
第一篇 营养学 PART 1 NUTRITION 1.营养:是指人体摄取、消化吸收、利用食物中营养物质和排除 废 物的生物学过程。 It is a biological process which nutrients and functional compositions in the foods are ingested, digested, absorbed, transported ,utilized and the waste are excreted. 2.营养素: (1) 定义:食物中可给人体提供能量、机体构成成分和组织修复 以及有生理调节功能的化学成分。 Chemical substances obtained from food and used in the body to provide energy,structural materials,and repair of the body’s tissues; Nutrients may also reduce the risk ofsome diseases
第一篇 营养学 PART 1 NUTRITION 1.营养:是指人体摄取、消化吸收、利用食物中营养物质和排除 废 物的生物学过程。 It is a biological process which nutrients and functional compositions in the foods are ingested, digested, absorbed, transported ,utilized and the waste are excreted. 2.营养素: (1) 定义:食物中可给人体提供能量、机体构成成分和组织修复 以及有生理调节功能的化学成分。 Chemical substances obtained from food and used in the body to provide energy,structural materials,and repair of the body’s tissues; Nutrients may also reduce the risk ofsome diseases
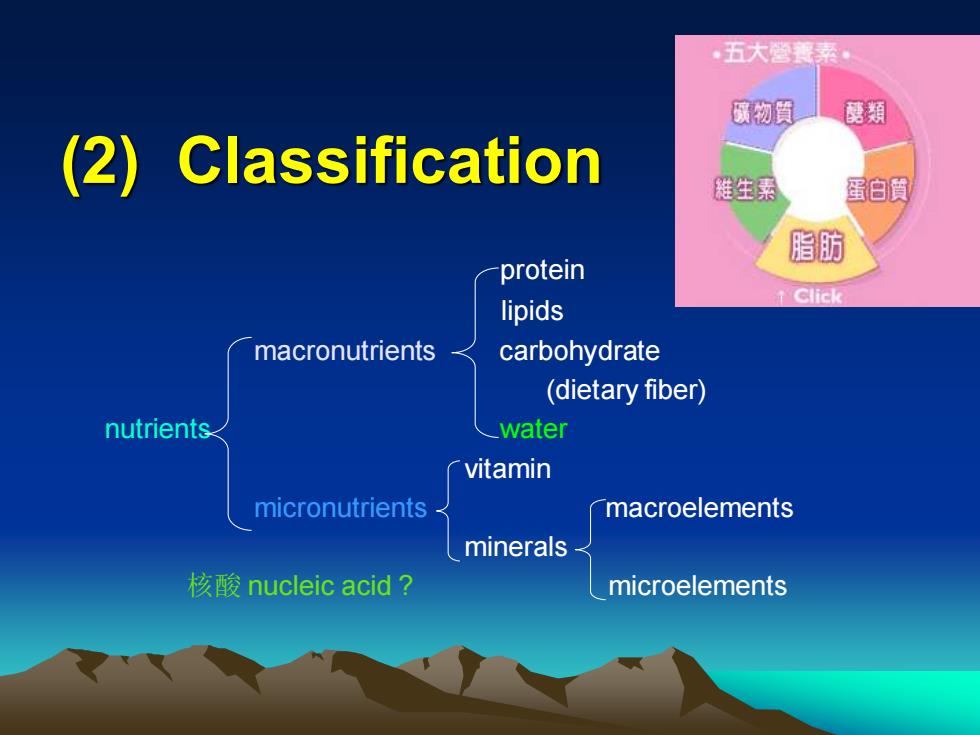
(2) Classification protein lipids macronutrients carbohydrate (dietary fiber) nutrients water vitamin micronutrients macroelements minerals 核酸 nucleic acid ? microelements
