
生物信息字 普通高等教育 “十二五”规划教材 生物信息学 Bioinformatics 。。 第十二章:第二代测序技术 及其应用 Sequence 2.0
第十二章:第二代测序技术 及其应用 普通高等教育 “十二五”规划教材 生物信息学 Bioinformatics Sequence 2.0

Web 2.0 Coined by Darcy DiNucci in 1999. Resurface in 2003. 2004,O'Reilly Media and MediaLive hosted the first Web 2.0 conference. Examples of Web 2.0 include web-based communities, hosted services,web applications,social-networking sites,video-sharing sites,wikis,blogs,mashups and folksonomies.A Web 2.0 site allows its users to interact with other users or to change website content,in contrast to non-interactive websites where users are limited to the passive viewing of information that is provided to them. Ajax/Flash/Flex etc
Web 2.0 Coined by Darcy DiNucci in 1999. Resurface in 2003. 2004, O'Reilly Media and MediaLive hosted the first Web 2.0 conference. Examples of Web 2.0 include web-based communities, hosted services, web applications, social-networking sites, video-sharing sites, wikis, blogs, mashups and folksonomies. A Web 2.0 site allows its users to interact with other users or to change website content, in contrast to non-interactive websites where users are limited to the passive viewing of information that is provided to them. Ajax/Flash/Flex etc

Web 2.0 Meme Map Fllckr.del.iclo.us: PageRank. Blogs:Participation. BItTorrent Tagging. eBayre0pu的on, Not publishing Amazon revews:user Radical Decentr阳2aton not taxpnomy as contributor Gmall,Google Google AdSense: Maps and AIAX: customer self-servoe Wiklpedia: Rich User Experences enabling the long tall Radical Trust Strategic Positioning: The Wob as Platform User Posltioning: "An amtude,not You control your own data Trust your users a technology Core Competencles: Services,not packaged software Architecture of Particlpatlon Cost-effective scalablllty Small Pleces The Long Tail Remlxable data source and data transformations Loosely Joined Sottware abovo the lovel of a single device (web as components) Harnessing collective intelligence Data as the "intel Inside" Sofware that gets Rich User Experlence The perpetual beta better Play the more people use it Granular Addressabllty The Right to Remix Emergent:User of content Hackability behavor not Some rights reserved" predetermined
