
Chapter 6 DECISION MAKING: DROB BI NS ACOULTER THE ESSENCE OF THE MANAGER'S JOB ©Prentice Hall,.2002 6-1
Chapter 6 DECISION MAKING: THE ESSENCE OF THE MANAGER’S JOB © Prentice Hall, 2002 6-1

Learning Objectives You should learn to: -Outline the steps in the decision-making process Explain why decision making is so pervasive in organizations Describe the rational decision maker Contrast the perfectly rational and boundedly rational approaches to decision making Explain the role that intuition plays in the decision-making process ©Prentice Hal,2002 6-2
Learning Objectives You should learn to: – Outline the steps in the decision-making process – Explain why decision making is so pervasive in organizations – Describe the rational decision maker – Contrast the perfectly rational and boundedly rational approaches to decision making – Explain the role that intuition plays in the decision-making process © Prentice Hall, 2002 6-2

Learning Objectives (cont. You should learn to: Identify the two types of decision problems and the two types of decisions that are used to solve them Differentiate the decision conditions of certainty. risk,and uncertainty Describe the different decision-making styles ©Prentice Hall,.2002 6-3
Learning Objectives (cont.) You should learn to: – Identify the two types of decision problems and the two types of decisions that are used to solve them – Differentiate the decision conditions of certainty, risk, and uncertainty – Describe the different decision-making styles © Prentice Hall, 2002 6-3

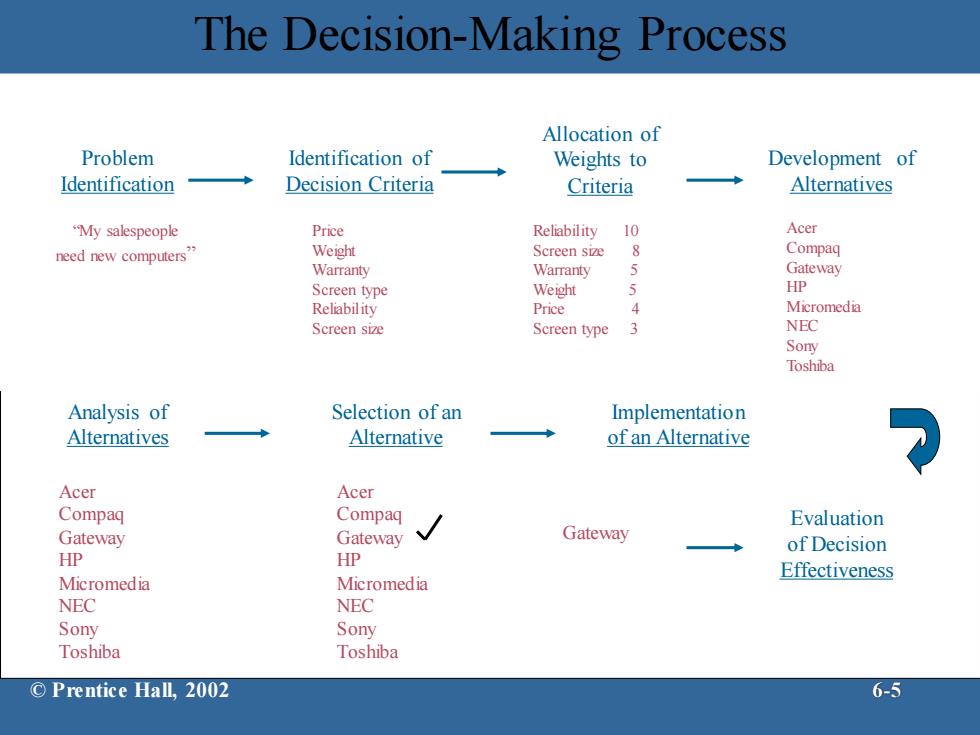
Decision Making Decisions choices from two or more alternatives all organizational members make decisions Decision-Making Process a comprehensive,8-step process Step I-Identifying a Problem problem-discrepancy between an existing and a desired state of affairs -must be such that it exerts pressure to act manager is unlikely to characterize a situation as a problem unless s/he has resources necessary to act ©Prentice Hall,.2002 6-4
Decisions – choices from two or more alternatives – all organizational members make decisions Decision-Making Process – a comprehensive, 8-step process – Step 1 - Identifying a Problem • problem - discrepancy between an existing and a desired state of affairs –must be such that it exerts pressure to act –manager is unlikely to characterize a situation as a problem unless s/he has resources necessary to act Decision Making © Prentice Hall, 2002 6-4
The Decision-Making Process Allocation of Problem Identification of Weights to Development of Identification Decision Criteria Criteria Alternatives "My salespeople Price Reliability 10 Acer need new computers” Weight Screen size 8 Compaq Warranty Warranty 5 Gateway Screen type Weight 5 HP Reliability Price 4 Micromedia Screen size Screen type 3 NEC Sony Toshiba Analysis of Selection of an Implementation Alternatives Alternative of an Alternative Acer Acer Compaq Compaq Evaluation Gateway Gateway Gateway of Decision HP HP Micromedia Micromedia Effectiveness NEC NEC Sony Sony Toshiba Toshiba ©Prentice Hall,2002 6-5
The Decision-Making Process Problem Identification “My salespeople need new computers” Identification of Decision Criteria Price Weight Warranty Screen type Reliability Screen size Allocation of Weights to Criteria Reliability 10 Screen size 8 Warranty 5 Weight 5 Price 4 Screen type 3 Development of Alternatives Acer Compaq Gateway HP Micromedia NEC Sony Toshiba Implementation of an Alternative Gateway Evaluation of Decision Effectiveness Analysis of Alternatives Acer Compaq Gateway HP Micromedia NEC Sony Toshiba Selection of an Alternative Acer Compaq Gateway HP Micromedia NEC Sony Toshiba © Prentice Hall, 2002 6-5

