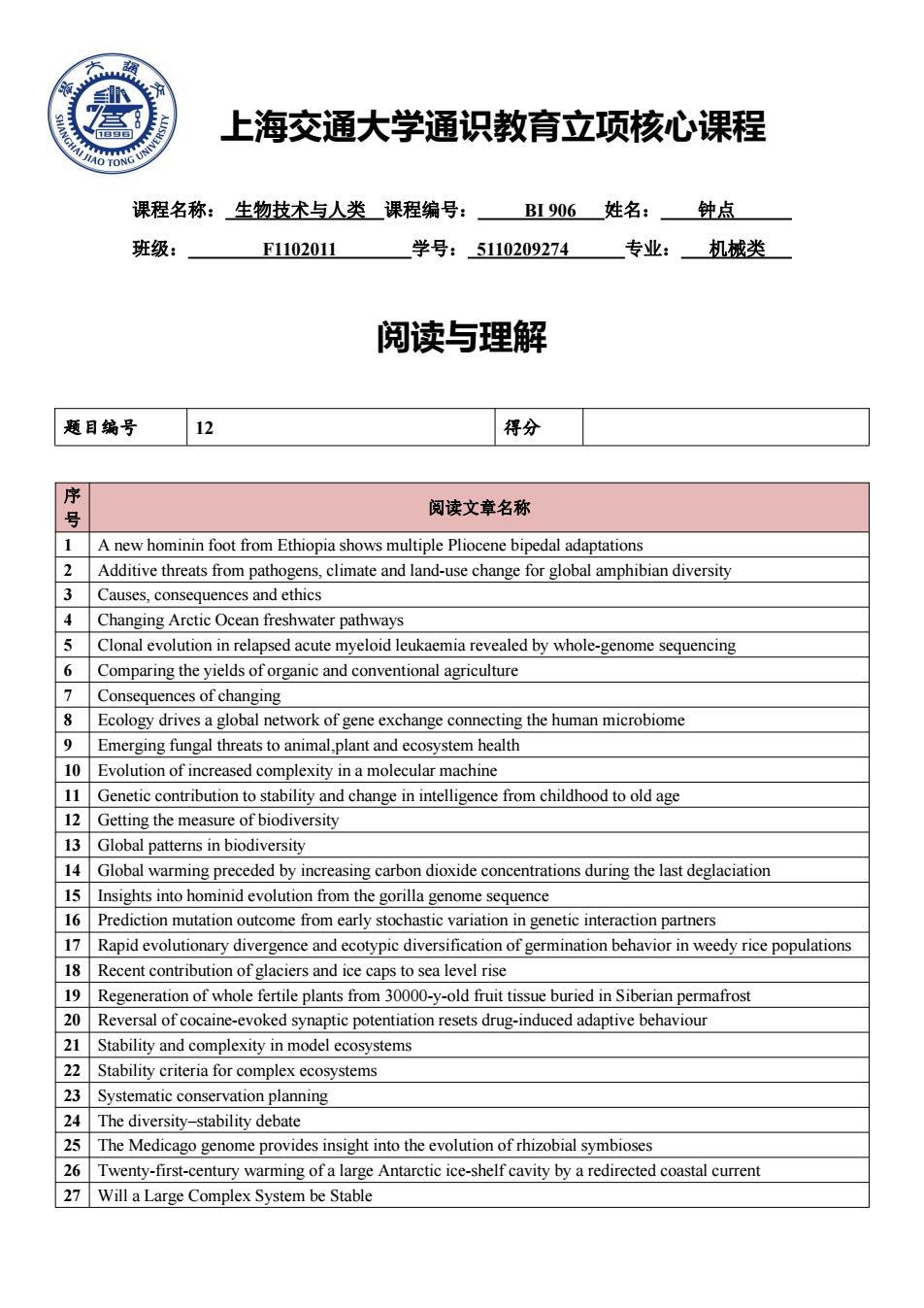
上海交通大学通识教育立项核心课程 课程名称:生物技术与人类课程编号: B1906姓名: 钟点 班级: F1102011 学号:5110209274 专业: 机械类 阅读与理解 题目编号 12 得分 序 阅读文章名称 1 A new hominin foot from Ethiopia shows multiple Pliocene bipedal adaptations 2 Additive threats from pathogens,climate and land-use change for global amphibian diversity 3 Causes,consequences and ethics 4 Changing Arctic Ocean freshwater pathways 5 Clonal evolution in relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia revealed by whole-genome sequencing 6 Comparing the yields of organic and conventional agriculture 7 Consequences of changing 8 Ecology drives a global network of gene exchange connecting the human microbiome 9 Emerging fungal threats to animal,plant and ecosystem health 10 Evolution of increased complexity in a molecular machine 11 Genetic contribution to stability and change in intelligence from childhood to old age 12 Getting the measure of biodiversity 13 Global patterns in biodiversity 14 Global warming preceded by increasing carbon dioxide concentrations during the last deglaciation 15 Insights into hominid evolution from the gorilla genome sequence 16 Prediction mutation outcome from early stochastic variation in genetic interaction partners 17 Rapid evolutionary divergence and ecotypic diversification of germination behavior in weedy rice populations 18 Recent contribution of glaciers and ice caps to sea level rise 19 Regeneration of whole fertile plants from 30000-y-old fruit tissue buried in Siberian permafrost 20 Reversal of cocaine-evoked synaptic potentiation resets drug-induced adaptive behaviour 21 Stability and complexity in model ecosystems 22 Stability criteria for complex ecosystems 23 Systematic conservation planning 24 The diversity-stability debate 25 The Medicago genome provides insight into the evolution of rhizobial symbioses 26 Twenty-first-century warming of a large Antarctic ice-shelf cavity by a redirected coastal current 27 Will a Large Complex System be Stable
