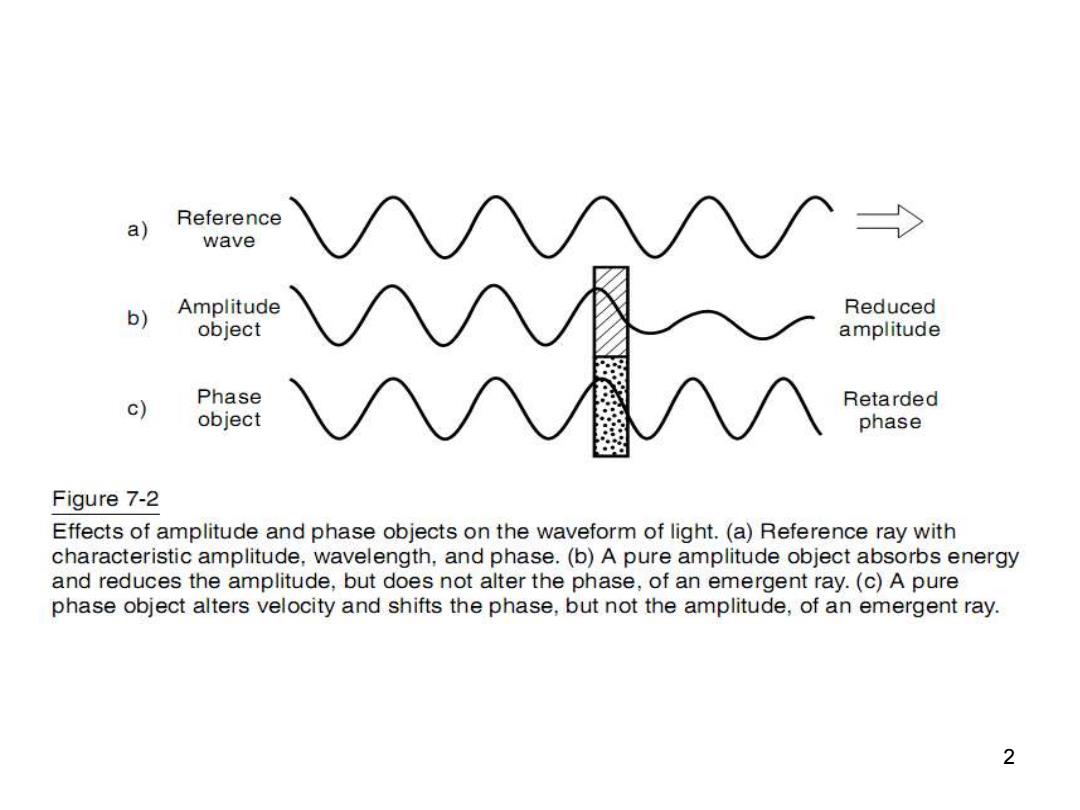
a) Reference wave b) Amplitude Reduced object amplitude c) Phase Retarded object phase Figure 7-2 Effects of amplitude and phase objects on the waveform of light.(a)Reference ray with characteristic amplitude,wavelength,and phase.(b)A pure amplitude object absorbs energy and reduces the amplitude,but does not alter the phase,of an emergent ray.(c)A pure phase object alters velocity and shifts the phase,but not the amplitude,of an emergent ray. 2
2

Imaging the atom columns in periodical structure Phase contrast and high resolution TEM Lanting Zhang School of Matertals Science and Engineering SJTU antingzh@sjtu.edu.cn 2 nm
2 nm Phase contrast and high resolution TEM Lanting Zhang School of Materials Science and Engineering, SJTU lantingzh@sjtu.edu.cn 3 Imaging the atom columns in periodical structure
