
management ninth edition STEPHEN P.ROBBINS MARY COULTER Chapter Introduction to Management and Organizations Rag7erameh,1nc PEARSON PowopolaBUang义GttAeSoat
ninth edition STEPHEN P. ROBBINS STEPHEN P. ROBBINS MARY COULTER MARY COULTER Chapter Introduction to 1 Management and Organizations PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook The University of West Alabama © 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved

LEARNING OUTLINE Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. Who Are Managers? Explain how managers differ from non-managerial employees. Describe how to classify managers in organizations. What Is Management? ·Define management. Explain why efficiency and effectiveness are important to management. 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 1-2
LEARNING OUTLINE L E A R N I N G O U T L I N E Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. Who Are Managers? • Explain how managers differ from non Explain how managers differ from non-managerial managerial employees. • Describe how to classify managers in organizations. What Is Management? • Define management. • Explain why efficiency and effectiveness are important to management. © 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–2

LEARNING OUTLINE (cont'd) Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. What Do Managers Do? Describe the four functions of management. Explain Mintzberg's managerial roles. Describe Katz's three essential managerial skills and how the importance of these skills changes depending on managerial level. Discuss the changes that are impacting managers'jobs. Explain why customer service and innovation are important to the manager's job. 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 1-3
L E A R N I N G O U T L I N E (cont L E A R N I N G O U T L I N E (cont d) (cont d) ’ Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. What Do Managers Do? • Describe the four functions of management. • Explain Mintzberg’s managerial roles. • Describe Katz’s three essential managerial skills and how the importance of these skills changes depending on managerial level. • Discuss the changes that are impacting managers’ jobs Discuss Discuss the changes changes that are impacting impacting managers’ managers’ jobs. • Explain why customer service and innovation are important important to the manager important to the manager s manager s’ job. © 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–3

LEARNING OUTLINE (cont'd) Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. What Is An Organization? Describe the characteristics of an organization. Explain how the concept of an organization is changing Why Study Management? Explain the universality of management concept. Discuss why an understanding of management is important. Describe the rewards and challenges of being a manager. 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 1-4
L E A R N I N G O U T L I N E (cont L E A R N I N G O U T L I N E (cont d) (cont d) ’ Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. What Is An Organization? • Describe the characteristics of an organization. • Explain how the concept of an organization is changing. Wh yy g Stud y Mana gement? • Explain the universality of management concept. • Discuss why an understanding of management is Discuss Discuss why an understanding understanding of management management is important. • Describe the rewards and challen Describe the rewards and challen g gg es of bein es of bein g a mana ger. © 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–4

Who Are Managers? 。Manager >Someone who coordinates and oversees the work of other people so that organizational goals can be accomplished. 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 1-5
Who Are Managers? • Manager ¾S h di t d th k f Someone w omeone who coordinates and oversees oversees the work of other people so that organizational goals can be accomplished. © 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–5

Classifying Managers First-line Managers >Individuals who manage the work of non-managerial employees. ·Middle Managers >Individuals who manage the work of first-line managers. 。Top Managers >Individuals who are responsible for making organization-wide decisions and establishing plans and goals that affect the entire organization. 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 1-6
Classif Classifyg g in Managers • First-line Managers line Managers ¾I di id l h th k f Individuals who manage o manage the work of non-manager manageri l a employees. • Middl M Middle Managers ¾Individuals who manage the work of first Individuals who manage the work of first-line managers. • Top Managers ¾Individuals who are responsible for making organization organization-wide decisions and establishing plans wide decisions and establishing plans and goals that affect the entire organization and goals that affect the entire organization organization. © 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–6
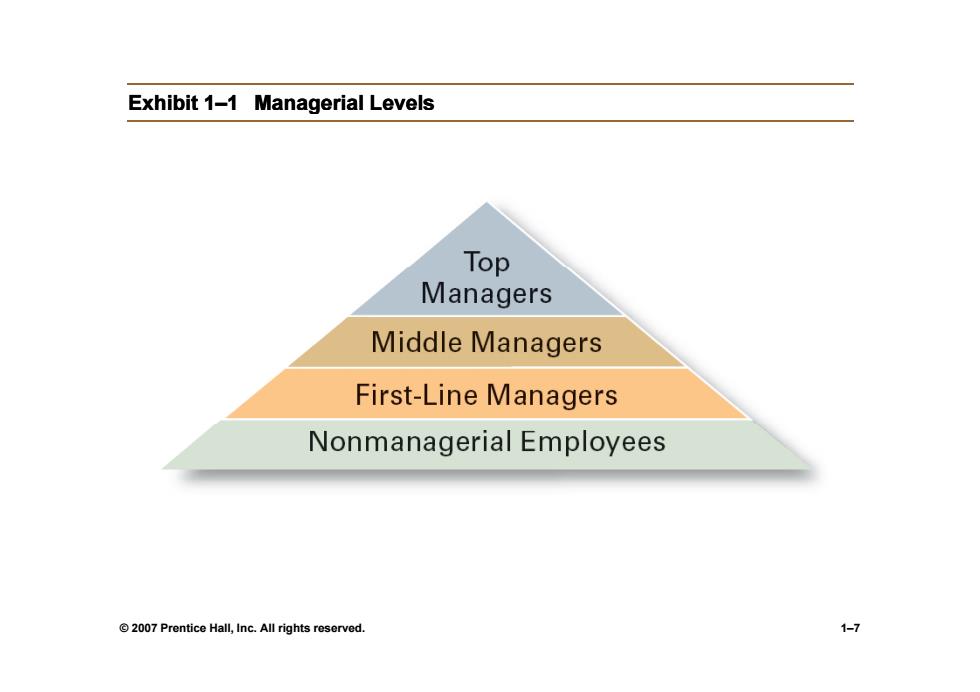
Exhibit 1-1 Managerial Levels Top Managers Middle Managers First-Line Managers Nonmanagerial Employees 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 1-7
Exhibit 1 Exhibit 1–1 Managerial Levels © 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–7

What Is Management? ·Managerial Concerns >Efficiency g“Doing things right'" -Getting the most output for the least inputs >Effectiveness g“Doing the right things” -Attaining organizational goals 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 1人8
What Is Mana gement? • Managerial Concerns ¾Effi i c ency “Doing things right” – Getting the most output Getting Getting the most output for the least inputs ¾Effectiveness “Doing the right things” – Attaining organizational goals © 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–8

Exhibit 1-2 Effectiveness and Efficiency in Management Efficiency (Means) Effectiveness(Ends) Resource Goal Usage Attainment Low Waste High Attainment Management Strives for: Low Resource Waste (high efficiency) High Goal Attainment(high effectiveness) 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 1-9
Exhibit 1 Exhibit 1–2 Effectiveness and Efficienc Effectiveness and Efficiency g in Management © 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–9

What Do Managers Do? ·Functional Approach >Planning Defining goals,establishing strategies to achieve goals, developing plans to integrate and coordinate activities. >Organizing Arranging and structuring work to accomplish organizational goals. >Leading Working with and through people to accomplish goals. >Controlling Monitoring,comparing,and correcting work. 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 1-10
What Do Managers Do? • Functional Approach ¾Pl i ann ng Defining goals, establishing strategies to achieve goals, developing developing plans to integrate and coordinate activities. developing plans to integrate integrate and coordinate coordinate activities. activities. ¾Organizing Arrangg g p g ing and structurin and structuring work to accom work to accomplish or lish organizational anizational goals. ¾Leading Working with and through people to accomplish goals. ¾Controlling M it i i d ti k Monitoring, compar ng, comparing, and correcting work. © 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 1–10