
management ninth edition STEPHEN P.ROBBINS MARY COULTER Chapter Decision-Making:The Essence of the Manager's Job 定决策:管理者工作的实 第6章质 PEARSON 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc. PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook All rights reserved. The University of WestAlabama
ninth edition STEPHEN P. ROBBINS PowerPoint Presentation by Charlie Cook The University of West Alabama MARY COULTER © 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. Decision-Making: The Essence of the Manager’s Job 制定决策:管理者工作的实 质 Chapter 6 第6章

LEARNING OUTLINE要点概览 Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. 按如下概要学习本章。 The Decision-Making Process决策制定过程 Define decision and decision-making process. ·定义决策和决策制定过程。 Describe the eight steps in the decision-making process. ·描述决策制定过程的八个步骤。 The Manager as Decision Maker作为决策者的管理者 Discuss the assumptions of rational decision making. ·详述理性决策的假设。 Describe the concepts of bounded rationality,satisficing,and escalation of commitment. ·描述有限理性、满意和承诺升级的概念。 Explain intuitive decision making. ·解释直觉决策。 Contrast programmed and nonprogrammed decisions. ·比较程序化和非程序化决策。 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 6-2
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 6–2 L E A R N I N G O U T L I N E要点概览 Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. 按如下概要学习本章。 The Decision-Making Process决策制定过程 • Define decision and decision-making process. • 定义决策和决策制定过程。 • Describe the eight steps in the decision-making process. • 描述决策制定过程的八个步骤。 The Manager as Decision Maker作为决策者的管理者 • Discuss the assumptions of rational decision making. • 详述理性决策的假设。 • Describe the concepts of bounded rationality, satisficing, and escalation of commitment. • 描述有限理性、满意和承诺升级的概念。 • Explain intuitive decision making. • 解释直觉决策。 • Contrast programmed and nonprogrammed decisions. • 比较程序化和非程序化决策

LEARNING OUTLINE(cont'd)要点概览(续) Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. 按如下概要学习本章。 The Manager as Decision Maker(cont'd)作为决策者的管理者 Contrast the three decision-making conditions. ·比较决策制定的三个条件。 Explain maximax,maximin,and minimax decision choice approaches. ·解释最大最大、最大最小和最小最大三种决策选择的准则。 Describe the four decision making styles. ·描述决策制定的四种风格。 Discuss the twelve decision-making biases managers may exhibit. ·详述管理者可能表现出来的12种决策制定的偏见。 Describe how manager can deal with the negative effects of decision errors and biases. ·描述管理者如何应对决策错误和偏见的负面影响。 Explain the managerial decision-making model. ·解释管理上的决策制定模型。 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 6–3 L E A R N I N G O U T L I N E (cont’d)要点概览 (续) Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. 按如下概要学习本章。 The Manager as Decision Maker (cont’d)作为决策者的管理者 • Contrast the three decision-making conditions. • 比较决策制定的三个条件。 • Explain maximax, maximin, and minimax decision choice approaches. • 解释最大最大、最大最小和最小最大三种决策选择的准则。 • Describe the four decision making styles. • 描述决策制定的四种风格。 • Discuss the twelve decision-making biases managers may exhibit. • 详述管理者可能表现出来的12种决策制定的偏见。 • Describe how manager can deal with the negative effects of decision errors and biases. • 描述管理者如何应对决策错误和偏见的负面影响。 • Explain the managerial decision-making model. • 解释管理上的决策制定模型

LEARNING OUTLINE(cont'd)要点概览(续) Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. 按如下概要学习本章。 Decision Making for Today's World当今世界决策的制定 Explain how managers can make effective decisions in today's world. ·解释在当今世界中管理者如何制定有效决策。 List six characteristics of an effective decision-making process. ·列出有效的决策制定过程的六个特点。 Describe the five habits of highly reliable organizations. ·描述高度可靠性组织的五个特点。 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 6-4
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 6–4 L E A R N I N G O U T L I N E (cont’d)要点概览 (续) Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this chapter. 按如下概要学习本章。 Decision Making for Today’s World当今世界决策的制定 • Explain how managers can make effective decisions in today’s world. • 解释在当今世界中管理者如何制定有效决策。 • List six characteristics of an effective decision-making process. • 列出有效的决策制定过程的六个特点。 • Describe the five habits of highly reliable organizations. • 描述高度可靠性组织的五个特点

