
3.2.Constraints between a body and ground (Absolute constraints) Absolute x constraint Absolute y constraint Absolute angle constraint Absolute distance constraint
• Absolute x constraint • Absolute y constraint • Absolute angle constraint • Absolute distance constraint 3.2. Constraints between a body and ground (Absolute constraints)
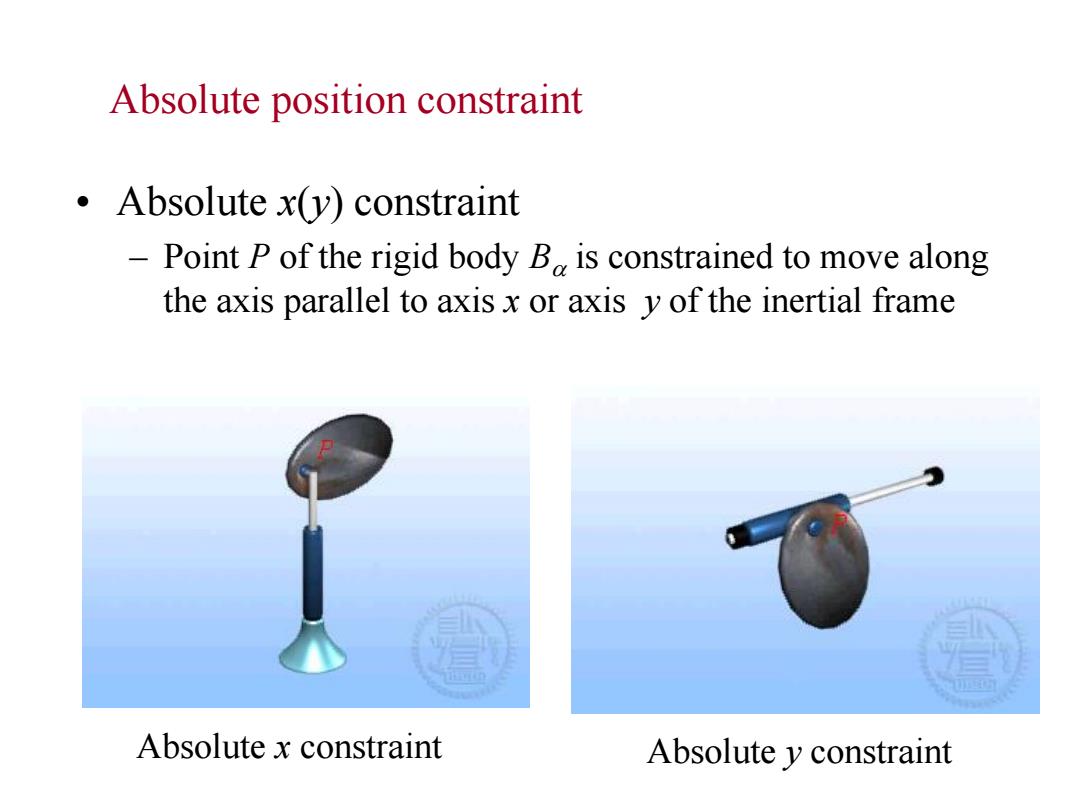
Absolute position constraint .Absolute x(y)constraint Point P of the rigid body B is constrained to move along the axis parallel to axis x or axis y of the inertial frame Absolute x constraint Absolute y constraint
Absolute position constraint • Absolute x(y) constraint – Point P of the rigid body Ba is constrained to move along the axis parallel to axis x or axis y of the inertial frame Absolute x constraint Absolute y constraint
