
Statistical Detection Theory Statistical Detection Theory Il Wenhui Xiong NCL UESTC whxiong@uestc.edu.cn
whxiong@uestc.edu.cn Statistical Detection Theory Statistical Detection Theory II Wenhui Xiong NCL UESTC
System Model ●Summary of NP rule: ·Hypothesis test Deterministic->known signal Random signal->known pdf How about the hypothesis test with unknown or partially known pdf? Composite test whxiong@uestc.edu.cn 2
whxiong@uestc.edu.cn System Model 2 Summary of NP rule: Hypothesis test Deterministic -> known signal Random signal ->known pdf How about the hypothesis test with unknown or partially known pdf? Composite test

Composite Test-One-sided Test E.g.,Positive DC in WGN with known noise statistics Ho xIn]wln] A>0 H xIn]A+wln] n=0,1..W-1 whxiong@uestc.edu.cn
whxiong@uestc.edu.cn Composite Test—One-sided Test H1 x[n] = A + w[n] E.g., Positive DC in WGN with known noise statistics H0 x[n] = w[n] n=0,1…N-1 A>0

Composite Test-One-sided Test E.g.,Positive DC in WGN with known noise statistics Ho xIn]wln] A>0 H xIn]=A+wln] n=01..W-1 Apply NP rule P(X;A,H1) exp(-∑(xnl-A2 P(x:A,Ho) >Y exp(-2a∑2[n]) whxiong@uestc.edu.cn 4
whxiong@uestc.edu.cn Composite Test—One-sided Test 4 H1 x[n] = A + w[n] E.g., Positive DC in WGN with known noise statistics H0 x[n] = w[n] n=0,1…N-1 Apply NP rule A>0 P(x; A; H1) P(x; A; H0) = exp (¡ 1 2¾2 P(x[n] ¡ A) 2 exp(¡ 1 2¾2 Px 2[n]) > °

Composite Test-One-sided Test E.g.,Positive DC in WGN with known noise statistics Ho xIn]wln] A>0 H xIn]=A+wln] n=01..W-1 Apply NP rule P(x;A,H1) exp(-2石∑(cn-A2 P(x;A,Ho) >Y exp(-2a∑2[m]) -京(-2A∑n+N4)>1n whxiong@uestc.edu.cn
whxiong@uestc.edu.cn Composite Test—One-sided Test H1 x[n] = A + w[n] E.g., Positive DC in WGN with known noise statistics H0 x[n] = w[n] n=0,1…N-1 Apply NP rule A>0 P(x; A; H1) P(x; A; H0) = exp (¡ 1 2¾2 P(x[n] ¡ A) 2 exp(¡ 1 2¾2 Px 2[n]) > ° ¡ 1 2¾2 ³ ¡2A Xx[n] + NA 2 ´ > ln°

Composite Test-One-sided Test E.g.,Positive DC in WGN with known noise statistics Ho xIn]wln] A>0 H xIn]=A+wln] n=01..W-1 Apply NP rule P(x;A,H1) eXxp(-a∑(x[n-A)2 P(x;A,Ho) >Y exp(-2a∑x2[m) -2(-2A∑m+N4)>1n ↓4>0 ∑xm>清ny+ A → 2 NA 2 whxiong@uestc.edu.cn 6
whxiong@uestc.edu.cn Composite Test—One-sided Test 6 H1 x[n] = A + w[n] E.g., Positive DC in WGN with known noise statistics H0 x[n] = w[n] n=0,1…N-1 Apply NP rule A>0 P(x; A; H1) P(x; A; H0) = exp (¡ 1 2¾2 P(x[n] ¡ A) 2 exp(¡ 1 2¾2 Px 2[n]) > ° ¡ 1 2¾2 ³ ¡2A Xx[n] + NA 2 ´ > ln° Xx[n] > ¾2 A ln °+ NA 2 2 A>0 x¹> ¾2 NA ln°+ A 2 = ° 0

Composite Test The detectio statistics倒-∑rn Constant False Alarm,e.g.,PrA P(H1;Ho) whxiong@uestc.edu.cn 7
whxiong@uestc.edu.cn Composite Test 7 The detection statistics Constant False Alarm, e.g., T(x) = 1 N Xx[n] PFA = P(H1; H0)

Composite Test The detection statistics Constant False Alarm,e.g.,PrA P(H1;Ho) Under Ho T(x)~N(0,02/N) whxiong@uestc.edu.cn 8
whxiong@uestc.edu.cn Composite Test 8 The detection statistics Constant False Alarm, e.g., T(x) = 1 N Xx[n] PFA = P(H1; H0) Under H0 T(x) » N(0; ¾ 2 =N)

