
第8卷第4期 智能系统学报 Vol.8 No.4 2013年8月 CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems Aug.2013 D0I:10.3969/i.issn.1673-4785.201304033 网络出版地址:http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1538.TP.20130621.1541.003.html 基于卡尔曼滤波的自主式水下航行器大尺度编队控制 袁健2,周忠海12,金光虎12,徐娟2,李俊晓12 (1.山东省海洋环境监测技术重点实验室,山东青岛266001:2.山东省科学院海洋仪器仪表研究所,山东青岛 266001)】 摘要:针对网络环境下环境噪声对自主式水下航行器编队控制的影响,提出一种利用卡尔曼滤波实时估计AUV最 优运动状态的编队控制方法将空间间隔较远的多AV系统建模为多智能体系统,从大尺度上研究其编队控制问 题.为了得到每个AUV速度状态的最优估计值,每个AUV都嵌人一个全局卡尔曼滤波器,利用该全局滤波器进行最 优估计从而计算出噪声环境下其自身的最优位置.仿真结果验证了所给出的控制策略的有效性。 关键词:自主式水下航行器:卡尔曼滤波;一致性:大尺度编队控制 中图分类号:TP273文献标志码:A文章编号:1673-4785(2013)04-0344-05 中文引用格式:袁健,周忠海,金光虎,等基于卡尔曼滤波的自主式水下航行器大尺度编队控制[J].智能系统学报,2013,8(4): 344.348. 英文引用格式:YUAN Jian,ZHOU Zhonghai,JIN Guanghu,etal.Large-scale formation control for autonomous underwater vehi- cles based on Kalman filtering[J].CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems,2013,8(4):344-348. Large-scale formation control for autonomous underwater vehicles based on Kalman filtering YUAN Jian'2,ZHOU Zhonghai2,JIN Guanghu'2,XU Juan'2,LI Junxiao2 (1.Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Ocean Environment Monitoring Technology,Qingdao 266001,China;2.Institute of Ocea- nographic Instrumentation of Shandong Academy of Sciences,Qingdao 266001,China) Abstract:Aiming at investigating the influence of environmental noise on autonomous underwater vehicles(AUV) formation control,a formation control for estimating AUV optimal motion states in real time is proposed.We mod- eled multiple AUVs with larger interval in space as a multi-agent system in order to investigate the large-scale for- mation control.Each AUV is embedded with one global Kalman filter to obtain the optimal estimation of each AUV speed states.And thus the optimal position of AUV in a noisy environment can be calculated by the optimal estima- tion with the global filter.Finally,some simulations were demonstrated to show the effectiveness of the proposed for- mation control scheme. Keywords:autonomous underwater vehicle;Kalman filtering;consensus;large-scale formation control 多个自主水下航行器的协同控制对于海洋科学多方面的应用能力.与空间以及陆地多机器人编队 考察、海洋开发以及军事应用等方面都具有重要的 控制技术相比,水下多AUV编队控制非常困难] 理论和现实意义.多自主水下航行器的编队控制是 除了AUV自身运动控制技术比较难实现外,在信号 多机器人协调控制中的一个典型科学问题).多自 传输方面,水声通信方式随着通信距离的增加,通信 主水下航行器的编队控制可以显著提高AUV在海 质量显著下降,主要表现在信号的延迟、衰减和环境 洋采样、监视和通信以及海洋环境监测等在内的众 噪声对信号的污染[).信号的衰减和失真,会导致系 统丢失真实系统状态、信号状态的误判:网络环境下 收稿日期:2013-04-15.网络出版日期:2013-06-21. 的环境噪声会导致系统状态转化为随机状态[46] 基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(61074092):山东省自然科学 这些影响因素会给系统状态带来不确定性和不稳定 基金资助项目(ZR2012FL18):山东省科学院博士基金项 目(201244):青岛科技发展计划项目(13-+1-4172-jh): 性.因此为了克服或减小不利因素对多AUV编队控 国际科技合作资助项目(2011DFR60810). 制的影响,必须从受环境噪声污染的系统状态中实 通信作者:袁健.E-mail:jyuanjian801209g163.com 时估计出动态系统的最优状态