(2) Classification protein lipids macronutrients carbohydrate (dietary fiber) nutrients water vitamin micronutrients macroelements minerals 核酸 nucleic acid ? microelements

3. 合理营养(Rational Diet) 通过合理的膳食和科学地烹调加工,能向机体提供足够数量 的热能和各种营养素,并保证各种营养素之间的数量平衡,以满 足人体的正常生理需要,并保持人体健康。 Nutrients intakes meet the requirements of the body 5.膳食营养供给量(Recommended Dietary Allowance, RDA) 是对各种人群提出的保证人体营养需要的膳食中应含有的热 能和营养素的适宜量。 The average daily amount of a nutrient considered adequate to meet the known nutrient needs of practically all healthy people; a goal for dietary intake by individuals. 4. 营养生理需要量(Nutritional Requirement) 是指能保持人体健康,达到应有发育水平和能充分有效地完成 各项体力和脑力活动所需要的热能和各种营养素的必需量。 The lowest continuing intake of energy and nutrients that maintain the specified criterion of adequacy (that will maintain the specific biochemical and physiologicalfunctions of the body)
3. 合理营养(Rational Diet) 通过合理的膳食和科学地烹调加工,能向机体提供足够数量 的热能和各种营养素,并保证各种营养素之间的数量平衡,以满 足人体的正常生理需要,并保持人体健康。 Nutrients intakes meet the requirements of the body 5.膳食营养供给量(Recommended Dietary Allowance, RDA) 是对各种人群提出的保证人体营养需要的膳食中应含有的热 能和营养素的适宜量。 