
第二讲 人类的感官与感觉(下)
第二讲 人类的感官与感觉(下)

三、嗅觉和食品嗅感
三、嗅觉和食品嗅感

嗅觉 olfaction • 气味刺激鼻腔内嗅觉细胞而产生的感觉。 嗅(to smell) 感受或试图感受某种气味
嗅觉 olfaction • 气味刺激鼻腔内嗅觉细胞而产生的感觉。 嗅(to smell) 感受或试图感受某种气味

The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2004 • Richard Axel : 1/2 of the prize, USA , Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Columbia University, Hammer Health Sciences Center ,New York, NY, USA , b. 1946 • Linda B. Buck :1/2 of the prize ,USA , Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center Seattle, WA, USA , b. 1947 "for their discoveries of odorant receptors and the organization of the olfactory system
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2004 • Richard Axel : 1/2 of the prize, USA , Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Columbia University, Hammer Health Sciences Center ,New York, NY, USA , b. 1946 • Linda B. Buck :1/2 of the prize ,USA , Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center Seattle, WA, USA , b. 1947 "for their discoveries of odorant receptors and the organization of the olfactory system
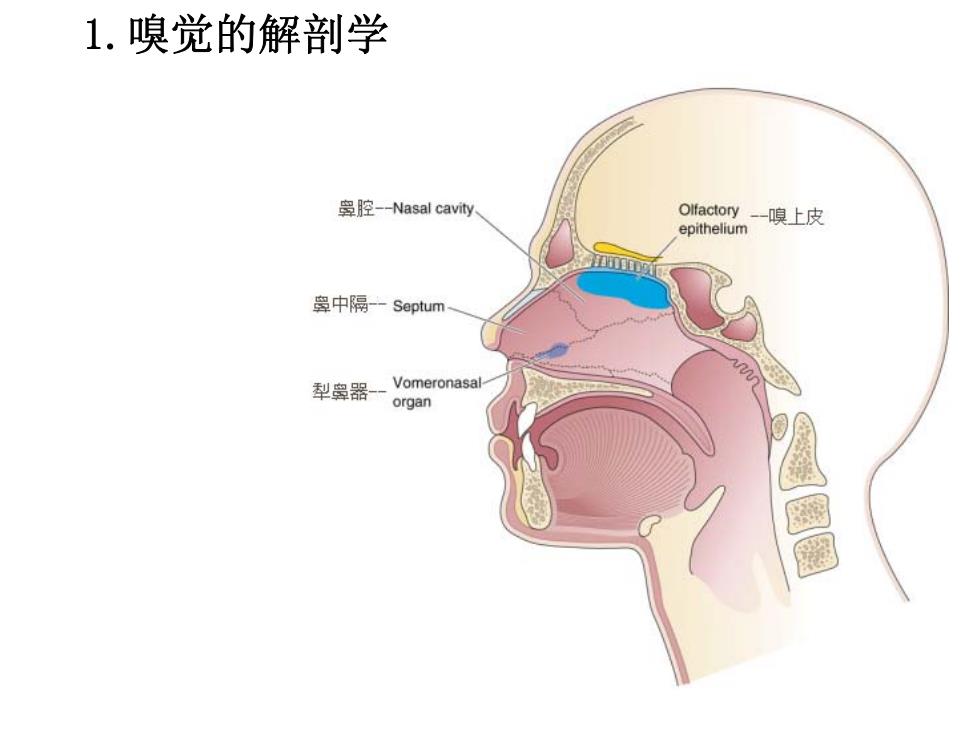
1.嗅觉的解剖学
1.嗅觉的解剖学
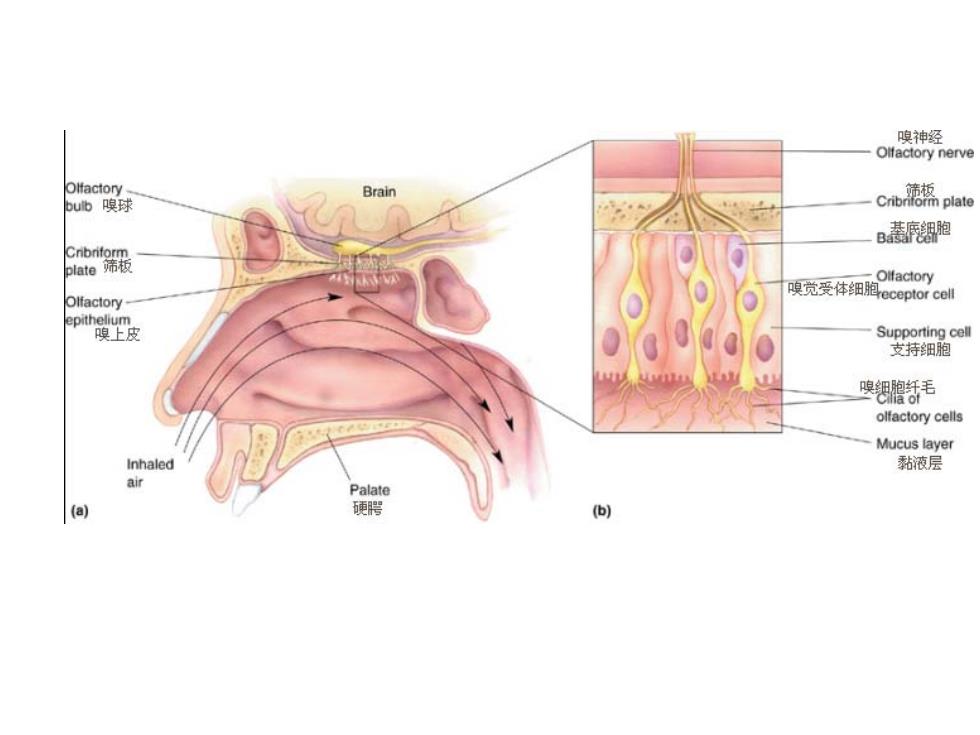
嗅神经 Olfactory nerve Olfactory Brain bub嗅球 Cb糖热pate B基铟跑 8器 Olfactory- 嗅觉受体细胞eceptor cel epithelium 嗅上皮 Supporting cell 支持细胞 嗅缌膻牙毛 olfactory cells Mucus layer Inhaled 黏液层 air Palate (a) 硬腭 )