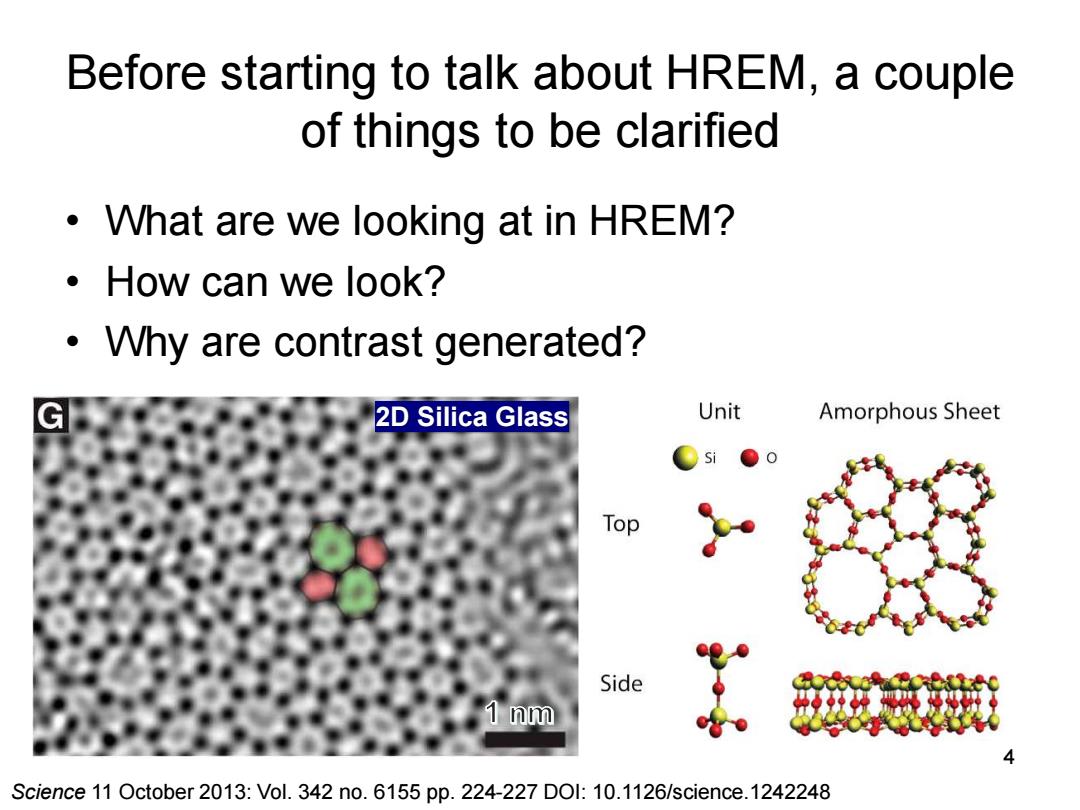
Before starting to talk about HREM,a couple of things to be clarified What are we looking at in HREM? ·How can we look? Why are contrast generated? 2D Silica Glass Unit Amorphous Sheet Top Side 1 nm Science 11 October 2013:Vol.342 no.6155 pp.224-227 DOI:10.1126/science.1242248
Before starting to talk about HREM, a couple of things to be clarified • What are we looking at in HREM? • How can we look? • Why are contrast generated? 4 Science 11 October 2013: Vol. 342 no. 6155 pp. 224-227 DOI: 10.1126/science.1242248 2D Silica Glass
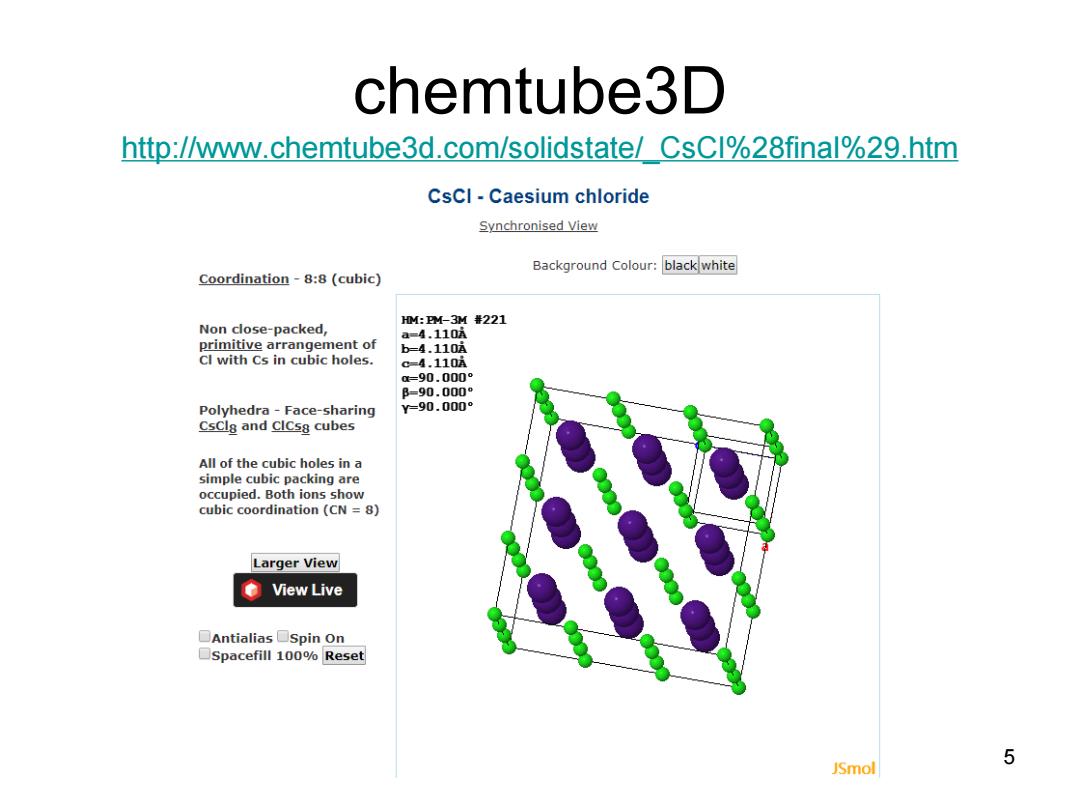
chemtube3D http://www.chemtube3d.com/solidstate/CsCl%28final%29.htm CsCl-Caesium chloride Synchronised View Background Colour:black white Coordination-8:8(cubic) HM:PM-3M #221 Non close-packed, a=4.110 