
Measuring the Linear Expansion Coefficient of Metals by Optical Lever Method Almost all objects have the property of "Expanding with heat and contracting with cold",which should be considered in engineering design,precision meter design, welding and processing of materials,etc.Under the case of one dimension,the length increase of solid when being heated is called linear expansion,which is used to characterize difference of solid. In reality,to measure the linear expansion coefficient of solid is to actually measure the slight extension of solid in a certain temperature range.The measuring methods can be the optical lever method,spiral micrometer method,interference method,etc.The optical lever method,with extremely high accuracy,will be applied in this experiment. Purpose: 1.Learning to measure the slight change of solid length by optical lever method 2.Measuring the linear expansion coefficient of metal rods Principle: When the solid is heated,its volume will increase.This is the properties "Expanding with heat and contracting with cold"for common objects.The increase of length when the solid is heated is called "linear expansion".The relationship of L and temperature is: L=Lo(1+aT+βT2+.) (1) where Lo is the length when temperature T-OC,a,B...are coefficients related to the sample materials,all with very small value.The coefficients after B are extremely small compared to a,therefore can be neglected at normal temperature,so Eq.(1)can be written like: L=Lo(1+aT) (2) Where a is the so called linear expansion coefficient,which indicates the ratio of the length increase when temperature rises one degree of Celsius to that at zero degree of Celsius,whose unit is C-1 If the length of the metal rod is LI and L2 at Ti and T2,respectively,then: L1=Lo(1+0T1) (3) 1
1 Measuring the Linear Expansion Coefficient of Metals by Optical Lever Method Almost all objects have the property of “Expanding with heat and contracting with cold”, which should be considered in engineering design, precision meter design, welding and processing of materials, etc. Under the case of one dimension, the length increase of solid when being heated is called linear expansion, which is used to characterize difference of solid. In reality, to measure the linear expansion coefficient of solid is to actually measure the slight extension of solid in a certain temperature range. The measuring methods can be the optical lever method, spiral micrometer method, interference method, etc. The optical lever method, with extremely high accuracy, will be applied in this experiment. Purpose: 1. Learning to measure the slight change of solid length by optical lever method 2. Measuring the linear expansion coefficient of metal rods Principle: When the solid is heated, its volume will increase. This is the properties “Expanding with heat and contracting with cold” for common objects. The increase of length when the solid is heated is called “linear expansion”. The relationship of L and temperature is: L=L0(1+αT+βT 2+…) (1) where L0 is the length when temperature T=0oC, α, β…are coefficients related to the sample materials, all with very small value. The coefficients after β are extremely small compared to α, therefore can be neglected at normal temperature, so Eq. (1) can be written like: L=L0(1+αT) (2) Where α is the so called linear expansion coefficient, which indicates the ratio of the length increase when temperature rises one degree of Celsius to that at zero degree of Celsius, whose unit is oC-1 . If the length of the metal rod is L1 and L2 at T1 and T2, respectively, then: L1=L0(1+αT1) (3)