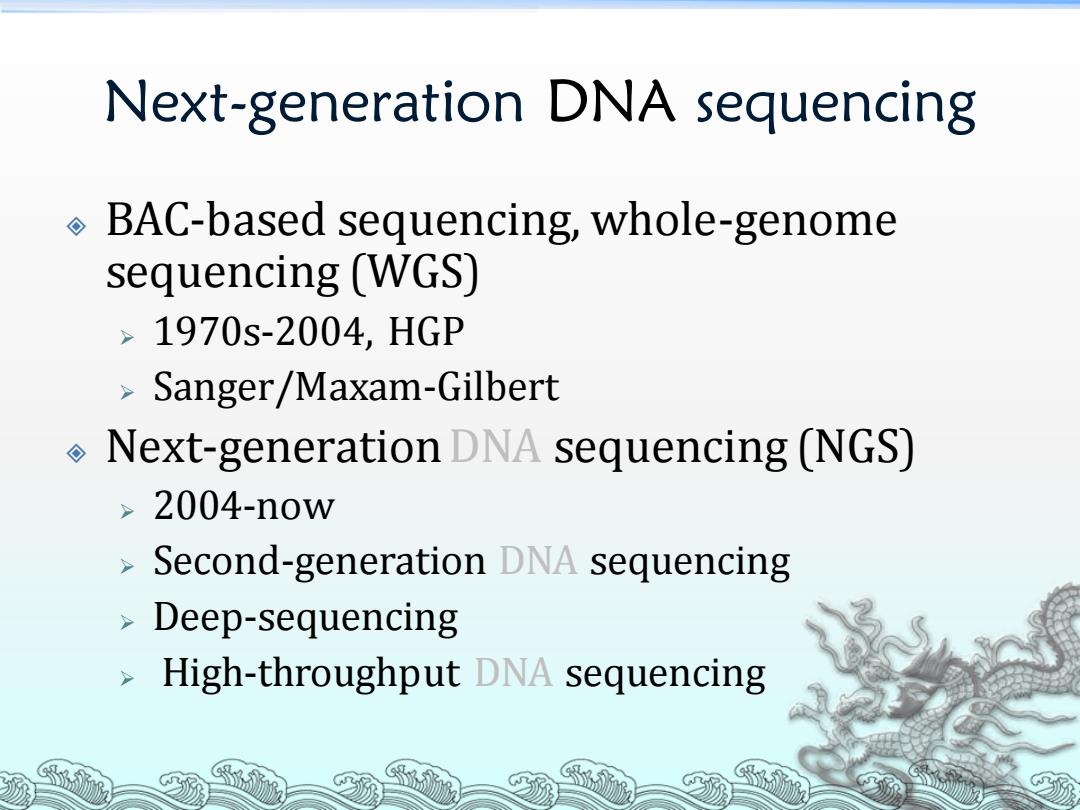
Next-generation DNA sequencing BAC-based sequencing,whole-genome sequencing (WGS) >1970s-2004,HGP Sanger/Maxam-Gilbert Next-generation DNA sequencing (NGS) >2004-now Second-generation DNA sequencing Deep-sequencing High-throughput DNA sequencing
Next-generation DNA sequencing BAC-based sequencing, whole-genome sequencing (WGS) ➢ 1970s-2004, HGP ➢ Sanger/Maxam-Gilbert Next-generation DNA sequencing (NGS) ➢ 2004-now ➢ Second-generation DNA sequencing ➢ Deep-sequencing ➢ High-throughput DNA sequencing
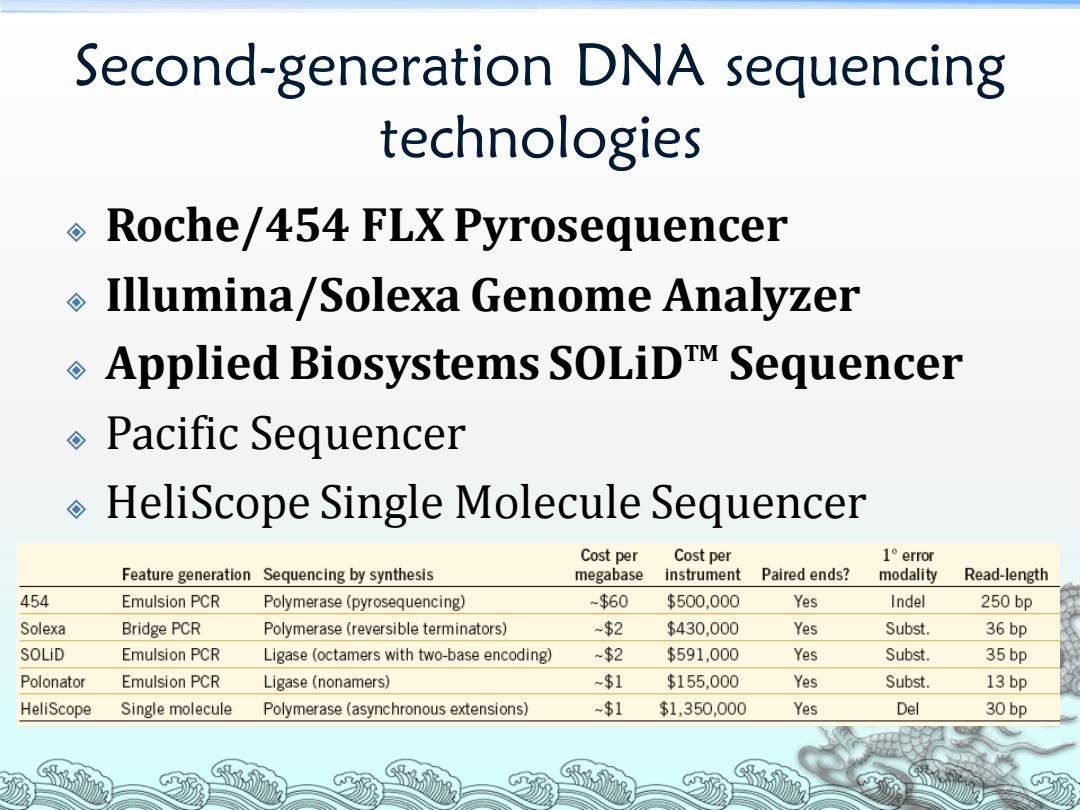
Second-generation DNA sequencing technologies Roche/454 FLX Pyrosequencer Illumina/Solexa Genome Analyzer Applied Biosystems SOLiDTM Sequencer Pacific Sequencer HeliScope Single Molecule Sequencer Cost per Cost per 1°error Feature generation Sequencing by synthesis megabase instrument Paired ends? modality Read-length 454 Emulsion PCR Polymerase(pyrosequencing) -$60 $500.000 Yes Indel 250bp Solexa Bridge PCR Polymerase (reversible terminators) -$2 $430.000 Yes Subst. 36bp SOLiD Emulsion PCR Ligase (octamers with two-base encoding) -$2 $591,000 Yes Subst. 35 bp Polonator Emulsion PCR Ligase(nonamers) -$1 $155.000 Yes Subst. 13bp HeliScope Single molecule Polymerase (asynchronous extensions) -$1 $1,350,000 Yes Del 30 bp
Second-generation DNA sequencing technologies Roche/454 FLX Pyrosequencer Illumina/Solexa Genome Analyzer Applied Biosystems SOLiDTM Sequencer Pacific Sequencer HeliScope Single Molecule Sequencer

DNA library preparation 4.5 hours Ligation .Genome fragmented by nebulization Selection .No cloning;no colony (isolate AB picking Emulsion PCR 8 hours Sequencing 7.5 hours .Well diameter:average of 44 um .400,000 reads obtained in parallel .A single cloned amplified sstDNA bead is deposited per well Amplified sstDNA library beads Quality filtered bases