primitive arrangement of b=4.110A Cl with Cs in cubic holes. c=4.110i 0=90.000 B-90.000° Polyhedra-Face-sharing =90.000° CsCls and CICs8 cubes All of the cubic holes in a simple cubic packing are occupied.Both ions show cubic coordination (CN =8) Larger View View Live ☐Antialias□Spin On □Spacefill100%Reset 5 JSmol
chemtube3D http://www.chemtube3d.com/solidstate/_CsCl%28final%29.htm 5
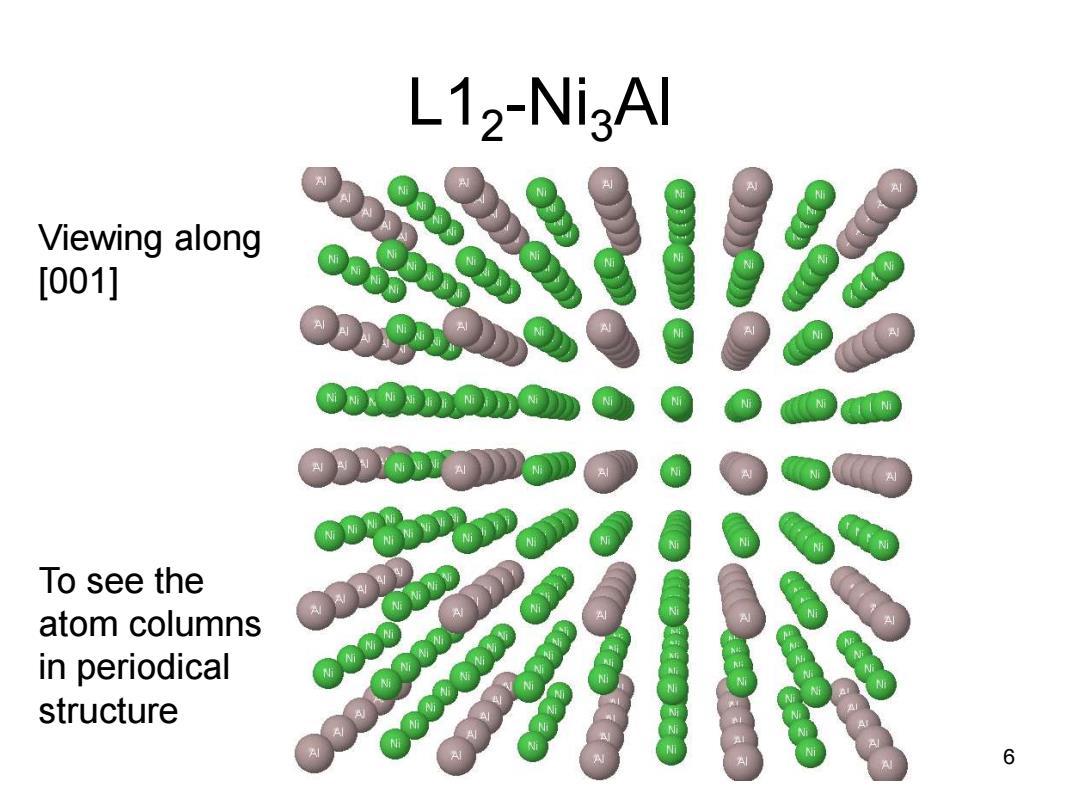
L12-NigAl Viewing along [001] To see the atom columns in periodical structure 6
L12 -Ni3Al 6 Viewing along [001] To see the atom columns in periodical structure
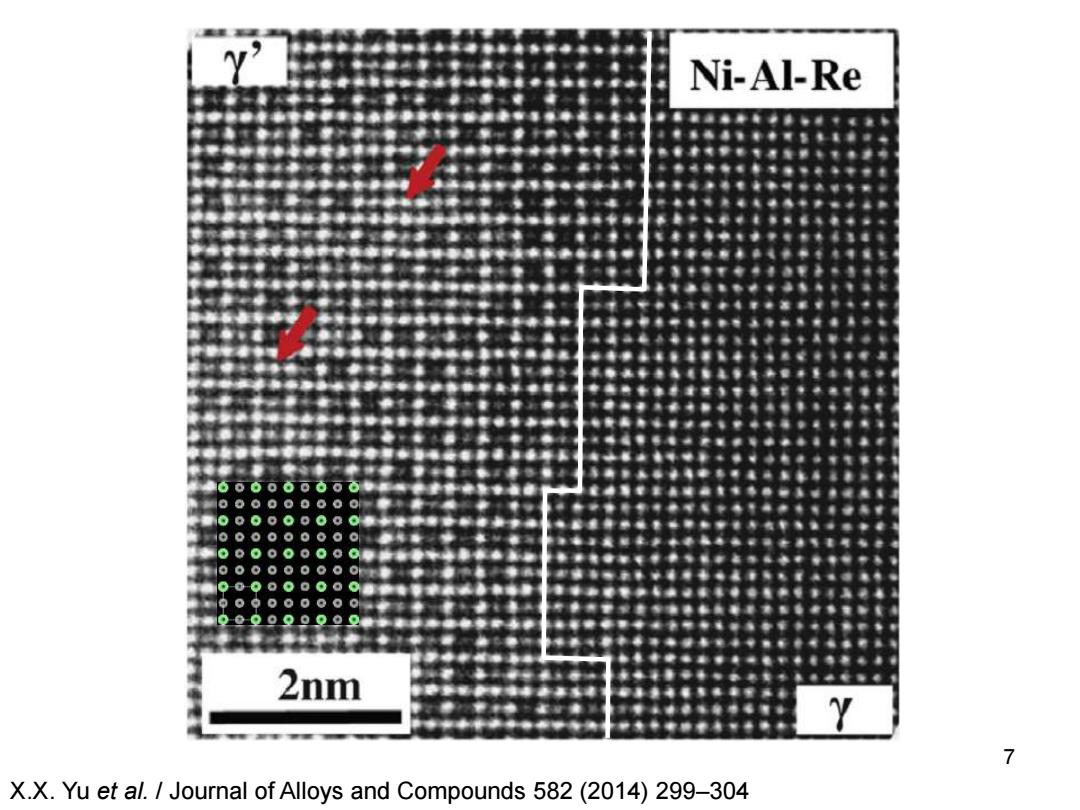
Ni-Al-Re 2nm Y 7 X.X.Yu et al.Journal of Alloys and Compounds 582(2014)299-304
7 X.X. Yu et al. / Journal of Alloys and Compounds 582 (2014) 299–304

Imaging atom columns/lattice planes Go to a zone axis orientation Low index zone axis is preferred ·eg.[110],[001]or[111]for fcc It is because of the resolution limit of the EMs. 8
Imaging atom columns/lattice planes • Go to a zone axis orientation • Low index zone axis is preferred • eg. [110], [001] or [111] for fcc • It is because of the resolution limit of the EMs. 8

Imaging using more than one beam ●透射波 ·衍射波 (a) (b) (c) Bright field Dark field HREM Amplitude contrast 9
Imaging using more than one beam 9 Bright field Dark field HREM Amplitude contrast

Conditions for HRTEM imaging 1.In pole Incident beam B 2.Use all the beams, both direct and diffracted Thin foil specimen <20nm Diffracted beam Direct beam G1 G G3 GA 61 10
Conditions for HRTEM imaging 10 Incident beam B Diffracted beam Direct beam 1. In pole 2. Use all the beams, both direct and diffracted