
Suggested outlines of the final presentation(in English) ·Background Model and Methodology Results and discussions benchmark adsorption structures physical/chemical properties electronic analyses(DOS,band,or charge density) ·Conclusions 。References ·Contributions达
Suggested outlines of the final presentation (in English) Background Model and Methodology Results and discussions benchmark adsorption structures physical/chemical properties electronic analyses (DOS, band, or charge density) Conclusions References Contributions

Computational Platforms ·FLAPW ·VASP QUANTUMESPRESSO ienna Materials Studio Gaussian accelrys' siesta CRYSTAL Quantum Espresso Dmol3 abinit.org CP2K RESCU ·SIESTA ·Abinit RESCU(Real space Electronic Structure CalcUlator)
Computational Platforms FLAPW VASP Materials Studio Gaussian CRYSTAL Quantum Espresso CP2K SIESTA Abinit RESCU (Real space Electronic Structure CalcUlator)
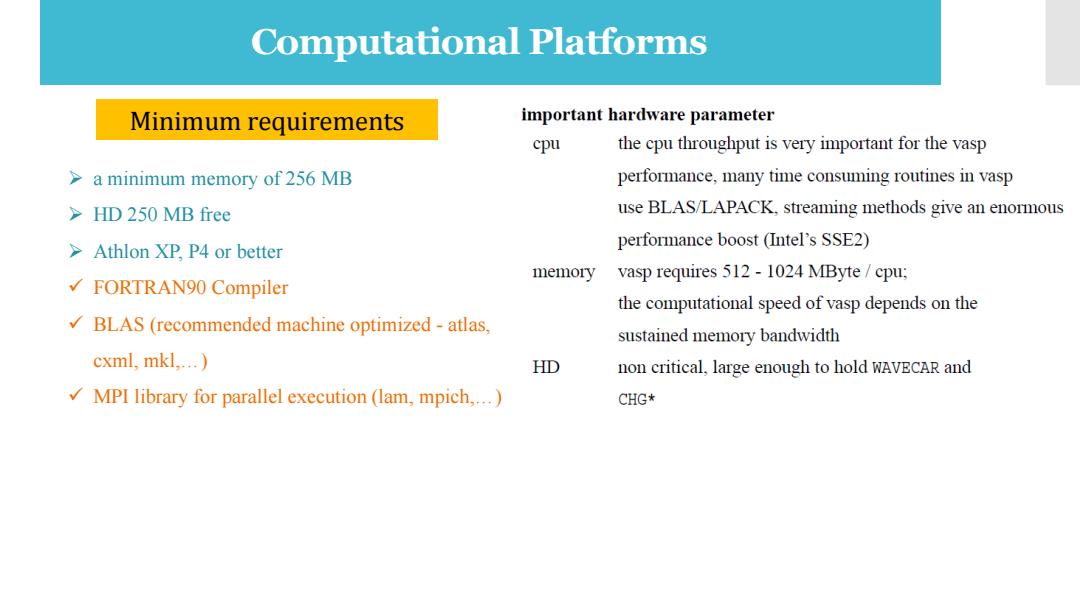
Computational Platforms Minimum requirements important hardware parameter cpu the cpu throughput is very important for the vasp >a minimum memory of 256 MB performance,many time consuming routines in vasp >HD 250 MB free use BLAS/LAPACK,streaming methods give an enormous >Athlon XP,P4 or better performance boost(Intel's SSE2) memory vasp requires 512-1024 MByte/cpu; √FORTRAN90 Compiler the computational speed of vasp depends on the BLAS (recommended machine optimized-atlas, sustained memory bandwidth cxml,mkl,...) HD non critical,large enough to hold WAVECAR and MPI library for parallel execution(lam,mpich,...) CHG*
