
Measurement of the Refractive Index with the abbe Refractometer Refractive index is an important optical constant of transparent materials.There are many ways of measuring the refractive indices of transparent materials.The minimum deflection angle method can measure the refractive index directly and has many advantages like high accuracy,no limit on the refractive index range,and no need for standard materials with known refractive indices.However,the measured material has to be made into a prism with high quality,which prevents its wide application for rapid measurement.Total reflection method is a comparative method.Despite the facts that the accuracy is low (about Anp=3 x 104), the range of the measurable refractive index is limited (np is about 1.3-1.7),solid materials also need to be made into specimen before measurement,the total reflection method is easy to operate,has low requirements for test conditions and no need ofmonochromatic lighting. Abbe refractometer is based on the total reflection method and is particularly suitable for the measurement of refractive index and the average dispersion n-nc of transparent or semi-transparent liquids.It can also be used to measure the sugar concentration in sugar solutions.It is one of the standard instruments widely used in petrochemical,optical,food industry factories,research organizations and institutions. Experimental Objective 1.Understand how to measure refractive indices using the grazing incidence method; 2.Learn to use Abbe refractometer; 3.Determine the alcohol concentration by measuring the refractive index; 4.Understand the refractive index vs.temperature relationship through the measurement of refractive indices of water at different temperatures. Experimental Principle The Abbe refractometer uses the grazing incidence method to measure the refractive index of material which is based on the principle of total reflection. As shown in Fig.1,when light propagates from medium with refractive index n to medium with refractive index N,according to the refraction law,incidence angle i and refraction angle r have the following relationship: nsini Nsinr (1) If n <N,i.e.,when light propagates from optical thin medium to optical dense medium,the refracted light is close to the interface nomal direction,ie.r <i.When the incident angle ranges from 0to 90,the refraction angle can be calculated using Eq.(1).When the incident angle reaches the maximum of i=90 the refraction angle also reaches the maximum r =re.The incident light is called grazing incidence under this condition,the corresponding refraction angle re is referred to as the critical refraction angle or also known as
1 Measurement of the Refractive Index with the Abbe Refractometer Refractive index is an important optical constant of transparent materials. There are many ways of measuring the refractive indices of transparent materials. The minimum deflection angle method can measure the refractive index directly and has many advantages like high accuracy, no limit on the refractive index range, and no need for standard materials with known refractive indices. However, the measured material has to be made into a prism with high quality, which prevents its wide application for rapid measurement. Total reflection method is a comparative method. Despite the facts that the accuracy is low (about ΔnD = 3 × 10-4 ), the range of the measurable refractive index is limited (nD is about 1.3-1.7), solid materials also need to be made into specimen before measurement, the total reflection method is easy to operate, has low requirements for test conditions and no need of monochromatic lighting. Abbe refractometer is based on the total reflection method and is particularly suitable for the measurement of refractive index and the average dispersion nF-nC of transparent or semi-transparent liquids. It can also be used to measure the sugar concentration in sugar solutions. It is one of the standard instruments widely used in petrochemical, optical, food industry factories,research organizations and institutions. Experimental Objective 1. Understand how to measure refractive indices using the grazing incidence method; 2. Learn to use Abbe refractometer; 3. Determine the alcohol concentration by measuring the refractive index; 4. Understand the refractive index vs. temperature relationship through the measurement of refractive indices of water at different temperatures. Experimental Principle