
儿童心理健康促进
儿童心理健康促进

一、认识儿童的心理行为发育 心理行为发育是指儿童的心理活 动、个性特征和行为方式随年龄增 长而发生的变化 Figure 1-3 A major difference among developmental theories is (a)whether development occu in distinct stages,as Piaget, Freud,and Erikson maintained Stage theory Continuity (Discontinuity) or(b)whether it proceeds continuously,as learning 创 (b) theorists and information- processing theorists propose
一、认识儿童的心理行为发育 心理行为发育是指儿童的心理活 动、个性特征和行为方式随年龄增 长而发生的变化
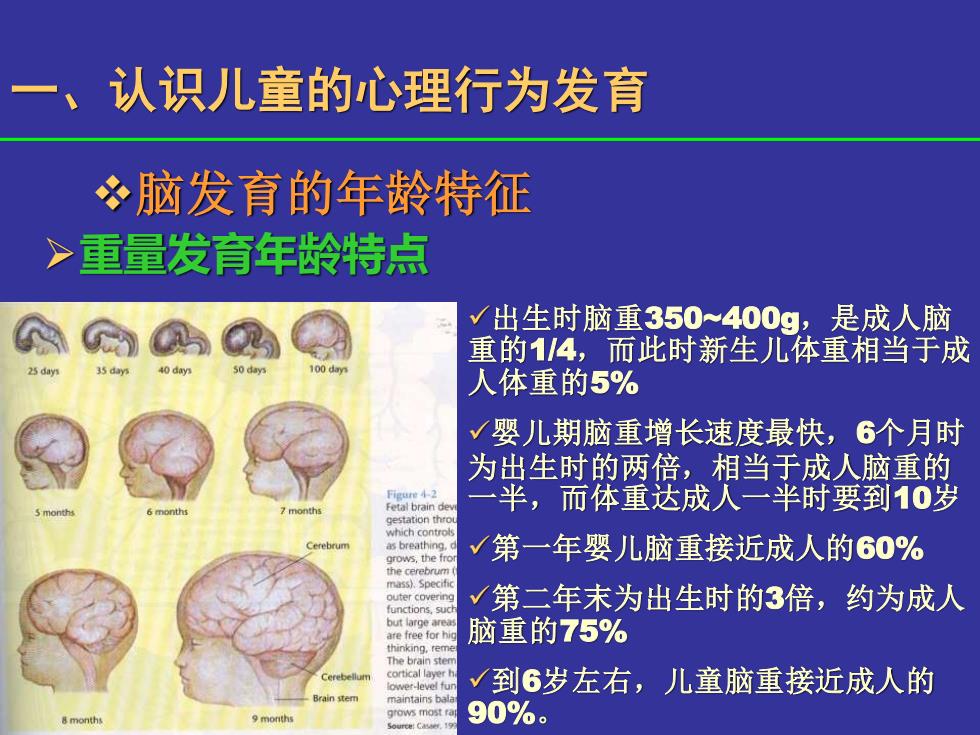
认识儿童的心理行为发育 冬脑发育的年龄特征 >重量发育年龄特点 √出生时脑重350~400g,是成人脑 重的1/4,而此时新生儿体重相当于成 25 da 人体重的5% √婴儿期脑重增长速度最快,6个月时 为出生时的两倍,相当于成人脑重的 一半,而体重达成人一半时要到10岁 gestation thro which controls as breathing. grows,the fror 第一年婴儿脑重接近成人的60% the cerebrum mass).Specific