Computational Platforms Minimum requirements ➢ a minimum memory of 256 MB ➢ HD 250 MB free ➢ Athlon XP, P4 or better ✓ FORTRAN90 Compiler ✓ BLAS (recommended machine optimized - atlas, cxml, mkl,…) ✓ MPI library for parallel execution (lam, mpich,…)

Computational Platforms First make the vasp library Benchmark calculations Then make vasp always use the same vasp version,otherwise the timings are not comparable makefiles in vasp use the best compiler options and the fastest makefile.cray makefile.hp available blas for the test platform makefile.rs6000 makefile.sun makefile.linux abs makefile.linux ifc_ath cray CRAY C9O.J90.T90 600 makefile.t3d makefile.fujitsu dec DEC ALPHA True 64 Unix HP PA AMD XP1800+100MBit 500 makefile.linux_pg makefile.sgi Xeon 2.2 GHz i7500 1000MBi limix_abs Limx,Absoft compiter P4 P4GSX 1000MBit makefile.gen makefile.linux ifc limrx alpha Limx,Alpha processors fort compiler AMD XP1700+1000MBir 400 HPes451 Ghz quad山ics linrx ifc.P4 Linurx.Intel fortran compiler(ifc),P4 optimisation makefile.sp2 makefile.vpp limrx ifc.ath Limux.Intel fortran compiler(ifc).Athlon optimisation makefile.linux ifc p4 limx_pg Limx.Portland group compiler 首0 makefile.dec nec NEC vector computer Is6000 IBM AIX xl0 compiler 