Decision Making (cont. Decision-Making Process (cont. Step 2-Identifying Decision Criteria decision criteria-what's relevant in making a decision Step 3-Allocating Weights to the Criteria must weight the criteria to give them appropriate priority in the decision -Step 4-Developing Alternatives list the viable alternatives that could resolve the problem without evaluating them Step 5-Analyzing Alternatives each alternative is evaluated against the criteria ©Prentice Hall,2002 6-6
Decision-Making Process (cont.) – Step 2 - Identifying Decision Criteria • decision criteria - what’s relevant in making a decision – Step 3 - Allocating Weights to the Criteria • must weight the criteria to give them appropriate priority in the decision – Step 4 - Developing Alternatives • list the viable alternatives that could resolve the problem without evaluating them – Step 5 - Analyzing Alternatives • each alternative is evaluated against the criteria Decision Making (cont.) © Prentice Hall, 2002 6-6

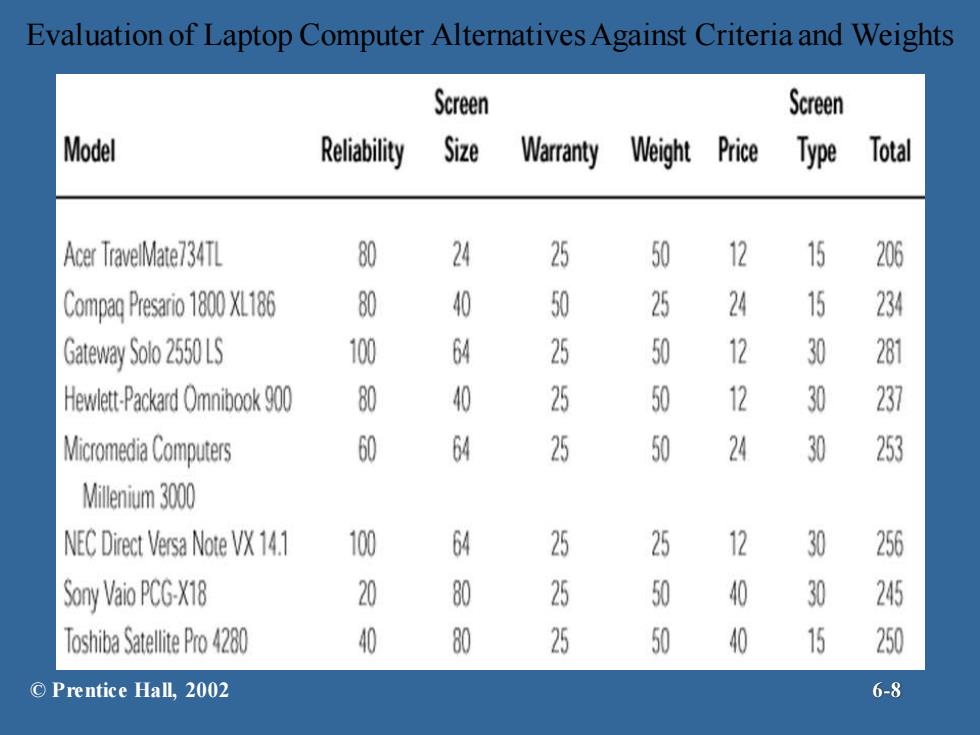
Assessed Values of Notebook Computer Alternatives Against Decision Criteria Screen Screen Model Reliability Size Warranty Weight Price Type Acer TraveMate734TL 8 3 5 10 3 5 Compa Psi8XL186 8 5 10 5 6 5 Gateway So 2550LS 10 8 5 10 3 10 Hewlett-Packard Omnibook 900 8 5 5 10 3 10 Micromedia Computers 6 8 5 10 6 10 Milenium30 NEC Direct Versa Note VX 14.1 10 8 5 5 3 10 Sony VaoP℃G-X18 2 10 5 10 10 10 TsaSate2 4 10 5 10 10 5 ©Prentice Hall,2002 6-7
Assessed Values of Notebook Computer Alternatives Against Decision Criteria © Prentice Hall, 2002 6-7
Evaluation of Laptop Computer Alternatives Against Criteria and Weights Screen Screen Model Reliability Size Warranty Weight Price Type Total Acer TravelMate734TL 80 24 25 50 12 15 206 Compa Prsari8XL186 80 40 50 25 24 15 234 Gateway550LS 10 64 25 50 12 30 281 Hewlett-Packard Omib9 80 40 25 50 12 30 237 Micromedia Computers 60 64 25 50 24 30 253 Milenium3 NEC Direct Versa Note VX 14.1 100 64 25 25 12 30 256 m Vai PC-X18 20 80 25 50 40 30 245 oshiba Sateie 428 40 80 25 50 40 15 250 ©Prentice Hall,2002 6-8
