
Lecture 2 Classical Power Spectral Estimation Methods and Biomedical Applications Prof.N.Rao
Lecture 2 Classical Power Spectral Estimation Methods and Biomedical Applications Prof. N. Rao
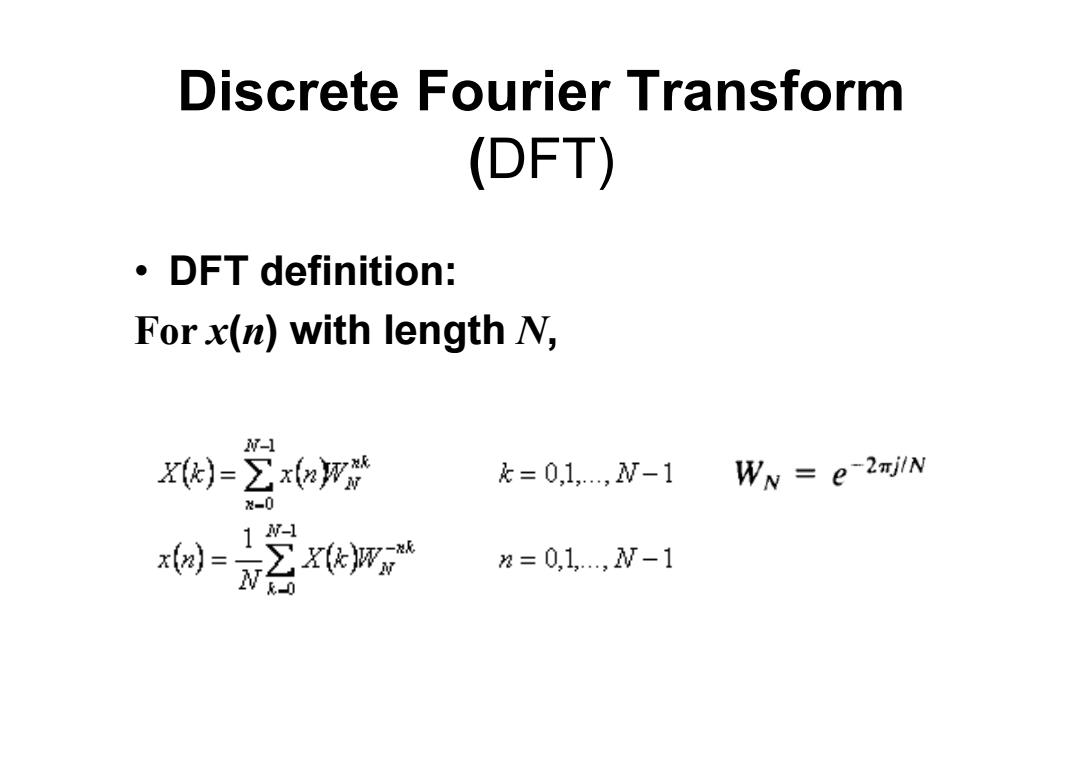
Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) 。DFT definition: Forx(n)with length N, N-1 X)=∑xaw k=0,1,,W-11 WN=e-2m时jlN -0 1-1 树=之w 2=0,1,,W-1
Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) • DFT definition: For x ( n) with length N

·DFT Properties: (1)Linearity (2)Orthogonality (3)Displacement(移位性) (4)Symmetry
• DFT Properties: (1) Linearity (2) Orthogonality (3) Displacement (移位性) (4) Symmetry

Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) FFT is a fast algorithm for computing DFT. Cooley and Tukey proposed FFT DFT:multiplying number:N2 Adding number:N (N-1) FFT multiplying number:(N/2)log2M
Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) FFT is a fast algorithm for computing DFT. Cooley and Tukey proposed FFT DFT: multiplying number: N2 Adding number: N ( N-1 ) FFT : multiplying number: ( N/2 )log 2 N

FFT computing cost For instance,if N=1024 DFT multiplying number is 1048576 FFT multiplying number is 5120,taking up 4.88%of DFT multiplication
