
系统综述和Meta分析(预习) 张博恒 复旦大学附属中山医院 循证医学中心
系统综述和Meta分析(预习) 张博恒 复旦大学附属中山医院 循证医学中心

什么是系统综述? ·对一个特定的问题系统全面地收集相关证 据,用统一的科学评价标准,筛选出符合 标准的文献,综合结果,以得到可靠的结 论
什么是系统综述? ⚫ 对一个特定的问题系统全面地收集相关证 据,用统一的科学评价标准,筛选出符合 标准的文献,综合结果,以得到可靠的结 论
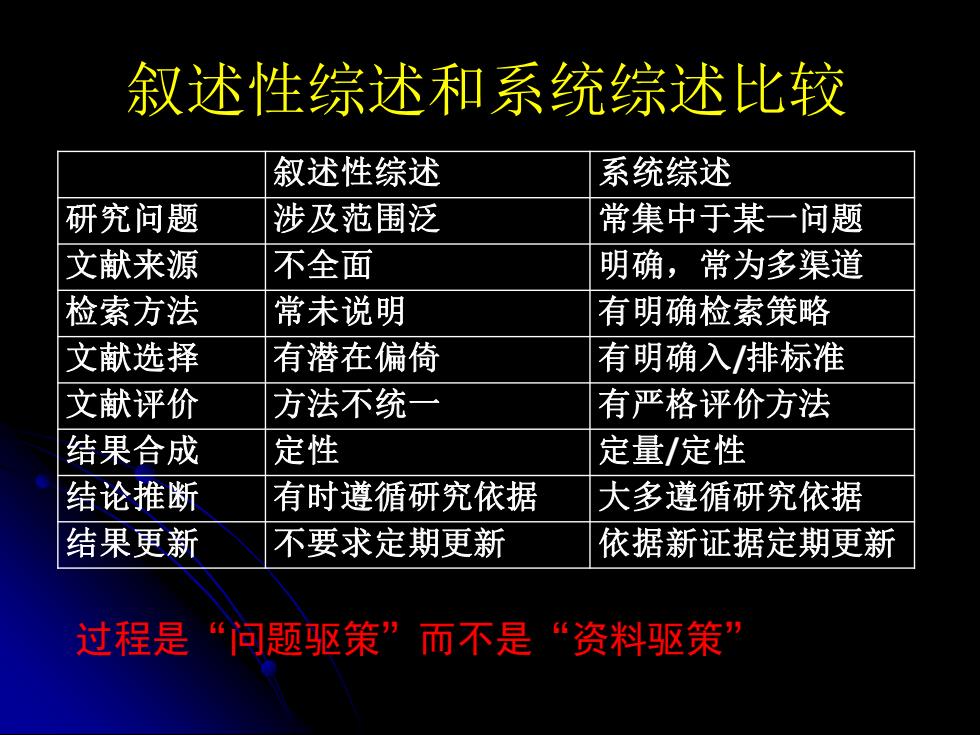
叙述性综述和系统综述比较 叙述性综述 系统综述 研究问题 涉及范围泛 常集中于某一问题 文献来源 不全面 明确,常为多渠道 检索方法 常未说明 有明确检索策略 文献选择 有潜在偏倚 有明确入/排标准 文献评价 方法不统一 有严格评价方法 结果合成 定性 定量/定性 结论推断 有时遵循研究依据 大多遵循研究依据 结果更新 不要求定期更新 依据新证据定期更新 过程是“问题驱策”而不是“资料驱策
叙述性综述和系统综述比较 过程是“问题驱策”而不是“资料驱策” 叙述性综述 系统综述 研究问题 涉及范围泛 常集中于某一问题 文献来源 不全面 明确,常为多渠道 检索方法 常未说明 有明确检索策略 文献选择 有潜在偏倚 有明确入/排标准 文献评价 方法不统一 有严格评价方法 结果合成 定性 定量/定性 结论推断 有时遵循研究依据 大多遵循研究依据 结果更新 不要求定期更新 依据新证据定期更新