第 8 卷第 4 期 智 能 系 统 学 报 Vol.8 №.4 2013 年 8 月 CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems Aug. 2013 DOI:10.3969 / j.issn.1673⁃4785.201304033 网络出版地址:http: / / www.cnki.net / kcms/ detail / 23.1538.TP.20130621.1541.003.html 基于卡尔曼滤波的自主式水下航行器大尺度编队控制 袁健1,2 ,周忠海1,2 ,金光虎1,2 ,徐娟1,2 ,李俊晓1,2 (1. 山东省海洋环境监测技术重点实验室,山东 青岛 266001; 2. 山东省科学院 海洋仪器仪表研究所,山东 青岛 266001) 摘 要:针对网络环境下环境噪声对自主式水下航行器编队控制的影响,提出一种利用卡尔曼滤波实时估计 AUV 最 优运动状态的编队控制方法.将空间间隔较远的多 AUV 系统建模为多智能体系统,从大尺度上研究其编队控制问 题.为了得到每个 AUV 速度状态的最优估计值,每个 AUV 都嵌入一个全局卡尔曼滤波器,利用该全局滤波器进行最 优估计从而计算出噪声环境下其自身的最优位置.仿真结果验证了所给出的控制策略的有效性. 关键词:自主式水下航行器;卡尔曼滤波;一致性;大尺度编队控制 中图分类号:TP273 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1673⁃4785(2013)04⁃0344⁃05 中文引用格式:袁健,周忠海,金光虎,等.基于卡尔曼滤波的自主式水下航行器大尺度编队控制[ J]. 智能系统学报,2013, 8( 4): 344⁃348. 英文引用格式:YUAN Jian, ZHOU Zhonghai, JIN Guanghu,et al. Large⁃scale formation control for autonomous underwater vehi⁃ cles based on Kalman filtering[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2013, 8(4): 344⁃348. Large⁃scale formation control for autonomous underwater vehicles based on Kalman filtering YUAN Jian 1,2 , ZHOU Zhonghai 1,2 , JIN Guanghu 1,2 , XU Juan 1,2 , LI Junxiao 1,2 (1. Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Ocean Environment Monitoring Technology, Qingdao 266001, China; 2. Institute of Ocea⁃ nographic Instrumentation of Shandong Academy of Sciences, Qingdao 266001, China) Abstract:Aiming at investigating the influence of environmental noise on autonomous underwater vehicles(AUV) formation control, a formation control for estimating AUV optimal motion states in real time is proposed. We mod⁃ eled multiple AUVs with larger interval in space as a multi⁃agent system in order to investigate the large⁃scale for⁃ mation control. Each AUV is embedded with one global Kalman filter to obtain the optimal estimation of each AUV speed states. And thus the optimal position of AUV in a noisy environment can be calculated by the optimal estima⁃ tion with the global filter. Finally, some simulations were demonstrated to show the effectiveness of the proposed for⁃ mation control scheme. Keywords:autonomous underwater vehicle; Kalman filtering; consensus; large⁃scale formation control 收稿日期:2013⁃04⁃15. 网络出版日期:2013⁃06⁃21. 基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(61074092);山东省自然科学 基金资助项目( ZR2012FL18);山东省科学院博士基金项 目(201244);青岛科技发展计划项目( 13⁃+ 1⁃4⁃172⁃jch); 国际科技合作资助项目(2011DFR60810). 通信作者:袁健. E⁃mail:jyuanjian801209@ 163.com. 多个自主水下航行器的协同控制对于海洋科学 考察、海洋开发以及军事应用等方面都具有重要的 理论和现实意义.多自主水下航行器的编队控制是 多机器人协调控制中的一个典型科学问题[1] .多自 主水下航行器的编队控制可以显著提高 AUV 在海 洋采样、监视和通信以及海洋环境监测等在内的众 多方面的应用能力.与空间以及陆地多机器人编队 控制技术相比,水下多 AUV 编队控制非常困难[2] . 除了 AUV 自身运动控制技术比较难实现外,在信号 传输方面,水声通信方式随着通信距离的增加,通信 质量显著下降,主要表现在信号的延迟、衰减和环境 噪声对信号的污染[3] .信号的衰减和失真,会导致系 统丢失真实系统状态、信号状态的误判;网络环境下 的环境噪声会导致系统状态转化为随机状态[4⁃6] , 这些影响因素会给系统状态带来不确定性和不稳定 性.因此为了克服或减小不利因素对多 AUV 编队控 制的影响,必须从受环境噪声污染的系统状态中实 时估计出动态系统的最优状态.

