
Homework assignment(released on April 2nd)
Homework assignment(released on April 2nd)

1.Calculate the Multiplicity,LP factor (using the equation in the lecture note,=1.54 A),and Structure Factor(Fpki)for the first 5 peaks in Mg(HCP structure).There are two atoms per unit cell at (0,0,0)and at (1/3,2/3,1/2)respectively 1.Peaks of HCP Mg For HCP Mg.the lattice constants a=b=0.32nm,c=0.52nm.According to Braggs'Law: 2dhk1sin0hkl=入 first peaks occur when lattice spacing is large.For hexagonal structures, 1= 4(h2+hk+k2)2 di 3a2 +C2 and structure extinction happens when I is odd and h+2k=3n. The largest lattice spacings and corresponding indices are (hkil) dhkl/nm 0hk/° Multiplicity LP (1010) 0.28 16.1 6 23.1 传+) 0.26 17.2 2 20.1 2f (0002) (1011) 0.25 18.4 12 17.5 0.19 24.0 12 9.6 (1012) (1120) 0.16 28.8 6 6.3 The calculated parameters are appended to the table above.Note that LP factor is calculated by 1+c0s220 LP= cos0 sin20 And structure factor by =∑fep2ai0+ky+z
1. Calculate the Multiplicity, LP factor (using the equation in the lecture note, =1.54 A), and Structure Factor (Fhkl) for the first 5 peaks in Mg (HCP structure). There are two atoms per unit cell at (0, 0, 0) and at (1 /3 , 2 /3 , 1 /2 ) respectively

