Uncertainties Efficiency Scoring Monte Carlo PDFs Sampling RNGs
Monte Carlo Uncertainties Efficiency PDFs RNGs Sampling Scoring

(Pseudo)Random numbers Non-correlated sequences of numbers generated by an iterative equation. Repeatability after a very long number of random numbers. Non-uniform sequence. 0.015 ·Reproducible:“seed', 10k 0.014 1M siue. 100M 0.013 Ij+1=(aI;+c)mod m 0.012 where 0.011 a =663608941 0.01 0.009 C =0 0.008 m 232 0.007 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 X
(Pseudo) Random numbers • Non-correlated sequences of numbers generated by an iterative equation. • Repeatability after a very long number of random numbers. • Non-uniform sequence. • Reproducible: “seed”. Ij+1 = (aIj + c) mod m where: a = 663608941 c = 0 m = 232

Random numbers >Uniformly distributed numbers in [0,1] Most useful method for obtaining random numbers for computer use is a pseudo random number generator >How random are these pseudo random numbers? Anyone who considers arithmetical methods of producing random digits is,of course,in a state of sin. John von Neumann(1951)
Random Numbers Uniformly distributed numbers in [0,1] Most useful method for obtaining random numbers for computer use is a pseudo random number generator How random are these pseudo random numbers? Anyone who considers arithmetical methods of producing random digits is, of course, in a state of sin. John von Neumann (1951)

Next: Using a computer to generate random events: We need to be able to generate random numbers X with any given probability function f(x),or a given cumulative distribution c(x). 1)Uniformly distributed random numbers 2)General random numbers:can be obtained from a sequence of independent uniform random numbers
Next: Using a computer to generate random events: We need to be able to generate random numbers X with any given probability function f(x), or a given cumulative distribution c(x) . 1) Uniformly distributed random numbers 2) General random numbers: can be obtained from a sequence of independent uniform random numbers
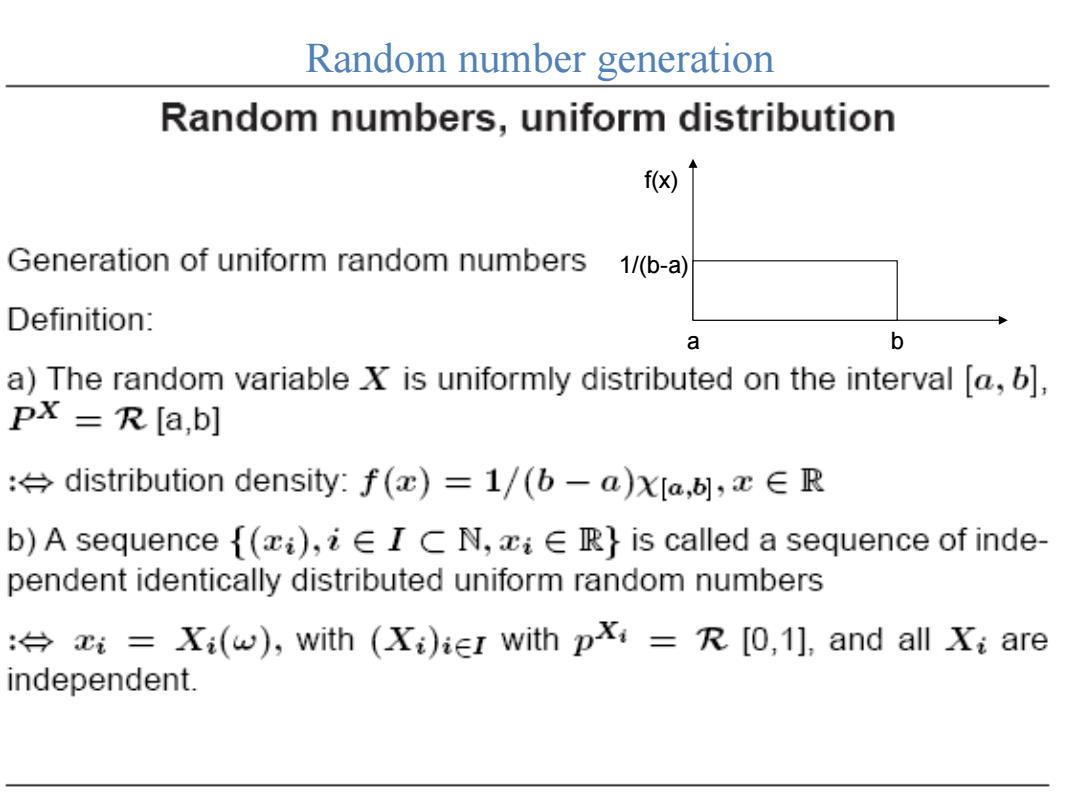
Random number generation Random numbers,uniform distribution f(x) Generation of uniform random numbers 1/(b-a) Definition: a b a)The random variable X is uniformly distributed on the interval [a,b], PX =R [a,b] :distribution density:f()=1/(b-a)x[a,6],E R b)A sequence f(xi),iE I C N,xiE R}is called a sequence of inde- pendent identically distributed uniform random numbers :=Xi(w),with (Xi)ier with p=R [0,1],and all Xi are independent
a b f(x) 1/(b-a) Random number generation