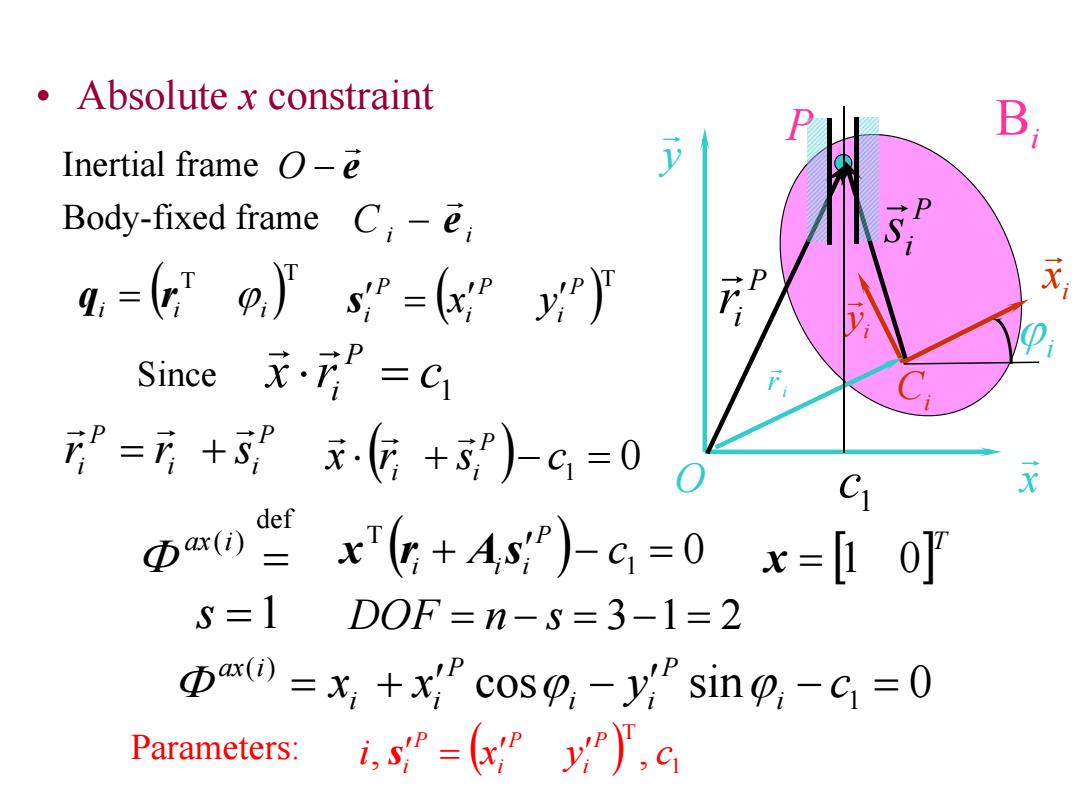
Absolute x constraint B, Inertial frame O-e Body-fixed frame C,-e ,=(9,'sP=x”P Since=C =元+.匠+)-c=0 C x def x6+4s)-G=0x=[0] S=1 DOF=n-S=3-1=2 pax()=x,+x cosp-y sinpi-c=0 Parameters: i,sP=(xy),c
• Absolute x constraint Bi y x O i x i y Ci i r i P P ir P i s 1 c e Inertial frame O Ci i e Body-fixed frame T T i i i q r T P i P i P i s x y 1 x r c P i P i i P ir r s def ( ) ax i 0 x r s c1 P i i 0 1 T c P i i i x r A s cos sin 0 1 ( ) x x y i c P i i P i i ax i Since Parameters: 1 T i, x y , c P i P i P i s T x 1 0 s 1 DOF n s 31 2
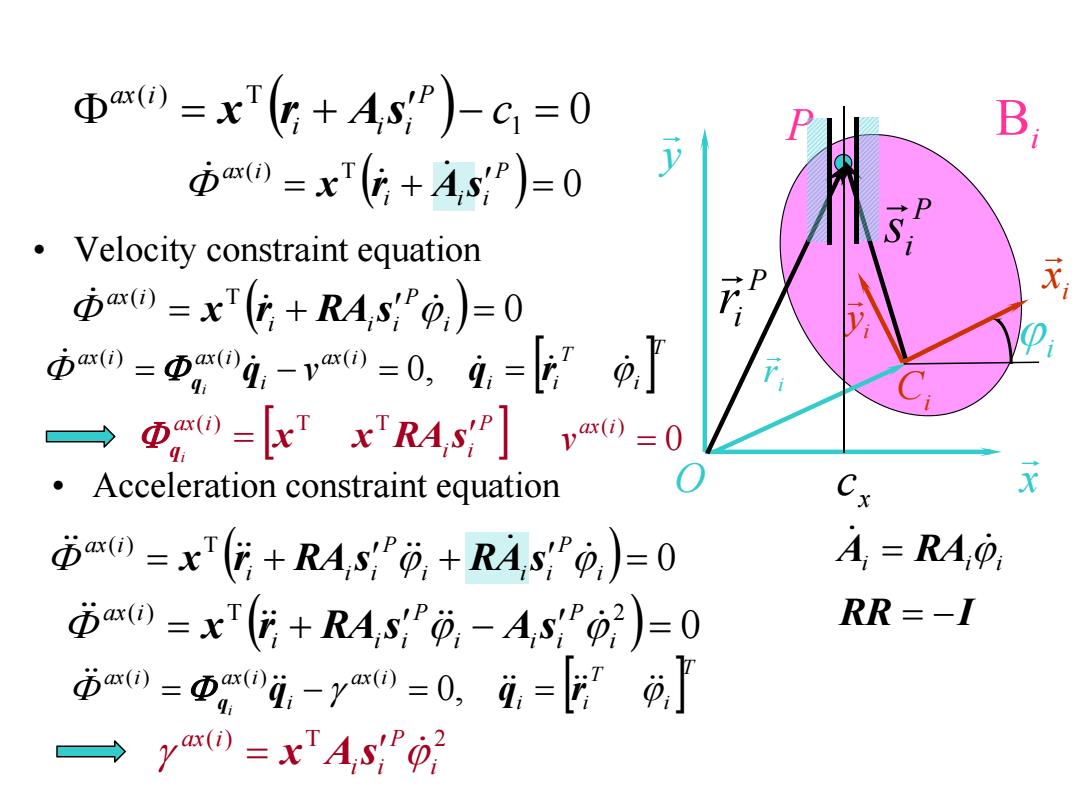
Φ)=xTG+AsP)-c=0 B 本0=xr(+AsP)=0 y Velocity constraint equation 市o=xr(G+RAsf0,)=0 市w=西,meg,-vaw=0,g,=上,J →Dm=erx'r4g]va0=0 Acceleration constraint equation Cx X p)=x"(+RAs",+RAs)=O A=RAO 本0=xT+RAs,-As2)=0 RR=-1 市m0=Φ,0i,-y0=0,4= →ym0=xAs02
