
management ninth edition STEPHEN P.ROBBINS MARY COULTER Chapter 16 Motivating Employees 第16章 激励员工 PEARSON 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc. PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook All rights reserved. The University of WestAlabama
ninth edition STEPHEN P. ROBBINS PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook The University of West Alabama MARY COULTER © 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Motivating Employees 激励员工 Chapter 16 第16章

LEARNING OUTLINE 要点概览 Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. 当你阅读和学习本章时根据这些要点概览来学 What Is Motivation? 什么是动机 。Define motivation. 。 动机的定义 Explain motivationas a need-satisfying process. ·解释动机作为满足需要的过程 Early Theories of Motivation 早期的动机理论 Describe Maslow's hierarchy of needs and how it can be used to motivate. ·描述马斯洛需要层次理论以及这一理论以及如何用它来进行激励 Discusshow Theory X and Theory Y managers approach motivation. ·讨论根据X理论和Y理论,管理者如何实现员工激励 Describe Herzberg's motivation-hygiene theory. ·讨论赫茨伯格的激励保健理论 Explain Herzberg's views of satisfaction and dissatisfaction. ·解释赫茨伯格的满意和不满意观 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 16-2
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 16–2 L E A R N I N G O U T L I N E 要点概览 Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. 当你阅读和学习本章时根据这些要点概览来学 What Is Motivation? 什么是动机 • Define motivation. • 动机的定义 • Explain motivation as a need-satisfying process. • 解释动机作为满足需要的过程 Early Theories of Motivation 早期的动机理论 • Describe Maslow’s hierarchy of needs and how it can be used to motivate. • 描述马斯洛需要层次理论以及这一理论以及如何用它来进行激励 • Discuss how Theory X and Theory Y managers approach motivation. • 讨论根据X理论和Y理论,管理者如何实现员工激励 • Describe Herzberg’s motivation-hygiene theory. • 讨论赫茨伯格的激励-保健理论 • Explain Herzberg’s views of satisfaction and dissatisfaction. • 解释赫茨伯格的满意和不满意观

LEARNING OUTLINE (cont'd) 要点概览(续) Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. 当你阅读和学习本章时根据这些要点概览来学 Contemporary Theories of Motivation 当代激励理论 Describe the three needs McClelland proposed as being present in work settings. ·描述麦克里兰提出的工作环境中现存的三种需要 Explain how goal-setting and reinforcement theories explain employee motivation. ·阐述目标设置理论和强化理论是如何解释员工激励的 Describe the job characteristics modelas a way to design motivating jobs. ·描述具有激励作用的工作设计方法-工作特征模型 Discuss the motivation implications of equity theory. ·描述公平理论对员工激励问题的意义 Contrast distributive justice and proceduraljustice. ·比较分配公平和程序公平 Explain the three key linkages in expectancy theory and their role in motivation. ·解释期望理论中的三种关键联系以及它们在激励中的作用 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 16-3
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 16–3 L E A R N I N G O U T L I N E (cont’d) 要点概览(续) Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. 当你阅读和学习本章时根据这些要点概览来学 Contemporary Theories of Motivation 当代激励理论 • Describe the three needs McClelland proposed as being present in work settings. • 描述麦克里兰提出的工作环境中现存的三种需要 • Explain how goal-setting and reinforcement theories explain employee motivation. • 阐述目标设置理论和强化理论是如何解释员工激励的 • Describe the job characteristics model as a way to design motivating jobs. • 描述具有激励作用的工作设计方法-工作特征模型 • Discuss the motivation implications of equity theory. • 描述公平理论对员工激励问题的意义 • Contrast distributive justice and procedural justice. • 比较分配公平和程序公平 • Explain the three key linkages in expectancy theory and their role in motivation. • 解释期望理论中的三种关键联系以及它们在激励中的作用

LEARNING OUTLINE (cont'd) 要点概览(续) Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. 当你阅读和学习本章时根据这些要点概览来学 Current Issues in Motivation 当代动机问题 Describe the cross-cultural challenges of motivation. ·描述激励问题中的跨文化挑战 Discuss the challenges managers face in motivating unique groups of workers. ·讨论管理者在激励新型劳动力时面临的挑战 Describe open-book management,employee recognition, pay-for-performance,and stock option programs. ·描述账目公开管理、员工认可方案、绩效工资方案和股票期权 方案 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 16-4
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 16–4 L E A R N I N G O U T L I N E (cont’d) 要点概览(续) Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. 当你阅读和学习本章时根据这些要点概览来学 Current Issues in Motivation 当代动机问题 • Describe the cross-cultural challenges of motivation. • 描述激励问题中的跨文化挑战 • Discuss the challenges managers face in motivating unique groups of workers. • 讨论管理者在激励新型劳动力时面临的挑战 • Describe open-book management, employee recognition, pay-for-performance, and stock option programs. • 描述账目公开管理、员工认可方案、绩效工资方案和股票期权 方案