上海交通大学通识教育立项核心课程 课程名称: 生物技术与人类 课程编号: BI 906 姓名: 钟点 班级: F1102011 学号: 5110209274 专业: 机械类 阅读与理解 题目编号 12 得分 序 号 阅读文章名称 1 A new hominin foot from Ethiopia shows multiple Pliocene bipedal adaptations 2 Additive threats from pathogens, climate and land-use change for global amphibian diversity 3 Causes, consequences and ethics 4 Changing Arctic Ocean freshwater pathways 5 Clonal evolution in relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia revealed by whole-genome sequencing 6 Comparing the yields of organic and conventional agriculture 7 Consequences of changing 8 Ecology drives a global network of gene exchange connecting the human microbiome 9 Emerging fungal threats to animal,plant and ecosystem health 10 Evolution of increased complexity in a molecular machine 11 Genetic contribution to stability and change in intelligence from childhood to old age 12 Getting the measure of biodiversity 13 Global patterns in biodiversity 14 Global warming preceded by increasing carbon dioxide concentrations during the last deglaciation 15 Insights into hominid evolution from the gorilla genome sequence 16 Prediction mutation outcome from early stochastic variation in genetic interaction partners 17 Rapid evolutionary divergence and ecotypic diversification of germination behavior in weedy rice populations 18 Recent contribution of glaciers and ice caps to sea level rise 19 Regeneration of whole fertile plants from 30000-y-old fruit tissue buried in Siberian permafrost 20 Reversal of cocaine-evoked synaptic potentiation resets drug-induced adaptive behaviour 21 Stability and complexity in model ecosystems 22 Stability criteria for complex ecosystems 23 Systematic conservation planning 24 The diversity–stability debate 25 The Medicago genome provides insight into the evolution of rhizobial symbioses 26 Twenty-first-century warming of a large Antarctic ice-shelf cavity by a redirected coastal current 27 Will a Large Complex System be Stable