2.A face centered cubic structured single crystal with a lattice constant of ao is studied by a monochromatic X-ray radiation whose wavelength is A=a/2: 1)Illustrate by drawing the reciprocal lattice of this crystal and indicate its lattice constant. 1/ao 2/a0 2
2.A face centered cubic structured single crystal with a lattice constant of a0 is studied by a monochromatic X-ray radiation whose wavelength is λ= a0 /2: 1)Illustrate by drawing the reciprocal lattice of this crystal and indicate its lattice constant. 1/a0 2/a0 ?

Reciprocal lattice ●Defined by its primitive vectors(原胞基矢)(a1,a2,a3); Generating three reciprocal primitive vectors(a*,b*,c*) a*=a2Xa3la1●(a2Xag) b*=a3xa/a2(a3xa) c*=a xa2/a3(a xa2) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reciprocal lattice
Reciprocal lattice ⚫ Defined by its primitive vectors(原胞基矢)(a1 ,a2 ,a3 ); ⚫ Generating three reciprocal primitive vectors(a*,b*,c*) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reciprocal_lattice a*=a2xa3 /a1 •(a2xa3 ) b*=a3xa1 /a2 •(a3xa1 ) c*=a1xa2 /a3 •(a1xa2 )
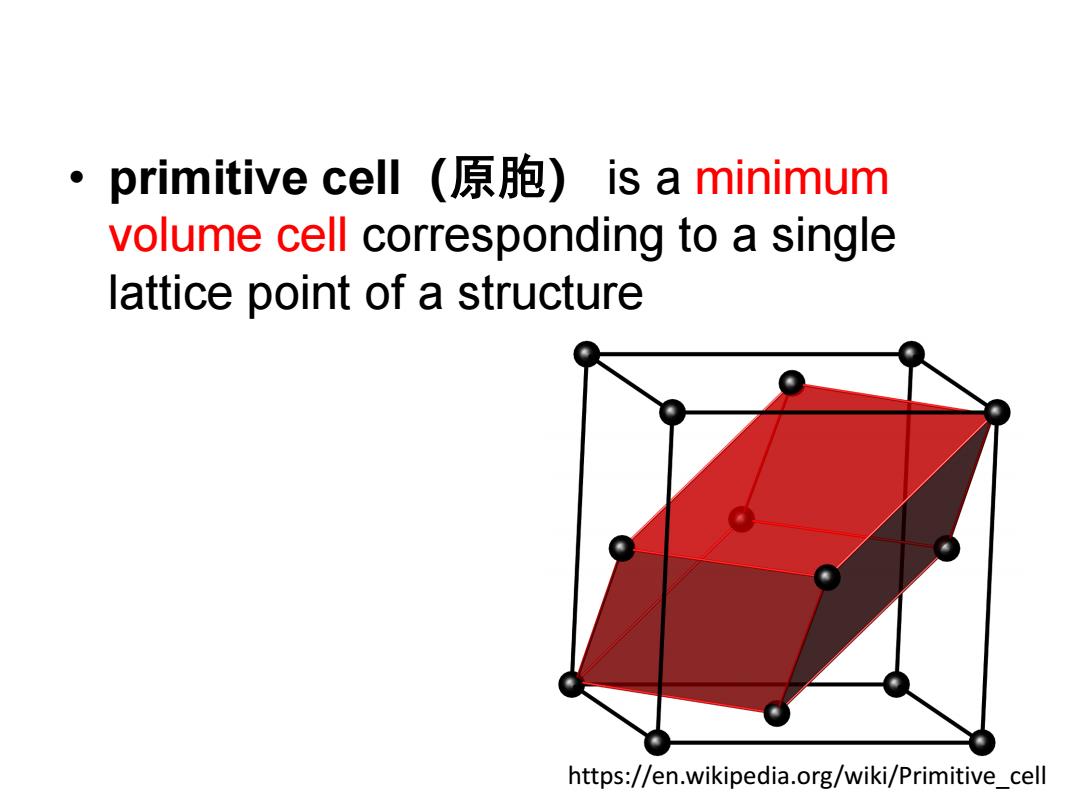
primitive cell(原胞)is a minimum volume cell corresponding to a single lattice point of a structure https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Primitive cell
