
Diffraction in TEM and its analysis Lanting Zhang School of Materials Science and Engineering,SJTU lantingzh@sjtu.edu.cn
1

Basic principles Electrons (SEM) BSE X-rays(EDS) Diffraction (elastic interaction) -X-rays -Electrons ·ED in TEM and EBSD in SEM Neutrons SE E=Eo E<Eo (EELS) The same basic theory for all waves. (TEM and ED) 2
Basic principles 2 The same basic theory for all waves. • Diffraction (elastic interaction) – X-rays – Electrons • ED in TEM and EBSD in SEM – Neutrons
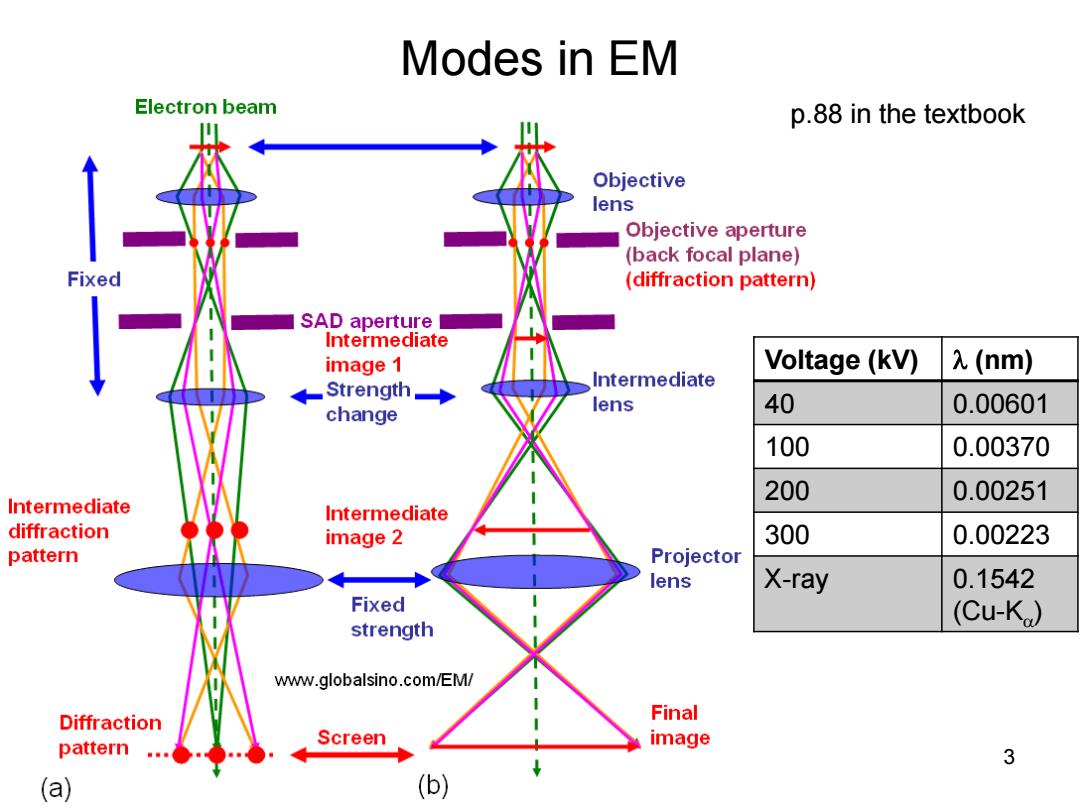
Modes in EM Electron beam p.88 in the textbook Objective lens Objective aperture (back focal plane) Fixed (diffraction pattern) SAD aperture Intermediate image 1 Voltage (kV) 2(nm) Strength Intermediate change lens 40 0.00601 100 0.00370 200 0.00251 Intermediate Intermediate diffraction image 2 300 0.00223 pattern Projector lens X-ray 0.1542 Fixed (Cu-K) strength www.globalsino.com/EM/ Diffraction Final pattern Screen image 3 (a) (b)