• Velocity constraint equation 1 0 ( ) T c P i i i ax i x r As 0 ( ) T P i i i ax i x r A s 0 ( ) T i P i i i ax i x r RA s i ii ( ) T 0 A RA i P i i i P i i i ax i x r RA s RA s RR I 0 ( ) T 2 i P i i i P i i i ax i x r RA s A s • Acceleration constraint equation T i T i i ax i i ax i ax i v i q q r q 0, ( ) ( ) ( ) P i i ax i i x x RA s q ( ) T T T i T i i ax i i ax i ax i i q q r q 0, ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) T 2 i P i i ax i x A s Bi y x O i x i y Ci i r i P P ir P i s x c 0 ( ) ax i v
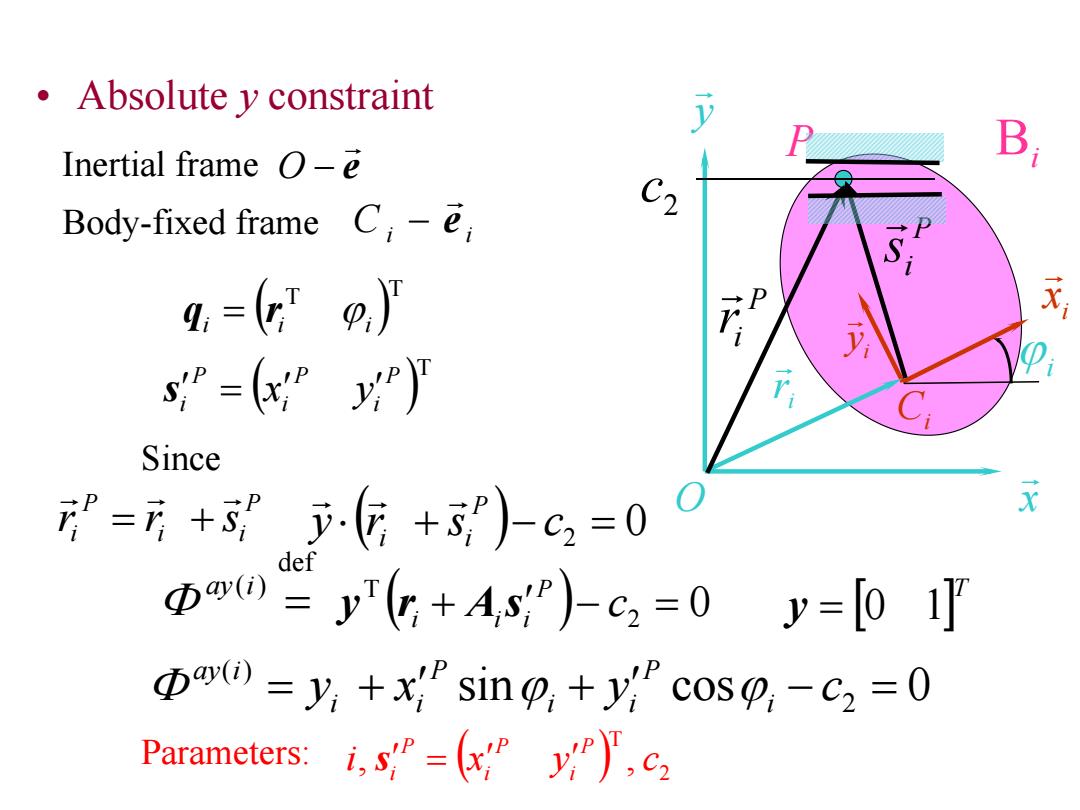
Absolute y constraint Inertial frame o-e B Body-fixed frame C-e C2 sP=(PP)J Since =元+5”,(+5)-02=00 X B0)=y+A,s;")-c2=0 y=[0 1 pardi)=y,+x sin +y cosp-c2=0 Parameters:,s=c