• primitive cell(原胞) is a minimum volume cell corresponding to a single lattice point of a structure https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Primitive_cell
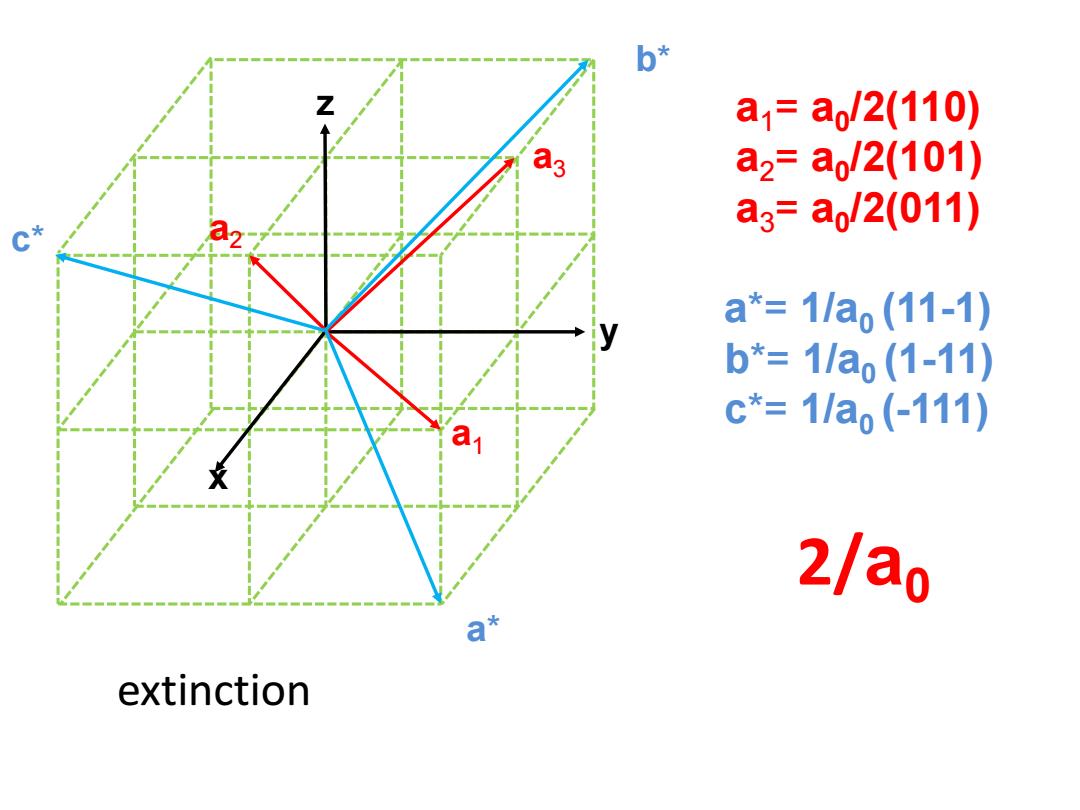
b* a1=a,/2(110) a2=a,/2(101) a3=a/2(011) a*=1/a(11-1) b*=1/a,(1-11) c*=1/a,(-111) 2/ao 日米 extinction
a 1 y z x a 3 a 2 a * c * b * a 1 = a 0 /2(110) a 2 = a 0 /2(101) a 3 = a 0 /2(011) a*= 1/a0 (11 -1) b*= 1/a0 (1 -11) c*= 1/a0 ( -111) 2/ a 0 extinction

2.A face centered cubic structured single crystal with a lattice constant of ap is studied by a monochromatic X-ray radiation whose wavelength is A=a/2: 2)If the incident beam direction is along the [010]direction of the crystal,please deduce the possible directions of diffracted beams. 衍射斑点:(2-20),(-2-20), (2-20) (0-2-2),(0-22),(0-40) 衍射方向:[200],[-200], [002][00-2],[0-20] (0-2-2) Incident> (0-40) (000) beam (0-20) [010] (0-22) -2-20)
2.A face centered cubic structured single crystal with a lattice constant of a0 is studied by a monochromatic X-ray radiation whose wavelength is λ= a0 /2: 2)If the incident beam direction is along the [010] direction of the crystal, please deduce the possible directions of diffracted beams. (0-20) O Incident beam (0-2-2) (2-20) (0-22) (-2-20) (000) [010] (0-40) 衍射斑点:(2-20),(-2-20), (0-2-2),(0-22),(0-40) 衍射方向:[200],[-200], [002],[00-2],[0-20] k0 k1