Modes in EM 3 Voltage (kV) (nm) 40 0.00601 100 0.00370 200 0.00251 300 0.00223 X-ray 0.1542 (Cu-K ) p.88 in the textbook
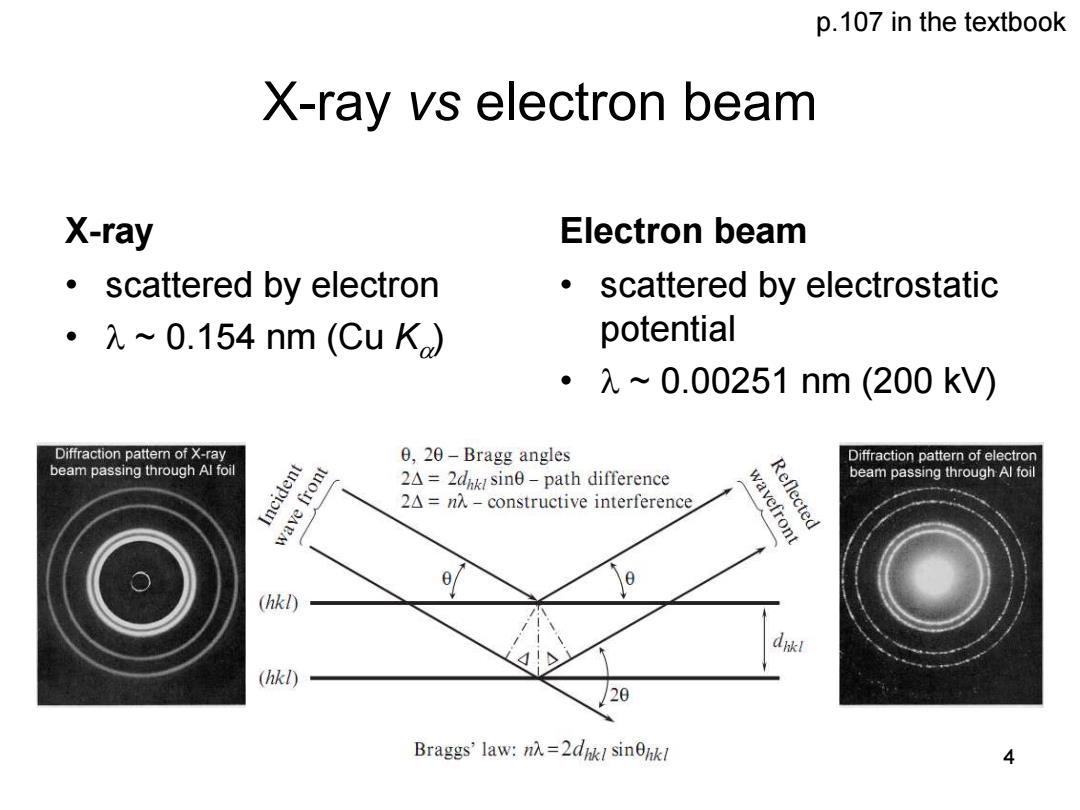
p.107 in the textbook X-ray vs electron beam X-ray Electron beam scattered by electron scattered by electrostatic 。元~0.154nm(CuKa potential ·λ~0.00251nm(200kV) Diffraction pattern of X-ray 0,20-Bragg angles Diffraction pattern of electron beam passing through Al foil Incident 2A=2dik sine-path difference Reflected beam passing through Al foil wave front 2A=nA-constructive interference wavefront (hkl) (hkl) Braggs'law:n=2d sink 4
X-ray vs electron beam X-ray • scattered by electron • ~ 0.154 nm (Cu K ) Electron beam • scattered by electrostatic potential • ~ 0.00251 nm (200 kV) 4 p.107 in the textbook