Bi y x O i x i y Ci i r i P P ir P i s 2 c • Absolute y constraint e Inertial frame O Ci i e Body-fixed frame T T i i i q r T P i P i P i s x y P i i P ir r s def ( ) ay i 0 y r s c2 P i i 0 2 T c P i i i y r A s sin cos 0 2 ( ) y x y i c P i i P i i ay i Since T y 0 1 Parameters: 2 T i, x y , c P i P i P i s
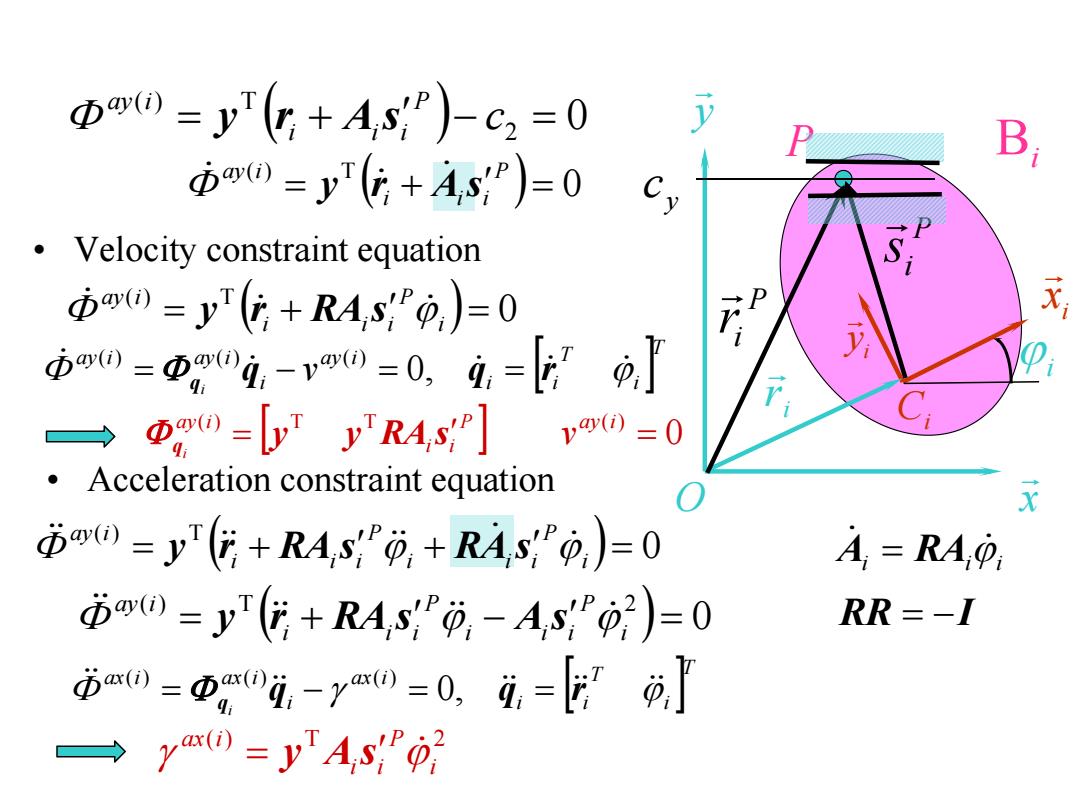
Φ0=yT(+AsP)c2=0 B 市0=y(+AsP)=0 Velocity constraint equation D0=y(G+RAs0,)=0 市0=Da0豆-vm0=0,g,=上0 →( )=yT yRA,s;()=0 Acceleration constraint equation 市o=y+R4sy,+RAsp,)=0 A,=RA 市0=y+RAs-As2)=0 RR=-1 市0=Φ,0,-y0=0,,=, →y0=yAs02
• Velocity constraint equation 0 2 ( ) T c P i i i ay i y r A s 0 ( ) T P i i i ay i y r A s 0 ( ) T i P i i i ay i y r RA s i ii 0 A RA ( ) T i P i i i P i i i ay i y r RA s RA s 0 