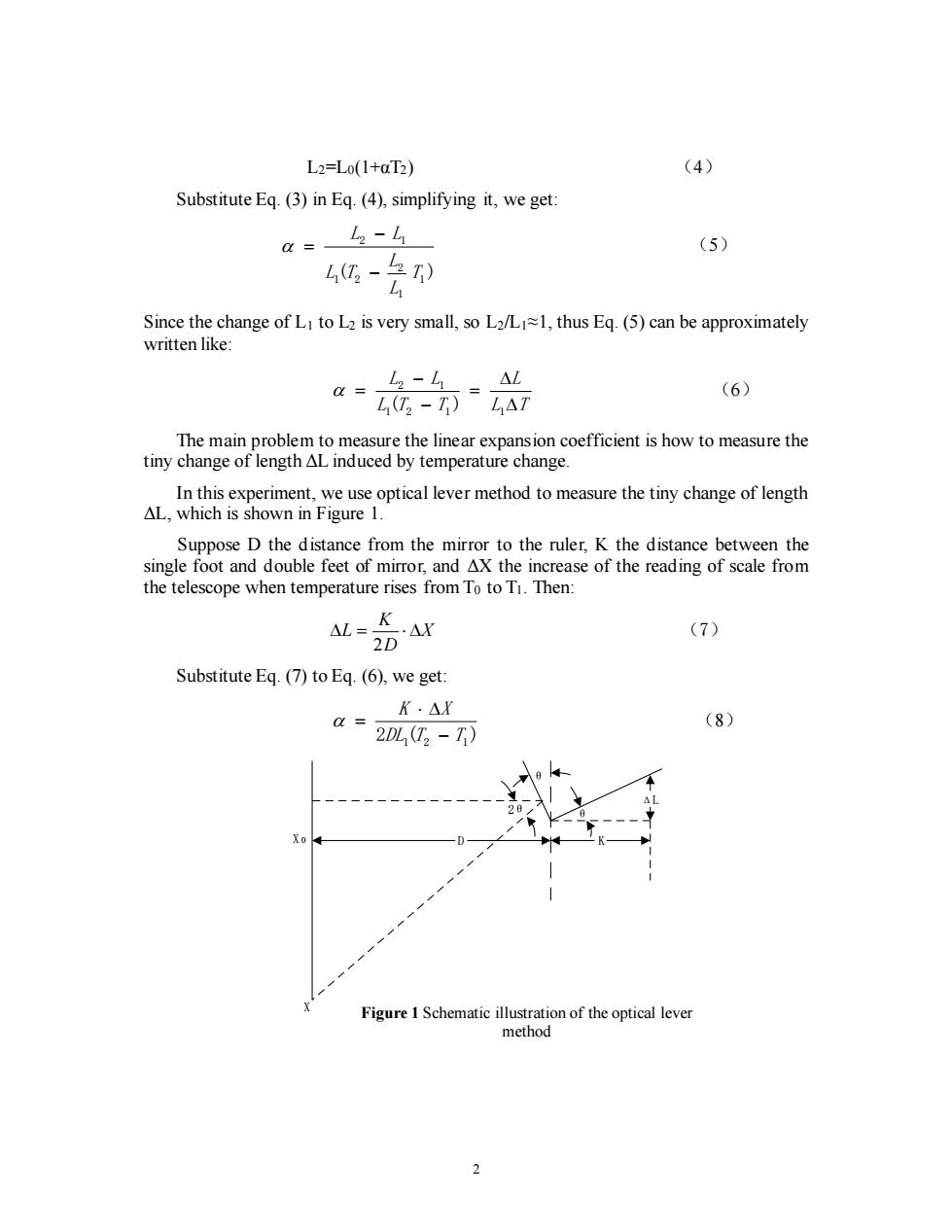
L2=Lo(1+aT2) (4) Substitute Eq.(3)in Eq.(4),simplifying it,we get: = L2 (5) 4还-先刊 Since the change of LI to L2 is very small,so L2/LI~1,thus Eq.(5)can be approximately written like: a=4-4。 △L (6) L(T2-T)L△T The main problem to measure the linear expansion coefficient is how to measure the tiny change of length AL induced by temperature change. In this experiment,we use optical lever method to measure the tiny change of length AL,which is shown in Figure 1. Suppose D the distance from the mirror to the ruler,K the distance between the single foot and double feet of mirror,and AX the increase of the reading of scale from the telescope when temperature rises from To to Ti.Then: L=K·AX (7) 2D Substitute Eq.(7)to Eq.(6),we get: K·△X a= (8) 2DL(T2-T) Xo Figure 1 Schematic illustration of the optical lever method 2
2 L2=L0(1+αT2) (4) Substitute Eq. (3) in Eq. (4), simplifying it, we get: ( 1 ) 1 2 1 2 2 1 T L L L T L L − − = (5) Since the change of L1 to L2 is very small, so L2/L1≈1, thus Eq. (5) can be approximately written like: L T L L T T L L = − − = 1 2 1 1 2 1 ( ) (6) The main problem to measure the linear expansion coefficient is how to measure the tiny change of length ΔL induced by temperature change. In this experiment, we use optical lever method to measure the tiny change of length ΔL, which is shown in Figure 1. Suppose D the distance from the mirror to the ruler, K the distance between the single foot and double feet of mirror, and ΔX the increase of the reading of scale from the telescope when temperature rises from T0 to T1. Then: X D K L = 2 (7) Substitute Eq. (7) to Eq. (6), we get: 2DL1(T2 T1 ) K X − = (8) θ θ 2θ ΔL X 0 D K X Figure 1 Schematic illustration of the optical lever method

The metal rod in this experiment is normal brass,whose linear expansion coefficient is: 0s=1.89×105.℃-l c Figure 2 Type 501 super thermostat Equipment: 1.Type 501 super thermostat The Type 501 super thermostat is shown in Figure 2.It has a cylinder-shaped metal shell with a brass cover,equipped with a pump and motor,one contacting thermometer, one liquid inlet nozzle,two set of heaters and inlet and outlet nozzles for condenser pipe. The outer tube is steel and inner tube is brass,with glass fibers filled in between for heat preservation.The electronic relays and power are all installed in the control box. The temperature can be adjusted between 0 to 100 C,and can export hot water with constant temperature. The temperature adjustment is aided by the contacting thermometer,choose the objecting temperature at the contacting thermometer and turn on the heating switch. When the indicating light of constant temperature is in flashing status,it means the temperature is already at constant and the heating switch can be turned off.When the displayed temperature of the standard thermometer is different from the objecting temperature,the contacting thermometer should be adjusted again. Adjusting the contacting thermometer:rotate the drum-shaped screw cap embedded with permanent magnet on top of the thermometer.Use the magnetic field to lead the movable screw inside the thermometer,let the screw move up and down to the specified temperature and control the water temperature in the super thermostat.The scale on the contacting thermometer is normally just for reference.The real temperature should be read from the standard thermometer. 3
