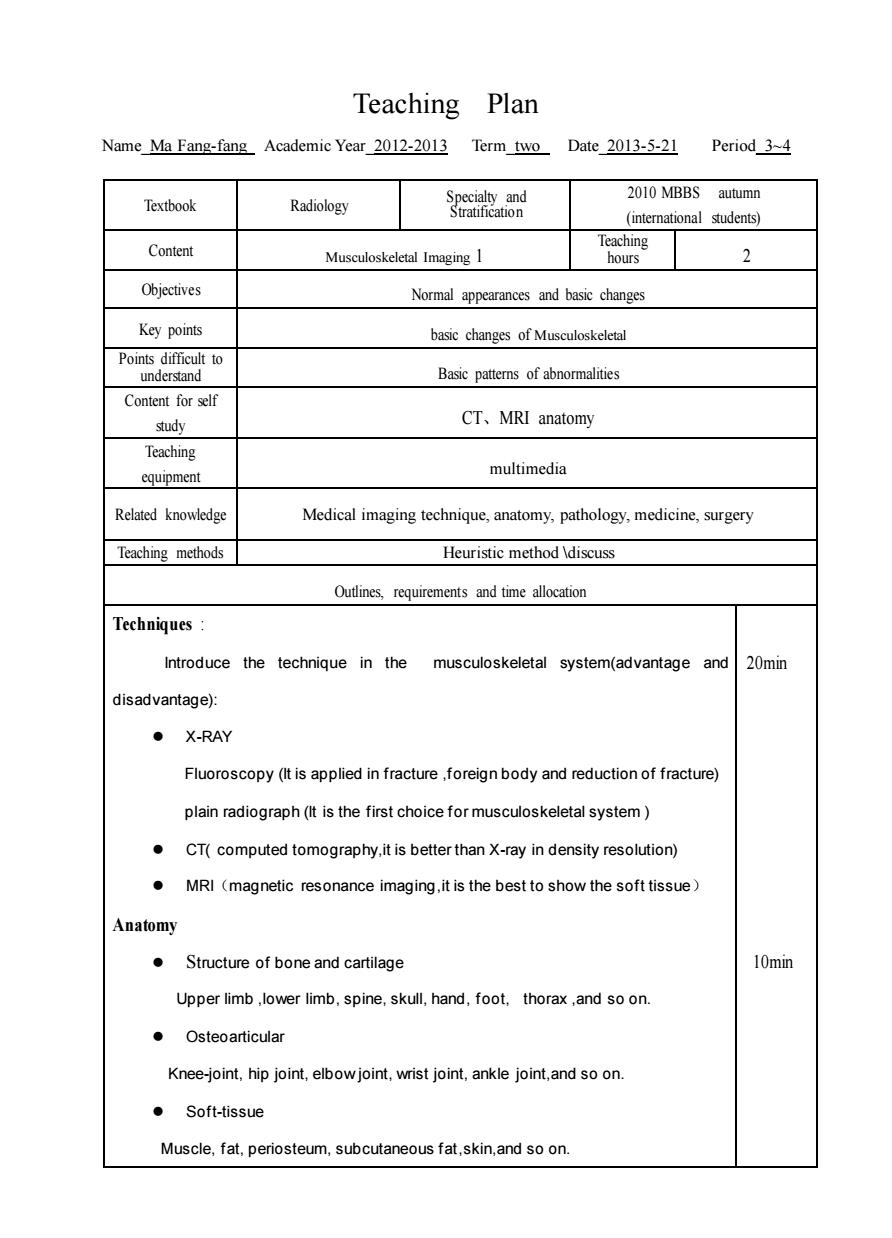
Teaching Plan Name Ma Fang-fang Academic Year 2012-2013 Term two Date 2013-5-21 Period 3-4 Textbook Radiology d 2010 MBBS autumn (international students) Content Musculoskeletal Imaging I 2 Objectives Normal appearances and basic changes Key points basic changes of Musculoskeletal 可 Basic patterns of abnormalities Content for self study CT、MRI anatomy Teaching equipment multimedia Related knowledge Medical imaging technique,anatomy,pathology,medicine,surgery Teaching methods Heuristic method Vdiscuss Outines,requirements and time allocation Techniques Introduce the technique in the musculoskeletal system(advantage and 20min disadvantage): ·X-RAY Fluoroscopy(It is applied in fracture.foreign body and reduction of fracture) plain radiograph(It is the first choice for musculoskeletal system) .CT(computed tomography,it is better than X-ray in density resolution) MRI(magnetic resonance imaging.it is the best to show the soft tissue) Anatomy .Structure of bone and cartilage 10min Upper limb,lower limb,spine,skull,hand,foot,thorax,and so on. ●Osteoarticular Knee-joint,hip joint,elbowjoint,wrist joint,ankle joint,and soon. ·Soft-tissue Muscle.fat.periosteum.subcutaneous fat,skin.and so on
Teaching Plan Name_Ma Fang-fang Academic Year_2012-2013 Term_two Date_2013-5-21 Period_3~4 Textbook Radiology Specialty and Stratification 2010 MBBS autumn (international students) Content Musculoskeletal Imaging 1 Teaching hours 2 Objectives Normal appearances and basic changes Key points basic changes of Musculoskeletal Points difficult to understand Basic patterns of abnormalities Content for self study CT、MRI anatomy Teaching equipment multimedia Related knowledge Medical imaging technique, anatomy, pathology, medicine, surgery Teaching methods Heuristic method \discuss Outlines, requirements and time allocation Techniques : Introduce the technique in the musculoskeletal system(advantage and disadvantage): ⚫ X-RAY Fluoroscopy (It is applied in fracture ,foreign body and reduction of fracture) plain radiograph (It is the first choice for musculoskeletal system ) ⚫ CT( computed tomography,it is better than X-ray in density resolution) ⚫ MRI(magnetic resonance imaging,it is the best to show the soft tissue) Anatomy ⚫ Structure of bone and cartilage Upper limb ,lower limb, spine, skull, hand, foot, thorax ,and so on. ⚫ Osteoarticular Knee-joint, hip joint, elbow joint, wrist joint, ankle joint,and so on. ⚫ Soft-tissue Muscle, fat, periosteum, subcutaneous fat,skin,and so on. 20min 10min

Outlines requirements and time allcaion Basic changes 1、Osteoporosis 10min It is a common metabolic disorder of bone characterized by qualitatively nommal but quantitatively deficient bone. .It can be divided into generalized,regional,and localized types and accompanies a variety of disease processes. Radiographic manifestations of osteoporosis include changes in radiolucency trabecular pattem.and shape or vertebral bodies in the spine (wedge-shaped vertebrae.compressed vertebrae.fish vertebrae).Schmorls nodes.acute and insufficiency fractures and bone bars(reinforcement lines) 2、Osteomalacia 15min which is a group of disorders resulting from inadequate or delayed mineralization of osteoid in mature cortical and spongy bone. Osteomalacia is characterized by abnormal quantities of osteoid coating the surfaces of trabeculae and lining the haversian canals in the cortex (osteoid seams). Loosers zones or Milkmans pseudofractures are strongly suggestive but not diagnostic of osteomalacia.Frequently osteitis fibrosa cystica is superimposed on the lesions of osteomalacia 3、Osteosclerosis 15min Which is an abnormal hardening or increased density of bone on radiographs Osteosclerosis may accompany a great variety of disorders,including hyperparathyroidism or renal osteodystrophy.osteoarthritis,sickle cell anaemia,Pagets disease,systemic mastocytosis,skeletal metastasis myelofibrosis,oxalosis,leukaemias and osteomyelitis