RR I ( ) T 2 i P i i i P i i i ay i y r RA s A s • Acceleration constraint equation Bi y x O i x i y Ci i r i P P ir P i s y c T i T i i ax i i ax i ax i i q q r q 0, ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) T 2 i P i i ax i y A s T i T i i ay i i ay i ay i v i q q r q 0, ( ) ( ) ( ) P i i ay i i y y RA s q ( ) T T 0 ( ) ay i v
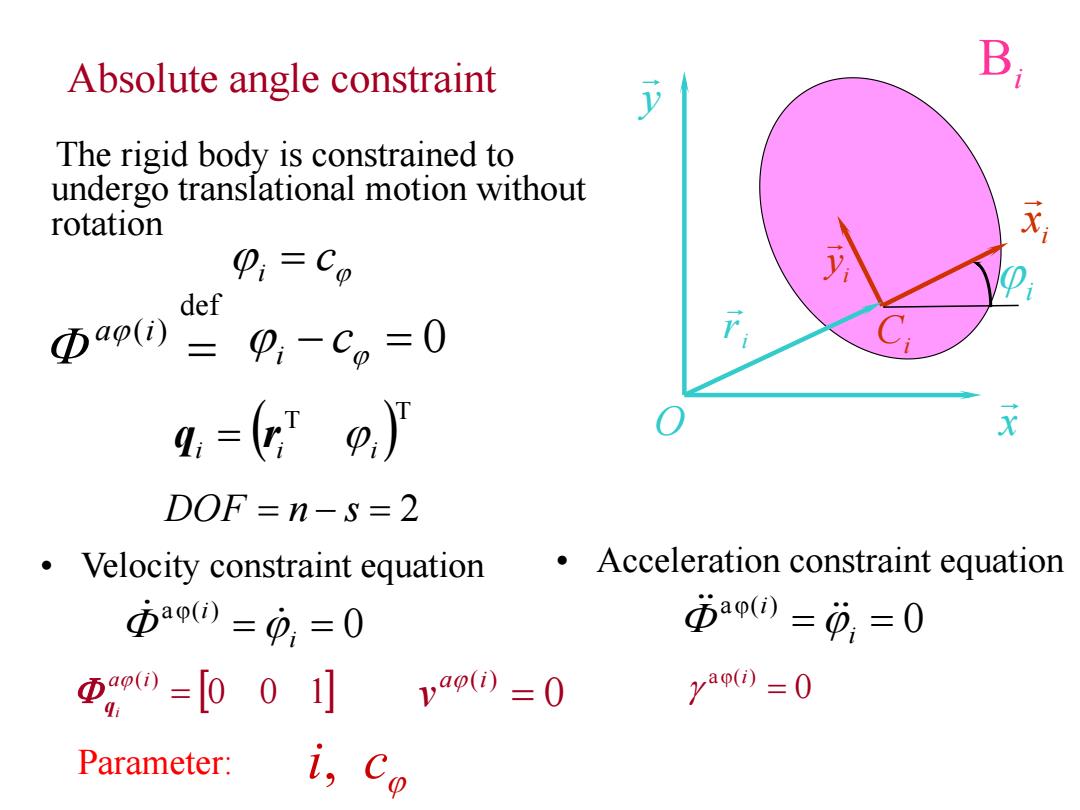
Absolute angle constraint B The rigid body is constrained to undergo translational motion without rotation p,=C0 def Φao() =,-C=0 g,=(p,) DOF=n-s=2 Velocity constraint equation Acceleration constraint equation 本a90=0,=0 iao0)=0,=0 Φ0=[00] vap(i)=0 (=O Parameter: i Co
The rigid body is constrained to undergo translational motion without rotation i c 0 def ( ) a i c i • Velocity constraint equation 0 a ( ) i i • Acceleration constraint equation 0 a ( ) i i Parameter: i, c i r Bi y x O i x i y Ci i DOF n s 2 T T i i i q r Absolute angle constraint 0 0 1 ( ) a i i q 0 a ( ) i 0 ( ) a i v
Absolute distance constraint The distance between point P of B,and a fixed point on the ground is constant Absolute distance constraint
• The distance between point P of Bi and a fixed point on the ground is constant Absolute distance constraint Absolute distance constraint
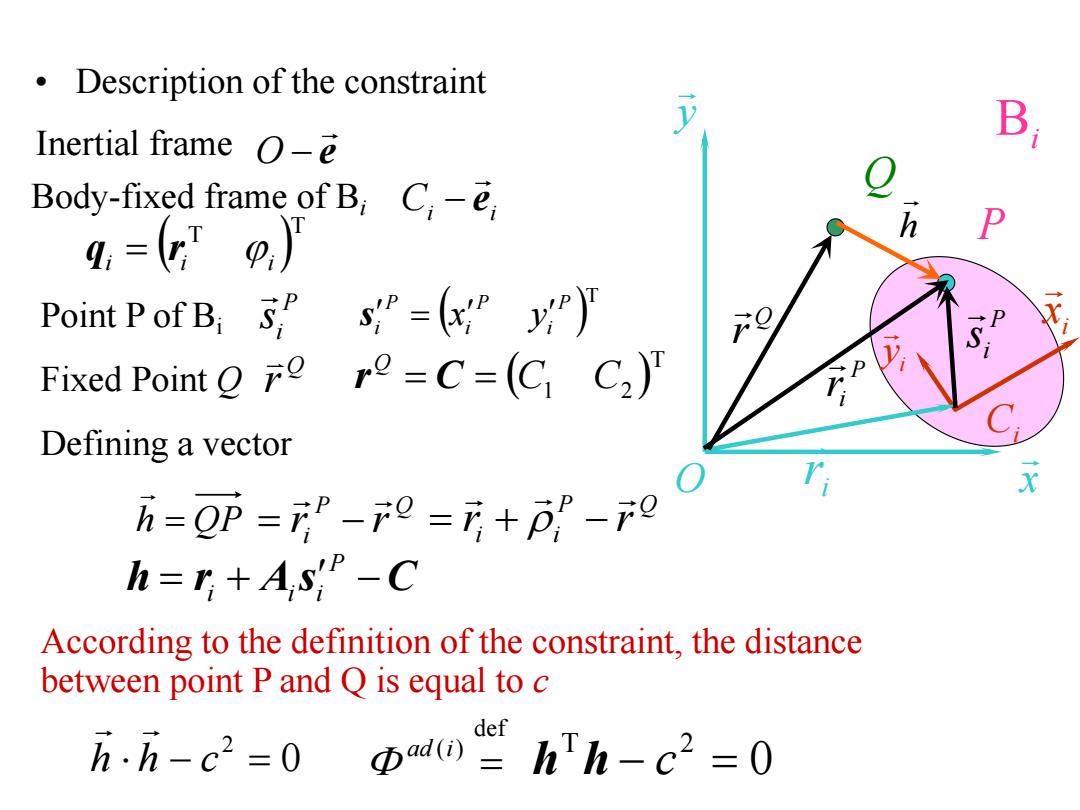
Description of the constraint Inertial frame o-e B Body-fixed frame of Bi C-e 4,=Tp,) h P Point P of B:sP=y) 9 Fixed Point r=C=(C C2) Defining a vector h=⑨丽=P-=方+p-0 h=n+As-C According to the definition of the constraint,the distance between point P and Q is equal to c def h.h-c2=0 Φadi=hTh-c2=0