The Abbe refractometer uses the grazing incidence method to measure the refractive index of material which is based on the principle of total reflection. As shown in Fig. 1, when light propagates from medium with refractive index n to medium with refractive index N, according to the refraction law, incidence angle i and refraction angle r have the following relationship: n i N r sin sin = (1) r rc N n i If n <N, i.e., when light propagates from optical thin medium to optical dense medium, the refracted light is close to the interface normal direction, i.e. r <i. When the incident angle ranges from 0 ° to 90 °, the refraction angle can be calculated using Eq. (1). When the incident angle reaches the maximum of i = 90 °, the refraction angle also reaches the maximum r = rc . The incident light is called grazing incidence under this condition, the corresponding refraction angle rc is referred to as the critical refraction angle or also known as

the angle oftotal reflection.Substituting this angle into(1): nsin90°=N sin r. (2) n=Nsin r If N is known and re can be measured,we can calculate the refractive index of the medium under measurement. Right-angle prism(with known N)is normally used in the experiment.As shown in Fig.(2),when grazing incidence light propagates from medium(refractive index n)to right-angle prism ABC (refractive index N),it is totally refracted at the interface with refraction angle re,and then propagates into the air with an exit angle io For lights incident on the prism ABC,the angle of refraction is always less than re since the incidence angle is always less than 90,as a result,its exit angle from the AB edge of the prism is always greater than io.Mounting a telescope close to the exit surface side of the prism,parallel rays with different exit angles will focus onto different positions of the focal plane of the telescope.When the optical axis of the telescope is parallel with the light with exit angle i,it can be seen from the eyepiece that half of the view is bright and the other half is dark,and a boundary line exists in the middle,i.e.the 'half dark view'.At this condition,the angle between the optical axis of the telescope with the AB surface normal direction is io.Since io is related to critical angle re,we substitute the relationship into Eq.(2)and obtain(see Appendix 1): n=sin AN2-sin2io -cos A-sin io (3) From the above equation,it is clear that once the prism apex angle A,the refractive index N,and exit angle io are known,the refractive index n of the substance can be calculated. In real Abbe refractometer,io is measured by rotating the prism to match the telescope with materials with different refractive indices n.The scale on the telescope (indexing disc)has already been calibrated by converting the exit angle io into refractive index value according to formula (3),in other words,the readings from the telescope are the refractive indices directly, ☒ Figure2 Experimental Contents 1.Carefully read the instrument manual to understand how to use theAbbe refractometer. 2.Determine the relationship between concentration in alcohol solutions with its refractive index. For a solution at a certain temperature with a certain concentration,its refractive index is constant. Different concentrations of solutions will have different refractive indices,ie.there exists certain relationship between the concentration and the refractive index.This current experiment will measure the relationship curve between the alcohol concentration and its refractive index. Read product manual (Figure 6).Open the small reflection mirror(4),adjust the big mirror (18)to brighten the field of view for both telescopes,adjust the eyepiece of the illumination telescope(6),until the scale line (X-type alignment)on the reticle is seen clearly,then adjust the reading telescope eyepiece (6),and tum the prism hand wheel (2),until being able to see the scale value clearly,then turn on the