What Is Motivation? 什么是动机 ·Motivation ·动机 Is the result of an interaction between the person and a situation;it is not a personal trait. >动机是个人与环境相互作用的产物吗?它是一种内在的个人特质吗? >Is the process by which a person's efforts are energized,directed,and sustained towards attaining a goal. >动机是个人为了实现目标而付出努力的强度、方向和坚持性的过程吗? Energy:a measure of intensity or drive. 。努力:强度或内驱动力指标 Direction:toward organizational goals 。方向:组织目标指向 Persistence:exerting effort to achieve goals. 。坚持性:竭力实现组织目标 Motivation works best when individual needs are compatible with organizational goals. >当个人需要同组织目标相一致时动机可以发挥最大作用 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 16-5
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 16–5 What Is Motivation? 什么是动机 • Motivation • 动机 ➢ Is the result of an interaction between the person and a situation; it is not a personal trait. ➢ 动机是个人与环境相互作用的产物吗?它是一种内在的个人特质吗? ➢ Is the process by which a person’s efforts are energized, directed, and sustained towards attaining a goal. ➢ 动机是个人为了实现目标而付出努力的强度、方向和坚持性的过程吗? ❖ Energy: a measure of intensity or drive. ❖ 努力:强度或内驱动力指标 ❖ Direction:toward organizational goals ❖ 方向:组织目标指向 ❖ Persistence: exerting effort to achieve goals. ❖ 坚持性:竭力实现组织目标 ➢ Motivation works best when individual needs are compatible with organizational goals. ➢ 当个人需要同组织目标相一致时动机可以发挥最大作用

Early Theories of Motivation 早期的动机理论 Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs ·马斯洛的需要层次理论 MacGregor's Theories X and Y ·麦格雷戈的X理论和Y理论 Herzberg's Two-Factor Theory ·赫茨伯格的双因素理论 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 16-6
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 16–6 Early Theories of Motivation 早期的动机理论 • Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs • 马斯洛的需要层次理论 • MacGregor’s Theories X and Y • 麦格雷戈的X理论和Y理论 • Herzberg’s Two-Factor Theory • 赫茨伯格的双因素理论

Early Theories of Motivation 早期的动机理论 Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs Theory ·马斯洛的需要层次理论 Needs were categorized as five levels of lower-to higher-order needs. >需要由低到高可分为五个层次 Individuals must satisfy lower-order needs before they can satisfy higher order needs. ·个人必须在低层次需要得到满足后才能满足高层次需要 Satisfied needs will no longer motivate. ÷已经满足的需要就不再起激励作用 Motivating a person depends on knowing at what level that person is on the hierarchy. 。激励一个人必须要知道他的需要处在什么水平上 >Hierarchy of needs >需要层次 Lower-order (external):physiological,safety 。低级需要(外部因素):生理需要,安全需要 Higher-order (internal):social,esteem,self-actualization 。高级需要(内部因素):社交需要,尊重需要,自我实现需要 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 16-7
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 16–7 Early Theories of Motivation 早期的动机理论 • Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Theory • 马斯洛的需要层次理论 ➢ Needs were categorized as five levels of lower- to higher-order needs. ➢ 需要由低到高可分为五个层次 ❖ Individuals must satisfy lower-order needs before they can satisfy higher order needs. ❖ 个人必须在低层次需要得到满足后才能满足高层次需要 ❖ Satisfied needs will no longer motivate. ❖ 已经满足的需要就不再起激励作用 ❖ Motivating a person depends on knowing at what level that person is on the hierarchy. ❖ 激励一个人必须要知道他的需要处在什么水平上 ➢ Hierarchy of needs ➢ 需要层次 ❖ Lower-order (external): physiological, safety ❖ 低级需要(外部因素):生理需要,安全需要 ❖ Higher-order (internal): social, esteem, self-actualization ❖ 高级需要(内部因素):社交需要,尊重需要,自我实现需要
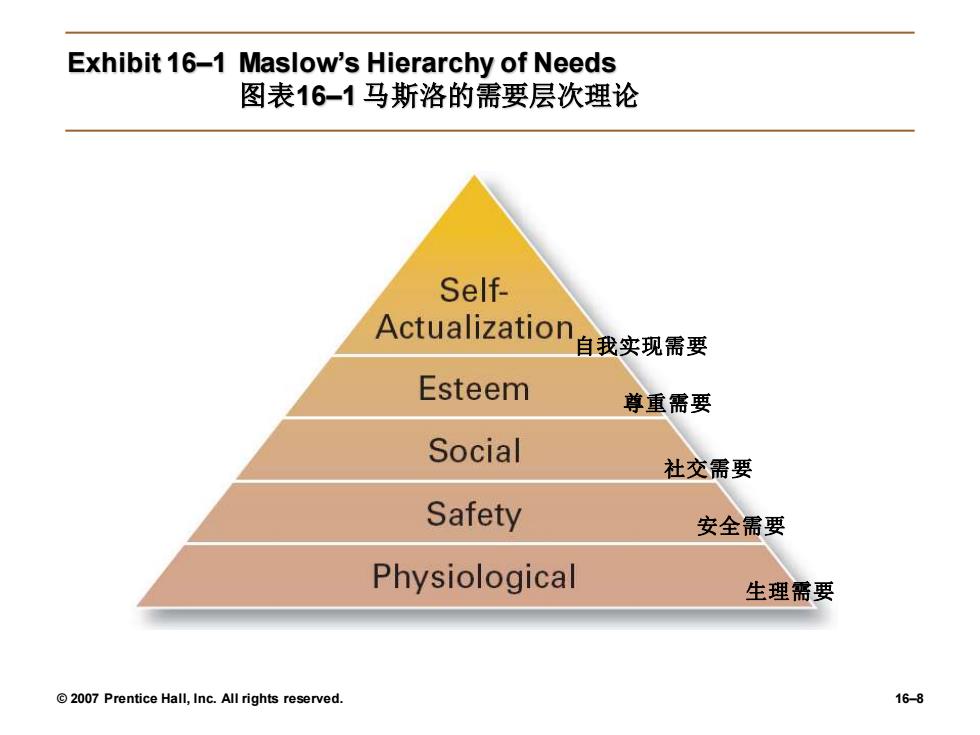
Exhibit 16-1 Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs 图表16-1马斯洛的需要层次理论 Self- Actualization自我实现需要 Esteem 尊重需要 Social 社交需要 Safety 安全需要 Physiological 生理需要 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 16-8
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 16–8 Exhibit 16–1 Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs 图表16–1 马斯洛的需要层次理论 生理需要 安全需要 社交需要 尊重需要 自我实现需要