第4期 袁健,等:基于卡尔曼滤波的自主式水下航行器大尺度编队控制 ·345. 本文对于空间相距较远的多AUV系统,从大尺 u.(t)=a(x(t-7)-x(t)).(3) 度上研究其编队控制问题.将多AUV系统建模为多 EN 智能体系统,研究其三维空间编队控制问题.考虑到 式中:N表示个体i的邻居个体集;a>0为有向图 因水下水声通信距离的约束,导致多智能体系统的 G=(V,E,A)的邻接矩阵A的邻接权重.水下环境噪 声的影响会导致系统的状态变为随机状态,此时系 拉普拉斯矩阵L(k)为时变矩阵,故A(k)和H(k) 也为时变矩阵,本文为减轻或者克服水下网络环境 统一致性协议为 对多AUV系统造成的影响,提出一种AUV,利用其 (t)=∑a,(x(t)-x(4)+ 嵌入的全局滤波器对系统状态进行滤波的编队控制 bio(xo(t)x(t))+w(tg). 方法,利用卡尔曼滤波器进行系统滤波从而得到每 式中:为系统采样时刻,w:(t)为t:时刻的过程噪 个AUV自身运动状态的最优估计值,以此最优估计 声.为了减小环境噪声对多AUV编队控制的影响, 值构成一致性编队控制律 必须从一系列的噪声测量中,估计出动态系统的 1编队控制问题 状态 有向图G描述各AUV间的相互通信.设p阶加 2基于卡尔曼滤波的一致性协议 权有向图G=(V,E,A)由节点集V={U1,2,…,,}、 本文提出一种AUV利用其嵌人的全局滤波器 边集ECV×V以及加权邻接矩阵A=(a:)∈R 对系统状态进行滤波的编队控制方法.所提出受噪 (a:≥0)构成在加权有向图G中从节点:到节点 声影响的一致性跟踪协议为: 的有向边可表示为e=(:,y)∈E,节点下标i属于 ,(t)=∑a,(x,(4)-x,()+ 一个有限集合P={1,2,…,P},第i个节点代表第i 个AUV,邻接矩阵A中对应于G的有向边e:的邻 ba(xo(t)-x (t))+wi(t), 接权值a,为正,即a>0.节点:的邻居节点集表示 z.(t4)=h,(t)x:(t)+v(tk) 为N:={∈V:(:,)∈E},有向边(:,)表示节点 式中:w:(t4)为过程白噪声,,(t2)为量测白噪声 i和j间的一个有向的信息交换,则称AUV,为AUV 令 的邻近AUV. X=[xx对… x], 为了实现多AUV的空间编队,对每个AUV进 W=[w{eg… w], 行运动方程建模.对于三维空间AUV:运动方程可 Z=[zz… ], 以用以下方程进行描述: V=[y… P(t+i)=P(t)+△Tv(tz)sinp'(tz)cosf(te), ], 则多智能体系统方程可以写成矩阵形式: P()=P()+ATv()sin ()sin () P()=P(t)+ATv(t)cos '(t). X(t)=(L(t)-I)X(t)+b(t)+W(t), Z(t)=H(t)X(1)+V(t). (4) 式中:(P(t),P(4),P(t))和(P(+1), P(t+1),P(tk)分别表示AUV:当前时刻和下一 式中:状态x。(t)为常数向量,L(t)为相应维数的时 时刻的实时位置,△T为仿真步长 变拉普拉斯矩阵,b。为相应维数的常数矩阵.对于系 统方程(4)求其方程的解则系统方程的解为 在多AUV系统中个体AUV的运动学方程描述为 x:(t)=u:(t),i∈P (1) X(t)=e(u)-D(-tX(to)+borod +W(t). 式中:x,(t)=[(t)(t),(t)],表示t时刻需 对上式进行形式上的离散化,所以 要一致性协商的个体AUV的状态,u(t)表示t时刻 X((k+1)AT)=e(Ut)-DATX(kAT)+ 控制输入,为相应维数控制向量.多AUV编队控制 r(k+1)△T boxodr W(kAT). 的目的是:当t≥t。时,‖:(t)-号(t)‖=0, ‖9.(t)-0,(t)‖=0和‖9:(t)-g,(t)‖=0,所以t 式中:△T为仿真步长,进一步有 时刻之后所有AUV取得了一致的运动状态.对于运 K(k+1)=e)-arK(k)+△Tb。+W(k), 动学方程(1),文献[7]采用的一致性协议为: 整理得 u,()=∑a,(x(t)-x() X(k+1)=A(k)X(k)+u(k)+W(k), (2) EN 式中:A(k)=e(-a7,u(k)=△Tb 对于具有网络时延的多AUV系统,文献[7]采 同理,将系统方程(4)第2个公式离散化得 用了如下的带有时延的一致性协议: Z(k)=H(k)X(k)+V()
本文对于空间相距较远的多 AUV 系统,从大尺 度上研究其编队控制问题.将多 AUV 系统建模为多 智能体系统,研究其三维空间编队控制问题.考虑到 因水下水声通信距离的约束,导致多智能体系统的 拉普拉斯矩阵 L(k)为时变矩阵,故 A(k)和 H( k) 也为时变矩阵.本文为减轻或者克服水下网络环境 对多 AUV 系统造成的影响,提出一种 AUV,利用其 嵌入的全局滤波器对系统状态进行滤波的编队控制 方法,利用卡尔曼滤波器进行系统滤波从而得到每 个 AUV 自身运动状态的最优估计值,以此最优估计 值构成一致性编队控制律. 1 编队控制问题 有向图 G 描述各 AUV 间的相互通信.设 p 阶加 权有向图 G = (V,E,A)由节点集 V = {v1 ,v2 ,…,vp}、 边集 E⊆V × V 以及加权邻接矩阵 A = aij ( ) ∈R p×p (aij≥0)构成.在加权有向图 G 中从节点 vi 到节点 vj 的有向边可表示为 eij = (vi,vj)∈E,节点下标 i 属于 一个有限集合 P = {1,2,…,p},第 i 个节点代表第 i 个 AUV, 邻接矩阵 A 中对应于 G 的有向边 eij的邻 接权值 aij为正, 即 aij>0.节点 vi 的邻居节点集表示 为 Ni = {vj∈V:(vi,vj)∈E},有向边(vi,vj)表示节点 i 和 j 间的一个有向的信息交换,则称 AUVi 为AUVj 的邻近 AUV. 为了实现多 AUV 的空间编队,对每个 AUV 进 行运动方程建模.