Composite Test The detection statistics Constant False Alarm,e.g.,PrA=P(H1;Ho) Under Ho I(x)~N(0,02/N) PrA=P(T(a)>Y;Ho)=fHo(t)dt=Q(/VTN ↓Y=Vge whxiong@uestc.edu.cn 9
whxiong@uestc.edu.cn Composite Test 9 The detection statistics Constant False Alarm, e.g., T(x) = 1 N Xx[n] PFA = P(H1; H0) Under H0 T(x) » N(0; ¾ 2 =N) PFA = P(T(x) > ° 0 ; H0) = Z 1 °0 fH0 (t)dt = Q ³ ° 0 = p ¾2 =N ´ ° 0 = r ¾2 N Q ¡1 (PFA)
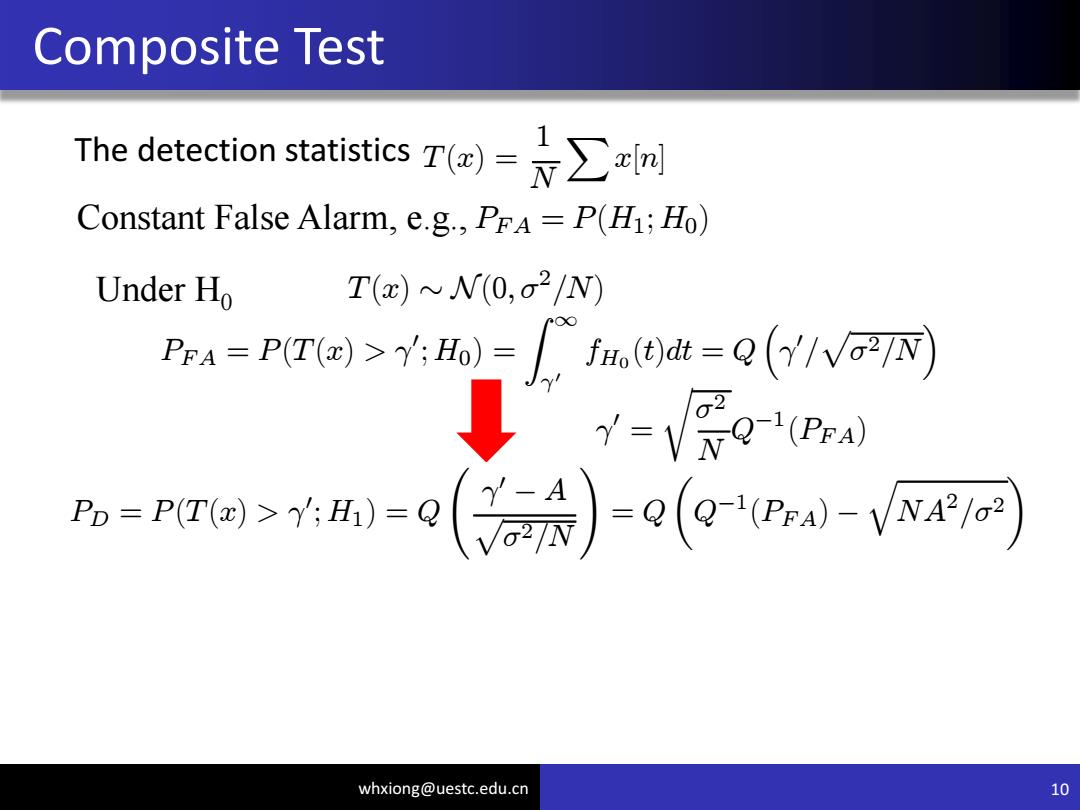
Composite Test The detection statisticsT Constant False Alarm,e.g.,PrA=P(H1;Ho) Under Ho I(x)~N(0,02/N) PrA=P(T()>Y;Ho)=fH.(t)dt=Q(Y/VTN ↓-VQ =PTa>=Q()-o(g-i-o) whxiong@uestc.edu.cn 10
whxiong@uestc.edu.cn Composite Test 10 The detection statistics Constant False Alarm, e.g., T(x) = 1 N Xx[n] PFA = P(H1; H0) Under H0 T(x) » N(0; ¾ 2 =N) PFA = P(T(x) > ° 0 ; H0) = Z 1 °0 fH0 (t)dt = Q ³ ° 0 = p ¾2 =N ´ ° 0 = r ¾2 N Q ¡1 (PFA) PD = P(T(x) > ° 0 ; H1) = Q Ã °0 ¡ A p ¾2 =N ! = Q µ Q ¡1 (PFA) ¡ q NA 2 =¾2 ¶