Early Theories of Motivation(cont'd) 早期动机理论(续) McGregor's Theory X and Theory Y ·麦格雷戈的X理论和Y理论 >Theory X >X理论 Assumes that workers have little ambition,dislike work,avoid responsibility, and require close supervision. 。认为员工没有雄心大志,不喜欢工作,逃避责任,需要严格的监控 >Theory Y >Y理论 Assumes that workers can exercise self-direction,desire responsibility,and like to work. ·认为员工可以自我指导,愿意承担责任并且喜欢工作 >Assumption: >假设: Motivation is maximized by participative decision making,interesting jobs, and good group relations. ÷通过让员工参与决策制定,使工作有趣,良好的工作关系可使激励作用最大化 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 16-9
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 16–9 Early Theories of Motivation (cont’d) 早期动机理论(续) • McGregor’s Theory X and Theory Y • 麦格雷戈的X理论和Y理论 ➢ Theory X ➢ X理论 ❖ Assumes that workers have little ambition, dislike work, avoid responsibility, and require close supervision. ❖ 认为员工没有雄心大志,不喜欢工作,逃避责任,需要严格的监控 ➢ Theory Y ➢ Y理论 ❖ Assumes that workers can exercise self-direction, desire responsibility, and like to work. ❖ 认为员工可以自我指导,愿意承担责任并且喜欢工作 ➢ Assumption: ➢ 假设: ❖ Motivation is maximized by participative decision making, interesting jobs, and good group relations. ❖ 通过让员工参与决策制定,使工作有趣,良好的工作关系可使激励作用最大化

Early Theories of Motivation (cont'd) 早期的动机理论(续) Herzberg's Motivation-Hygiene Theory ·赫茨伯格的激励一保健理论 Job satisfaction and job dissatisfaction are created by different factors. >导致工作满意和工作不满的因素是有不同的因素引起的 Hygiene factors:extrinsic (environmental)factors that create job dissatisfaction. ÷保健因素:外部(环境的)因素引起工作不满 Motivators:intrinsic(psychological)factors that create job satisfaction. ·激励因素:内部(心理的)因素带来工作满意 >Attempted to explain why job satisfaction does not result in increased performance. >试着解释工作满意为什么不能导致绩效增加 The opposite of satisfaction is not dissatisfaction,but rather no satisfaction. ÷满意的对立面不是不满意,而是没有不满意 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 16-10
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 16–10 Early Theories of Motivation (cont’d) 早期的动机理论(续) • Herzberg’s Motivation-Hygiene Theory • 赫茨伯格的激励—保健理论 ➢ Job satisfaction and job dissatisfaction are created by different factors. ➢ 导致工作满意和工作不满的因素是有不同的因素引起的 ❖ Hygiene factors: extrinsic (environmental) factors that create job dissatisfaction. ❖ 保健因素:外部(环境的)因素引起工作不满 ❖ Motivators: intrinsic (psychological) factors that create job satisfaction. ❖ 激励因素:内部(心理的)因素带来工作满意 ➢ Attempted to explain why job satisfaction does not result in increased performance. ➢ 试着解释工作满意为什么不能导致绩效增加 ❖ The opposite of satisfaction is not dissatisfaction, but rather no satisfaction. ❖ 满意的对立面不是不满意,而是没有不满意