对于三维空间 AUVi 运动方程可 以用以下方程进行描述: P i x(t k+1 ) = P i x(t k) + ΔTv i (t k)sin φ i (t k)cos θ i (t k), P i y(t k+1 ) = P i y(t k) + ΔTv i (t k)sin φ i (t k)sin θ i (t k), P i z(t k+1 ) = P i z(t k) + ΔTv i (t k)cos φ i (t k). ì î í ï ï ï ï 式中: ( P i x ( t k ), P i y ( t k ), P i z ( t k )) 和 (P i x(t k+1 ), P i y(t k+1 ),P i z(t k+1 ))分别表示 AUVi 当前时刻和下一 时刻的实时位置,ΔT 为仿真步长. 在多 AUV 系统中个体 AUV 的运动学方程描述为 ̇xi(t) = ui(t),i ∈ P. (1) 式中:xi(t)= vi(t) θ [ i(t) φi(t) ] T ,表示 t 时刻需 要一致性协商的个体 AUV 的状态,ui(t)表示 t 时刻 控制输入,为相应维数控制向量.多 AUV 编队控制 的目 的 是: 当 t ≥ t e 时, ‖ vi ( t ) - vj ( t ) ‖ = 0, ‖θi(t)-θj(t)‖= 0 和‖φi( t) -φj( t)‖ = 0,所以 t e 时刻之后所有 AUV 取得了一致的运动状态.对于运 动学方程(1),文献[7]采用的一致性协议为: ui(t) = ∑vj∈Ni aij(xj(t) - xi(t)). (2) 对于具有网络时延的多 AUV 系统, 文献[7]采 用了如下的带有时延的一致性协议: ui(t) = ∑vj∈Ni aij(xj(t - τij) - xi(t - τij)). (3) 式中:Ni 表示个体 i 的邻居个体集; aij >0 为有向图 G= (V,E,A)的邻接矩阵 A 的邻接权重.水下环境噪 声的影响会导致系统的状态变为随机状态,此时系 统一致性协议为 ̇xi(t k) = ∑vj∈Ni aij(xj(t k) - xi(t k)) + bi0(x0(t k) - xi(t k)) + wi(t k). 式中:t k 为系统采样时刻,wi(t k)为 t k 时刻的过程噪 声.为了减小环境噪声对多 AUV 编队控制的影响, 必须从一系列的噪声测量中,估计出动态系统的 状态. 2 基于卡尔曼滤波的一致性协议 本文提出一种 AUV 利用其嵌入的全局滤波器 对系统状态进行滤波的编队控制方法.所提出受噪 声影响的一致性跟踪协议为: ̇xi(t k) = ∑vj∈Ni aij(xj(t k) - xi(t k)) + bi0(x0(t k) - xi(t k)) + wi(t k), zi(t k) = hi(t k)xi(t k) + vi(t k). 式中:wi(t k)为过程白噪声,vi(t k)为量测白噪声. 令 X = x T 1 x T 2 … x T 7 [ ] T , W = w T 1 w T 2 … w T 7 [ ] T , Z = z T 1 z T 2 … z T 7 [ ] T , V = v T 1 v T 2 … v T 7 [ ] T , 则多智能体系统方程可以写成矩阵形式: X · (t) = (L(t) - I)X(t) + b0 x0(t) + W(t), Z(t) = H(t)X(t) + V(t). (4) 式中:状态 x0(t)为常数向量,L(t)为相应维数的时 变拉普拉斯矩阵,b0 为相应维数的常数矩阵.对于系 统方程(4)求其方程的解.则系统方程的解为 X(t) = e (L(t) -I)(t-t0 )X(t 0 ) + ∫ t t0 b0 x0 dτ + W(t). 对上式进行形式上的离散化,所以 X((k + 1)ΔT) = e (L(k) -I)ΔTX(kΔT) + ∫ (k+1)ΔT kΔT b0 x0 dτ + W(kΔT). 式中:ΔT 为仿真步长,进一步有 X(k + 1) = e (L(k) -I)ΔTX(k) + ΔTb0 x0 + W(k), 整理得 X(k + 1) = A(k)X(k) + u(k) + W(k), 式中:A(k)= e (L(k)-I)ΔT ,u(k)= ΔTb0 x0 . 同理,将系统方程(4)第 2 个公式离散化得 Z(k) = H(k)X(k) + V(k). 第 4 期 袁健,等:基于卡尔曼滤波的自主式水下航行器大尺度编队控制 ·345·
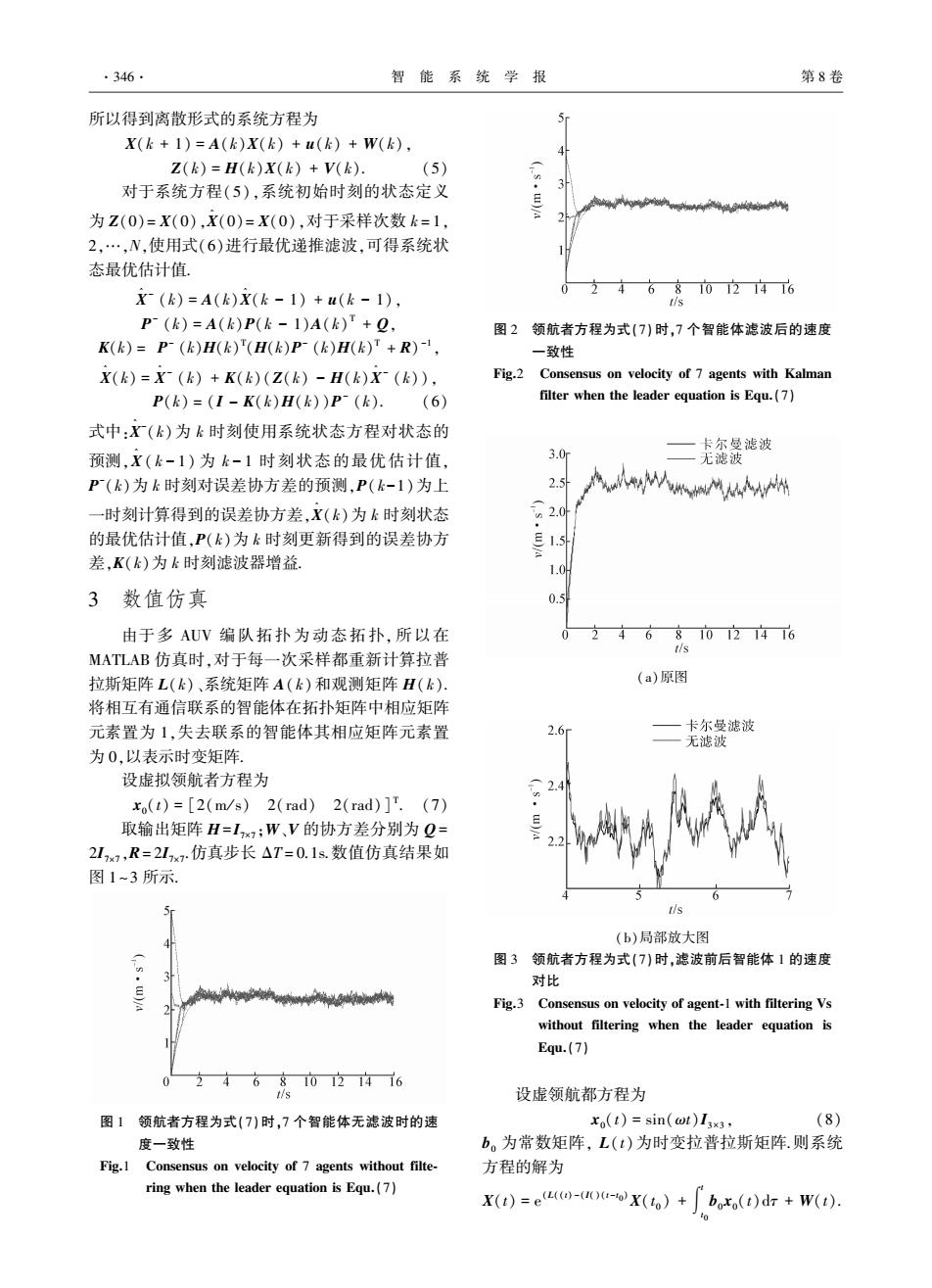
·346. 智能系统学报 第8卷 所以得到离散形式的系统方程为 X(k+1)=A(k)X(k)+u(k)+W(k), Z(k)=H(k)X(k)+V(k). (5) 对于系统方程(5),系统初始时刻的状态定义 为Z(0)=X(0),X(0)=X(0),对于采样次数k=1, 2,…,N,使用式(6)进行最优递推滤波,可得系统状 态最优估计值。 X(k)=A(k)X(k-1)+u(k-1), 2468102146 P-(k)=A(k)P(k-1)A(k)"+, 图2领航者方程为式(7)时,7个智能体滤波后的速度 K(k)=P-(kH(k)(H(k)P-(k)H(k)+R)-, 一致性 X(k)=X(k)+K()(Z(k)-H()()), Fig.2 Consensus on velocity of 7 agents with Kalman P(k)=(I-K()H(k)P(k).(6) filter when the leader equation is Equ.(7) 式中:X(k)为k时刻使用系统状态方程对状态的 卡尔曼滤波 预测,X(k-1)为k-1时刻状态的最优估计值, 3.0m 无滤波 P(k)为k时刻对误差协方差的预测,P(k-1)为上 2.5 州 一时刻计算得到的误差协方差,X(k)为k时刻状态 n2.0 的最优估计值,P(k)为k时刻更新得到的误差协方 E1.5 差,K(k)为k时刻滤波器增益. 1.0H 3数值仿真 0.5 由于多AUV编队拓扑为动态拓扑,所以在 46810121416 t/s MATLAB仿真时,对于每一次采样都重新计算拉普 拉斯矩阵L(k)、系统矩阵A(k)和观测矩阵H(k). (a)原图 将相互有通信联系的智能体在拓扑矩阵中相应矩阵 元素置为1,失去联系的智能体其相应矩阵元素置 2.6 卡尔曼滤波 无滤波 为0,以表示时变矩阵。 