FFT computing cost • For instance ,if N=1024 • DFT multiplying number is 1048576 • FFT multiplying number is 5120, taking up 4.88% of DFT multiplication
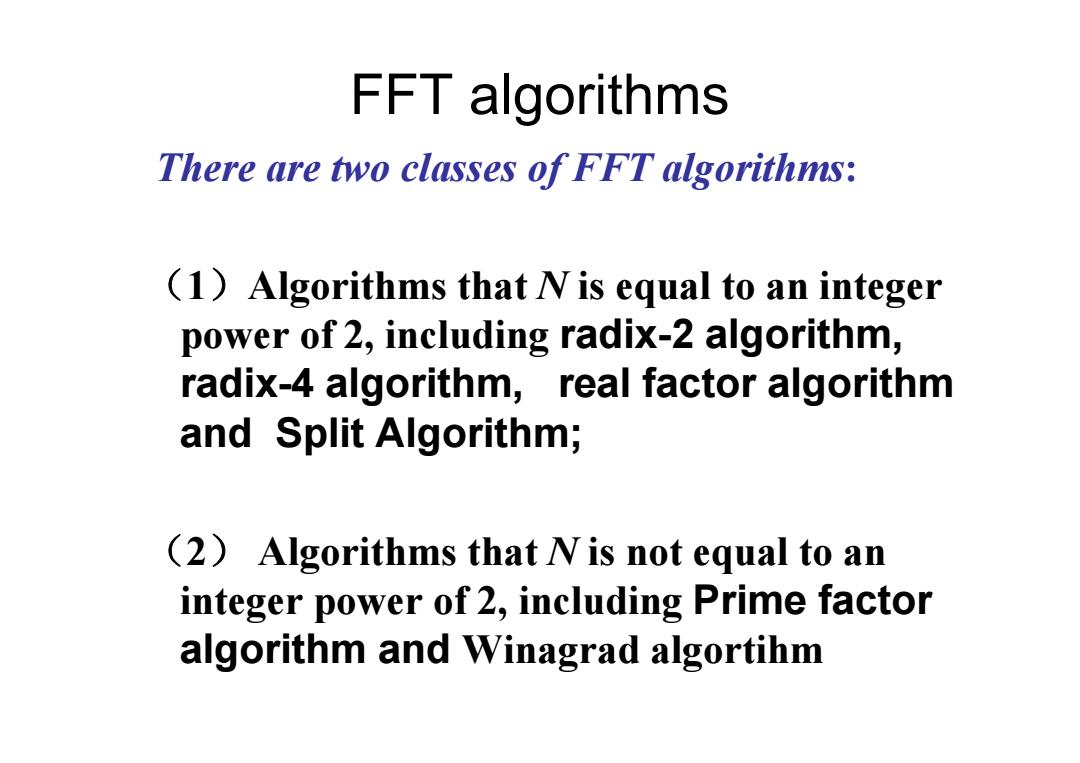
FFT algorithms There are two classes of FFT algorithms: (1)Algorithms that Nis equal to an integer power of 2,including radix-2 algorithm, radix-4 algorithm,real factor algorithm and Split Algorithm; (2)Algorithms that N is not equal to an integer power of 2,including Prime factor algorithm and Winagrad algortihm
FFT algorithms There are two classes of FFT algorithms : ( 1 )Algorithms that N is equal to an integer power of 2, including radix-2 algorithm, radix-4 algorithm, real factor algorithm and Split Algorithm; ( 2 ) Algorithms that N is not equal to an integer power of 2, including Prime factor algorithm and Winagrad algortihm

Periodogram A classical power spectral estimation method. PSD (Power Spectral Density): Assume that y(n)is a bounded digital sequence with length N
Periodogram • A classical power spectral estimation method. • PSD (Power Spectral Density) : Assume that y ( n ) is a bounded digital sequence with length N
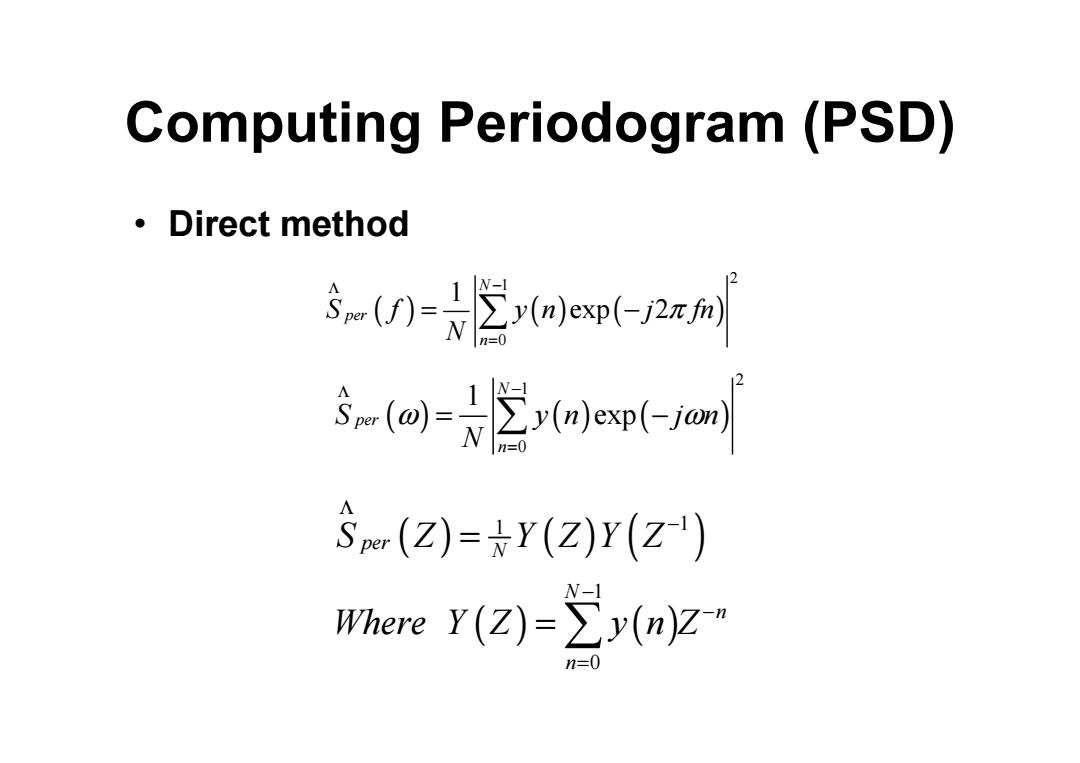