Getting the measure of biodiversity Purvis A,Hector A.Getting the measure of biodiversity.Nature.2000.405.P212-219 衡量生物多样性 一、背景知识 生物多样性是从基因到生态系统水平的生物变化的总和。挑战在于以一个有效的方式来 衡量这个宏大的概念。我们证实了,尽管生物多样性不能以一个简单的数字来概括,但研究 特殊事例可以得出快速的、激动人心的、以及时而令人吃惊的发现。动植物种类史和暂时的 研究揭示了生态学,并且进化形成了如今的生物多样性。无可置疑人类正以惊人的速度来破 坏这个多样性,出现的一个严重的问题就是这些损失将会对生态系统的功能有多么坏的影响。 尽管最近的研究努力让人印象深刻,但在面对未知的多样性的数目和紧急且重要的任务上, 还是显得微不足道。 二、创新点 一开始文章就指出任何衡量生物多样性方式所遇到的问题,即生物多样性是从根本上的 多维的概念,不可能明智地缩小到一个简单数字的范畴。然后指出生物圈正在扩大,可以从 生命树进行研究,并且介绍生物多样性的现有模型,再次指出了人类活动会使得生物圈缩小, 最后提到了生物多样性和生态系统稳定和功能的关系。全文条理清晰,图文并茂,援引大量 数据和图表来论证了作者的观点。 三、个人感想 文章很长而且生词较多,而且背景知识不是特别了解,在阅读过程中常常会出现单词都 懂可具体意思完全不明白的情况,但是通过上下文的推理并且结合背景可以大概猜测介绍的 内容。这次阅读是我第一次专业性外文论文的阅读,虽然理解得不透彻,大多数仅仅停留在 字面上的层次,但我或多或少还是了解到一些有关生物多样性的内容,知道了生物多样性并 不是一个简单的数的概念,而是一个复杂的全面的概念,衡量生物多样性,可以了解生态环 境的变化和功能,以及让人类反思自身对自然的影响,是非常有意义的。除此之外,我还积 累了一些专业词汇术语,知道怎么去检索需要的文献,还是颇有收获的
Getting the measure of biodiversity Purvis A, Hector A.Getting the measure of biodiversity. Nature.2000. 405.P212-219 衡量生物多样性 一、背景知识 生物多样性是从基因到生态系统水平的生物变化的总和。挑战在于以一个有效的方式来 衡量这个宏大的概念。我们证实了,尽管生物多样性不能以一个简单的数字来概括,但研究 特殊事例可以得出快速的、激动人心的、以及时而令人吃惊的发现。动植物种类史和暂时的 研究揭示了生态学,并且进化形成了如今的生物多样性。无可置疑人类正以惊人的速度来破 坏这个多样性,出现的一个严重的问题就是这些损失将会对生态系统的功能有多么坏的影响。 尽管最近的研究努力让人印象深刻,但在面对未知的多样性的数目和紧急且重要的任务上, 还是显得微不足道。 二、创新点 一开始文章就指出任何衡量生物多样性方式所遇到的问题,即生物多样性是从根本上的 多维的概念,不可能明智地缩小到一个简单数字的范畴。然后指出生物圈正在扩大,可以从 生命树进行研究,并且介绍生物多样性的现有模型,再次指出了人类活动会使得生物圈缩小, 最后提到了生物多样性和生态系统稳定和功能的关系。全文条理清晰,图文并茂,援引大量 数据和图表来论证了作者的观点。 三、个人感想 文章很长而且生词较多,而且背景知识不是特别了解,在阅读过程中常常会出现单词都 懂可具体意思完全不明白的情况,但是通过上下文的推理并且结合背景可以大概猜测介绍的 内容。这次阅读是我第一次专业性外文论文的阅读,虽然理解得不透彻,大多数仅仅停留在 字面上的层次,但我或多或少还是了解到一些有关生物多样性的内容,知道了生物多样性并 不是一个简单的数的概念,而是一个复杂的全面的概念,衡量生物多样性,可以了解生态环 境的变化和功能,以及让人类反思自身对自然的影响,是非常有意义的。除此之外,我还积 累了一些专业词汇术语,知道怎么去检索需要的文献,还是颇有收获的