
Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Color Fundamentals and models Pseudo-Color Image Processing Full-color Image processing 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Color Fundamentals and models Pseudo-Color Image Processing Full-color Image processing
Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Pseudocolor Image Processing Pseudocolor (also called false color)image processing consists of assigning colors to gray values based on a specified criterion. The principal use of pseudocolor is for human visualization and interpretation of gray-scale events in an image or sequence of images. 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez &R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Pseudocolor Image Processing Pseudocolor (also called false color) image processing consists of assigning colors to gray values based on a specified criterion. The principal use of pseudocolor is for human visualization and interpretation of gray-scale events in an image or sequence of images
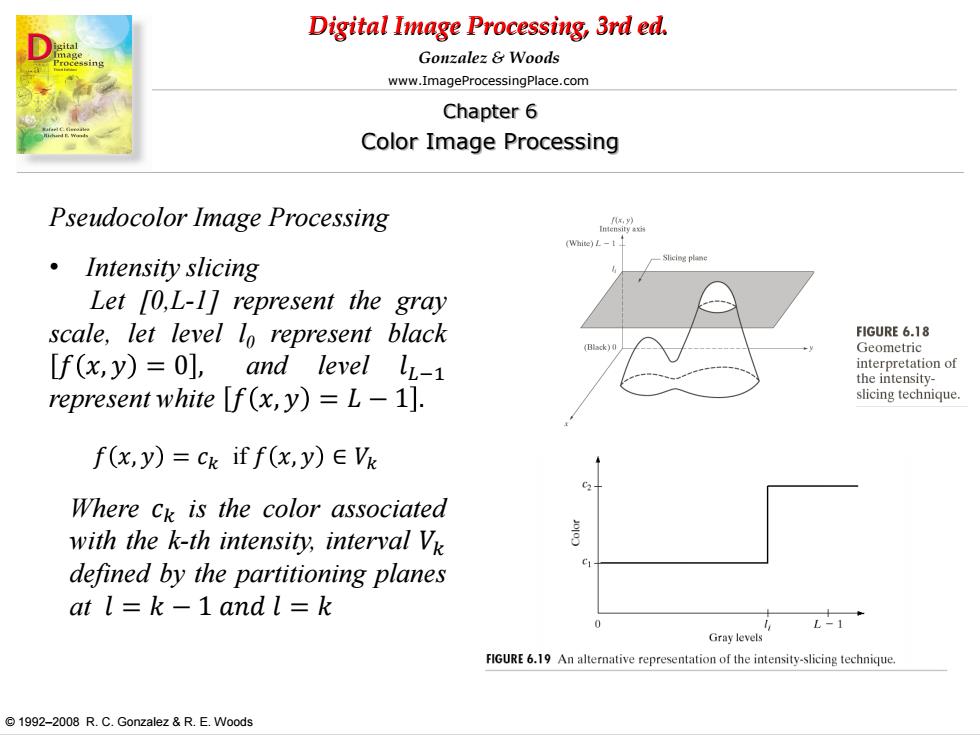
Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Pseudocolor Image Processing (Whice)L1 ·Intensity slicing Let [0,L-1]represent the gray scale,let level lo represent black FIGURE 6.18 Geometric [f(x,y)=0],and level lL-1 tereo represent white [f(x,y)=L-1]. slicing technique f(x,y)=ck if f(x,y)E Vk Where ck is the color associated with the k-th intensity,interval Vk defined by the partitioning planes at l=k-1and l=k L-1 Gray levels FIGURE 6.19 An alternative representation of the intensity-slicing technique. 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Pseudocolor Image Processing • Intensity slicing Let [0,L-1] represent the gray scale, let level l0 represent black 𝑓 𝑥, 𝑦 = 0 , and level 𝑙𝐿−1 represent white 𝑓 𝑥, 𝑦 = 𝐿 − 1 . 𝑓 𝑥, 𝑦 = 𝑐𝑘 if 𝑓 𝑥, 𝑦 ∈ 𝑉𝑘 Where 𝑐𝑘 is the color associated with the k-th intensity, interval 𝑉𝑘 defined by the partitioning planes at 𝑙 = 𝑘 − 1 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑙 = 𝑘
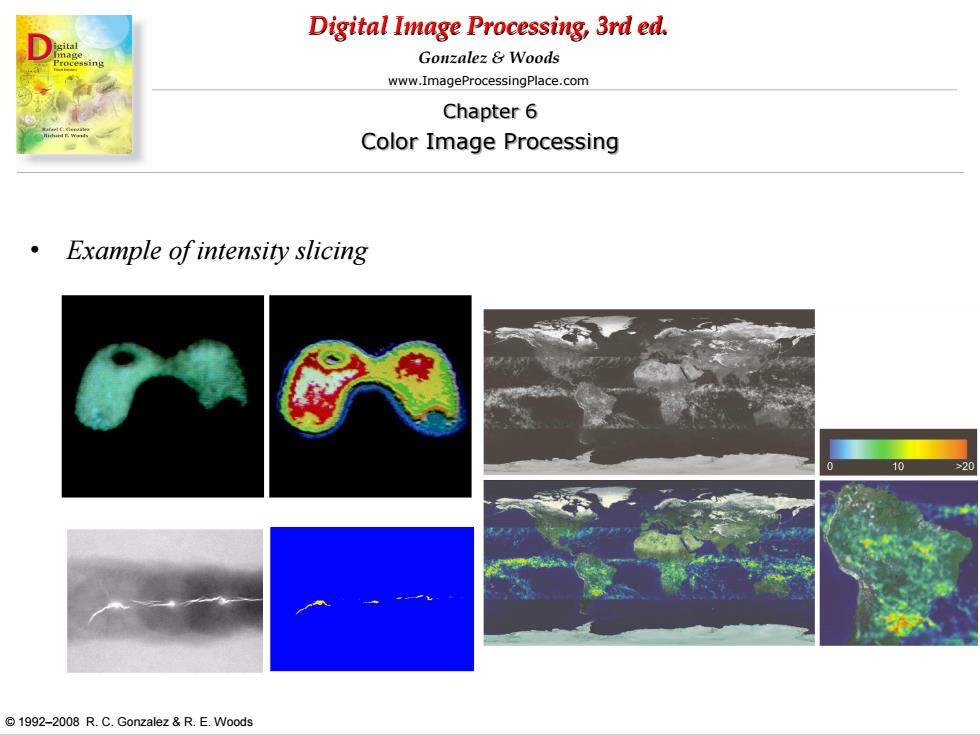
Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez&Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Example of intensity slicing 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing • Example of intensity slicing
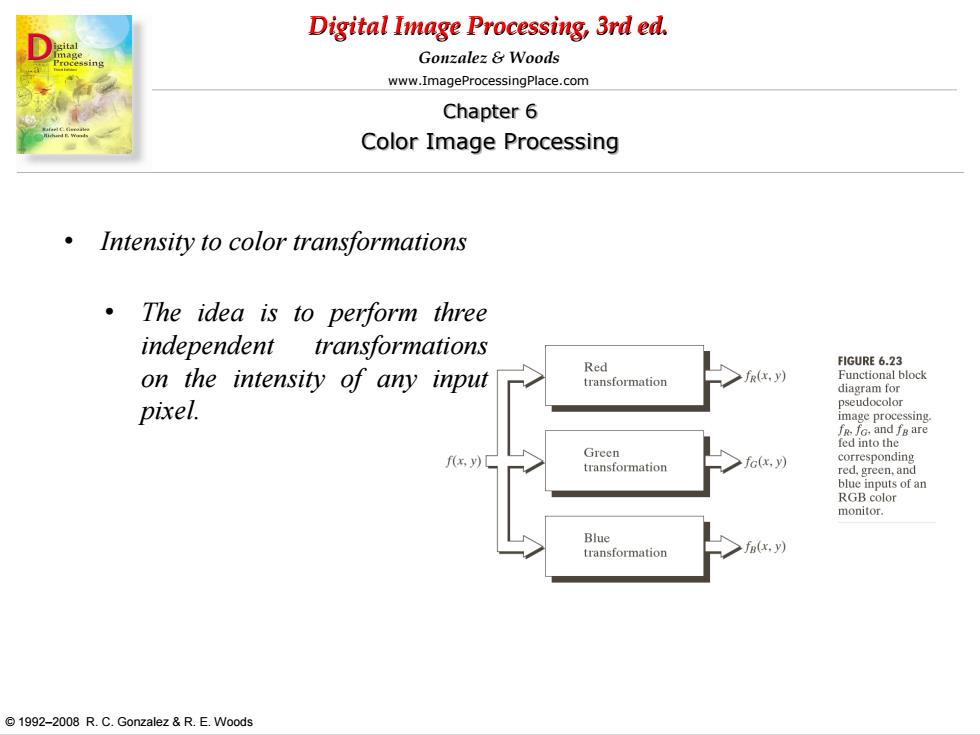
Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Intensity to color transformations The idea is to perform three independent transformations Red FIGURE 6.23 on the intensity of any input transformation fr(x.y) Functional block diagram for pixel. pseudocolor edto fxy)口 Green transformation fc(x.y) corresponding red,green,and blue inputs of an RGB color monitor. Blue transformation fg(x.y) 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing • Intensity to color transformations • The idea is to perform three independent transformations on the intensity of any input pixel
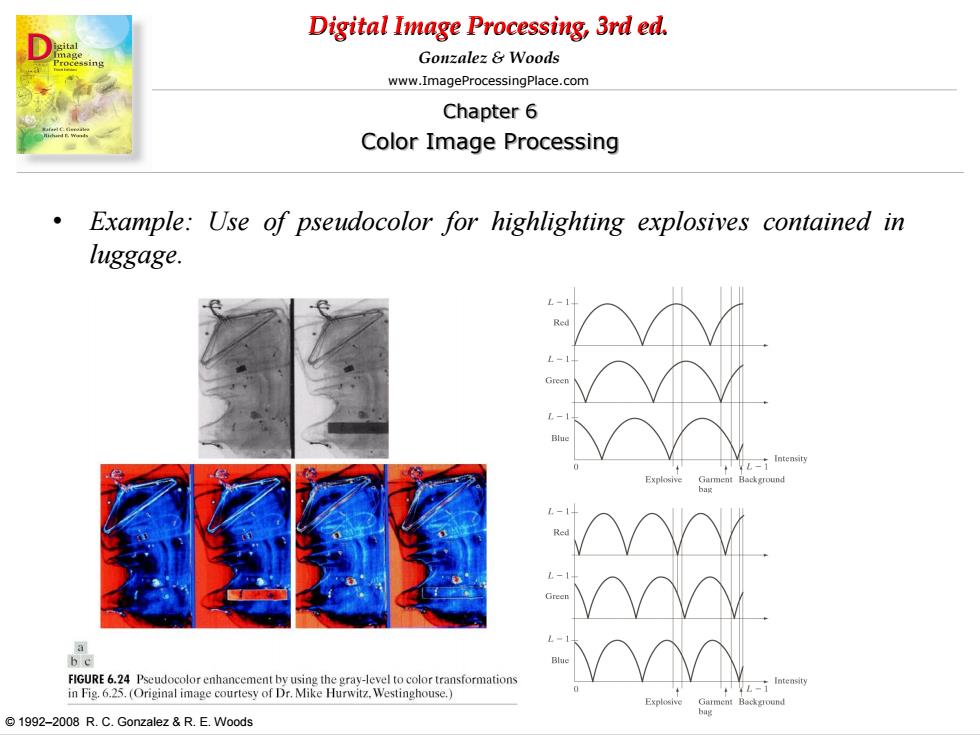
Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing 。 Example:Use of pseudocolor for highlighting explosives contained in luggage L-1 L- be Intensit Explosive 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing • Example: Use of pseudocolor for highlighting explosives contained in luggage
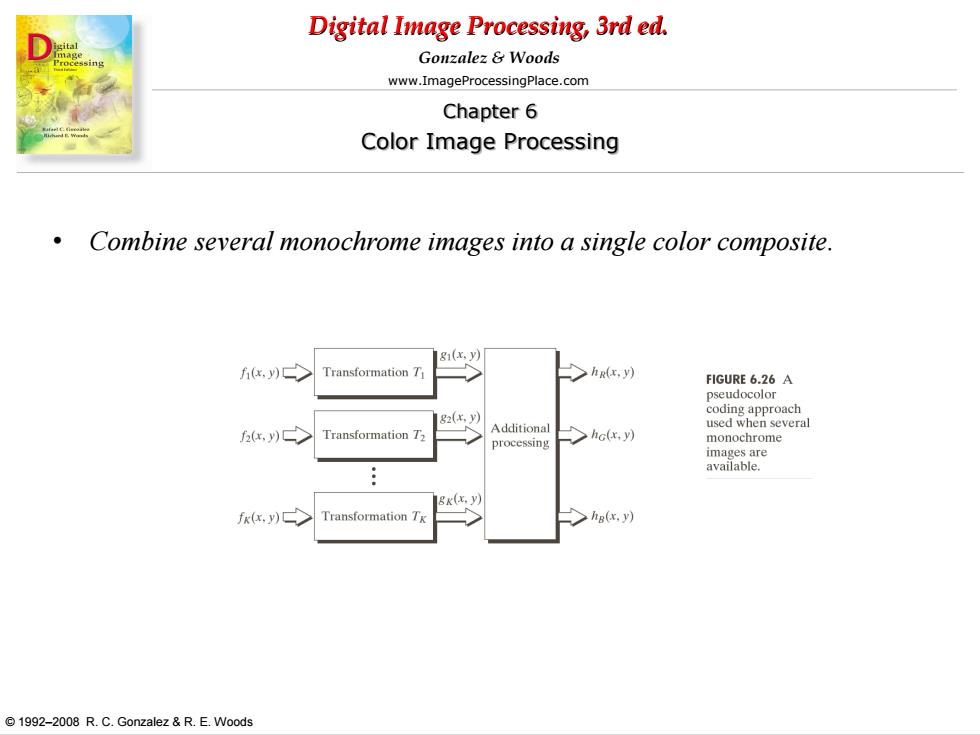
Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Combine several monochrome images into a single color composite. 1g1(x,y) x,)> Transformation T hR(x.y) FIGURE 6.26 A pseudocolor 82(x,y) 6,)> Transformation T Additiona >hc(x,y) processing monochrome images are available gx(x.y) fk(x.y) Transformation Tg hg(x.y) 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing • Combine several monochrome images into a single color composite