2 the angle of total reflection. Substituting this angle into (1): = = c c n N r n N r sin sin 90 sin (2) If N is known and rc can be measured, we can calculate the refractive index of the medium under measurement. Right-angle prism (with known N) is normally used in the experiment. As shown in Fig. (2), when grazing incidence light propagates from medium (refractive index n) to right-angle prism ABC (refractive index N), it is totally refracted at the interface with refraction angle rc , and then propagates into the air with an exit angle i0. For lights incident on the prism ABC, the angle of refraction is always less than rc since the incidence angle is always less than 90 °, as a result, its exit angle from the AB edge of the prism is always greater than i0. Mounting a telescope close to the exit surface side of the prism, parallel rays with different exit angles will focus onto different positions of the focal plane of the telescope. When the optical axis of the telescope is parallel with the light with exit angle i0, it can be seen from the eyepiece that half of the view is bright and the other half is dark, and a boundary line exists in the middle, i.e. the ‘half dark view’. At this condition, the angle between the optical axis of the telescope with the AB surface normal direction is i0. Since i0 is related to critical angle rc , we substitute the relationship into Eq. (2) and obtain (see Appendix 1): 0 0 2 2 n = sin A N − sin i − cos Asin i ( 3 ) From the above equation, it is clear that once the prism apex angle A, the refractive index N, and exit angle i0 are known, the refractive index n of the substance can be calculated. In real Abbe refractometer ,i0 is measured by rotating the prism to match the telescope with materials with different refractive indices n. The scale on the telescope (indexing disc) has already been calibrated by converting the exit angle i0 into refractive index value according to formula (3), in other words, the readings from the telescope are the refractive indices directly, Experimental Contents 1. Carefully read the instrument manual to understand how to use the Abbe refractometer. 2. Determine the relationship between concentration in alcoholsolutions with its refractive index. For a solution at a certain temperature with a certain concentration, its refractive index is constant. Different concentrations of solutions will have different refractive indices, i.e. there exists certain relationship between the concentration and the refractive index. This current experiment will measure the relationship curve between the alcohol concentration and its refractive index. Read product manual (Figure 6). Open the small reflection mirror (4), adjust the big mirror (18) to brighten the field of view for both telescopes, adjust the eyepiece of the illumination telescope (6), until the scale line (X-type alignment) on the reticle is seen clearly , then adjust the reading telescope eyepiece (6), and turn the prism hand wheel (2), until being able to see the scale value clearly, then turn on the rc N n i0 A 3′ 1 2 3 2′ 1′ C Figure 2

composite prism group (13),clean the prism surface with alcohol,drop a certain concentration (the concentration of all five alcohol solutions in the current experiment are known)of the alcohol onto the frosted surface of the illumination prism with a pipette and make it fomm a uniform thin layer.Close the prism,rotate prism hand wheel (2)until the"half dark view"can be seen in the illumination telescope, subsequently,rotate hand wheel of the achromatic prism (10)until the edge of the dark area can be seen clearly,and then adjust the hand wheel(2)so that the edge of the dark area happens to coincide with the crosshair.Record the refractive index from the dial. And then apply other known concentrations of alcohol after re-cleaning the surface of the prism,also measure the refractive indices.Draw the relationship curve using the refractive index as the horizontal coordinate,and concentration as the vertical coordinate. 3.Measure alcohol concentration using the obtained curve Determine the refractive indices of the two kinds of alcohol solutions with unknown concentrations with method(2),find their corresponding alcohol concentration from the curve obtained. 4.Measure the relationship curve between the refractive index and temperature of distilled water For a certain liquid,its refractive index will change when the temperature changes,ie.there exists certain relationship curve between the refractive index and the temperature. Similar to the method described in (2),the alcohol is switched to distilled water,then connect the themostat controller (see manual)with the refractometer thermostat connector,the water temperature is changed by adjusting the themmostat controller,refractive index is measured when the water temperature is increased every 5-10,then draw the relationship curve between the refractive index and the temperature. *5.Determine of the refractive index ofthe glass using grazing incidence and reflection method respectively. Notes 1.Be caution not to touch the prism surface when adding liquid using the pipette since the prism is soft and it can scratch the surface.Be caution not to create air bubbles in the liquid layer when closing the prism. 