Computing Periodogram(PSD) ·Direct method $()=2小ep(-2x例 s(oj=2o小em(-am S(Z)=★Y(Z)Y(Z) Where y(Z)=∑y(n)Z n=0
Computing Periodogram (PSD) • Direct method ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 1 0 1 exp 2 N per n S f y n j fn N π Λ − = = − ∑ ( ) ( ) ( ) 2 1 0 1 exp N per n S y n j n N ω ω Λ − = = − ∑ ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 1 1 0 per N N n n S Z Y Z Y Z Where Y Z y n Z Λ − − − = = = ∑
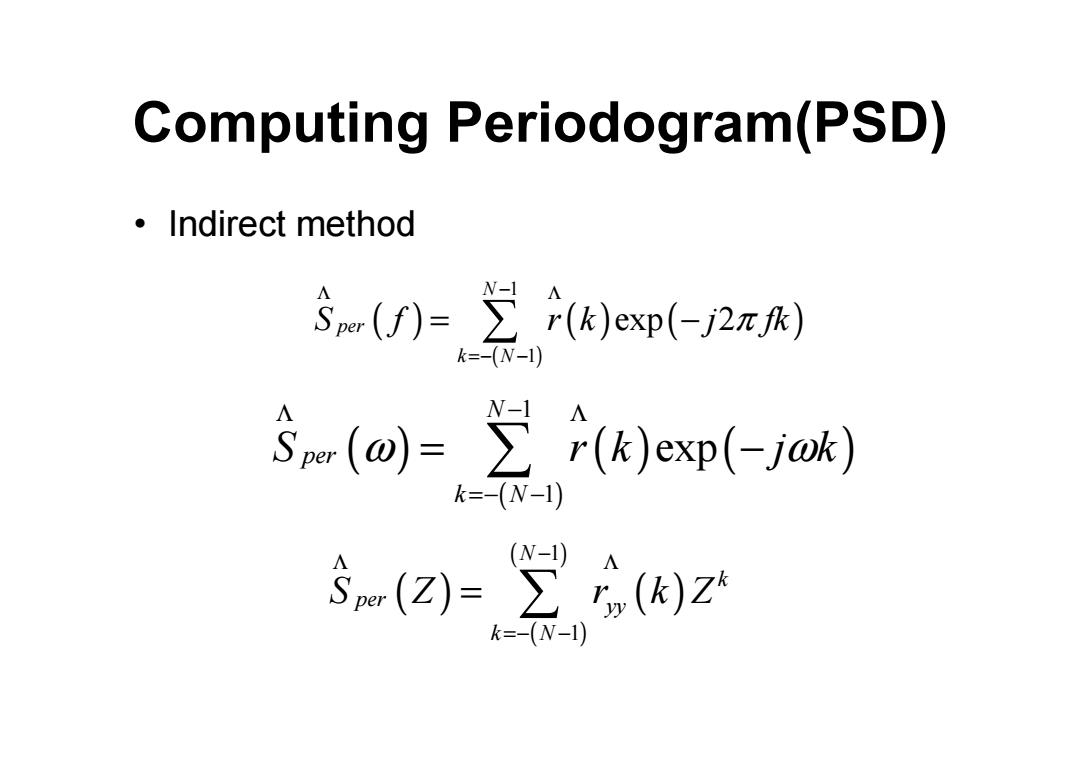
Computing Periodogram(PSD) ·Indirect method S()=∑t(k)exp(-2π) k=-(N-1) 3m(o)-(k)exp(-jok) k=-(N-1) s(2=2z k=-(N-1)
Computing Periodogram(PSD) • Indirect method ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 1 exp 2 N per k N S f r k j fk π Λ Λ − =− − = − ∑ ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 1 exp N per k N S r k j k ω ω Λ Λ − =− − = − ∑ ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) 1 1 N k per yy k N S Z r k Z − Λ Λ =− − = ∑
Periodogram Properties Properties: (1)An biased estimator; (2)Not a consistent estimator; (3)Frequency resolution &N
Periodogram Properties Properties: (1) An biased estimator; (2) Not a consistent estimator; (3) Frequency resolution ∝ N