Evaluation of Laptop Computer Alternatives Against Criteria and Weights © Prentice Hall, 2002 6-8

Decision Making (cont.) Decision-Making Process (cont.) Step 6-Selecting an Alternative choosing the best alternative from among those considered Step 7-Implementing the Alternative oimpllemmentution conveying the decision to those affected by it and getting their commitment to it participation in decision-making process inclines people to support the decision decision may fail if it is not implemented properly Step 8-Evaluating Decision Effectiveness determine whether the problem is resolved ©Prentice Hall,.2002 6-9
Decision Making (cont.) Decision-Making Process (cont.) – Step 6 - Selecting an Alternative • choosing the best alternative from among those considered – Step 7 - Implementing the Alternative • implementation - conveying the decision to those affected by it and getting their commitment to it – participation in decision-making process inclines people to support the decision – decision may fail if it is not implemented properly – Step 8 - Evaluating Decision Effectiveness • determine whether the problem is resolved © Prentice Hall, 2002 6-9

Decisions in the Management Functions Planning Leading What are thenizatinsn-trm objectives? How do I handle employees who appear to be low What strategies will best achieve those objectives? in motivation? What should the organization's short-term What is the most effective leadership style in a objectives be? given situation? How difficult should individual goals be? How will a specific change affect worker productivity? Organizing When is theright time to stimulate confic? How many employees should I have repor directly Controlling to me? What activities in the organization need to be How much centralization should there be in the controlled? organization? How should those activities be controlled? How should jobs be designed? When is a performance deviation significant? When should the organization implement a What type of management information system different structure? should the organization have? ©Prentice Hall,2002 6-10
Decisions in the Management Functions © Prentice Hall, 2002 6-10