Outlines, requirements and time allocation Basic changes 1、Osteoporosis ⚫ It is a common metabolic disorder of bone characterized by qualitatively normal but quantitatively deficient bone. ⚫ It can be divided into generalized, regional, and localized types and accompanies a variety of disease processes. ⚫ Radiographic manifestations of osteoporosis include changes in radiolucency, trabecular pattern, and shape or vertebral bodies in the spine (wedge-shaped vertebrae, compressed vertebrae, fish vertebrae), Schmorls nodes, acute and insufficiency fractures and bone bars (reinforcement lines). 2、Osteomalacia ⚫ which is a group of disorders resulting from inadequate or delayed mineralization of osteoid in mature cortical and spongy bone. ⚫ Osteomalacia is characterized by abnormal quantities of osteoid coating the surfaces of trabeculae and lining the haversian canals in the cortex (osteoid seams). ⚫ Loosers zones or Milkmans pseudofractures are strongly suggestive but not diagnostic of osteomalacia .Frequently osteitis fibrosa cystica is superimposed on the lesions of osteomalacia. 3、Osteosclerosis ⚫ Which is an abnormal hardening or increased density of bone on radiographs. ⚫ Osteosclerosis may accompany a great variety of disorders, including hyperparathyroidism or renal osteodystrophy, osteoarthritis, sickle cell anaemia, Pagets disease, systemic mastocytosis, skeletal metastasis, myelofibrosis, oxalosis, leukaemias and osteomyelitis. 10min 15min 15min

Outlines requirements and time allocation 4.Periosteal new bone formation 15min Which is a nonspecific response of the periosteum to a variety of causes:it may be focal or diffuse. In particular a spiculated"sunburst"pattem with undercutting of the margins possible causes including physiological,congenital.infective.inflammatory. traumatic.metabolic.neoplastic and idiopathic. The radiographic appearance may (Codmans triangle)suggests a primary bone malignancy:lkewise a laminated"onion skin"pattem can be seen with an aggressive lesion. 5、Sequestrum 15min .Sequestrum is a fragment of necrotic bone that becomes separated from healthy bone. Sequestra may occur in various conditions.such as osteomyelitis,tuberculous arthritis,tropical ulcer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma a sharply marginated bone lesion is seen as radiodense bone spicules caused by osseous necrosis.The sequestrum frequently lies in a space surrounded by granulation tissue
Outlines, requirements and time allocation 4、Periosteal new bone formation ⚫ Which is a nonspecific response of the periosteum to a variety of causes; it may be focal or diffuse. ⚫ In particular a spiculated "sunburst" pattern with undercutting of the margins possible causes including physiological, congenital, infective, inflammatory, traumatic, metabolic, neoplastic and idiopathic. ⚫ The radiographic appearance may (Codmans triangle) suggests a primary bone malignancy; likewise a laminated "onion skin" pattern can be seen with an aggressive lesion. 5、Sequestrum ⚫ Sequestrum is a fragment of necrotic bone that becomes separated from healthy bone. ⚫ Sequestra may occur in various conditions, such as osteomyelitis, tuberculous arthritis, tropical ulcer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma ⚫ a sharply marginated bone lesion is seen as radiodense bone spicules caused by osseous necrosis. The sequestrum frequently lies in a space surrounded by granulation tissue. 15min 15min