Random numbers,uniform distribution,cont. We will tactically assume that such sequences can be generated on our computers. The issue of producing such(reproducible (!)for code verification)se- quences leads into number theory,and too far away from the applicati- ons. Typical random number generators used today have a near perfect uni- form distribution,are near independent,and have a periodicity determi- ned by the largest integer which can be represented on a given machi- ne. (Note:in massively parallel computing,with many tens of millions samp- les drawn rapidly,this periodicity may require special attention
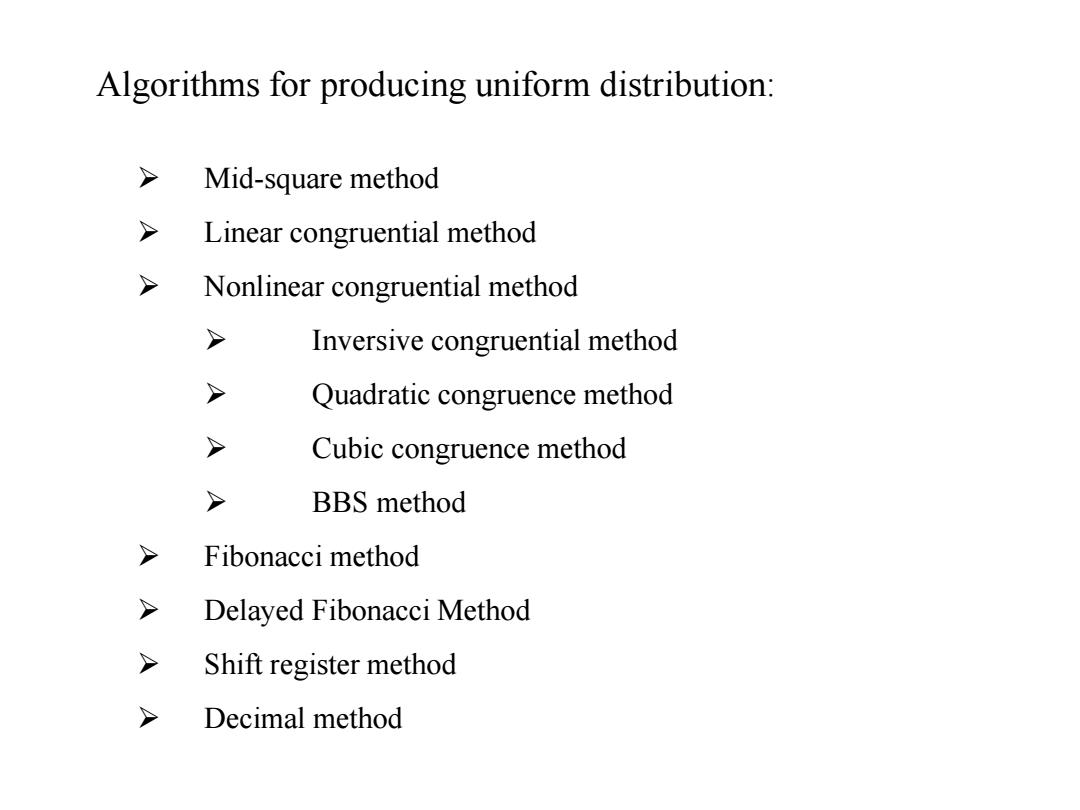
Algorithms for producing uniform distribution: > Mid-square method > Linear congruential method Nonlinear congruential method > Inversive congruential method > Quadratic congruence method > Cubic congruence method BBS method Fibonacci method > Delayed Fibonacci Method Shift register method > Decimal method
Algorithms for producing uniform distribution: Mid-square method Linear congruential method Nonlinear congruential method Inversive congruential method Quadratic congruence method Cubic congruence method BBS method Fibonacci method Delayed Fibonacci Method Shift register method Decimal method