3 The metal rod in this experiment is normal brass, whose linear expansion coefficient is: αs=1.89×10 -5· o C—1 Equipment: 1. Type 501 super thermostat The Type 501 super thermostat is shown in Figure 2. It has a cylinder-shaped metal shell with a brass cover, equipped with a pump and motor, one contacting thermometer, one liquid inlet nozzle, two set of heaters and inlet and outlet nozzles for condenser pipe. The outer tube is steel and inner tube is brass, with glass fibers filled in between for heat preservation. The electronic relays and power are all installed in the control box. The temperature can be adjusted between 0 to 100 oC, and can export hot water with constant temperature. The temperature adjustment is aided by the contacting thermometer, choose the objecting temperature at the contacting thermometer and turn on the heating switch. When the indicating light of constant temperature is in flashing status, it means the temperature is already at constant and the heating switch can be turned off. When the displayed temperature of the standard thermometer is different from the objecting temperature, the contacting thermometer should be adjusted again. Adjusting the contacting thermometer: rotate the drum-shaped screw cap embedded with permanent magnet on top of the thermometer. Use the magnetic field to lead the movable screw inside the thermometer, let the screw move up and down to the specified temperature and control the water temperature in the super thermostat. The scale on the contacting thermometer is normally just for reference. The real temperature should be read from the standard thermometer. Figure 2 Type 501 super thermostat
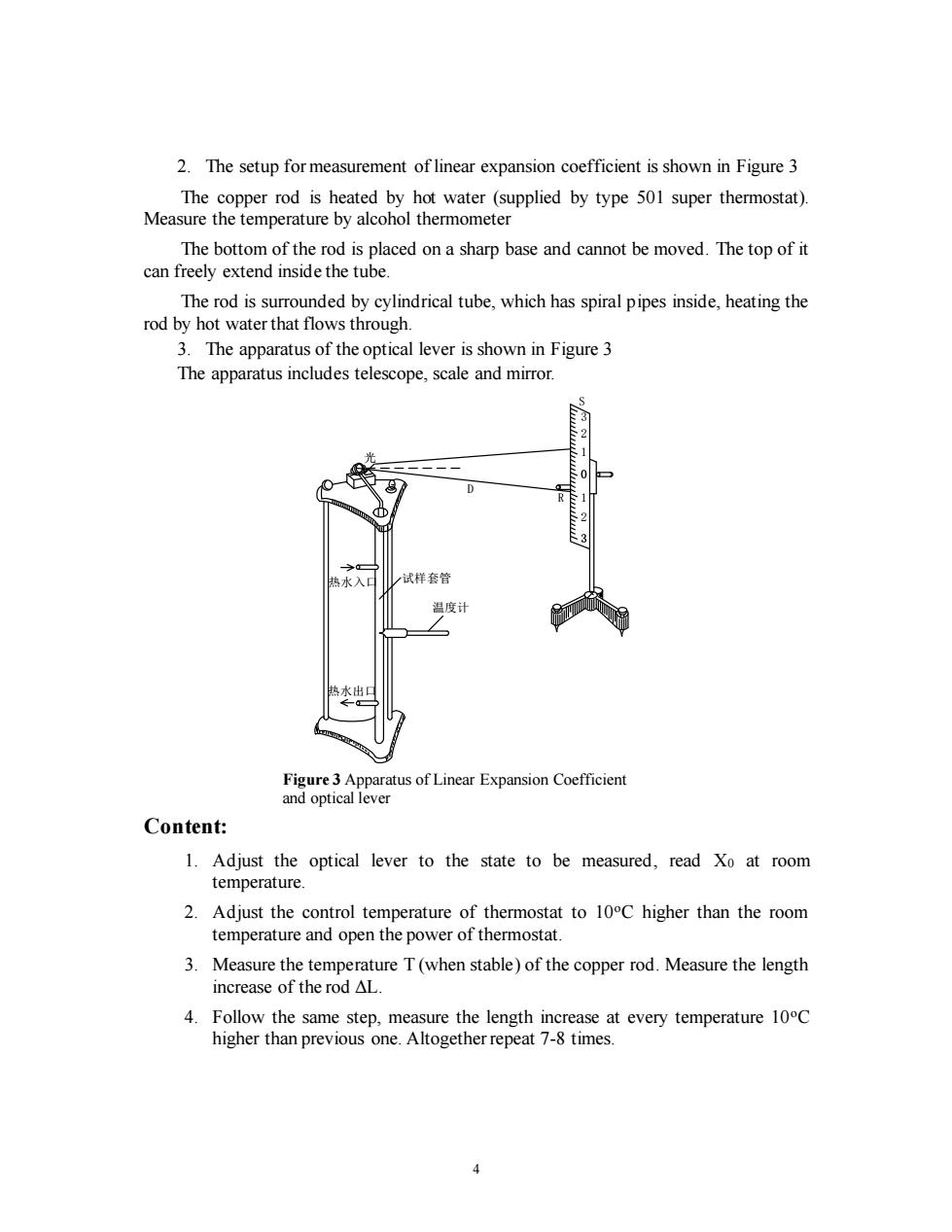
2.The setup for measurement of linear expansion coefficient is shown in Figure 3 The copper rod is heated by hot water(supplied by type 501 super thermostat). Measure the temperature by alcohol thermometer The bottom of the rod is placed on a sharp base and cannot be moved.The top of it can freely extend inside the tube. The rod is surrounded by cylindrical tube,which has spiral pipes inside,heating the rod by hot water that flows through. 3.The apparatus of the optical lever is shown in Figure 3 The apparatus includes telescope,scale and mirror. D 热水入口 /试样套管 温度计 热水出口 Figure 3 Apparatus of Linear Expansion Coefficient and optical lever Content: 1.Adjust the optical lever to the state to be measured,read Xo at room temperature. 2.Adjust the control temperature of thermostat to 10C higher than the room temperature and open the power of thermostat. 3.Measure the temperature T(when stable)of the copper rod.Measure the length increase of the rod△L. 4.Follow the same step,measure the length increase at every temperature 100C higher than previous one.Altogether repeat 7-8 times. 4