设虚拟领航者方程为 2.4 xo(t)=[2(m/s)2(rad)2(rad)]T.(7) 取输出矩阵H=Ix,:W、V的协方差分别为Q= 2Ix7,R=2Ix仿真步长△T=0.1s.数值仿真结果如 图1~3所示. (b)局部放大图 图3领航者方程为式(7)时,滤波前后智能体1的速度 对比 Fig.3 Consensus on velocity of agent-1 with filtering Vs without filtering when the leader equation is Equ.(7) 46810立1416 设虚领航都方程为 图1领航者方程为式(7)时,7个智能体无滤波时的速 xo(t)=sin(@t)I3x3, (8) 度一致性 b。为常数矩阵,L(t)为时变拉普拉斯矩阵.则系统 Fig.I Consensus on velocity of 7 agents without filte- 方程的解为 ring when the leader equation is Equ.(7) X(t)=e(t)+boxo(t)d +W(t)
所以得到离散形式的系统方程为 X(k + 1) = A(k)X(k) + u(k) + W(k), Z(k) = H(k)X(k) + V(k). (5) 对于系统方程(5),系统初始时刻的状态定义 为 Z(0)= X(0),X ^ (0)= X(0),对于采样次数 k = 1, 2,…,N,使用式(6)进行最优递推滤波,可得系统状 态最优估计值. X ^ - (k) = A(k)X ^ (k - 1) + u(k - 1), P - (k) = A(k)P(k - 1)A(k) T + Q, K(k) = P - (k)H(k) T (H(k)P - (k)H(k) T + R) -1 , X ^ (k) = X ^ - (k) + K(k)(Z(k) - H(k)X ^ - (k)), P(k) = (I - K(k)H(k))P - (k). (6) 式中:X ^ - (k)为 k 时刻使用系统状态方程对状态的 预测,X ^ ( k - 1) 为 k - 1 时刻状态的最优估计值, P - (k)为 k 时刻对误差协方差的预测,P( k-1)为上 一时刻计算得到的误差协方差,X ^ (k)为 k 时刻状态 的最优估计值,P(k)为 k 时刻更新得到的误差协方 差,K(k)为 k 时刻滤波器增益. 3 数值仿真 由于多 AUV 编队拓扑为动态拓扑, 所以在 MATLAB 仿真时,对于每一次采样都重新计算拉普 拉斯矩阵 L(k)、系统矩阵 A( k)和观测矩阵 H( k). 将相互有通信联系的智能体在拓扑矩阵中相应矩阵 元素置为 1,失去联系的智能体其相应矩阵元素置 为 0,以表示时变矩阵. 设虚拟领航者方程为 x0(t) = [2(m / s) 2(rad) 2(rad)] T . (7) 取输出矩阵 H= I7×7 ;W、V 的协方差分别为 Q = 2I7×7 ,R= 2I7×7 .仿真步长 ΔT = 0.1s.数值仿真结果如 图 1~3 所示. 图 1 领航者方程为式(7)时,7 个智能体无滤波时的速 度一致性 Fig.1 Consensus on velocity of 7 agents without filte⁃ ring when the leader equation is Equ.(7) 图 2 领航者方程为式(7)时,7 个智能体滤波后的速度 一致性 Fig.2 Consensus on velocity of 7 agents with Kalman filter when the leader equation is Equ.(7) (a)原图 (b)局部放大图 图 3 领航者方程为式(7)时,滤波前后智能体 1 的速度 对比 Fig.3 Consensus on velocity of agent⁃1 with filtering Vs without filtering when the leader equation is Equ.(7) 设虚领航都方程为 x0(t) = sin(ωt)I3×3 , (8) b0 为常数矩阵, L(t)为时变拉普拉斯矩阵.则系统 方程的解为 X(t) = e (L((t) -(I()(t-t0 )X(t 0 ) + ∫ t t0 b0 x0(t)dτ + W(t). ·346· 智 能 系 统 学 报 第 8 卷
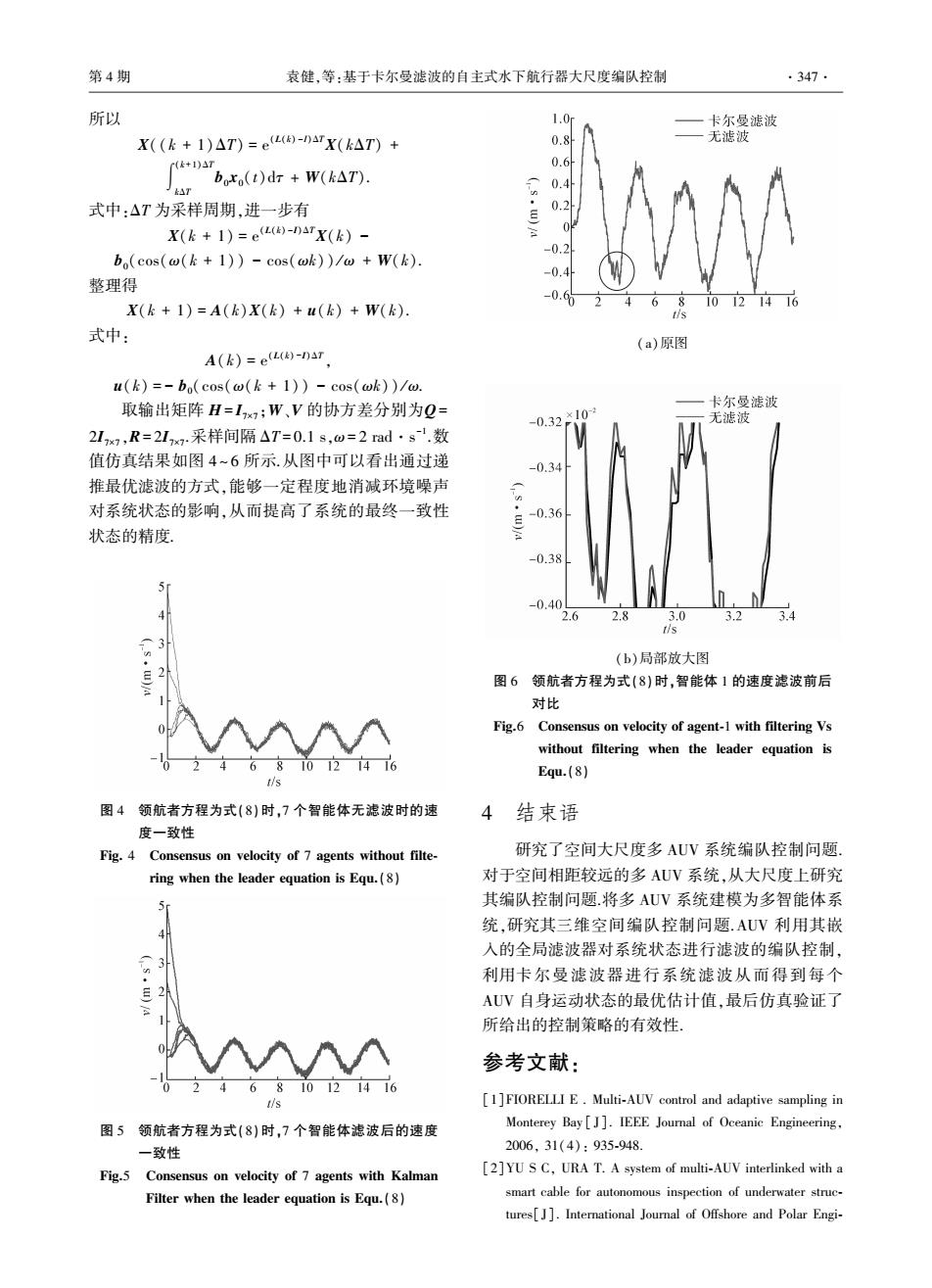
第4期 袁健,等:基于卡尔曼滤波的自主式水下航行器大尺度编队控制 ·347· 所以 1.0 一卡尔曼滤波 X((k+1)△T)=e)-naTX(k△T)+ 0.8 一无滤波 r(k+1)△T 0.6 ,bxo(t)dr+W(k△T). 式中:△T为采样周期,进一步有 0.2 X(k+1)=e()-Da7X(k)- 0 0.2 bo(cos(a(k +1))-cos(ak))/o +W(k). -0.4 整理得 0. X(k+1)=A(k)X(k)+u(k)+W(k). 6810121416 式中: (a)原图 A(k)=e(()-Da7 u(k)=-bo(cos(o(k+1))-cos(ok))/@. 取输出矩阵H=1x,;W、V的协方差分别为Q= 卡尔曼滤波 ×10 -0.32 无滤波 21x7,R=217x7.采样间隔△T=0.1s,o=2ad·s.数 值仿真结果如图4~6所示.从图中可以看出通过递 -0.34 推最优滤波的方式,能够一定程度地消减环境噪声 对系统状态的影响,从而提高了系统的最终一致性 -0.36 状态的精度 -0.38 -0.4 2.6 2.8 3.0 3.2 3.4 tis 3 (b)局部放大图 图6领航者方程为式(8)时,智能体1的速度滤波前后 对比 Fig.6 Consensus on velocity of agent-1 with filtering Vs without filtering when the leader equation is 024681012146 tis Equ.