Roche/454 FLX Pyrosequencer
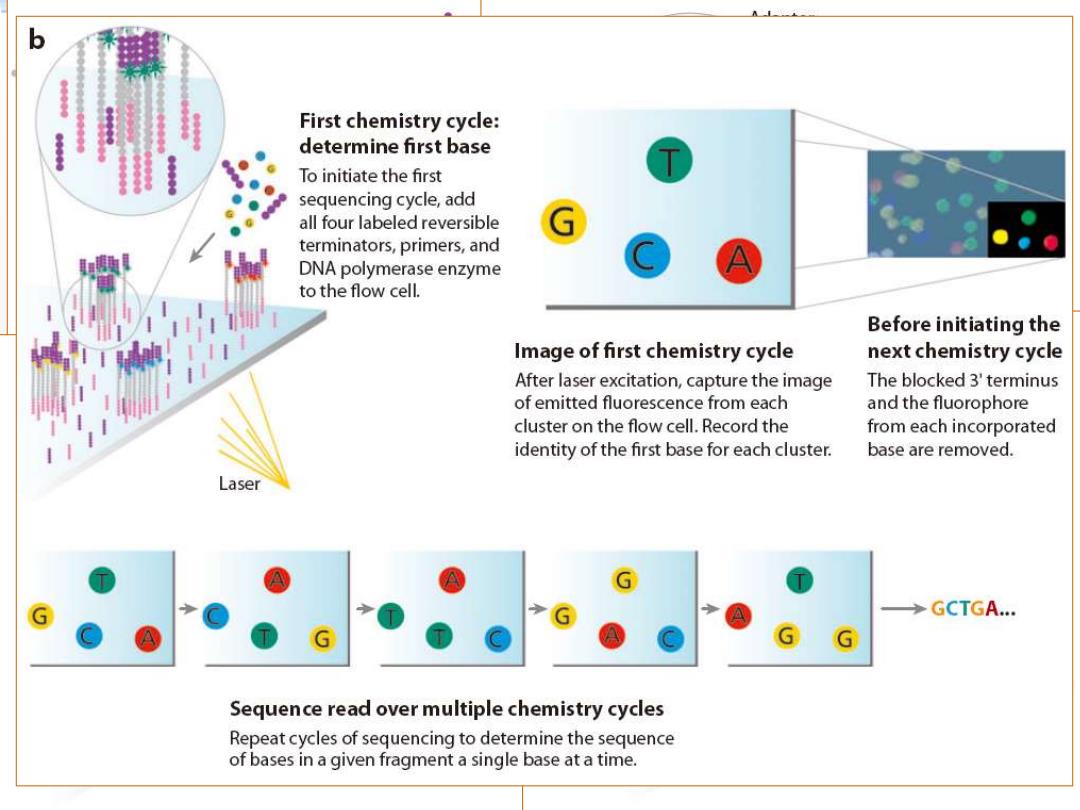
First chemistry cycle: determine first base To initiate the first sequencing cycle,add all four labeled reversible terminators,primers,and DNA polymerase enzyme to the flow cell. Before initiating the Image of first chemistry cycle next chemistry cycle After laser excitation,capture the image The blocked 3'terminus of emitted fluorescence from each and the fluorophore cluster on the flow cell.Record the from each incorporated identity of the first base for each cluster. base are removed. Laser GCTGA... A Sequence read over multiple chemistry cycles Repeat cycles of sequencing to determine the sequence of bases in a given fragment a single base at a time
Illumina Genome Analyzer

8.Repeat Reset with,n-2,n-3,n-4 primers Read position o1234s67so23141shd7lh8l12o2222242s222o到24 1 Universal seq primer (n) 3' Possible dinucleotides encoded by each color puno 2 Universal seq primer(n-1) 2nd base 3' Template sequence A C G 3 Universal seq primer(n-2) 3'm Bridge probe ●● 4 Universal seq primer (n-3) Bridge probe AT AC AA GA 3'i CA CC TC 5 Universal seq primer (n-4) C GT GG ● 3' Bridge probe TG TT T Indicates positions of interrogation Data collection and image analysis Collect Identif Double interrogation color image beads With 2 base encoding each base is defined twice T←G←G← A Collect color image Decoding Color space sequence Identify Identify TA AC AA GA bead color beads GC CA TC Possible dinucleotides CG GT GG AG Glass slide Base zero. ATXTG TT CT AT TG GG GA Decoded sequence Color space for Y IY this sequence AT G GA Base space sequence
Applied Biosystems SOLiDTM Sequencer

Applications of NGS Category Examples of applications Complete genome resequencing Comprehensive polymorphism and mutation discovery in individual human genomes Reduced representation sequencing Large-scale polymorphism discovery Targeted genomic resequencing Targeted polymorphism and mutation discovery Paired end sequencing Discovery of inherited and acquired structural variation