200 makefile.rs6000 pl sgi SGI Origin 200/2000/3000.Power Challenge.2ete. makefile.linux alpha sp2 IBM SP2,possibly also useful for RS6000 100 sun makefile.t3e SUN,Ultrasparc 13d Cray/SGI T3D 10 15 20 25 makefile.nec Be Cray/SGI T3E of CPU p fujitsu VPP,VPX
Computational Platforms makefiles in vasp First make the vasp library Then make vasp Benchmark calculations ✓ always use the same vasp version, otherwise the timings are not comparable ✓ use the best compiler options and the fastest available blas for the test platform
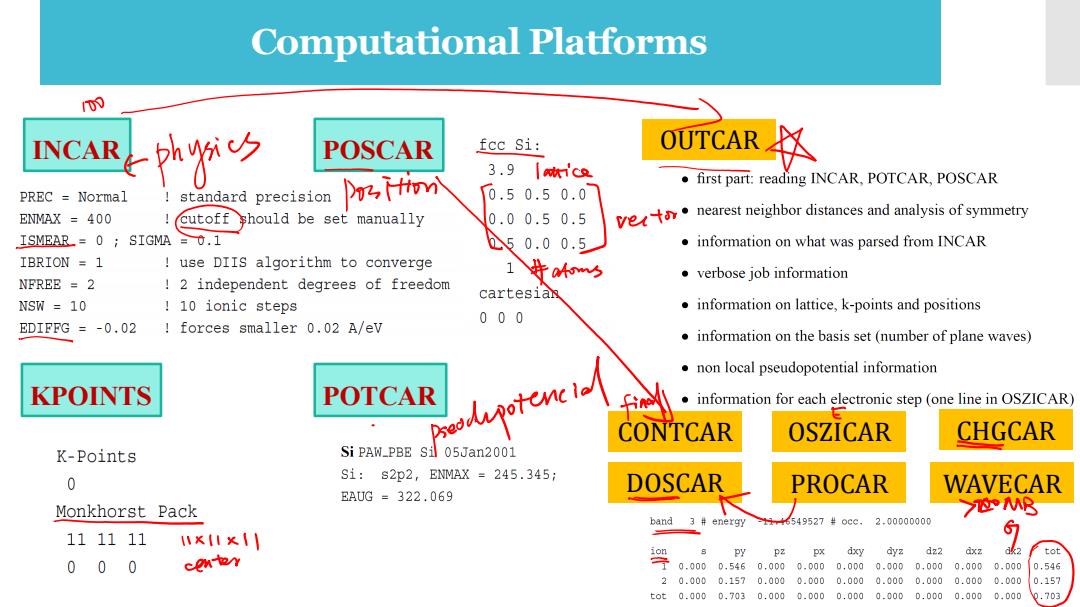
Computational Platforms 的 INCAR h%少 POSCAR fcc Si: OUTCAR 3.9|tc first part:reading INCAR,POTCAR,POSCAR PREC Normal standard precision Dri,(Hiom 0.50.50.0 ENMAX 400 1 cutoff should be set manually 0.00.50.5 enearest neighbor distances and analysis of symmetry ISMEAR=0;SIGMA 0.1 ①50.00.5 information on what was parsed from INCAR IBRION =1 use DIIS algorithm to converge atoms verbose job information NFREE =2 2 independent degrees of freedom cartesian NSW 10 !10 ionic steps information on lattice,k-points and positions 000 EDIFFG =-0.02 forces smaller 0.02 A/ev information on the basis set(number of plane waves) non local pseudopotential information KPOINTS POTCAR information for each electronic step (one line in OSZICAR) CONTCAR OSZICAR CHGCAR K-Points Si PAW_PBE Si 05Jan2001 Si:s2p2, ENMAX=245.345: 0 DOSCAR PROCAR WAVECAR