Decision Making制定决策 ·Decision决策 >Making a choice from two or more alternatives. >在两个或者更多的方案中做出选择。 ·The Decision-Making Process决策制定过程 >Identifying a problem and decision criteria and allocating weights to the criteria. >识别决策问题和确定决策标准,以及为每个决策标准分配权重。 >Developing,analyzing,and selecting an alternative that can resolve the problem. >开发、分析和选择备选方案,这些方案能够解决问题。 >Implementing the selected alternative.实施备择方案。 >Evaluating the decision's effectiveness.评估决策结果。 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 6-5
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 6–5 Decision Making制定决策 • Decision决策 ➢ Making a choice from two or more alternatives. ➢ 在两个或者更多的方案中做出选择。 • The Decision-Making Process决策制定过程 ➢ Identifying a problem and decision criteria and allocating weights to the criteria. ➢ 识别决策问题和确定决策标准,以及为每个决策标准分配权重。 ➢ Developing, analyzing, and selecting an alternative that can resolve the problem. ➢ 开发、分析和选择备选方案,这些方案能够解决问题。 ➢ Implementing the selected alternative.实施备择方案。 ➢ Evaluating the decision’s effectiveness.评估决策结果
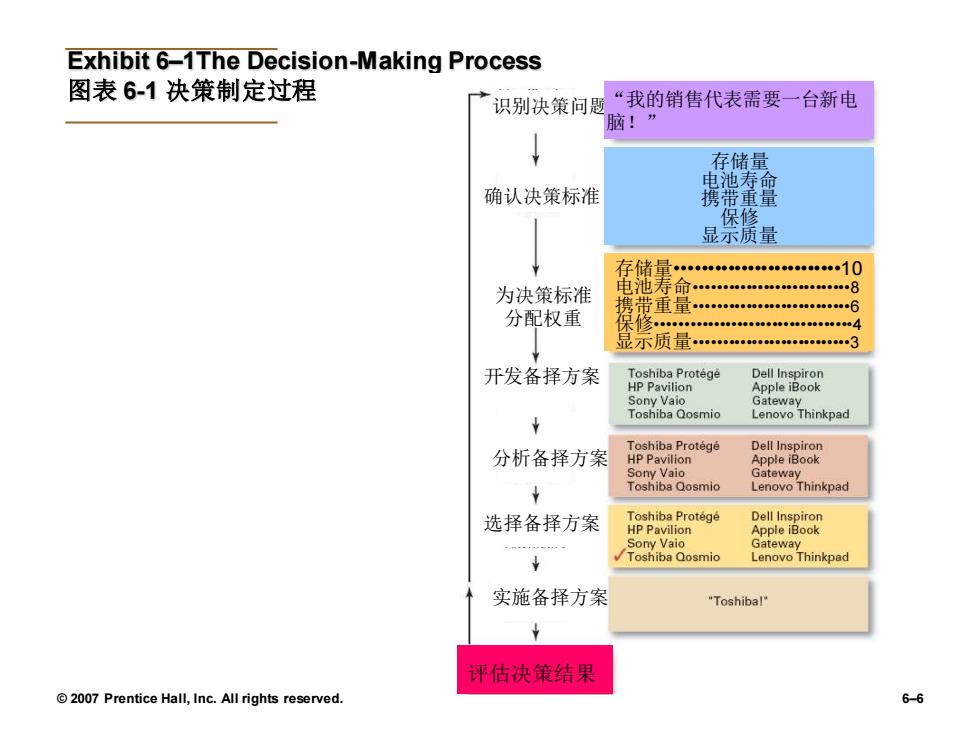
Exhibit 6-1The Decision-Making Process 图表6-1决策制定过程 一识别决策问题“我的销售代表需要一台新电 脑!” ↓ 存储量 电池寿命 确认决策标准 携带重量 保修 显示质量 存储量◆0*快*#快*电华他标。个0 为决策标准 中池寿命nn.8 携带車軍。6 分配权重 公分。●是年垂电。是金垂是品垂年香电量电0单垂是是单每语 显示质量.3 开发备择方案 Toshiba Protege Dell Inspiron HP Pavilion Apple iBook Sony Vaio Gateway Toshiba Qosmio Lenovo Thinkpad Toshiba Protege Dell Inspiron 分析备择方案 HP Pavilion Apple iBook Gateway Lenovo Thinkpad 选择备择方案 Toshiba Protege HP Pavilion e8 omio Gateway Lenovo Thinkpad 实施备择方案 "Toshibal" 评估决策结果 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 6-6
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 6–6 Exhibit 6–1The Decision-Making Process 图表 6-1 决策制定过程 识别决策问题 确认决策标准 为决策标准 分配权重 开发备择方案 分析备择方案 选择备择方案 实施备择方案 评估决策结果 “我的销售代表需要一台新电 脑!” 存储量 电池寿命 携带重量 保修 显示质量 存储量•••••••••••••••••••••••••10 电池寿命•••••••••••••••••••••••••••8 携带重量•••••••••••••••••••••••••••6 保修••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••••4 显示质量•••••••••••••••••••••••••••3