Why diffraction is useful? Electrons interacts 100-1000 times stronger with matter than X-rays more absorption (need thin samples) can detect weak reflections not observed with x-rays,eg. superlattice reflection ·Useful for Identify crystalline phase -Orient crystals Lattice constant,crystal structure,orientation relationship etc. Understanding image contrast,in both diffraction contrast and HREM 5
Why diffraction is useful? • Electrons interacts 100-1000 times stronger with matter than X-rays – more absorption (need thin samples) – can detect weak reflections not observed with x-rays, eg. superlattice reflection • Useful for – Identify crystalline phase – Orient crystals – Lattice constant, crystal structure, orientation relationship etc. • Understanding image contrast, in both diffraction contrast and HREM 5
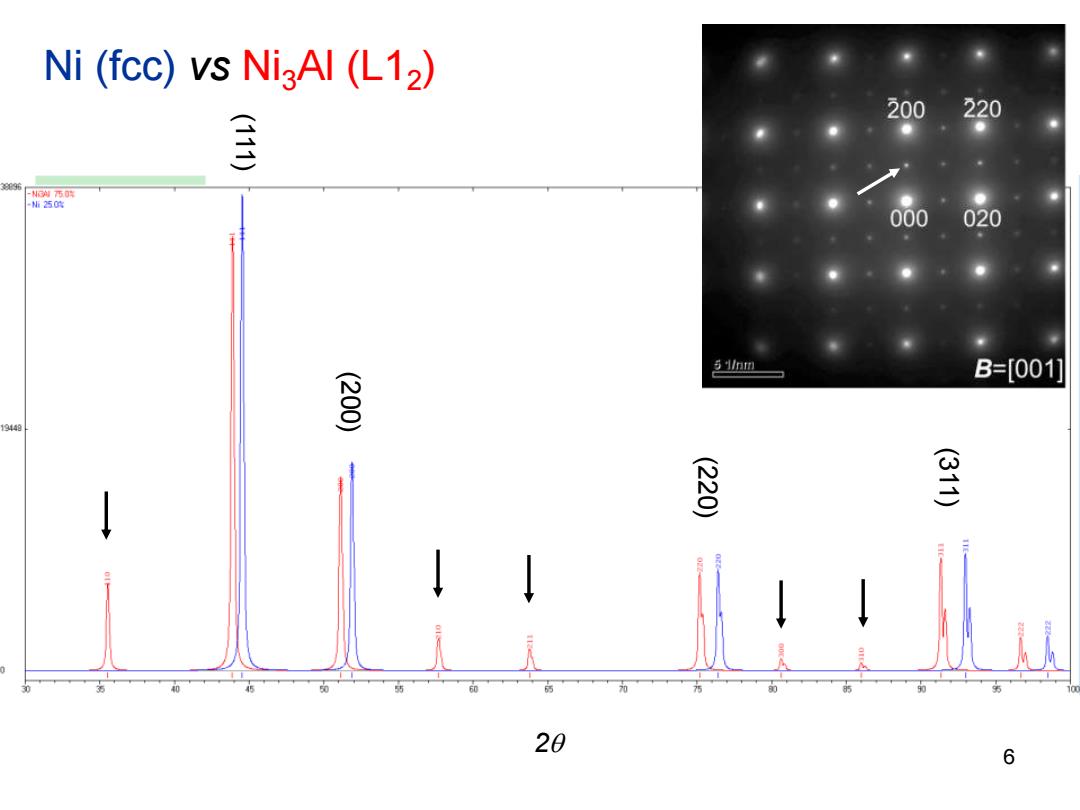
Ni(fcc)vs NigAl (L12) 200 220 E 利刹西裤 -插250黄 000 020 51/nm B=[001] 200 19440 220 311 60 70 20 6