• Description of the constraint Bi y x O i x i y Ci i r P P ir P i s e Inertial frame O Ci i e Body-fixed frame of Bi T T i i i q r Point P of Bi P i s T P i P i P i s x y Fixed Point Q Q r T C1 C2 Q r C Q h Q r h QP P Q ir r P Q i i r r h r A s C P i i i 0 2 h h c 0 T 2 h h c def ( ) ad i Defining a vector According to the definition of the constraint, the distance between point P and Q is equal to c
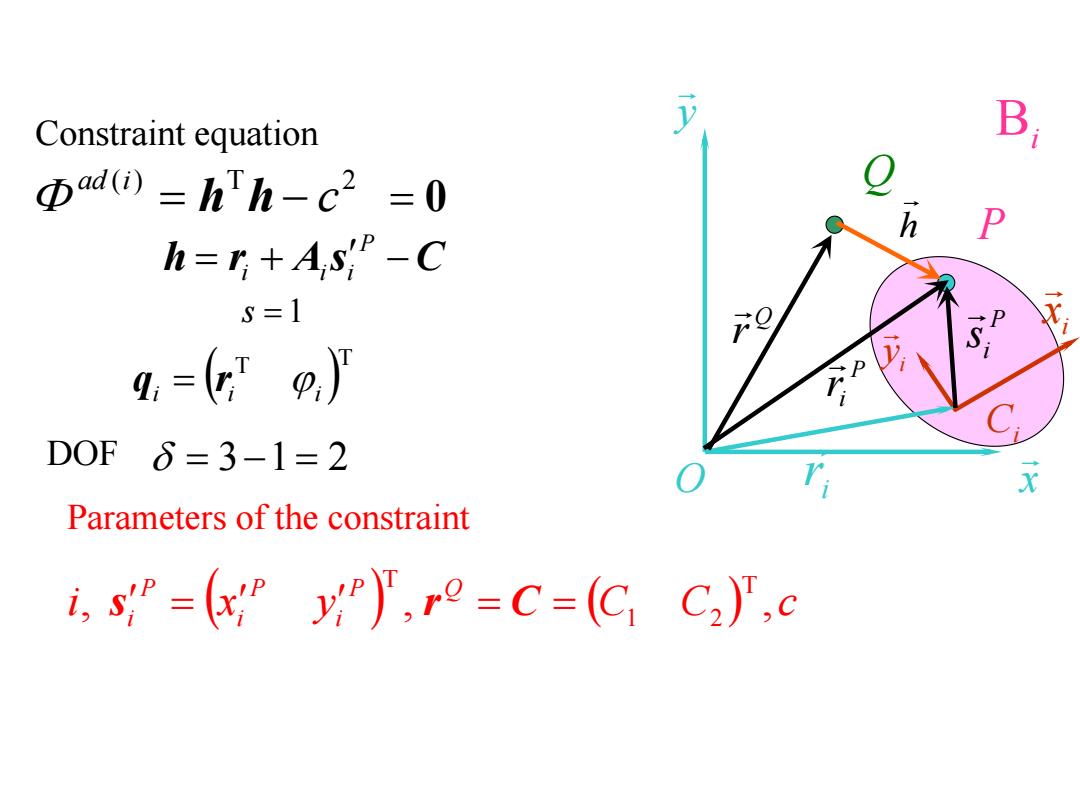
Constraint equation B Φad(=hTh-c2=0 h P h=n+AsP-C s=1 9 g,=g,) D0F8=3-1=2 r X Parameters of the constraint i,s=”y',r2=C=(CC2)》',c
Constraint equation 0 h r A s C P i i i ( ) T 2 c ad i h h s 1 DOF 31 2 T T i i i q r Parameters of the constraint i x y C C c P Q i P i P i , , , T 1 2 T s r C Bi y x O i x i y Ci i r P P ir P i s Q h Q r