Step 1:Identifying the Problem 步骤1:识别决策问题 ·Problem问题 >A discrepancy between an existing and desired state of affairs.现状与 希望状态之间的差异。 ·Characteristics of Problems问题的特征 >A problem becomes a problem when a manager becomes aware of it. >意识到问题一当管理者意识到一个问题时它才变成了问题 >There is pressure to solve the problem. >迫于压力采取行动。 The manager must have the authority,information,or resources needed to solve the problem. >管理者必须拥有解决问题所需的权利、信息和资源。 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 6-7
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 6–7 Step 1: Identifying the Problem 步骤1:识别决策问题 • Problem问题 ➢ A discrepancy between an existing and desired state of affairs.现状与 希望状态之间的差异。 • Characteristics of Problems问题的特征 ➢ A problem becomes a problem when a manager becomes aware of it. ➢ 意识到问题—当管理者意识到一个问题时它才变成了问题 ➢ There is pressure to solve the problem. ➢ 迫于压力采取行动。 ➢ The manager must have the authority, information, or resources needed to solve the problem. ➢ 管理者必须拥有解决问题所需的权利、信息和资源

Step2:Identifying Decision Criteria步骤2:确认决策标准 Decision criteria are factors that are important(relevant)to resolving the problem. ·决策标准是解决问题的重要因素。 >Costs that will be incurred(investments required) >会引起成本的发生(投资所需) Risks likely to be encountered(chance of failure) >可能会遇到风险(失败的可能) Step 3:Allocating Weights to the Criteria 步骤3:为决策标准分配权重 Decision criteria are not of equal importance: ·决策标准并非都是同等重要的: >Outcomes that are desired (growth of the firm) >渴望得到的结果(公司的成长) >Assigning a weight to each item places the items in the correct priority order of their importance in the decision making process. >为每一个指标分配一个权重,使该指标与其在决策制定过程中的重要性相 匹配。 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 6-8
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 6–8 Step 2: Identifying Decision Criteria步骤2:确认决策标准 • Decision criteria are factors that are important (relevant) to resolving the problem. • 决策标准是解决问题的重要因素。 ➢ Costs that will be incurred (investments required) ➢ 会引起成本的发生(投资所需) ➢ Risks likely to be encountered (chance of failure) ➢ 可能会遇到风险(失败的可能) Step 3: Allocating Weights to the Criteria 步骤3:为决策标准分配权重 • Decision criteria are not of equal importance: • 决策标准并非都是同等重要的: ➢ Outcomes that are desired (growth of the firm) ➢ 渴望得到的结果(公司的成长) ➢ Assigning a weight to each item places the items in the correct priority order of their importance in the decision making process. ➢ 为每一个指标分配一个权重,使该指标与其在决策制定过程中的重要性相 匹配
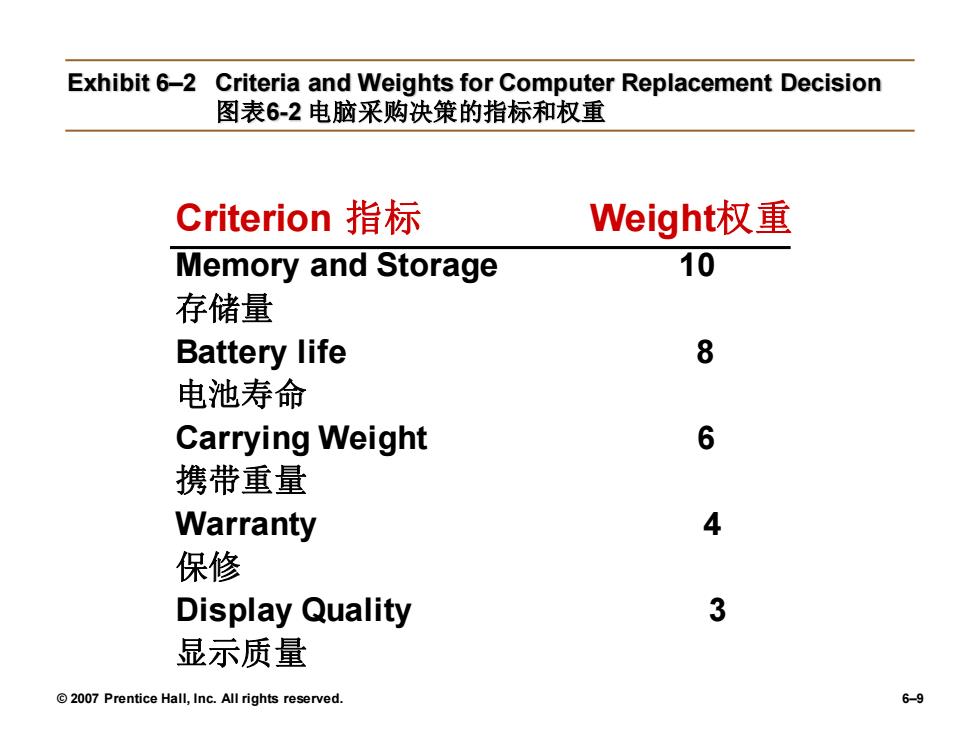
Exhibit 6-2 Criteria and Weights for Computer Replacement Decision 图表62电脑采购决策的指标和权重 Criterion指标 Weight权重 Memory and Storage 10 存储量 Battery life 8 电池寿命 Carrying Weight 6 携带重量 Warranty 4 保修 Display Quality 3 显示质量 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 6-9
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 6–9 Exhibit 6–2 Criteria and Weights for Computer Replacement Decision 图表6-2 电脑采购决策的指标和权重 Criterion 指标 Weight权重 Memory and Storage 10 存储量 Battery life 8 电池寿命 Carrying Weight 6 携带重量 Warranty 4 保修 Display Quality 3 显示质量

Step 4:Developing Alternatives 步骤4:开发备选方案 ·Identifying viable alternatives识别切实可行的备选方案 >Alternatives are listed (without evaluation)that can resolve the problem. >列出可以解决问题的备选方案(无需进行评估) Step 5:Analyzing Alternatives 步骤5:分析备选方案 Appraising each alternative's strengths and weaknesses评估每个方案的优缺点 >An alternative's appraisal is based on its ability to resolve the issues identified in steps 2 and 3. >对一个方案的评估是基于个人处理步骤2和步骤3问题 的能力的。 2007 Prentice Hall,Inc.All rights reserved. 6-10
© 2007 Prentice Hall, Inc. All rights reserved. 6–10 Step 4: Developing Alternatives 步骤4:开发备选方案 • Identifying viable alternatives识别切实可行的备选方案 ➢ Alternatives are listed (without evaluation) that can resolve the problem. ➢ 列出可以解决问题的备选方案(无需进行评估) Step 5: Analyzing Alternatives 步骤5:分析备选方案 • Appraising each alternative’s strengths and weaknesses评估每个方案的优缺点 ➢An alternative’s appraisal is based on its ability to resolve the issues identified in steps 2 and 3. ➢对一个方案的评估是基于个人处理步骤2和步骤3问题 的能力的