The average daily amount of a nutrient considered adequate to meet the known nutrient needs of practically all healthy people; a goal for dietary intake by individuals. 4. 营养生理需要量(Nutritional Requirement) 是指能保持人体健康,达到应有发育水平和能充分有效地完成 各项体力和脑力活动所需要的热能和各种营养素的必需量。 The lowest continuing intake of energy and nutrients that maintain the specified criterion of adequacy (that will maintain the specific biochemical and physiologicalfunctions of the body)

Chapter 1 Basic Nutrition 第 一 章 营 养 学 基 础 含量-16%——19%. 更新: 动态平衡,不断更新,每天约3%,肠和骨髓最快。 Section 1 Protein ( 蛋白质 ) 一、蛋白质 (一)人体中蛋白质: (二)功能: 1. 机体构成成分 2. 构成各种生理活性物质和重要的生理功能 3. 提供热能
Chapter 1 Basic Nutrition 第 一 章 营 养 学 基 础 含量-16%——19%. 更新: 动态平衡,不断更新,每天约3%,肠和骨髓最快。 Section 1 Protein ( 蛋白质 ) 一、蛋白质 (一)人体中蛋白质: (二)功能: 1. 机体构成成分 2. 构成各种生理活性物质和重要的生理功能 3. 提供热能
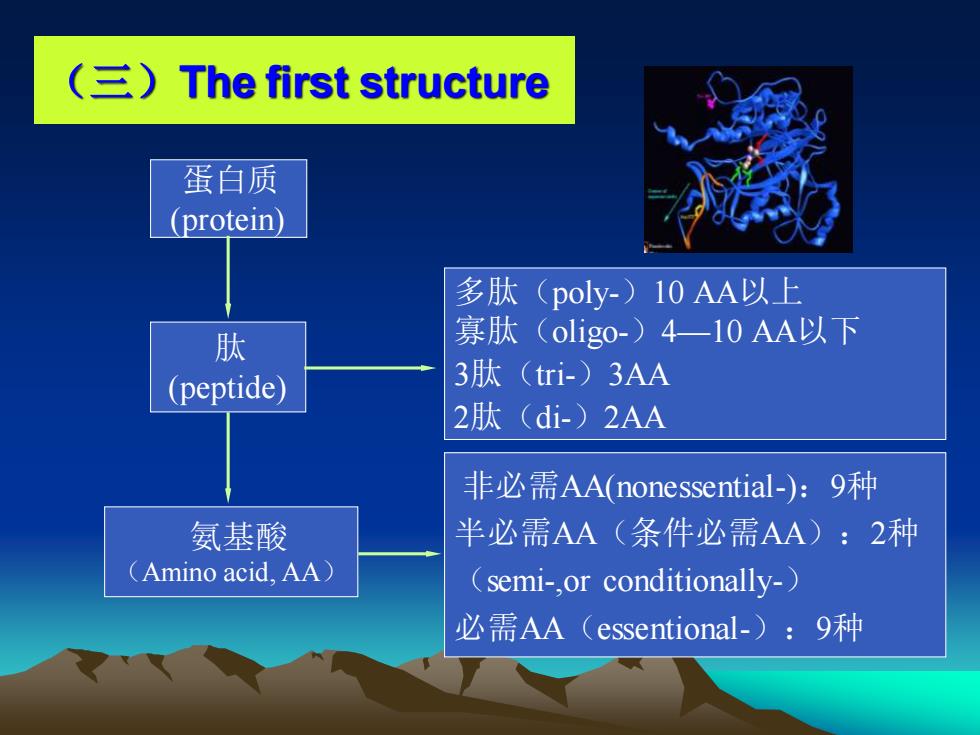
(三)The first structure 蛋白质 (protein) 氨基酸 (Amino acid, AA) 非必需AA(nonessential-):9种 半必需AA(条件必需AA):2种 (semi-,or conditionally-) 必需AA(essentional-):9种 多肽(poly-)10 AA以上 寡肽(oligo-)4—10 AA以下 3肽(tri-)3AA 2肽(di-)2AA 肽 (peptide)
(三)The first structure 蛋白质 (protein) 氨基酸 (Amino acid, AA) 非必需AA(nonessential-):9种 半必需AA(条件必需AA):2种 (semi-,or conditionally-) 必需AA(essentional-):9种 多肽(poly-)10 AA以上 寡肽(oligo-)4—10 AA以下 3肽(tri-)3AA 2肽(di-)2AA 肽 (peptide)