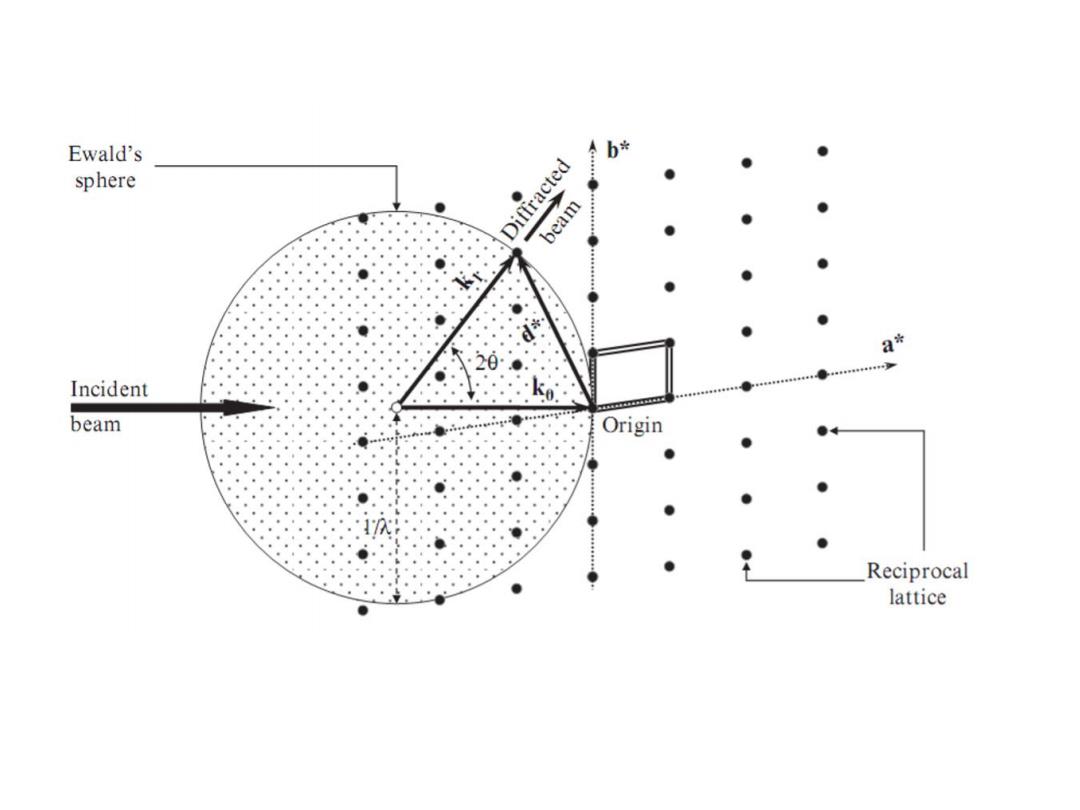
Ewald's 令b÷ sphere Diffracted ● beam Incident beam Origin Reciprocal lattice
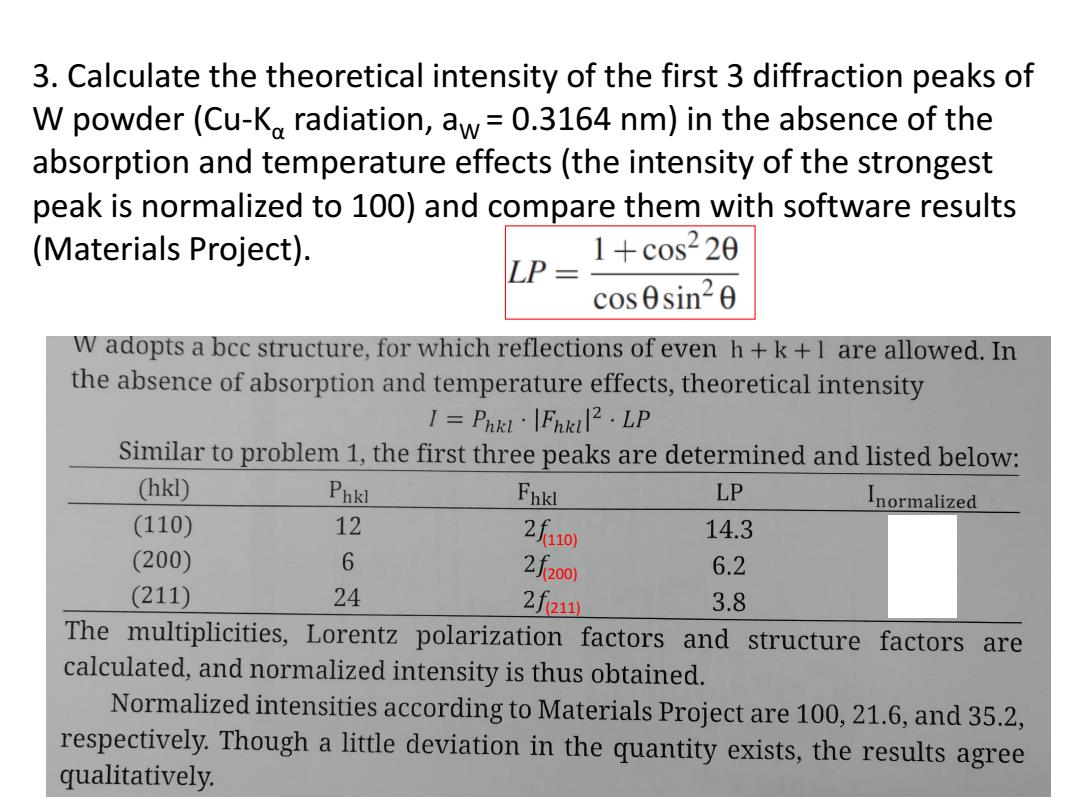
3.Calculate the theoretical intensity of the first 3 diffraction peaks of W powder(Cu-Ko radiation,aw=0.3164 nm)in the absence of the absorption and temperature effects(the intensity of the strongest peak is normalized to 100)and compare them with software results (Materials Project). LP= 1+cos220 cos0sin20 W adopts a bcc structure,for which reflections of even h+k+I are allowed.In the absence of absorption and temperature effects,theoretical intensity I=Pha·[Fnkil2·LP Similar to problem 1,the first three peaks are determined and listed below: (hkl) Pnkl Fbkl LP normalized (110) 12 2f10 14.3 (200) 6 2f2o0 6.2 (211) 24 2feu 3.8 The multiplicities,Lorentz polarization factors and structure factors are calculated,and normalized intensity is thus obtained. Normalized intensities according to Materials Project are 100,21.6,and 35.2, respectively.Though a little deviation in the quantity exists,the results agree qualitatively