6 2 (111) (200) (220) (311) Ni (fcc) vs Ni3Al (L12 )
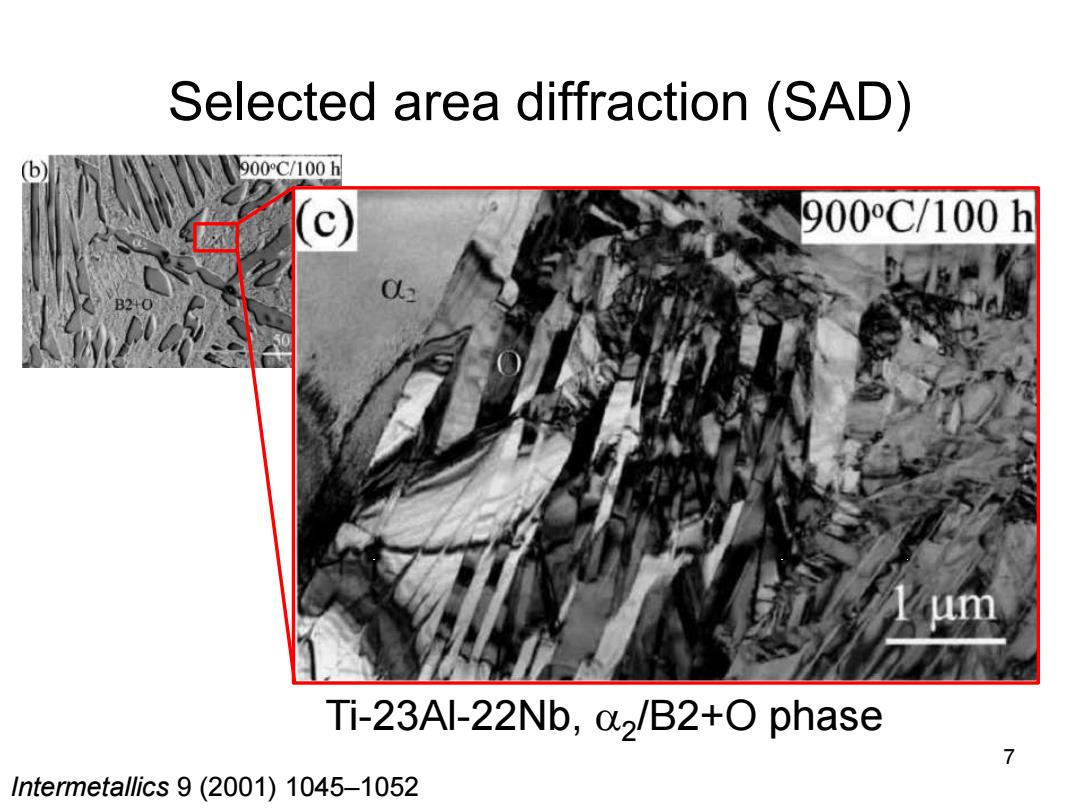

Selected area diffraction (SAD) D 900C/100h 900C/100h B2+O um Ti-23Al-22Nb,a2/B2+O phase 7 Intermetallics 9(2001)1045-1052
Selected area diffraction (SAD) 7 Ti-23Al-22Nb, 2 /B2+O phase Intermetallics 9 (2001) 1045–1052
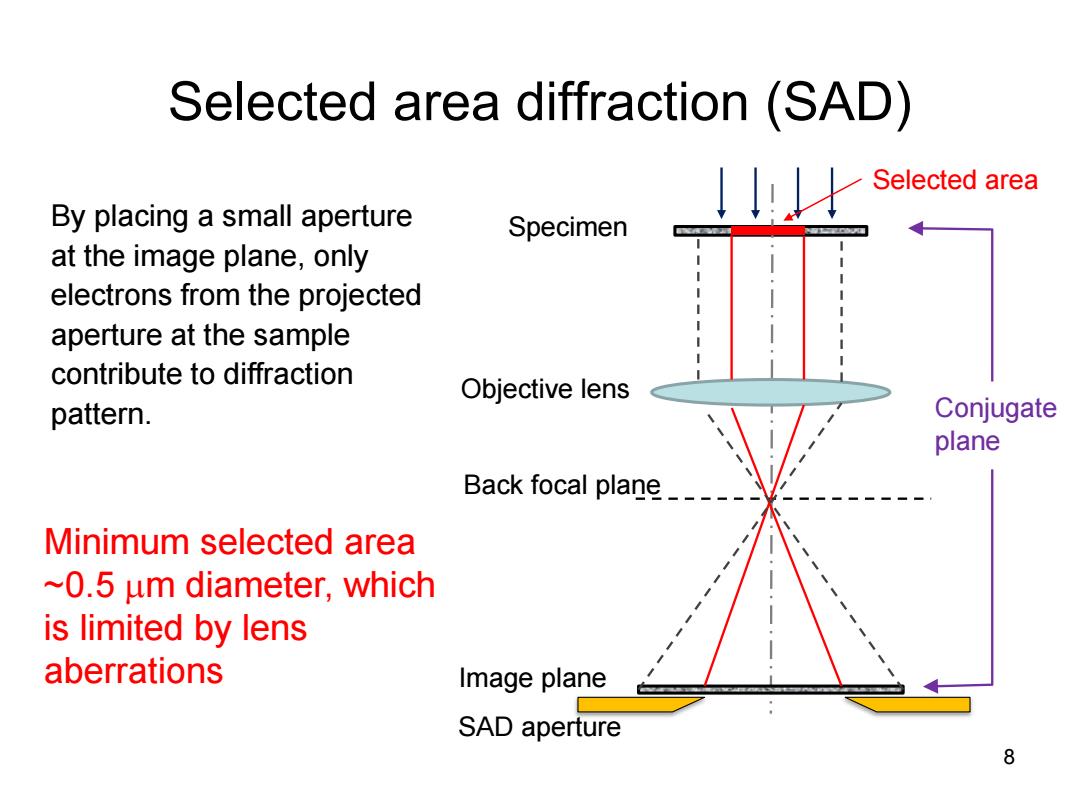
Selected area diffraction (SAD) Selected area By placing a small aperture Specimen at the image plane,only electrons from the projected aperture at the sample contribute to diffraction Objective lens pattern. Conjugate plane Back focal plane__ Minimum selected area ~0.5 um diameter,which is limited by lens aberrations Image plane SAD aperture 8
Selected area diffraction (SAD) 8 By placing a small aperture at the image plane, only electrons from the projected aperture at the sample contribute to diffraction pattern. Minimum selected area ~0.5 m