二、 氨基酸和必需AA( essential amino acid ,EAA) 1. 种类:20种 (1) 必需AA(EAA) (2) 非必需氨基酸(NEAA) (3) 半必需氨基酸 ( semi-EAA or conditional EAA) 半胱酸(Cysteine)——蛋氨酸(Methionine) 酪氨酸(Tyrosine)——苯丙氨酸(Phenylalanine) 2. 必需氨基酸: 人体不能合成或合成速度不能满足机体需要,必需从食物中直接获 得的AA。 Amino acids that the body cannot synthesize in amount sufficient to meet physiological needs and has to obtain them from foods
二、 氨基酸和必需AA( essential amino acid ,EAA) 1. 种类:20种 (1) 必需AA(EAA) (2) 非必需氨基酸(NEAA) (3) 半必需氨基酸 ( semi-EAA or conditional EAA) 半胱酸(Cysteine)——蛋氨酸(Methionine) 酪氨酸(Tyrosine)——苯丙氨酸(Phenylalanine) 2. 必需氨基酸: 人体不能合成或合成速度不能满足机体需要,必需从食物中直接获 得的AA。 Amino acids that the body cannot synthesize in amount sufficient to meet physiological needs and has to obtain them from foods
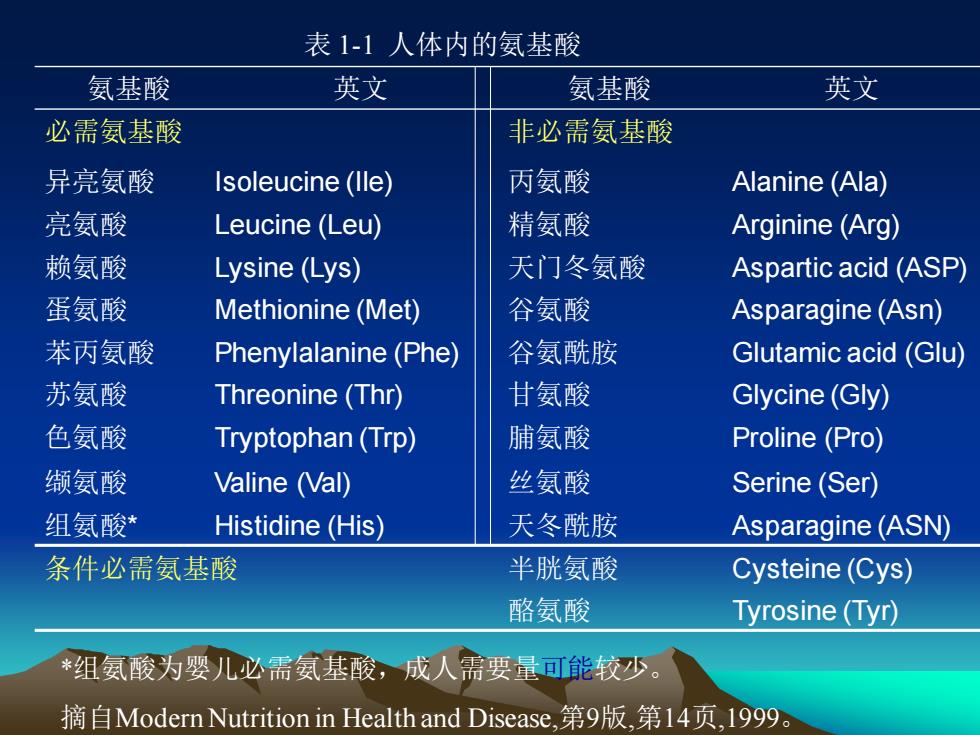
氨基酸 英文 氨基酸 英文 必需氨基酸 非必需氨基酸 异亮氨酸 Isoleucine (Ile) 丙氨酸 Alanine (Ala) 亮氨酸 Leucine (Leu) 精氨酸 Arginine (Arg) 赖氨酸 Lysine (Lys) 天门冬氨酸 Aspartic acid (ASP) 蛋氨酸 Methionine (Met) 谷氨酸 Asparagine (Asn) 苯丙氨酸 Phenylalanine (Phe) 谷氨酰胺 Glutamic acid (Glu) 苏氨酸 Threonine (Thr) 甘氨酸 Glycine (Gly) 色氨酸 Tryptophan (Trp) 脯氨酸 