
Chapter 12 HUMAN ROB B I N S COULTER RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM) ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-1
Chapter 12 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT (HRM) © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-1

Learning Objectives You should learn to: Explain the strategic importance of human resource management (HRM) -Describe the HRM process Differentiate between job descriptions and job specifications Contrast recruitment and derecruitment options Describe the selection devices that work best with various kinds of jobs ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-2
Learning Objectives You should learn to: – Explain the strategic importance of human resource management (HRM) – Describe the HRM process – Differentiate between job descriptions and job specifications – Contrast recruitment and derecruitment options – Describe the selection devices that work best with various kinds of jobs © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-2

Learning Objectives (cont.) You should learn to: Identify the various training categories Explain the various approaches to performance appraisal -Describe what an organization's compensation system should include -Discuss the current issues affecting HRM ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-3
Learning Objectives (cont.) You should learn to: – Identify the various training categories – Explain the various approaches to performance appraisal – Describe what an organization’s compensation system should include – Discuss the current issues affecting HRM © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-3

Why HRM Is Important All Managers Must Engage in Some HRM Activities -interview job candidates orient new employees evaluate work performance HRM Policies and Practices Have a Positive Impact on Performance -high performance work practices commit to improving knowledge and skills ·increase motivation retain quality employees encourage nonperformers to leave ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-4
Why HRM Is Important All Managers Must Engage in Some HRM Activities – interview job candidates – orient new employees – evaluate work performance HRM Policies and Practices Have a Positive Impact on Performance – high performance work practices • commit to improving knowledge and skills • increase motivation • retain quality employees • encourage nonperformers to leave © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-4

Examples of High-Performance Work Practices Self-directed work teams Implementation of employee suggestions 。Job rotation oingent pay basedn performance High levels of skills training Coaching and mentoring Problem-solving groups Sinificant amounts of information sharing Total quality management procedures and Use of employee attitude surveys processes Cross-functional integration Encouragement of innovative and creative behavior Comprehensive employee ritmntand Extensive employe involvement and training selection procedures Se:Basedn M.Huselid.The Impact of Human Resoue Management Practicesn Tumover,Prodctivity. and Corporate Financial Performance.Academyf Managemental,ne 995.p.635;and B.Becker and B.Gerhart,The mpact of Human Resource Managemetranizational Performance:Progress and Prospects,"Academy of Managementof ural.Auqust 1996.p.785 ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-5
Examples of High-Performance Work Practices © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-5

The HRM Process HRM Process 一 necessary for staffing the organization and sustaining high employee performance identify and select competent employees provide up-to-date knowledge and skills retain competent,high performing employees influenced by the external environment labor ion-represents workers and protects their interests through collective bargaining HRM decisions regulated by the terms of collective agreements ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-6
The HRM Process HRM Process – necessary for staffing the organization and sustaining high employee performance • identify and select competent employees • provide up-to-date knowledge and skills • retain competent, high performing employees – influenced by the external environment – labor union - represents workers and protects their interests through collective bargaining • HRM decisions regulated by the terms of collective agreements © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-6
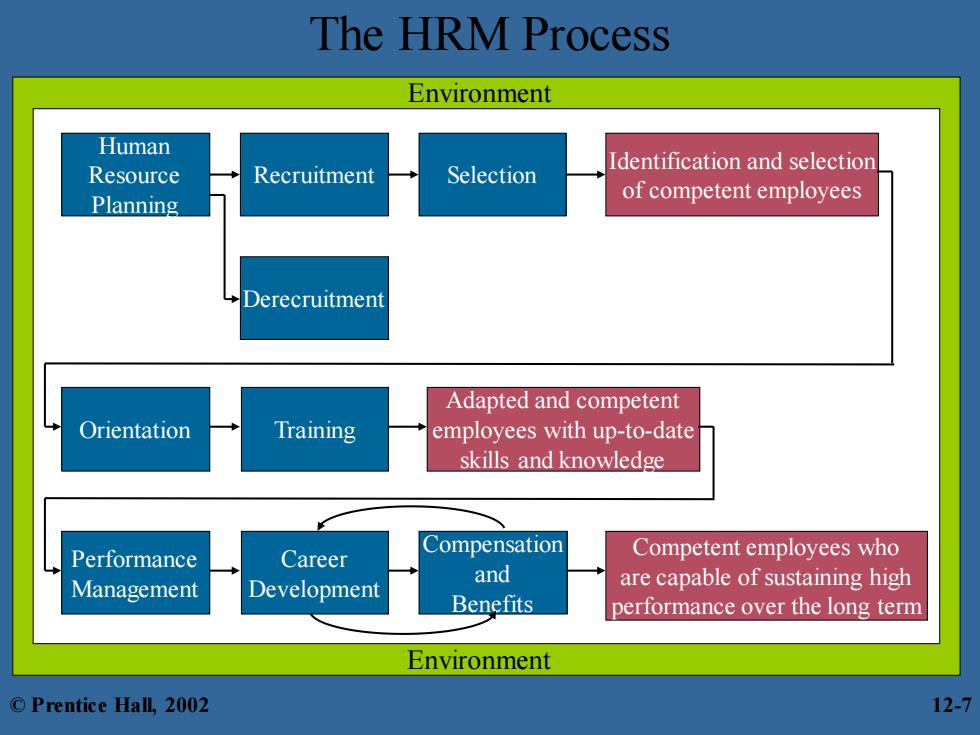
The HRM Process Environment Human Resource Identification and selection Recruitment Selection Planning of competent employees Derecruitment Adapted and competent Orientation Training employees with up-to-date skills and knowledge Performance Career Compensation Competent employees who and Management Development are capable of sustaining high Benefits performance over the long term Environment ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-7
The HRM Process Compensation and Benefits Career Development Performance Management Human Resource Planning Recruitment Derecruitment Selection Identification and selection of competent employees Orientation Training Adapted and competent employees with up-to-date skills and knowledge Competent employees who are capable of sustaining high performance over the long term Environment Environment © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-7