系统评价与Meta分析 ●1993.7BMJ: ●Systematic review=科学综述+meta分析 随机误差 系统误差
系统评价与Meta分析 ⚫ 1993.7 BMJ: ⚫ Systematic review=科学综述+meta分析

循证医学典范 1987年,Cochrane根据对妊娠和分娩后随访的大样本随机对 照试验结果进行系统评价研究,获得了令人信服的证据。 过去有关氢化可的松治疗早产高危孕妇的试验结果不一致,而 根据单个的临床试验结果难以确定该疗法是否利大于弊。 Cochrane的系统评价明确肯定:氢化可的松可以降低新生儿死 于早产并发症的危险,使早产儿死亡率下降30%~50%。 由于此前没有进行相关的系统评价分析和报道,多数产科医师 并未认识到该项治疗措施的效果,不仅导致成千上万早产儿可能因其 母亲未接受相应治疗而死亡,还耗费更多不必要的治疗费用。推广这 一科学结论将挽救千分之十早产婴儿的生命
循证医学典范 1987年,Cochrane根据对妊娠和分娩后随访的大样本随机对 照试验结果进行系统评价研究,获得了令人信服的证据。 过去有关氢化可的松治疗早产高危孕妇的试验结果不一致,而 根据单个的临床试验结果难以确定该疗法是否利大于弊。 Cochrane的系统评价明确肯定:氢化可的松可以降低新生儿死 于早产并发症的危险,使早产儿死亡率下降30%~50%。 由于此前没有进行相关的系统评价分析和报道,多数产科医师 并未认识到该项治疗措施的效果,不仅导致成千上万早产儿可能因其 母亲未接受相应治疗而死亡,还耗费更多不必要的治疗费用。推广这 一科学结论将挽救千分之十早产婴儿的生命

SR步骤 (2011 Cochrane SR手册) 1. 定义综述的问题并建立入组标准 2.文献检索 只有当研究 3.选择研究和收集数据 质量足够好 4.评价纳入研究存在偏倚的风险 5.分析数据并在可能的情况下进行meta-分析 6. 阐述报告的偏倚 7. 呈现结果和“结果总结表” 8. 解释结果,得出结论 http://handbook.cochrane.org/
SR步骤(2011 Cochrane SR 手册) 1. 定义综述的问题并建立入组标准 2. 文献检索 3. 选择研究和收集数据 4. 评价纳入研究存在偏倚的风险 5. 分析数据并在可能的情况下进行meta-分析 6. 阐述报告的偏倚 7. 呈现结果和“结果总结表” 8. 解释结果,得出结论 http://handbook.cochrane.org/