4 2. The setup for measurement of linear expansion coefficient is shown in Figure 3 The copper rod is heated by hot water (supplied by type 501 super thermostat). Measure the temperature by alcohol thermometer The bottom of the rod is placed on a sharp base and cannot be moved. The top of it can freely extend inside the tube. The rod is surrounded by cylindrical tube, which has spiral pipes inside, heating the rod by hot water that flows through. 3. The apparatus of the optical lever is shown in Figure 3 The apparatus includes telescope, scale and mirror. Content: 1. Adjust the optical lever to the state to be measured, read X0 at room temperature. 2. Adjust the control temperature of thermostat to 10oC higher than the room temperature and open the power of thermostat. 3. Measure the temperature T (when stable) of the copper rod. Measure the length increase of the rod ΔL. 4. Follow the same step, measure the length increase at every temperature 10oC higher than previous one. Altogether repeat 7-8 times. 3 2 1 0 1 2 3 D 试样套管 温度计 热水入口 热水出口 R 光 S Figure 3 Apparatus of Linear Expansion Coefficient 附图2 线膨胀系数仪及光杠杆装置 and optical lever

5.Measure the parameters K and D of the optical lever. 6.Be careful of the number of significant digit of the readings.Record the length of the metal rod Lo(detailed value will be offered by the lab) 7.Calculate the linear expansion coefficient a by linear fitting with least square method and draw the fitting curve. Note:If the time allows,when the temperature decreases,follow the same steps and measure△L,',take the mean value△L=(△L,+△L')2,then the systematic deviation can be reduced. Preparation: Try to analyze the main factor that influences the accuracy of this experiment. Discussion: 1.There are two metal rods of the same material but with different lengths.Do they have the same linear expansion coefficient in the same temperature range?How about their absolute linear expansions?Why? 2.There is an isotropic object with volume V.When heated,its relative volume increase is proportional to the change of temperature,i.e.,△VW=β△t,whereβis the coefficient of proportionality,called the volumetric expansion coefficient.Try to figure out the relationship of B and a. 5
5 5. Measure the parameters K and D of the optical lever. 6. Be careful of the number of significant digit of the readings. Record the length of the metal rod L0 (detailed value will be offered by the lab) 7. Calculate the linear expansion coefficient α by linear fitting with least square method and draw the fitting curve. Note:If the time allows, when the temperature decreases, follow the same steps and measure ΔLi′, take the mean value ΔL=(ΔLi+ΔLi′)/2, then the systematic deviation can be reduced. Preparation: Try to analyze the main factor that influences the accuracy of this experiment. Discussion: 1. There are two metal rods of the same material but with different lengths. Do they have the same linear expansion coefficient in the same temperature range? How about their absolute linear expansions? Why? 2. There is an isotropic object with volume V. When heated, its relative volume increase is proportional to the change of temperature, i.e., ΔV/V=βΔt,where β is the coefficient of proportionality, called the volumetric expansion coefficient. Try to figure out the relationship of β and α