The HRM Process (cont. HRM Process (cont.) expanding influence of federal regulations to assure equal employment opportunities gtirmaive action-ensures that decisions and practices enhance the employment,upgrading, and retention of members from protected groups organization: -refrains from discrimination actively seeks to enhance the status of members of protected groups ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-8
The HRM Process (cont.) HRM Process (cont.) – expanding influence of federal regulations to assure equal employment opportunities – affirmative action - ensures that decisions and practices enhance the employment, upgrading, and retention of members from protected groups • organization: –refrains from discrimination –actively seeks to enhance the status of members of protected groups © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-8

Major U.S.Federal Laws and Regulations Related to HRM Year Law or Regulation Description 1963 Equal Pay Act Prohibits pay differences based on sex for equal work 1964 Civil Rights Act,Title Vll Prohibits discrimination based on race,color,religion. (amended in 1972) national origin,or sex 1967 Age Discrimination in Prohibits age discrimination against employees between Employment Act 40 and 65 years of age 1973 Vocational Rehabilitation Act Prohibits discrimination on the basis of physical or mental disabilities 1974 Privacy Act Gives employees the legal right to examine personnel files and letters of reference concerning them 1978 Mandatory Retirement Act Prohibits the forced retirement of most employees before the age of 70:upper limit on age was removed in 1986 1986 Immigration Reform and Prohibits unlawful employment of aliens and unfair Control Act immigration-related employment practices 1988 Polygraph Protection Act Limits an employer's ability to use lie detectors 1988 Worker Adjustment and Requires employers with 100 or more employees to provide Retraining Notification Act 60 days'notice before a facility closing or mass layoff 1990 Americans with Disabilities Act Prohibits employers from discriminating against individuals with physical or mental disabilities or the chronically ill;also requires organizations to reasonably accommodate these individuals 1991 Civil Rights Act of 1991 Reaffirms and tightens prohibition of discrimination: permits individuals to sue for punitive damages in cases of international discrimination 1993 Family and Medical Leave Act Permit employees in organizations with 50 or more of1993 workers to take up to 12 weeks of unpaid leave each year for family or medical reasons ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-9
Major U.S. Federal Laws and Regulations Related to HRM © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-9

Human Resource Planning Ensures: that organization has the right number and kind of people in the right places and at the right time employees are capable of effectively and efficiently performing their assigned tasks Current Assessment -human resource inventory-review of organization's human resource status sophisticated databases contain background information on each employee ©Prentice Hall,2002 12-10
Human Resource Planning Ensures: – that organization has the right number and kind of people in the right places and at the right time – employees are capable of effectively and efficiently performing their assigned tasks Current Assessment – human resource inventory - review of organization’s human resource status • sophisticated databases contain background information on each employee © Prentice Hall, 2002 12-10