Metagenomic sequencing Discovery ofinfectious and commensal flora RNA-Seq Deep-sequencing shotgun libraries derived from mRNA/small RNAs.microRNA profiling/splice junctions/transcript boundaries/structural rearrangements/copy number variation DNA methylation Determining patterns of cytosine methylation in genomic DNA,large-scale analysis of DNA methylation,by deep sequencing of bisulfite-treated DNA Chromatin immunoprecipitation- Genome-wide mapping of protein-DNA interactions,by deep sequencing(ChIP-Seq) sequencing of DNA fragments pulled down by ChIP. Nuclease fragmentation and Nucleosome positioning sequencing Molecular barcoding Multiplex sequencing of samples from multiple individuals
Applications of NGS Category Examples of applications Complete genome resequencing Comprehensive polymorphism and mutation discovery in individual human genomes Reduced representation sequencing Large-scale polymorphism discovery Targeted genomic resequencing Targeted polymorphism and mutation discovery Paired end sequencing Discovery of inherited and acquired structural variation Metagenomic sequencing Discovery of infectious and commensal flora RNA-Seq Deep-sequencing shotgun libraries derived from mRNA/small RNAs. microRNA profiling/splice junctions/transcript boundaries/structural rearrangements/copy number variation DNA methylation Determining patterns of cytosine methylation in genomic DNA , large-scale analysis of DNA methylation, by deep sequencing of bisulfite-treated DNA Chromatin immunoprecipitation– sequencing (ChIP-Seq) Genome-wide mapping of protein-DNA interactions, by deep sequencing of DNA fragments pulled down by ChIP. Nuclease fragmentation and sequencing Nucleosome positioning Molecular barcoding Multiplex sequencing of samples from multiple individuals

We are interested in .. mRNA/small RNA analyses (RNA-Seq) Analysis of mRNA targets of miRNA/siRNA Epigenetic analyses (ChIP-Seq)
We are interested in … mRNA/small RNA analyses (RNA-Seq) Analysis of mRNA targets of miRNA/siRNA Epigenetic analyses (ChIP-Seq)