diameter, which is limited by lens aberrations Conjugate plane Image plane Objective lens Back focal plane Specimen SAD aperture Selected area

Selected area diffraction (SAD) (c) 900C/100h Ti-23Al-22Nb,a2/B2+O phase 9 Intermetallics 9(2001)1045-1052
Selected area diffraction (SAD) 9 Ti-23Al-22Nb, 2 /B2+O phase Intermetallics 9 (2001) 1045–1052
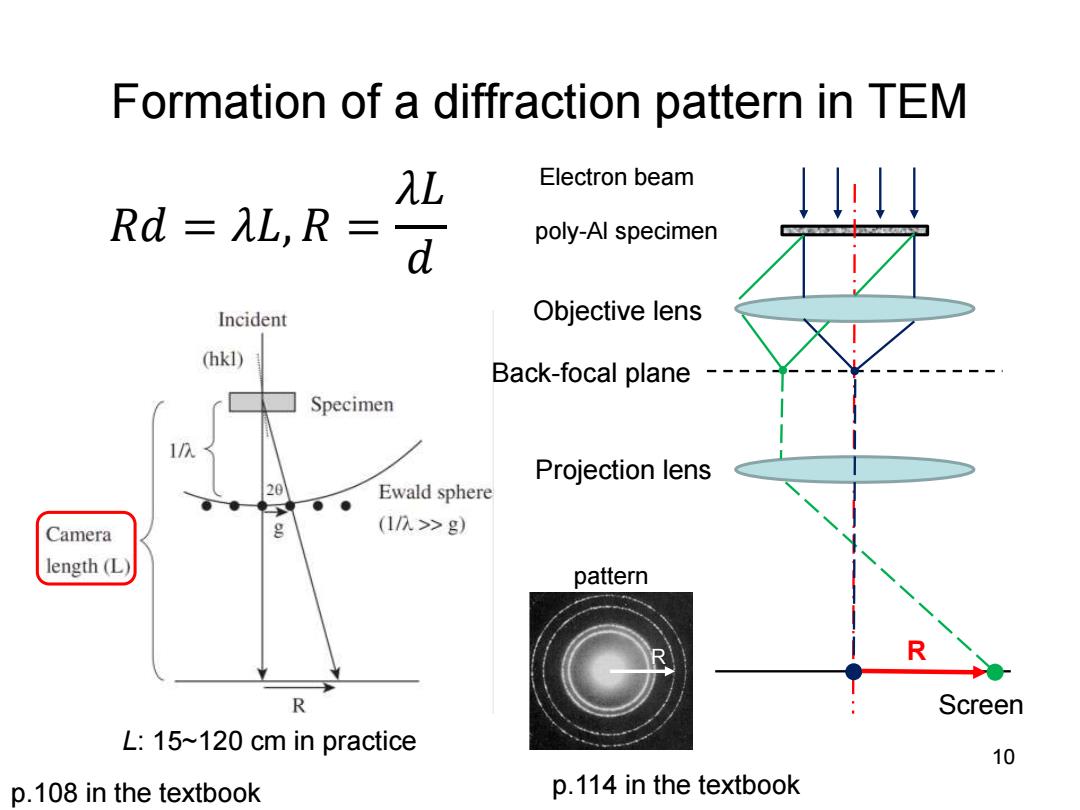
Formation of a diffraction pattern in TEM λL Electron beam Rd=λL,R= d poly-Al specimen Incident Objective lens (hkl) Back-focal plane Specimen Projection lens 20 Ewald sphere Camera g (1八>g) length (L) pattern R R Screen L:15~120 cm in practice 10 p.108 in the textbook p.114 in the textbook
Formation of a diffraction pattern in TEM poly-Al specimen R 𝑅𝑑 = 𝜆𝐿, 𝑅 = 𝜆𝐿 𝑑 L: 15~120 cm in practice 10 pattern Objective lens Projection lens Screen Back-focal plane Electron beam p.108 in the textbook R p.114 in the textbook