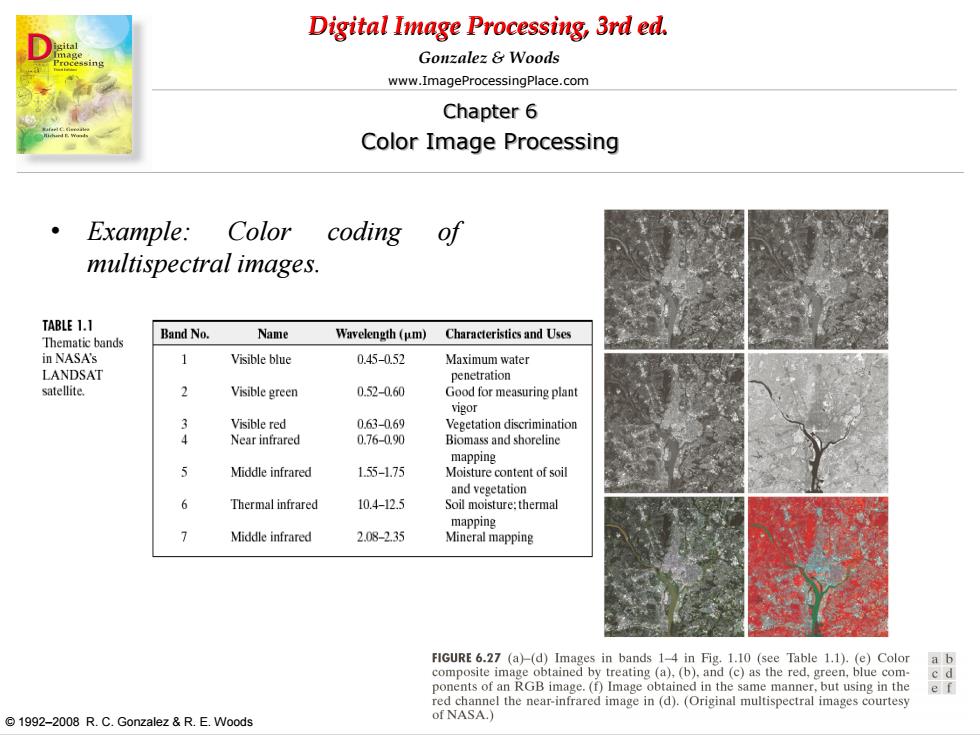
Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Example: Color coding of multispectral images. TABLE 1.1 Band No. Name Thematic bands Wavelength(um)Characteristics and Uses in NASA's 1 Visible blue 0.45-0.52 Maximum water LANDSAT penetration satellite. 2 Visible green 0.52-0.60 Good for measuring plant vigor 2 Visible red 0.63-0.69 Vegetation discrimination Near infrared 0.76-0.90 Biomass and shoreline mapping Middle infrared 155-1.75 Moisture content of soil and vegetation 6 Thermal infrared 10.4-12.5 Soil moisture:thermal mapping 7 Middle infrared 2.08-2.35 Mineral mapping FIGURE 6.27 (a)-(d)Images in bands 1-4 in Fig.1.10 (see Table 1.1).(e)Color a b composite image obtained by treating (a),(b).and (c)as the red,green,blue com- ponents of an RGB image.(f)Image obtained in the same manner,but using in the red channel the near-infrared image in (d).(Original multispectral images courtesy 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez &R.E.Woods of NASA.)