EAUG=322.069 Monkhorst Pack 8 band 3 energy 549527#0Ce,2.00000000 111111 ×I×I PY pz dxy dyz dz2 dxz 2 tot 000 con tr .60.0000.0000.0000.000.00 0.546 20.0000.1570.0000.0000.0000.0000.0000.0000.000 0.157 tot0.0000.7030.0000.0000.0000.0000.0000.0000.000 Q.703
Computational Platforms INCAR OUTCAR KPOINTS POSCAR POTCAR DOSCAR CHGCAR PROCAR CONTCAR OSZICAR WAVECAR
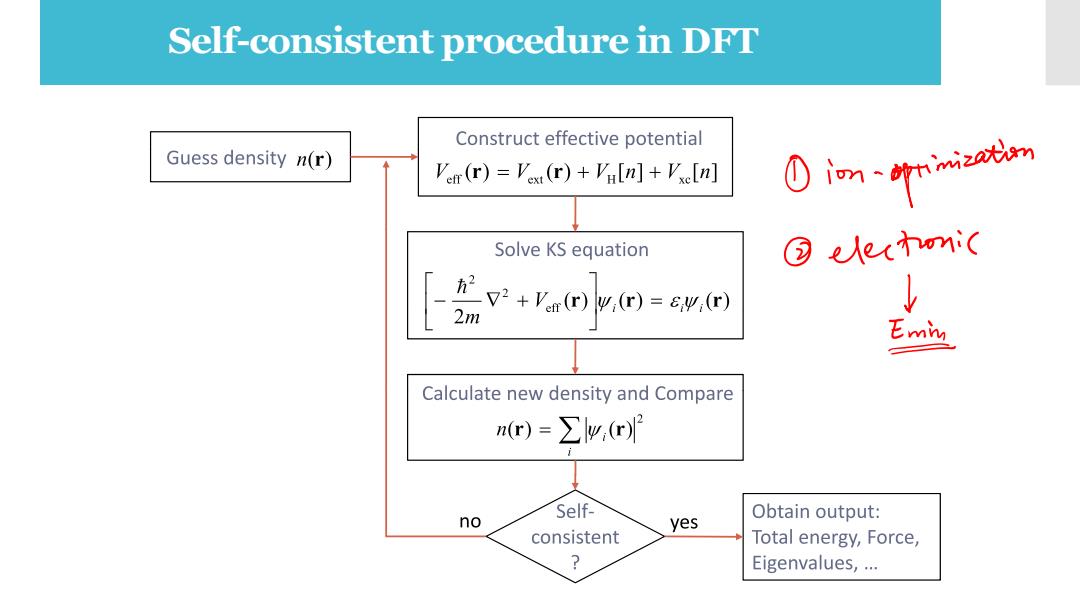
Self-consistent procedure in DFT Construct effective potential Guess density n(r) Ver (r)=Vest (r)+Vu[n]+Vse[n] 0imtniatn Solve KS equation @(hm( v.rtb.m-. Calculate new density and Compare r)=∑w,r) no Self- yes Obtain output: consistent Total energy,Force, ? Eigenvalues,…
Self-consistent procedure in DFT
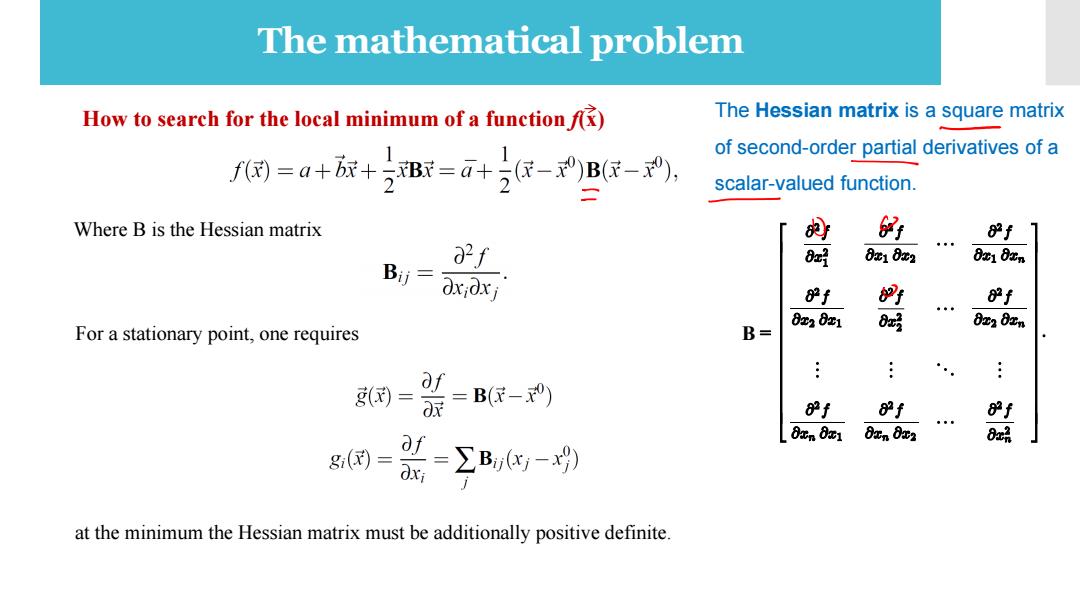
The mathematical problem How to search for the local minimum of a function f) The Hessian matrix is a square matrix of second-order partial derivatives of a f阀=a+脉+2B数=a+民-B民-。 scalar-valued function. Where B is the Hessian matrix 5 80f1 of 8r好 8r18r2 821 82n Bj Oxioxj 80f 8 80f 0r202x1 For a stationary point,one requires B= 8r好 8r20n g(= af 0派 =B(-) of of f 8xn 8x1 8zn Ox2 Bui g()= at the minimum the Hessian matrix must be additionally positive definite
The mathematical problem How to search for the local minimum of a function f(x) at the minimum the Hessian matrix must be additionally positive definite. B The Hessian matrix is a square matrix of second-order partial derivatives of a scalar-valued function. Where B is the Hessian matrix For a stationary point, one requires