2.The prism surface must be rinsed with distilled water after each measurement,the water should be wiped off gently with cotton lens cleaning paper. 3.The Abbe refractometer should be calibrated with distilled water or oil with known refractive indices before each measurement. 4.The contact fluid (a-bromo)amount should be appropriate when measuring solid refractive indices, otherwise the glass or solid can slide down and be damaged if applied amount is too much. 5.The instrument must be cleaned and put off properly after the experiment Prep Questions 1.What is the theoretical basis of the transmission method (the grazing incidence method)to determine refractive index of liquid?How is the"half dark view"formed? 2.Why illumination prism should be used in the transmission method?What is the influence of the incident light intensity?Why? Discussion Questions 1.Can the grazing incidence method be used if the refractive index n of the liquid is greater than refractive index N ofrefracting prism. 2.Why is Abbe refractometer formula still applicable when measuring the refractive index of the solid by
3 composite prism group (13), clean the prism surface with alcohol, drop a certain concentration (the concentration of all five alcohol solutions in the current experiment are known) of the alcohol onto the frosted surface of the illumination prism with a pipette and make it form a uniform thin layer. Close the prism, rotate prism hand wheel (2) until the “half dark view” can be seen in the illumination telescope, subsequently, rotate hand wheel of the achromatic prism (10) until the edge of the dark area can be seen clearly, and then adjust the hand wheel (2) so that the edge of the dark area happens to coincide with the crosshair. Record the refractive index from the dial. And then apply other known concentrations of alcohol after re-cleaning the surface of the prism, also measure the refractive indices. Draw the relationship curve using the refractive index as the horizontal coordinate, and concentration as the vertical coordinate. 3. Measure alcohol concentration using the obtained curve Determine the refractive indices of the two kinds of alcohol solutions with unknown concentrations with method (2), find their corresponding alcohol concentration from the curve obtained. 4. Measure the relationship curve between the refractive index and temperature of distilled water For a certain liquid, its refractive index will change when the temperature changes, i.e. there exists certain relationship curve between the refractive index and the temperature. Similar to the method described in (2), the alcohol is switched to distilled water, then connect the thermostat controller (see manual) with the refractometer thermostat connector, the water temperature is changed by adjusting the thermostat controller, refractive index is measured when the water temperature is increased every 5 -10 °, then draw the relationship curve between the refractive index and the temperature. *5. Determine of the refractive index of the glass using grazing incidence and reflection method respectively. Notes 1. Be caution not to touch the prism surface when adding liquid using the pipette since the prism is soft and it can scratch the surface. Be caution not to create air bubbles in the liquid layer when closing the prism. 2. The prism surface must be rinsed with distilled water after each measurement, the water should be wiped off gently with cotton lens cleaning paper. 3. The Abbe refractometer should be calibrated with distilled water or oil with known refractive indices before each measurement. 4. The contact fluid (α-bromo) amount should be appropriate when measuring solid refractive indices, otherwise the glass or solid can slide down and be damaged if applied amount is too much . 5. The instrument must be cleaned and put off properly after the experiment Prep Questions 1. What is the theoretical basis of the transmission method (the grazing incidence method) to determine refractive index of liquid? How is the “half dark view” formed? 2. Why illumination prism should be used in the transmission method? What is the influence of the incident light intensity? Why? Discussion Questions 1. Can the grazing incidence method be used if the refractive index n of the liquid is greater than refractive index N of refracting prism. 2. Why is Abbe refractometer formula still applicable when measuring the refractive index of the solid by