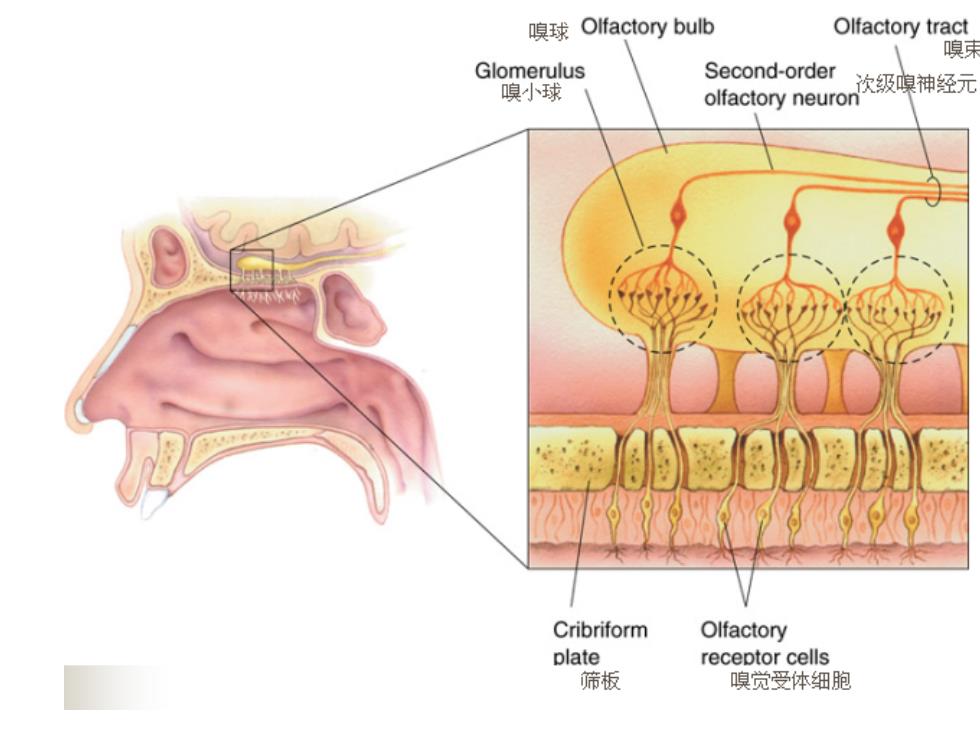
嗅球Olfactory bulb Olfactory tract 嗅 Glomerulus Second-order 嗅小球 次级嗅神经元 olfactory neuron Cribriform Olfactory plate receptor cells 筛板 嗅觉受体细胞
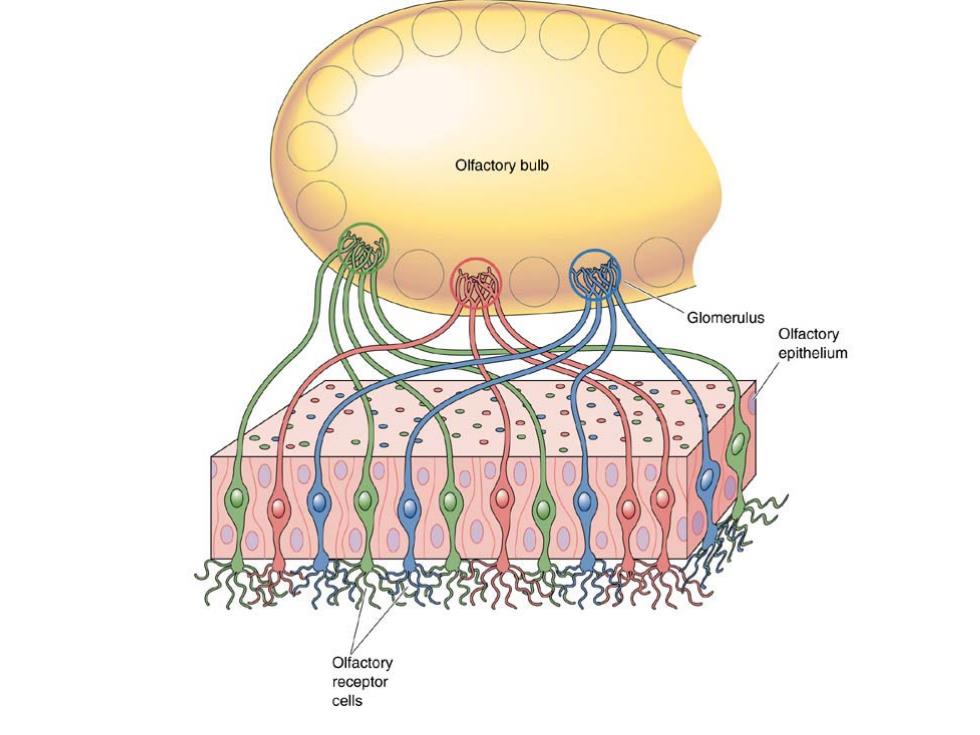
Olfactory bulb Glomerulus Olfactory epithelium Olfactory receptor cells
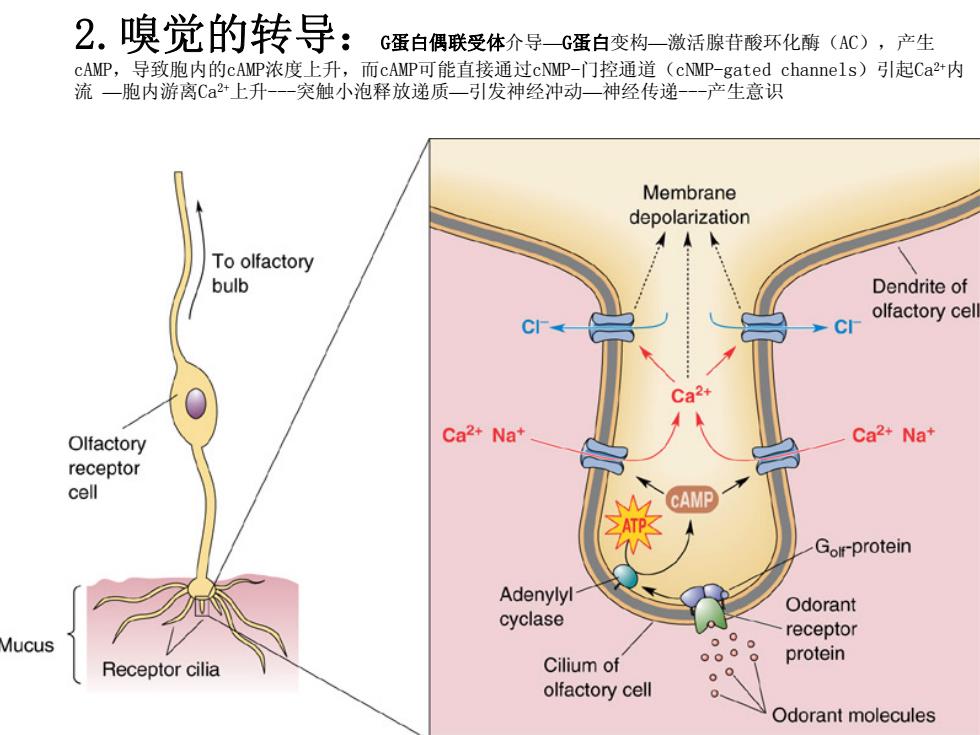
2.嗅觉的转导:G蛋白偶联受体介导—G蛋白变构—激活腺苷酸环化酶(AC),产生 cAMP,导致胞内的cAMP浓度上升,而cAMP可能直接通过cNMP-门控通道(cNMP-gated channels)引起Ca2+内 流 —胞内游离Ca2+上升-突触小泡释放递质—引发神经冲动—神经传递-产生意识
2.嗅觉的转导:G蛋白偶联受体介导—G蛋白变构—激活腺苷酸环化酶(AC),产生 cAMP,导致胞内的cAMP浓度上升,而cAMP可能直接通过cNMP-门控通道(cNMP-gated channels)引起Ca2+内 流 —胞内游离Ca2+上升-突触小泡释放递质—引发神经冲动—神经传递-产生意识

• 嗅觉器官感受到的感官特性。 3.气味 odour
• 嗅觉器官感受到的感官特性。 3.气味 odour