3. Calculate the theoretical intensity of the first 3 diffraction peaks of W powder (Cu-Kα radiation, aW = 0.3164 nm) in the absence of the absorption and temperature effects (the intensity of the strongest peak is normalized to 100) and compare them with software results (Materials Project). (110) (200) (211)
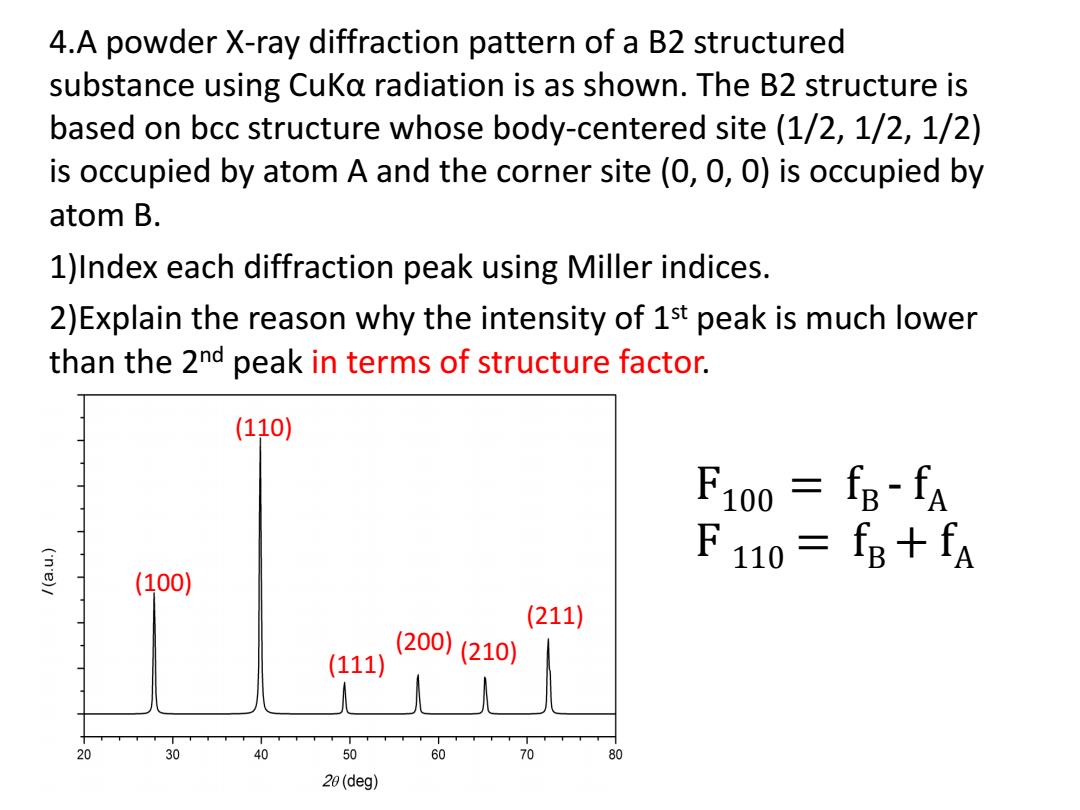
4.A powder X-ray diffraction pattern of a B2 structured substance using CuKa radiation is as shown.The B2 structure is based on bcc structure whose body-centered site(1/2,1/2,1/2) is occupied by atom A and the corner site(0,0,0)is occupied by atom B. 1)Index each diffraction peak using Miller indices. 2)Explain the reason why the intensity of 1st peak is much lower than the 2nd peak in terms of structure factor. (110) F100 fB-fA F110=fB+fA (100) (211) (111) (200)(210) 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 20(deg)
4.A powder X-ray diffraction pattern of a B2 structured substance using CuKα radiation is as shown. The B2 structure is based on bcc structure whose body-centered site (1/2, 1/2, 1/2) is occupied by atom A and the corner site (0, 0, 0) is occupied by atom B. 1)Index each diffraction peak using Miller indices. 2)Explain the reason why the intensity of 1st peak is much lower than the 2nd peak in terms of structure factor. (100) (110) (111) (210) (211) (200) F100 = fB - fA F 110 = fB+ fA