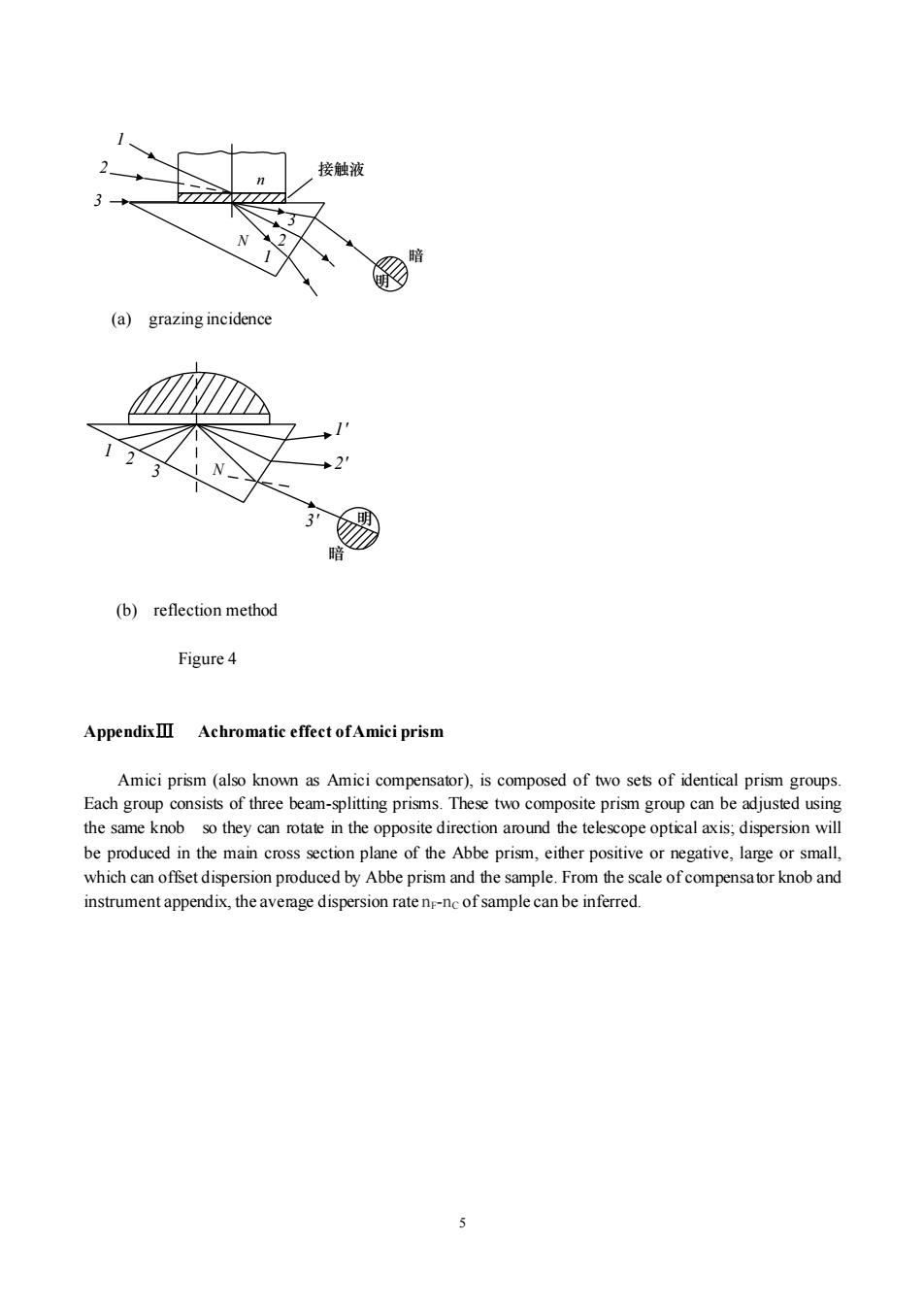
reflection method Under what circumstances should the reflection method be used? 3.What phenomenon can be observed if during the measurement of the relationship curve between the refractive index and temperature of distilled water,the water is fully evaporated?Why? Appendix I ☒ Starting withn=sin AN2-sin2i。-cosA·sini。: in Figure3∠A+∠a+∠B=180° and∠a+∠y+∠B+∠y'=l80° ∴.∠A=∠y+∠y' When angle of grazing incidence i=90,y=y,i'=io. and according to refraction law (1),we have: nsin90°=W siny Nsiny'=Isinio Figure 3 ∠A=∠Y。+∠Y y and y'are substituted into the formula,then: n=N siny=Nsin(A-y) Nsin Acosy'-(Nsiny)cos A =Nsin Av1-sin2y'-sinio cosA =sin AN2-N2sin2y'-sinio cosA =sin AN2-sin2io-sinio cos A Appendix II Measure solid refractive index by Abbe refractometer When measuring solid sample,if it is transparent,merge one of the polished surface of the sample with refraction prism (3),adding a layer of contact liquid (typically a-bromo np =1.6626)with refractive index between that of the sample and Abbe prism.The other side of sample does not need to be polished and can be measured as Fig.4(a),when sample is opaque or has only one polished surface,reflection method should be used as shown in Figure 4(b),the contact liquid is also needed between the sample and the Abbe prism
4 reflection method ? Under what circumstances should the reflection method be used? 3. What phenomenon can be observed if during the measurement of the relationship curve between the refractive index and temperature of distilled water, the water is fully evaporated? Why? Appendix Ⅰ Starting with 0 0 2 2 n = sin A N − sin i − cos Asin i : in Figure 3 A+ +B =180 and + + B + = 180 A = + . When angle of grazing incidence i=90°, c = ,i′=i0, and according to refraction law (1), we have: sin 90 sin c n N = 0 N I i sin sin = = + A c c and are substituted into the formula, then: sin sin( ) c n N N A = = − = − N A N A sin cos ( sin )cos 2 0 = − − N A i A sin 1 sin sin cos 2 2 2 0 = − − sin sin sin cos A N N i A 2 2 0 0 = − − sin sin sin cos A N i i A AppendixⅡ Measure solid refractive index by Abbe refractometer When measuring solid sample, if it is transparent, merge one of the polished surface of the sample with refraction prism (3), adding a layer of contact liquid (typically α-bromo nD = 1.6626) with refractive index between that of the sample and Abbe prism. The other side of sample does not need to be polished and can be measured as Fig. 4 (a), when sample is opaque or has only one polished surface, reflection method should be used as shown in Figure 4 (b), the contact liquid is also needed between the sample and the Abbe prism. N n i A i′ C B ′ α Figure 3
接触液 暗 (a)grazing incidence 暗 (b)reflection method Figure 4 AppendixIII Achromatic effect ofAmici prism Amici prism(also known as Amici compensator),is composed of two sets of identical prism groups Each group consists of three beam-splitting prisms.These two composite prism group can be adjusted using the same knob so they can rotate in the opposite direction around the telescope optical axis;dispersion will be produced in the main cross section plane of the Abbe prism,either positive or negative,large or small, which can offset dispersion produced by Abbe prism and the sample.From the scale of compensator knob and instrument appendix,the average dispersion rate n-nc of sample can be inferred. 5
5 1 2 3 1 2 3 N n 明 暗 接触液 (a) grazing incidence 1 2 3 N 明 暗 3′ 2′ 1′ (b) reflection method Figure 4 AppendixⅢ Achromatic effect of Amici prism Amici prism (also known as Amici compensator), is composed of two sets of identical prism groups. Each group consists of three beam-splitting prisms. These two composite prism group can be adjusted using the same knob so they can rotate in the opposite direction around the telescope optical axis; dispersion will be produced in the main cross section plane of the Abbe prism, either positive or negative, large or small, which can offset dispersion produced by Abbe prism and the sample. From the scale of compensator knob and instrument appendix, the average dispersion rate nF-nC of sample can be inferred