Proline (Pro) 缬氨酸 Valine (Val) 丝氨酸 Serine (Ser) 组氨酸* Histidine (His) 天冬酰胺 Asparagine (ASN) 条件必需氨基酸 半胱氨酸 Cysteine (Cys) 酪氨酸 Tyrosine (Tyr) 表 1-1 人体内的氨基酸 *组氨酸为婴儿必需氨基酸,成人需要量可能较少。 摘自Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease,第9版,第14页,1999
氨基酸 英文 氨基酸 英文 必需氨基酸 非必需氨基酸 异亮氨酸 Isoleucine (Ile) 丙氨酸 Alanine (Ala) 亮氨酸 Leucine (Leu) 精氨酸 Arginine (Arg) 赖氨酸 Lysine (Lys) 天门冬氨酸 Aspartic acid (ASP) 蛋氨酸 Methionine (Met) 谷氨酸 Asparagine (Asn) 苯丙氨酸 Phenylalanine (Phe) 谷氨酰胺 Glutamic acid (Glu) 苏氨酸 Threonine (Thr) 甘氨酸 Glycine (Gly) 色氨酸 Tryptophan (Trp) 脯氨酸 Proline (Pro) 缬氨酸 Valine (Val) 丝氨酸 Serine (Ser) 组氨酸* Histidine (His) 天冬酰胺 Asparagine (ASN) 条件必需氨基酸 半胱氨酸 Cysteine (Cys) 酪氨酸 Tyrosine (Tyr) 表 1-1 人体内的氨基酸 *组氨酸为婴儿必需氨基酸,成人需要量可能较少。 摘自Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease,第9版,第14页,1999
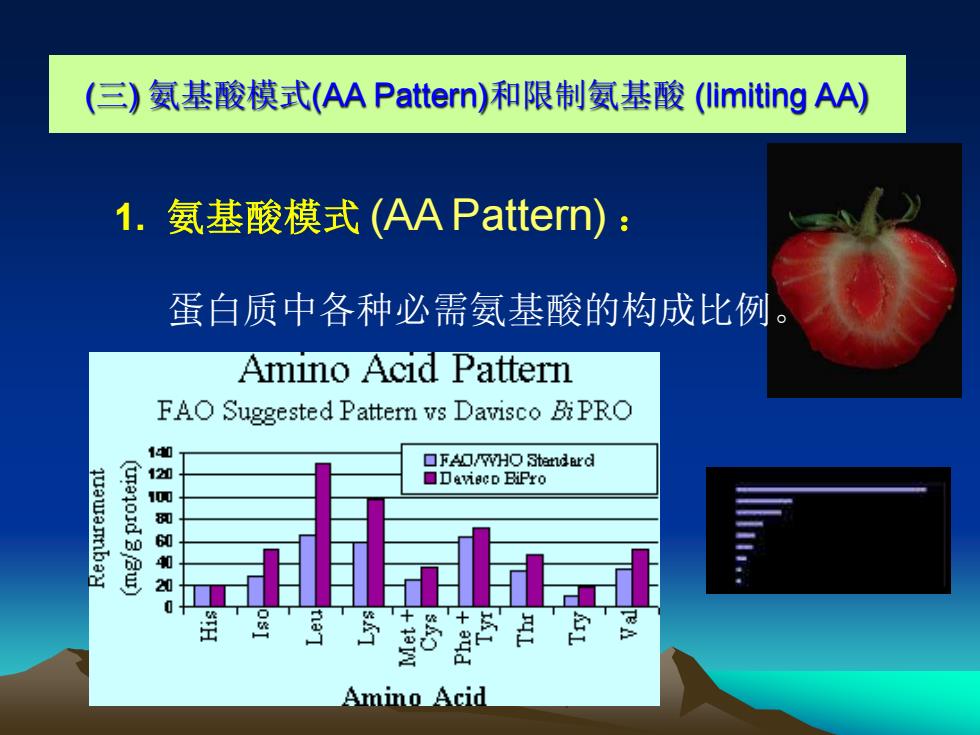
(三) 氨基酸模式(AA Pattern)和限制氨基酸 (limiting AA) 1. 氨基酸模式 (AA Pattern) : 蛋白质中各种必需氨基酸的构成比例
(三) 氨基酸模式(AA Pattern)和限制氨基酸 (limiting AA) 1. 氨基酸模式 (AA Pattern) : 蛋白质中各种必需氨基酸的构成比例
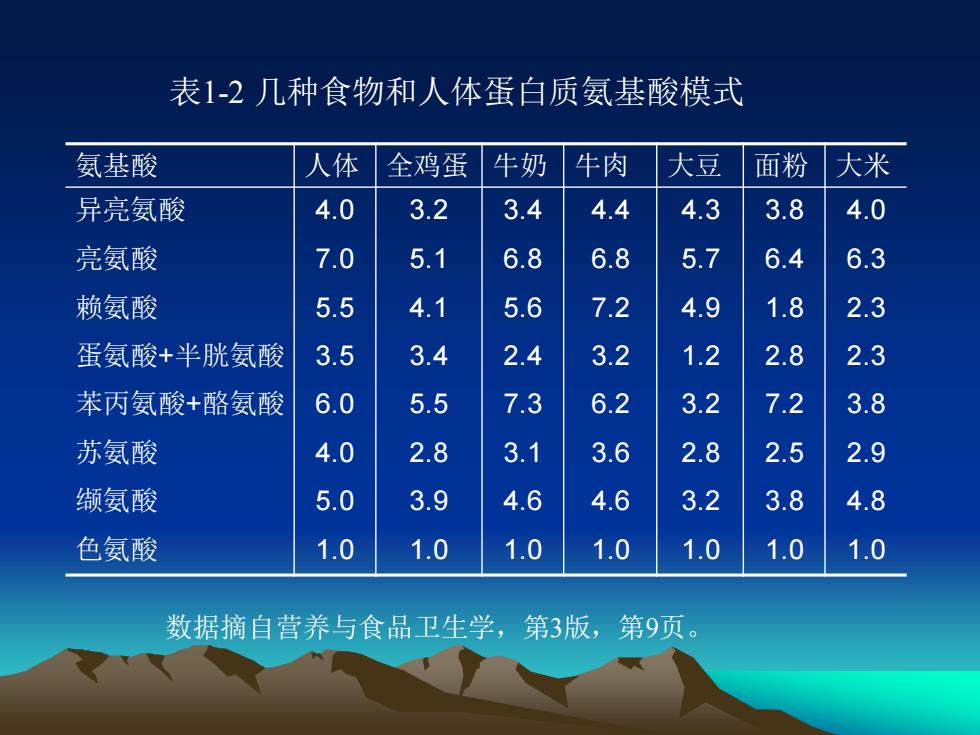
