
QUIZ 1. How many enterotoxins have been found in Staphylococcus aureus up to now? 2. Clostridium botulinum can produce a kind of highly fatal toxin, it is an enterotoxin or neurotoxin?What is the lethal dose of this toxin? 3. Where can we usually isolate Campylobacter?Why? 4. What is the basis of the classification of Salmonella spp.?And what is this basis determined by? 5. What makes Listeria monocytogenes highly hazardous to ready-to-eat foods?
1. How many enterotoxins have been found in Staphylococcus aureus up to now? 2. Clostridium botulinum can produce a kind of highly fatal toxin, it is an enterotoxin or neurotoxin? What is the lethal dose of this toxin? 3. Where can we usually isolate Campylobacter? Why? 4. What is the basis of the classification of Salmonella spp.? And what is this basis determined by? 5. What makes Listeria monocytogenes highly hazardous to ready-to-eat foods?

TOXIN-MEDIATED INFECTIONS (TOXICOINFECTION OR INTOXIFICATION) Clostridium perfringens Escherichia coli 0157:H7 x Bacillus cereus
Clostridium perfringens Escherichia coli O157:H7 Bacillus cereus
CLOSTRIDIUM PERFRINGENS 产气荚膜梭菌 x G+,厌氧,产芽孢,棒 杆菌 ×T:10-45°C(opt37-45°C) ×Min pH:5.0 ×aw0.93 NaCl 5%
G+,厌氧,产芽孢,棒 杆菌 T: 10-45˚C (opt 37-45˚C) Min pH : 5.0 aw 0.93 NaCl 5%

高危食品:炖制食品和肉汤 ×感染剂量:105 ×潜伏期:8-24 hours ×发病期:12-24 hours 通常不会致死
高危食品:炖制食品和肉汤 感染剂量:105 潜伏期: 8-24 hours 发病期: 12-24 hours 通常不会致死

PATHOGENIC E.COLI Enteropathogenic E.coli-(EPEC) 肠致病型大肠杆菌 108 cells Enterotoxigenic E.coli-(ETEC) 肠产毒型大肠杆菌 108 cells Enteroinvasive E.coli-(ElEC) 肠侵袭型大肠杆菌 unknown Enteroaggregative E.coli-(EAEC) 肠凝集型大肠杆菌 unknown Enterohemmorhagic E.coli-(EHEC,STEC)(includes VTEC 10 cells 0157:H7) 肠出血型大肠杆菌
Enteropathogenic E.coli - (EPEC) 肠致病型大肠杆菌 108 cells Enterotoxigenic E. coli - (ETEC) 肠产毒型大肠杆菌 108 cells Enteroinvasive E. coli - (EIEC) 肠侵袭型大肠杆菌 unknown Enteroaggregative E. coli - (EAEC) 肠凝集型大肠杆菌 unknown Enterohemmorhagic E. coli - (EHEC, STEC) (includes VTEC 10 cells O157:H7) 肠出血型大肠杆菌

HISTORY OF PATHOGENIC E.COLI ×大多数存在于动物胃肠道的E.coli不致病 可能在肠中对合成维生素K起作用 ×Shiga toxin基因水平转移到E.coli ×致病性E.coli慢慢分化成多个血清型
大多数存在于动物胃肠道的E. coli不致病 可能在肠中对合成维生素K起作用 Shiga toxin基因水平转移到E. coli 致病性E. coli 慢慢分化成多个血清型
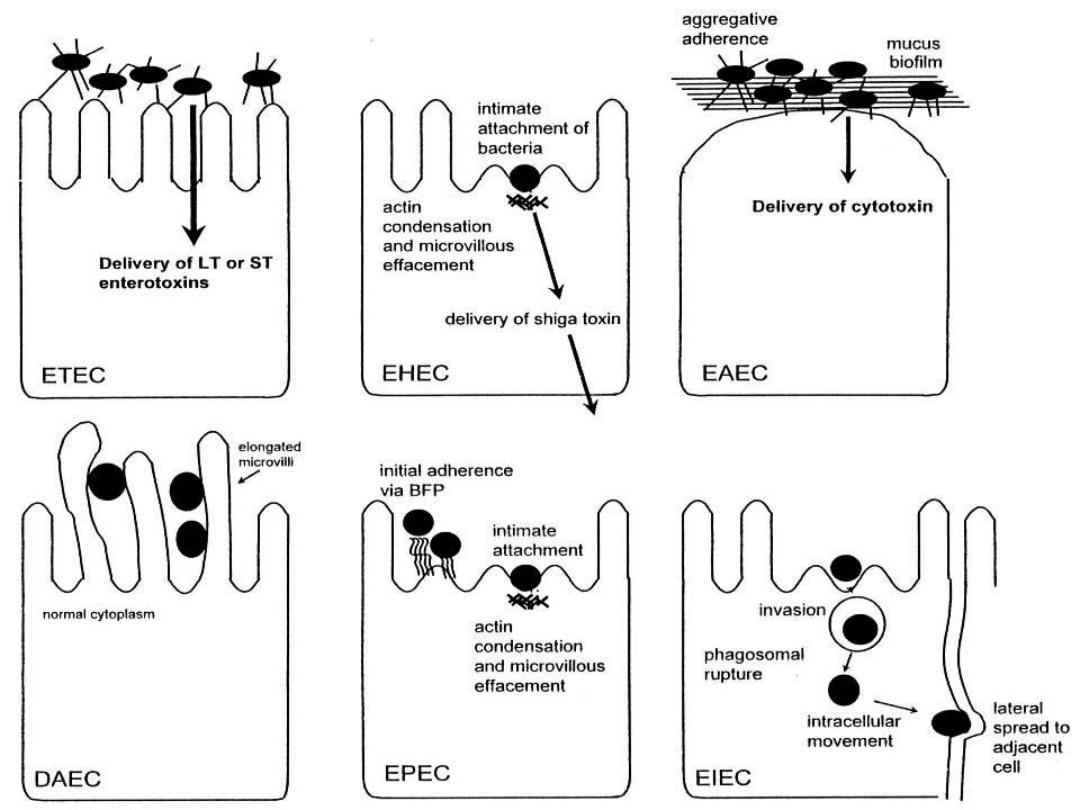
aggregative adherence mucus biofilm intimate attachment of bacteria actin Delivery of cytotoxin condensation and microvillous Delivery of LT or ST effacement enterotoxins delivery of shiga toxin ETEC EHEC EAEC elongated initial adherence via BFP intimate attachment normal cytoplasm invasion actin condensation phagosomal and microvillous rupture effacement lateral intracellular spread to movement adjacent cell DAEC EPEC EIEC

ESCHERICHIA CQLI Q157:H7 G,不形成芽孢,棒杆 菌 兼性厌氧 ×Temp10-50°C(opt30 37°C). ×Min aw0.93 × 低pH,低温下存活
G-,不形成芽孢,棒杆 菌 兼性厌氧 Temp 10-50˚C (opt 30- 37˚C). Min aW 0.93 低pH,低温下存活

×E.coi0157:H7近些年才出现 ×第一例:1984 Where has it been all this time?
E. coli O157:H7 近些年才出现 第一例:1984 Where has it been all this time?

secreted pelⅢ secretion apparatus intimin proteins o2m2w mm◆◇ escRSTU BcCl ecVN r U eae ePADB shiga toxin StxA t红B chromosome 60 MDa plasmid EHEC hemolysin ehuC A B D