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing • Example: Color coding of multispectral images

Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Color Fundamentals and models Pseudo-Color Image Processing Full-color Image processing 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Color Fundamentals and models Pseudo-Color Image Processing Full-color Image processing

Digital Image Processing,3rd ed. Gonzalez&Woods www.ImageProcessingPlace.com Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Basic of Full-Color Image Processing Let c represent an arbitrary vector in RGB color space: TCR] CR(x,y)] [R(x,y) C三 G c(x,y)= cc(x,y) G(x,y) LCB LB」 cB(x,y)] B(x,y)] ab FIGURE 6.29 Spatial masks for gray-scale and (y) RGB color (x.y) Spatial mask Spatial mask images. Gray-scale image RGB color image 1992-2008 R.C.Gonzalez R.E.Woods
Digital Image Processing, 3rd ed. www.ImageProcessingPlace.com © 1992–2008 R. C. Gonzalez & R. E. Woods Gonzalez & Woods Chapter 6 Color Image Processing Basic of Full-Color Image Processing • Let c represent an arbitrary vector in RGB color space: 𝑐 = 𝑐𝑅 𝑐𝐺 𝑐𝐵 = 𝑅 𝐺 𝐵 𝑐 𝑥, 𝑦 = 𝑐𝑅 𝑥, 𝑦 𝑐𝐺 𝑥, 𝑦 𝑐𝐵 𝑥, 𝑦 = 𝑅 𝑥, 𝑦 𝐺 𝑥, 𝑦 𝐵 𝑥, 𝑦