Ionic relaxation Steepest descent 1.initial guess 最速下降法 初始点 J6,0)。 2.calculate the gradient g( 3.make a step into the direction of the steepest descent 2=-1/Tmax(B)g() 最小值 4.repeat step 2 and 3 until convergence is reached for functions with long steep valleys convergence can be very slow max min
Ionic relaxation 最速下降法
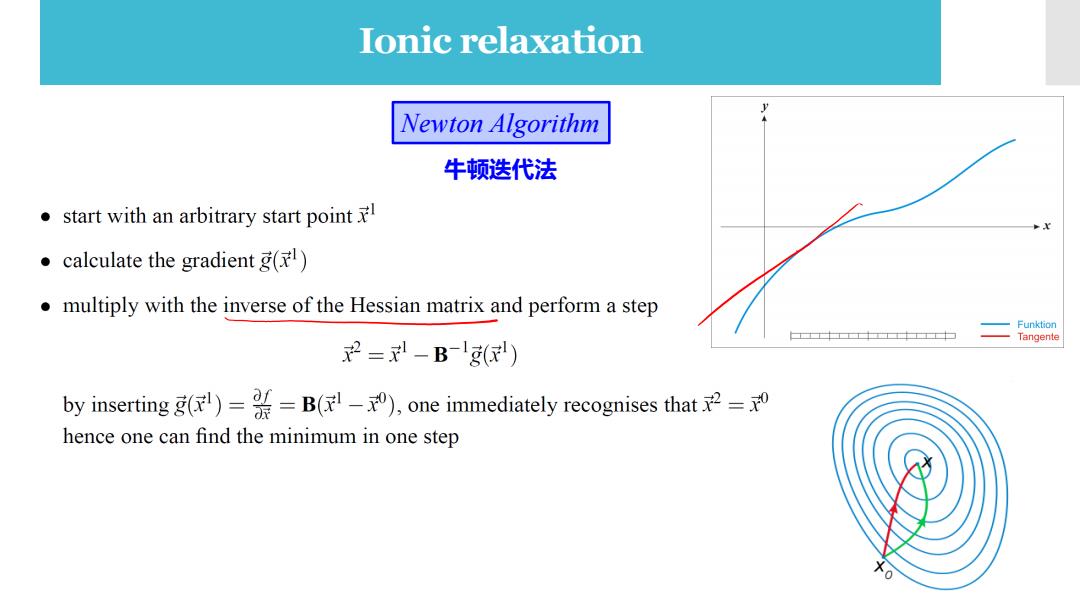
Ionic relaxation Newton Algorithm 牛顿迭代法 .start with an arbitrary start point .calculate the gradient g() multiply with the inverse of the Hessian matrix and perform a step 十 2=-B1() by inserting g()=B(),one immediately recognises that hence one can find the minimum in one step 0
Ionic relaxation 牛顿迭代法 Newton Algorithm
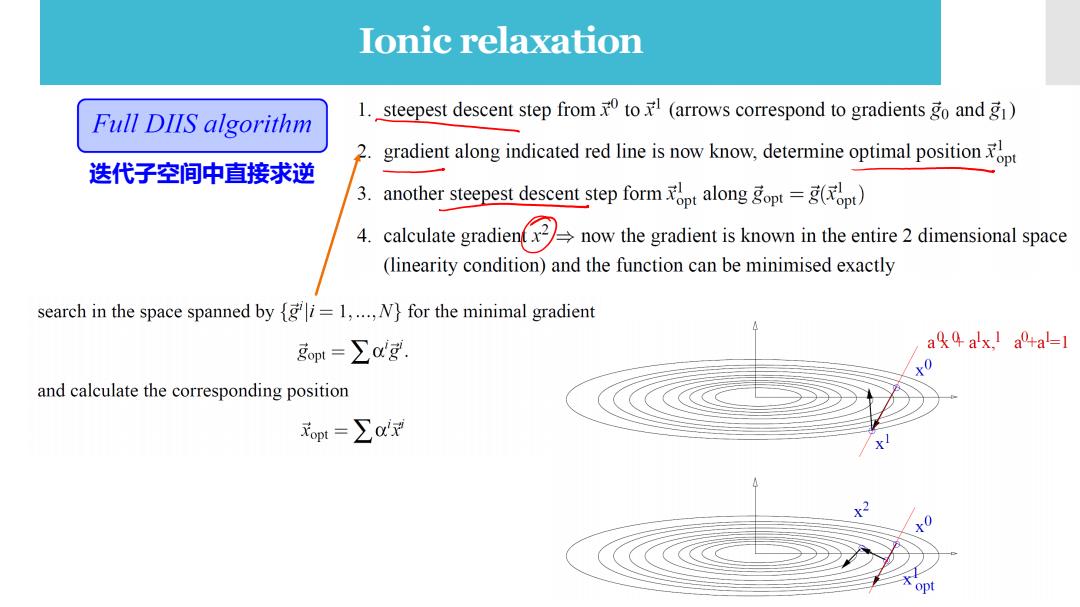
Ionic relaxation Full DIIS algorithm 1. steepest descent step from to(arrows correspond to gradients go andg) 2. gradient along indicated red line is now know.determine optimal position 迭代子空间中直接求逆 3. another steepest descent step formalong gopt=g() 4. caluateradinnowthe radient isknown in the entiredimensional space (linearity condition)and the function can be minimised exactly search in the space spanned by {gi=1,...,N}for the minimal gradient gpt=∑cdg. ak9 ax.I a+al=1 0 and calculate the corresponding position opt=∑c't 0 opt
Ionic relaxation 迭代子空间中直接求逆