(8) 图4领航者方程为式(8)时,7个智能体无滤波时的速 4结束语 度一致性 Fig.4 Consensus on velocity of 7 agents without filte- 研究了空间大尺度多AUV系统编队控制问题, ring when the leader equation is Equ.(8) 对于空间相距较远的多AUV系统,从大尺度上研究 其编队控制问题.将多AUV系统建模为多智能体系 统,研究其三维空间编队控制问题.AUV利用其嵌 入的全局滤波器对系统状态进行滤波的编队控制, 利用卡尔曼滤波器进行系统滤波从而得到每个 2 AUV自身运动状态的最优估计值,最后仿真验证了 所给出的控制策略的有效性. 参考文献: 0246810121416 [1]FIORELLI E.Multi-AUV control and adaptive sampling in 图5领航者方程为式(8)时,7个智能体滤波后的速度 Monterey Bay[J].IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 一致性 2006.31(4):935-948. Fig.5 Consensus on velocity of 7 agents with Kalman [2]YU S C,URA T.A system of multi-AUV interlinked with a Filter when the leader equation is Equ.(8) smart cable for autonomous inspection of underwater struc- tures[J].International Journal of Offshore and Polar Engi-
所以 X((k + 1)ΔT) = e (L(k) -I)ΔTX(kΔT) + ∫ (k+1)ΔT kΔT b0 x0(t)dτ + W(kΔT). 式中:ΔT 为采样周期,进一步有 X(k + 1) = e (L(k) -I)ΔTX(k) - b0(cos(ω(k + 1)) - cos(ωk)) / ω + W(k). 整理得 X(k + 1) = A(k)X(k) + u(k) + W(k). 式中: A(k) = e (L(k) -I)ΔT , u(k) = - b0(cos(ω(k + 1)) - cos(ωk)) / ω. 取输出矩阵 H = I7×7 ;W、V 的协方差分别为Q = 2I7×7 ,R= 2I7×7 .采样间隔 ΔT = 0.1 s,ω= 2 rad·s -1 .数 值仿真结果如图 4 ~ 6 所示.从图中可以看出通过递 推最优滤波的方式,能够一定程度地消减环境噪声 对系统状态的影响,从而提高了系统的最终一致性 状态的精度. 图 4 领航者方程为式(8)时,7 个智能体无滤波时的速 度一致性 Fig. 4 Consensus on velocity of 7 agents without filte⁃ ring when the leader equation is Equ.(8) 图 5 领航者方程为式(8)时,7 个智能体滤波后的速度 一致性 Fig.5 Consensus on velocity of 7 agents with Kalman Filter when the leader equation is Equ.(8) (a)原图 (b)局部放大图 图 6 领航者方程为式(8)时,智能体 1 的速度滤波前后 对比 Fig.6 Consensus on velocity of agent⁃1 with filtering Vs without filtering when the leader equation is Equ.(8) 4 结束语 研究了空间大尺度多 AUV 系统编队控制问题. 对于空间相距较远的多 AUV 系统,从大尺度上研究 其编队控制问题.将多 AUV 系统建模为多智能体系 统,研究其三维空间编队控制问题.AUV 利用其嵌 入的全局滤波器对系统状态进行滤波的编队控制, 利用卡尔曼滤波器进行系统滤波从而得到每个 AUV 自身运动状态的最优估计值,最后仿真验证了 所给出的控制策略的有效性. 参考文献: [1]FIORELLI E . Multi⁃AUV control and adaptive sampling in Monterey Bay [ J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2006, 31(4): 935⁃948. [2]YU S C, URA T. A system of multi⁃AUV interlinked with a smart cable for autonomous inspection of underwater struc⁃ tures[ J]. International Journal of Offshore and Polar Engi⁃ 第 4 期 袁健,等:基于卡尔曼滤波的自主式水下航行器大尺度编队控制 ·347·

·348. 智能系统学报 第8卷 neering,2004,14(4):264-272 作者简介: [3]DEREK P,ZHANG F M,LEONARD N E.Cooperative 袁健,男,1980年生,副研究员,博 control for ocean sampling:the glider coordinated control 士,主要研究方向为自主水下航行器的 system[J].IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technol- 编队控制参与国家自然科学基金、国 0gy,2008,16(4):735-744. 际科技合作项目、山东省自然科学基金 4]XIANG X B.Coordinated control for multi-AUV systems 等项目多项.发表学术论文20余篇. based on hybrid automata[C]//IEEE International Confer- ence on Robotics and Biomimetics.[S.1.],2007:2121- 2126. 周忠海.