提出临床问题:循证医学思路 PICO原则 ·P population/patients人群/病人群 ●I intervention/exposure干预/暴露 ●C comparison or control对照 ●0 outcome 结果
提出临床问题:循证医学思路 ⚫ P population/patients 人群/病人群 ⚫ I intervention/exposure 干预/暴露 ⚫C comparison or control 对照 ⚫O outcome 结果 PICO原则
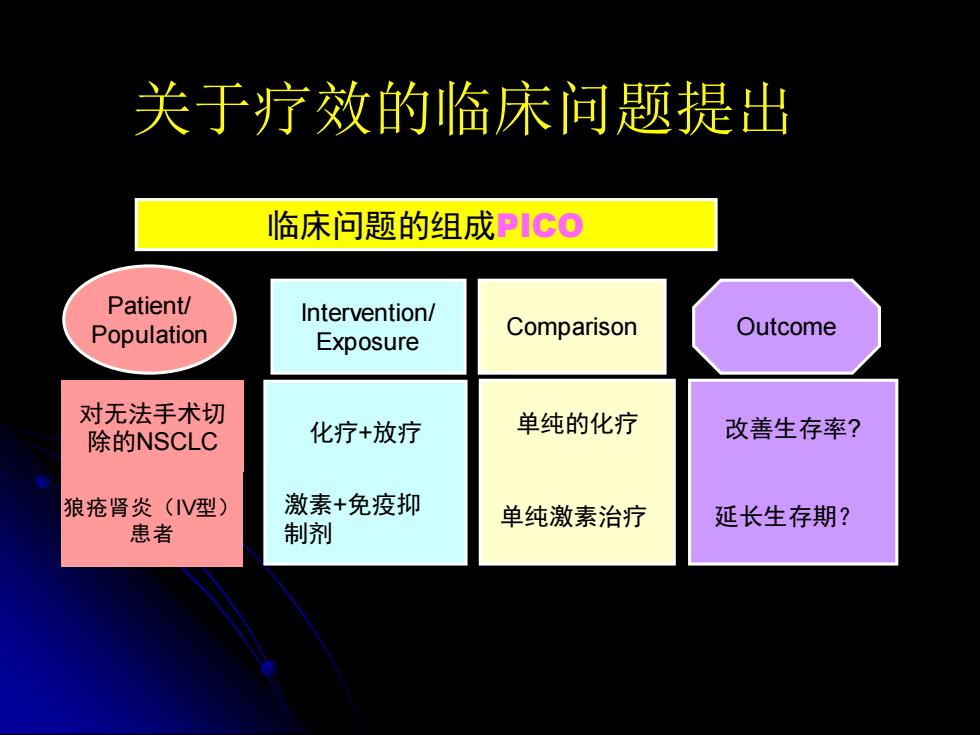
关于疗效的临床问题提出 临床问题的组成PICO Patient/ Intervention/ Population Comparison Outcome Exposure 对无法手术切 除的NSCLC 化疗+放疗 单纯的化疗 改善生存率? 狼疮肾炎(V型) 激素+免疫抑 单纯激素治疗 延长生存期? 患者 制剂
Patient/ Population Outcome Intervention/ Exposure Comparison 临床问题的组成PICO 对无法手术切 除的NSCLC 化疗+放疗 单纯的化疗 改善生存率? 狼疮肾炎(IV型) 患者 激素+免疫抑 制剂 单纯激素治疗 延长生存期? 关于疗效的临床问题提出

4.评价纳入研究存在偏倚的风险 COCHRANE偏倚风险评估工具
4.评价纳入研究存在偏倚的风险 COCHRANE偏倚风险评估工具

COCHRANE偏倚风险评估工具 Typeof bias Description Relevantdomains in the Collaboration's'Risk of bias'tool Selection bias.选择 Systematic differences between .Sequence generation. baseline characteristics of the .Allocation concealment. groups that are compared. Performance bias. Systematic differences between .Blinding of participants and personnel. 实施 groups in the care that is .Other potential threats to validity. provided,or in exposure to factors other than the interventions of interest. Detection bias Systematic differences between .Blinding of outcome assessment. groups in how outcomes are .Other potential threats to validity. determined. Attrition bias.退出 Systematic differences between .Incomplete outcome data groups in withdrawals from a study. Reporting bias:报道 Systematic differences between .Selective outcome reporting reported and unreported findings
COCHRANE偏倚风险评估工具 Figure 8.6.b: Example of a ‘Risk of bias graph’ figure Type of bias Description Relevant domains in the Collaboration’s ‘Risk of bias’ tool Selection bias.选择 Systematic differences between baseline characteristics of the groups that are compared. •Sequence generation. •Allocation concealment. Performance bias. 实施 Systematic differences between groups in the care that is provided, or in exposure to factors other than the interventions of interest. •Blinding of participants and personnel. •Other potential threats to validity. Detection bias检出 . Systematic differences between groups in how outcomes are determined. •Blinding of outcome assessment. •Other potential threats to validity. Attrition bias退出. Systematic differences between groups in withdrawals from a study. •Incomplete outcome data Reporting bias报道 . Systematic differences between reported and unreported findings. •Selective outcome reporting Table 8.4.a: A common classification scheme for bias •