氨基酸 人体 全鸡蛋 牛奶 牛肉 大豆 面粉 大米 异亮氨酸 4.0 3.2 3.4 4.4 4.3 3.8 4.0 亮氨酸 7.0 5.1 6.8 6.8 5.7 6.4 6.3 赖氨酸 5.5 4.1 5.6 7.2 4.9 1.8 2.3 蛋氨酸+半胱氨酸 3.5 3.4 2.4 3.2 1.2 2.8 2.3 苯丙氨酸+酪氨酸 6.0 5.5 7.3 6.2 3.2 7.2 3.8 苏氨酸 4.0 2.8 3.1 3.6 2.8 2.5 2.9 缬氨酸 5.0 3.9 4.6 4.6 3.2 3.8 4.8 色氨酸 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 表1-2 几种食物和人体蛋白质氨基酸模式 数据摘自营养与食品卫生学,第3版,第9页
氨基酸 人体 全鸡蛋 牛奶 牛肉 大豆 面粉 大米 异亮氨酸 4.0 3.2 3.4 4.4 4.3 3.8 4.0 亮氨酸 7.0 5.1 6.8 6.8 5.7 6.4 6.3 赖氨酸 5.5 4.1 5.6 7.2 4.9 1.8 2.3 蛋氨酸+半胱氨酸 3.5 3.4 2.4 3.2 1.2 2.8 2.3 苯丙氨酸+酪氨酸 6.0 5.5 7.3 6.2 3.2 7.2 3.8 苏氨酸 4.0 2.8 3.1 3.6 2.8 2.5 2.9 缬氨酸 5.0 3.9 4.6 4.6 3.2 3.8 4.8 色氨酸 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0 表1-2 几种食物和人体蛋白质氨基酸模式 数据摘自营养与食品卫生学,第3版,第9页

2. 限制氨基酸 (limiting amino acid): 与人体蛋白质模式比较,食物蛋白质中含量相对较 低的必需AA。 The essential amino acid found in the shortest supply relative to the amount needed for protein synthesis in the body. Four AA are most likely to be limiting: Lysine,Methionine,Threonine,Tryptophan
2. 限制氨基酸 (limiting amino acid): 与人体蛋白质模式比较,食物蛋白质中含量相对较 低的必需AA。 The essential amino acid found in the shortest supply relative to the amount needed for protein synthesis in the body. Four AA are most likely to be limiting: Lysine,Methionine,Threonine,Tryptophan