男,1975年生,研究员,博 [5]DO K D.Formation tracking control of unicycle-type mobile 士,主要研究方向为海洋环境监测技术 robots with limited sensing ranges[].IEEE Transactions on 先后承担了国家“863”计划、国际科技合 Control Systems Technology,2008,16(3):527-538. 作项目、海洋公益性项目和青岛市对外 [6]YANG E F,GU D B.Nonlinear formation-keeping and 合作项目现主持国家科技部国际科技 mooring control of multiple autonomous underwater vehicles 合作项目1项发表学术论文50余篇. [J].IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics,2007,2 (2):164-178. 金光虎,男,1979年生,副研究员, [7]JADBABAIE A,LIN J,MORSE A S.Coordination of 博士,主要研究方向为海洋传感技术。 groups of mobile autonomous agents using nearest neighbor 参与多项国际科技合作项目发表学术 rules[J.IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control,2003, 论文20余篇,获得专利10余项. 48(6):988-1001. 2014EEE机电一体化与自动化国际会议 The 2014 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation IEEE ICMA 2014) The 2014 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA 2014)will take place in Chengdu,Si- chuan,China from August 3 to August 6,2014.Tianjin is a tribute to China's proud history.Nestled in Tianjin,a time- honored city famous for its history,culture and landscapes. As the host city of ICMA 2014,Tianjin not only provides the attendees with a great venue for this event,but also an un- paralleled experience in Chinese history and culture.You are cordially invited to join us at IEEE ICMA 2014 in Tianjin to live this unique experience.The objective of ICMA 2014 is to provide a forum for researchers,educators,engineers,and government officials involved in the general areas of mechatronics,robotics,automation and sensors to disseminate their latest research results and exchange views on the future research directions of these fields.The topics of interest include, but not limited to the following: Intelligent mechatronics,robotics,biomimetics,automation and control systems opto-electronic elements and Materials,laser technology and laser processing Elements,structures,mechanisms,and applications of micro and nano systems Teleoperation,telerobotics,haptics,and teleoperated semi-autonomous systems Sensor design,multi-sensor data fusion algorithms and wireless sensor networks Biomedical and rehabilitation engineering,prosthetics and artificial organs Control system modeling and simulation techniques and methodologies .AI,intelligent control,neuro-control,fuzzy control and their applications ndustrial automation,process control,manufacturing process and automation Website:http://2014.ieee-icma.org/