We will see next Any continuous distribution can be generated from uniform random numbers on [0,1] Any discrete distribution can be generated from uniform random numbers on [0,1] Hence: Any given distribution can be generated from uniform random numbers on [0,1]
We will see next: Any continuous distribution can be generated from uniform random numbers on [0,1] Any discrete distribution can be generated from uniform random numbers on [0,1] Hence: Any given distribution can be generated from uniform random numbers on [0,1]

Random numbers,general distributions Transformation from uniform random numbers to random numbers with other distributions (e.g.:Maxwellian distribution,Poisson distr.,etc...) i.e..R[0,1]-P,with distribution P specified. Measure-theory:each "measure"can be decomposed into a weighted sum of three parts: part 1.)has a continuous distribution (with a probability density) part 2.)has a discrete distribution part 3.)is a "pathological"contribution,which is required for the ab- stract mathematical case only (general measurable spaces witho- algebras,....),but which does not occur in practical Monte-Carlo app- lications
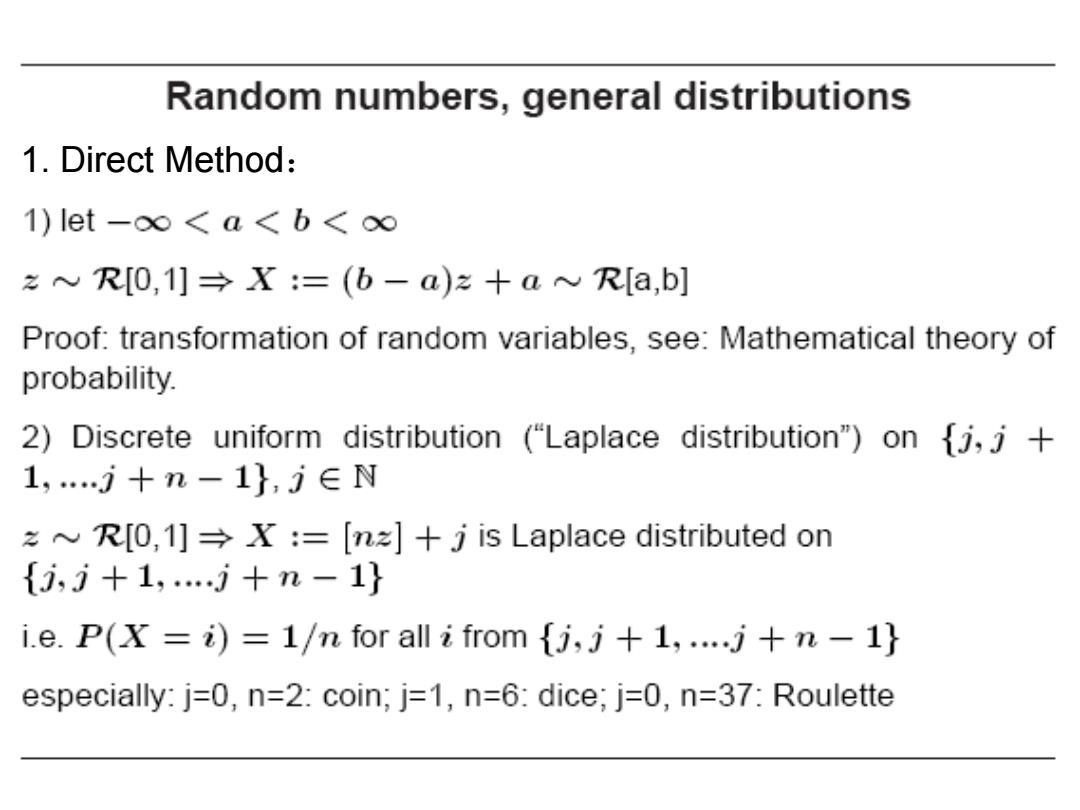
Random numbers,general distributions 1.Direct Method: 1)let-oo<a<b<oo R[0,1]:=(b-a)z+a R[a,b] Proof:transformation of random variables,see:Mathematical theory of probability. 2)Discrete uniform distribution ("Laplace distribution")on {j,j+ 1,j+n-1},j∈N R[0,1]X:=[nz]+j is Laplace distributed on {j,j+1,…j+n-1} i.e.P(X=i)=1/n for all i from fj,j+1,....j+n-1 especially:j=0,n=2:coin;j=1,n=6:dice;j=0,n=37:Roulette
1. Direct Method: