
a Chapter 11 MANAGERIAL DROBBI NS E01T10 ACOULTER COMMUNICATION AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY ©Prentice Hall,2002 11-1
Chapter 11 MANAGERIAL COMMUNICATION AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY © Prentice Hall, 2002 11-1

Learning Objectives You should learn to: Explain the barriers to effective interpersonal communication and how to overcome them Contrast the different organizational communication flows and networks Describe two developments in information technology that have had a significant impact on managerial communication -Discuss how information technology affects organizations ©Prentice Hall,2002 11-2
You should learn to: – Explain the barriers to effective interpersonal communication and how to overcome them – Contrast the different organizational communication flows and networks – Describe two developments in information technology that have had a significant impact on managerial communication – Discuss how information technology affects organizations 11-2 © Prentice Hall, 2002 Learning Objectives

Learning Objectives (cont.) You should learn to: -Define communication Explain the interpersonal communication process Describe the factors on which the different communication methods can be evaluated,and on what the choice of communication method depends Tell how nonverbal communication affects managers ©Prentice Hall,.2002 11-3
Learning Objectives (cont.) You should learn to: – Define communication – Explain the interpersonal communication process – Describe the factors on which the different communication methods can be evaluated, and on what the choice of communication method depends – Tell how nonverbal communication affects managers © Prentice Hall, 2002 11-3

Understanding Managerial Communication What is Communication? The transfer and understanding of meaning if no information has been conveyed,communication has not occurred 一 everything that a manager does involves communicating effective communication does not equal agreement ineffective communication is the basis for many managerial problems interpersonall communication occurs between people organizational communication-all the patterns, networks,and systems of communication in an organi☑ation ©Prentice Hall,.2002 11-4
Understanding Managerial Communication What is Communication? – The transfer and understanding of meaning • if no information has been conveyed, communication has not occurred – everything that a manager does involves communicating • effective communication does not equal agreement • ineffective communication is the basis for many managerial problems – interpersonal communication - occurs between people – organizational communication - all the patterns, networks, and systems of communication in an organization © Prentice Hall, 2002 11-4

Process Of Interpersonal Communication Elements of the Process -mexge-expresses the purpose of the communication encoding-converting the message in symbolic form affected by the skills,attitudes,and knowledge of the sender,and by the culture of the organization chaanel-medium for conveying the message decodfing-retranslating symbols into a message affected by personal characteristics of the receiver aoke-disturbances that interfere with the transmission, receipt,or feedback of a message message itself and channel can distort communications feedback also subject to same sources of noise ©Prentice Hal,2002 11-5
Process Of Interpersonal Communication Elements of the Process – message - expresses the purpose of the communication – encoding - converting the message in symbolic form • affected by the skills, attitudes, and knowledge of the sender, and by the culture of the organization – channel - medium for conveying the message – decoding - retranslating symbols into a message • affected by personal characteristics of the receiver – noise - disturbances that interfere with the transmission, receipt, or feedback of a message • message itself and channel can distort communications • feedback also subject to same sources of noise © Prentice Hall, 2002 11-5
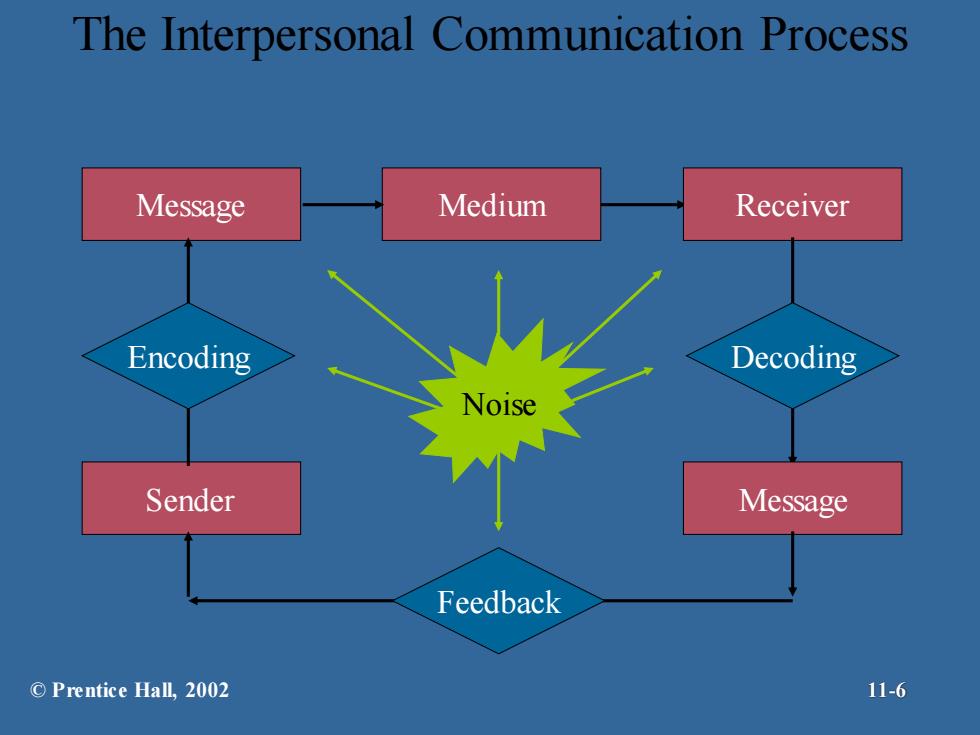
The Interpersonal Communication Process Message Medium Receiver Encoding Decoding Noise Sender Message Feedback ©Prentice Hall,.2002 11-6
The Interpersonal Communication Process Sender Message Medium Receiver Encoding Noise Feedback Message Decoding © Prentice Hall, 2002 11-6

Process Of Interpersonal Communication (cont.) Methods of Communicating Interpersonally -a wide variety of communication methods exist choice of a method should reflect: the needs of the sender the needs of the receiver the attributes of the message the attributes of the channel ©Prentice Hall,2002 11-7
Process Of Interpersonal Communication (cont.) Methods of Communicating Interpersonally – a wide variety of communication methods exist – choice of a method should reflect: – the needs of the sender – the needs of the receiver – the attributes of the message – the attributes of the channel © Prentice Hall, 2002 11-7

Evaluating Communication Methods FFeedback-how quickly can the receiver respond to the message? Complexity capacity-can the method effectively process complex messages? Breadth potential-how many different messages can be transmitted using this method? Confdentialliy-can communicators be reasonably sure their messages are received only by those intended? EEncoding ease-can sender easily and quickly use this channel? Decodingease-can receiver easily and quickly decode messages? Time-space constraint-do senders and receivers need to communicate at the same time and in the same space? Cost-how much does it cost to use this method? Interpersonal warth-how well does this method convey interpersonal warmth? Formality-does this method have the needed amount of formality? Scanabiity-does this method allow the message to be easily browsed or scanned for relevant information? Time of consumption-does sender or receiver exercise the most control over when the message is dealt with? ©Prentice Hall,2002 11-8
Evaluating Communication Methods Feedback - how quickly can the receiver respond to the message? Complexity capacity - can the method effectively process complex messages? Breadth potential- how many different messages can be transmitted using this method? Confidentiality - can communicators be reasonably sure their messages are received only by those intended? Encoding ease - can sender easily and quickly use this channel? Decoding ease - can receiver easily and quickly decode messages? Time-space constraint- do senders and receivers need to communicate at the same time and in the same space? Cost- how much does it cost to use this method? Interpersonal warmth - how well does this method convey interpersonal warmth? Formality - does this method have the needed amount of formality? Scanability - does this method allow the message to be easily browsed or scanned for relevant information? Time of consumption - does sender or receiver exercise the most control over when the message is dealt with? © Prentice Hall, 2002 11-8
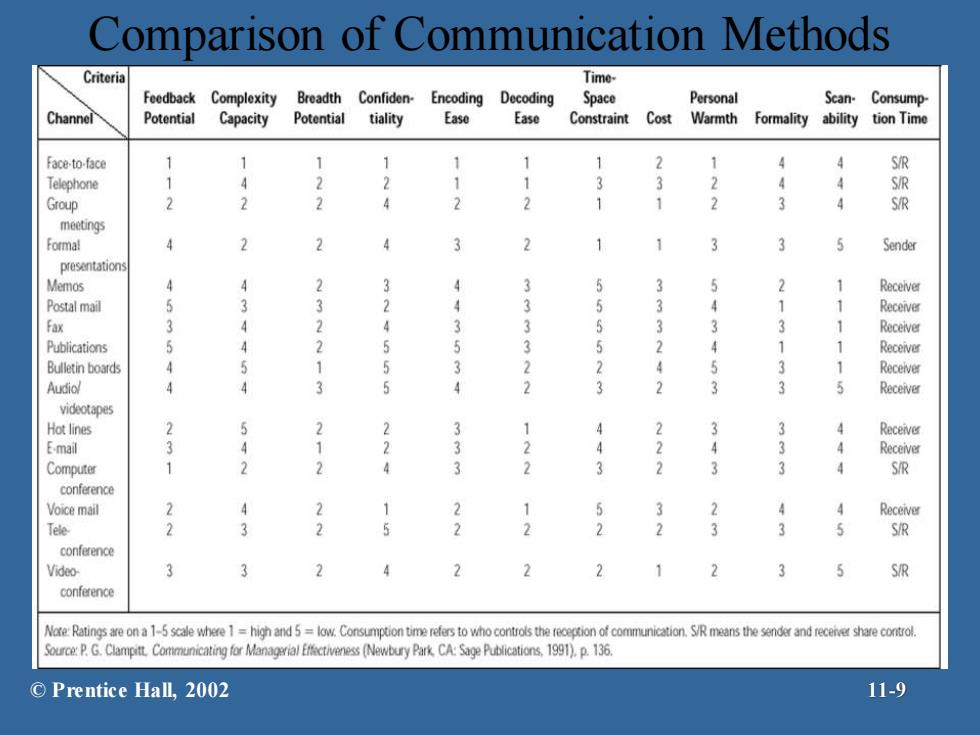
Comparison of Communication Methods Criteria Time- Feedback Complexity Breadth Confiden-Encoding Decoding Space Personal Scan-Consump Channel Potential Capacity Potential tiality Ease Ease Constraint Cost Warmth Formality ability tion Time Face-to-face 1 1 S/R Telephone 1 2 4 4 S/R Group 2 2 2 3 4 S/R meetings Formal 4 2 3 5 Sender presentations Memos 4 2 1 Receiver Postal mail 5 1 Receiver Fax 3 3 Receiver Publications 5 1 1 Receiver Bulletin boards 4 3 1 Receiver Audiol 4 Receiver videotapes Hot lines 2 Receiver Email 3 3 4 Receiver Computer 1 3 4 S/R conference Voice mail 2 2 4 Receiver Tele 2 3 2 3 3 S/R conference Video 3 2 2 2 3 S/R conference Nore:Ratings are on a 1-5 scale where 1=high and 5=low.Consumption time refers to who controls the reception of communication.S/R means the sender and recenve share control. PG.Clampitt Communcatngfor Mangrial Ecivness (Newbury Park CA:Sae Publications 1991).p.136. ©Prentice Hall,2002 11-9
Comparison of Communication Methods © Prentice Hall, 2002 11-9

Process Of Interpersonal Communication (cont. Methods of Communicating Interpersonally (cont.) nonverbal communication -communication without words ·types -body language-gestures,facial expressions,and other body movements that convey meaning verbal intonation emphasis someone gives to words or phrases that conveys meaning every oral communication is accompanied by a nonverbal message nonverbal component usually carries the greatest impact ©Prentice Hall,.2002 11-10
Process Of Interpersonal Communication (cont.) Methods of Communicating Interpersonally (cont.) – nonverbal communication - communication without words • types – body language - gestures, facial expressions, and other body movements that convey meaning – verbal intonation - emphasis someone gives to words or phrases that conveys meaning • every oral communication is accompanied by a nonverbal message • nonverbal component usually carries the greatest impact © Prentice Hall, 2002 11-10