outer covering functions sud 第二年末为出生时的3倍,约为成人 but large areas are free for hig 脑重的75% thinking,reme The brain sten cortical layer h ower-level fun √到6岁左右,儿童脑重接近成人的 rain stem maintains bala 90%
❖脑发育的年龄特征 ➢重量发育年龄特点 ✓出生时脑重350~400g,是成人脑 重的1/4,而此时新生儿体重相当于成 人体重的5% ✓婴儿期脑重增长速度最快,6个月时 为出生时的两倍,相当于成人脑重的 一半,而体重达成人一半时要到10岁 ✓第一年婴儿脑重接近成人的60% ✓第二年末为出生时的3倍,约为成人 脑重的75% ✓到6岁左右,儿童脑重接近成人的 90%。 一、认识儿童的心理行为发育
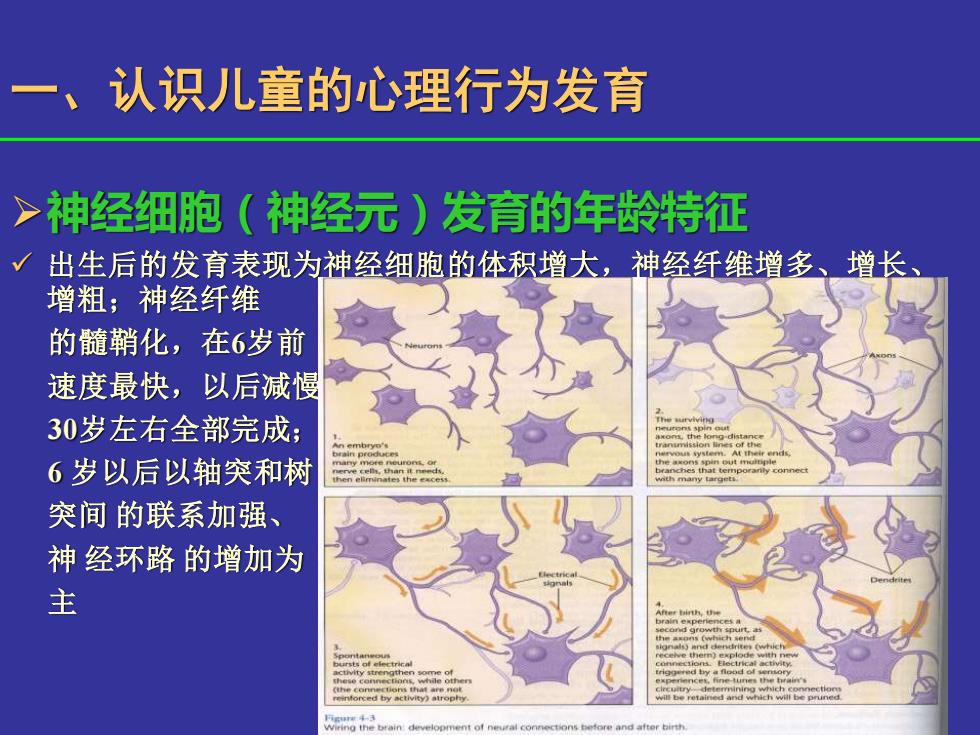
一、认识儿童的心理行为发育 >神经细胞(神经元)发育的年龄特征 出生后的发育表现为神经细胞的体积增大,神经纤维增多、增长 增粗;神经纤维 的髓鞘化,在6岁前 速度最快,以后减慢 30岁左右全部完成; 6岁以后以轴突和树 突间的联系加强、 神经环路的增加为 主 no the
➢神经细胞(神经元)发育的年龄特征 ✓ 出生后的发育表现为神经细胞的体积增大,神经纤维增多、增长、 增粗;神经纤维 的髓鞘化,在6岁前 速度最快,以后减慢, 30岁左右全部完成; 6 岁以后以轴突和树 突间 的联系加强、 神 经环路 的增加为 主 一、认识儿童的心理行为发育