neering, 2004, 14(4): 264⁃272. [3] DEREK P, ZHANG F M, LEONARD N E. Cooperative control for ocean sampling: the glider coordinated control system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technol⁃ ogy, 2008, 16(4): 735⁃744. [4] XIANG X B. Coordinated control for multi⁃AUV systems based on hybrid automata[C] / / IEEE International Confer⁃ ence on Robotics and Biomimetics. [ S. l.], 2007: 2121⁃ 2126. [5]DO K D. Formation tracking control of unicycle⁃type mobile robots with limited sensing ranges[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2008, 16(3): 527⁃538. [6] YANG E F, GU D B. Nonlinear formation⁃keeping and mooring control of multiple autonomous underwater vehicles [J]. IEEE/ ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2007, 2 (2): 164⁃178. [7 ] JADBABAIE A, LIN J, MORSE A S. Coordination of groups of mobile autonomous agents using nearest neighbor rules[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2003, 48(6): 988⁃1001. 作者简介: 袁健,男,1980 年生,副研究员,博 士,主要研究方向为自主水下航行器的 编队控制.参与国家自然科学基金、国 际科技合作项目、山东省自然科学基金 等项目多项.发表学术论文 20 余篇. 周忠海,男,1975 年生,研究员,博 士,主要研究方向为海洋环境监测技术. 先后承担了国家“863”计划、国际科技合 作项目、海洋公益性项目和青岛市对外 合作项目.现主持国家科技部国际科技 合作项目 1 项.发表学术论文 50 余篇. 金光虎,男,1979 年生,副研究员, 博士,主要研究方向为海洋传感技术. 参与多项国际科技合作项目.发表学术 论文 20 余篇,获得专利 10 余项. 2014 IEEE 机电一体化与自动化国际会议 The 2014 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation ( IEEE ICMA 2014) The 2014 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA 2014) will take place in Chengdu, Si⁃ chuan, China from August 3 to August 6, 2014. Tianjin is a tribute to China's proud history. Nestled in Tianjin, a time⁃ honored city famous for its history, culture and landscapes. As the host city of ICMA 2014, Tianjin not only provides the attendees with a great venue for this event, but also an un⁃ paralleled experience in Chinese history and culture. You are cordially invited to join us at IEEE ICMA 2014 in Tianjin to live this unique experience. The objective of ICMA 2014 is to provide a forum for researchers, educators, engineers, and government officials involved in the general areas of mechatronics, robotics, automation and sensors to disseminate their latest research results and exchange views on the future research directions of these fields. The topics of interest include, but not limited to the following: ·Intelligent mechatronics, robotics, biomimetics, automation and control systems ·opto⁃electronic elements and Materials, laser technology and laser processing ·Elements, structures, mechanisms, and applications of micro and nano systems ·Teleoperation, telerobotics, haptics, and teleoperated semi⁃autonomous systems ·Sensor design, multi⁃sensor data fusion algorithms and wireless sensor networks ·Biomedical and rehabilitation engineering, prosthetics and artificial organs ·Control system modeling and simulation techniques and methodologies ·AI, intelligent control, neuro⁃control, fuzzy control and their applications ·ndustrial automation, process control, manufacturing process and automation Website: http: / / 2014.ieee⁃icma.org / ·348· 智 能 系 统 学 报 第 8 卷