、认识儿童的心理行为发育 感觉 认知活动 知觉 心理活动 情绪活动 记忆 思维 意志活动 想像 倾向性 需要一动机一兴趣一态 个性 自我意识 度一世界观 个性特征 能力一气质一性格 行为 个体行为一社会行为
心理活动 认知活动 倾 向 性 情绪活动 意志活动 感 觉 知觉 记忆 想像 思维 个 性 个性特征 自我意识 需要-动机-兴趣-态 度-世界观 能力-气质-性格 行 为 个体行为-社会行为 一、认识儿童的心理行为发育

一、认识儿童的心理行为发育 ?心理发育阶段理论 年龄阶段 性心理发展阶 社会心理发展阶段 认知发展阶段理 段理论(Freud) 理论(Erikson) 论(Piaget) 01岁 口唇期 基本依恋 感觉运动期LIV期 23岁 肛门期 自主害羞与怀疑 感觉运动期V-VI期 36岁 性器期 积极-内疚 前运算期 711岁 潜伏期 勤奋-自卑 具体运算期 12~18岁 生殖器期 自我认同角色混乱 形式运算期
年龄阶段 性心理发展阶 段理论(Freud) 社会心理发展阶段 理论(Erikson) 认知发展阶段理 论(Piaget) 0~1岁 口唇期 基本依恋 感觉运动期I-IV期 2~3岁 肛门期 自主-害羞与怀疑 感觉运动期V-VI期 3~6岁 性器期 积极-内疚 前运算期 7~11岁 潜伏期 勤奋-自卑 具体运算期 12~18岁 生殖器期 自我认同-角色混乱 形式运算期 ❖心理发育阶段理论 一、认识儿童的心理行为发育

一、认识儿童的心理行为发育 Freud's Psychosexual Stages 口唇期(Oral,birth to 1 year) 肛门期(Anal,1to3 years 性器期(Phallic,3to 6yrs) The Viennese physician Sigmund Freud developed an original, 潜伏期(Latency,7: influential,and controversial theory of emotional development 11ys) in childhood,based on his adult patients'recollections.His 生殖器期(Genital, daughter,Anna,shown here with 12 to 18 yrs) her father,followed in his professional footsteps and constructed her own theories of personality development
Freud’s Psychosexual Stages 口唇期( Oral, birth to 1 year) 肛门期( Anal, 1 to 3 years ) 性器期( Phallic, 3 to 6 yrs ) 潜伏期( Latency, 7- 11yrs ) 生殖器期( Genital, 12 to 18 yrs) 一、认识儿童的心理行为发育

一、认识儿童的心理行为发育 Erikson's Psychosocial Stage 基本依恋(Basic trust vs. mistrust,0-1) 自主害羞与怀疑 Autonomy vs.Shame and doubt,1-3) 积极-内疚(Initiative vs. guilt,3-6 勤奋-自卑(Industry vs. The psychoanalyst Erik H. inferiorty,7-11 from Freudian theory in en 自我认同角色混乱 societal,rather than chiefl influences on personality (Identity vs.role confusion, development as proceedin 12-18) crises,or turning points,th life span. 亲密-孤独(Intimacy vs. isolation,Young adulthood)
Erikson’s Psychosocial Stage 基本依恋( Basic trust vs. mistrust, 0-1) 自主-害羞与怀疑 ( Autonomy vs. Shame and doubt, 1-3) 积极-内疚 ( Initiative vs. guilt, 3-6 ) 勤奋-自卑( Industry vs. inferiorty, 7-11 ) 自我认同-角色混乱 (Identity vs. role confusion, 12-18) 亲密-孤独( Intimacy vs. isolation, Young adulthood) 一、认识儿童的心理行为发育

一、认识儿童的心理行为发育 Piager's Periods of Deyelopment 感觉运动期 Sensomotor,Birth to 2 years) 前运算期 Preoperational subperiod,2-6 yrs) 具体运算期 concrete operational subperiod,7-11 yrs The Swiss psychologist Jean Piaget studied children's 形式运算期 cognitive development by observing and talking with Formal operational, his own youngsters and 12 yrs through others. adulthood
Piaget’s Periods of Development 感觉运动期 ( Sensomotor, Birth to 2 years) 前运算期 ( Preoperational subperiod, 2-6 yrs) 具体运算期 ( concrete operational subperiod, 7-11 yrs ) 形式运算期 ( Formal operational, 12 yrs through adulthood ) 一、认识儿童的心理行为发育

一、认识儿童的心理行为发育 Conservation of Number One of the rows is stretched out.The child is asked correspondence.The child admits their equality whether each row still has the same number. 8 2 Conservation of Length the child. He or she 3. Conservation of Area The child and the experimenter both have identical amount of space remaining. A 4.Conservation of Substance One of the balls is rolled out.The child is asked whether they still contain equal amounts 5.Conservation of Volume o balls of ciay are placed in two identi
+ ﹢/- 一、认识儿童的心理行为发育