
Measuring the Young Modulus of Metal by Dynamic Suspension Method The Young Modulus is an important physical parameter of engineering materials. It stands for the resistive ability of the material against elastic deformation.Nowadays the"dynamic suspension method"is often applied in engineering technology.Its basic method is:hang a sample (rod)with homogeneous cross section area below two sensors (one for exciting the vibration and another for detecting the vibration).Force it to vibrate freely under the condition that the two end are free.Measure the natural fundamental frequency and measure the Young modulus of the sample according to its parameters such as geometric size,density and so forth. Purpose: 1.Measuring the Young modulus of metal materials by dynamic suspension method 2.Studying the method to determine the resonance frequency at the sample nodes Requirement: 1.Calculate the resonance frequency at the node by epitaxial method. 2.Measure the Young modulus of metal materials at room temperature. Principle: According to the equation of transverse vibration of a rod: oy-0 0r2 (1) Solve the equation by method of separation of variables.For the round shaped rod,we get: E=1.6067尺 (2) In above two equations,E is the Young modulus,I is the length of the rod,d is the diameter of the rod,S is the area of the rod cross section,p is the density of rod,m is the mass,f is the natural frequency of the transverse vibration of the rod,J is the polar moment
Measuring the Young Modulus of Metal by Dynamic Suspension Method The Young Modulus is an important physical parameter of engineering materials. It stands for the resistive ability of the material against elastic deformation. Nowadays the “dynamic suspension method” is often applied in engineering technology. Its basic method is: hang a sample (rod) with homogeneous cross section area below two sensors (one for exciting the vibration and another for detecting the vibration). Force it to vibrate freely under the condition that the two end are free. Measure the natural fundamental frequency and measure the Young modulus of the sample according to its parameters such as geometric size, density and so forth. Purpose: 1. Measuring the Young modulus of metal materials by dynamic suspension method 2. Studying the method to determine the resonance frequency at the sample nodes Requirement: 1. Calculate the resonance frequency at the node by epitaxial method. 2. Measure the Young modulus of metal materials at room temperature. Principle: According to the equation of transverse vibration of a rod: 0 4 4 2 2 2 = + x y S EJ t y (1) Solve the equation by method of separation of variables. For the round shaped rod, we get: 2 4 3 1.6067 f d l m E = (2) In above two equations, E is the Young modulus, l is the length of the rod, d is the diameter of the rod, S is the area of the rod cross section, p is the density of rod, m is the mass, f is the natural frequency of the transverse vibration of the rod, J is the polar moment
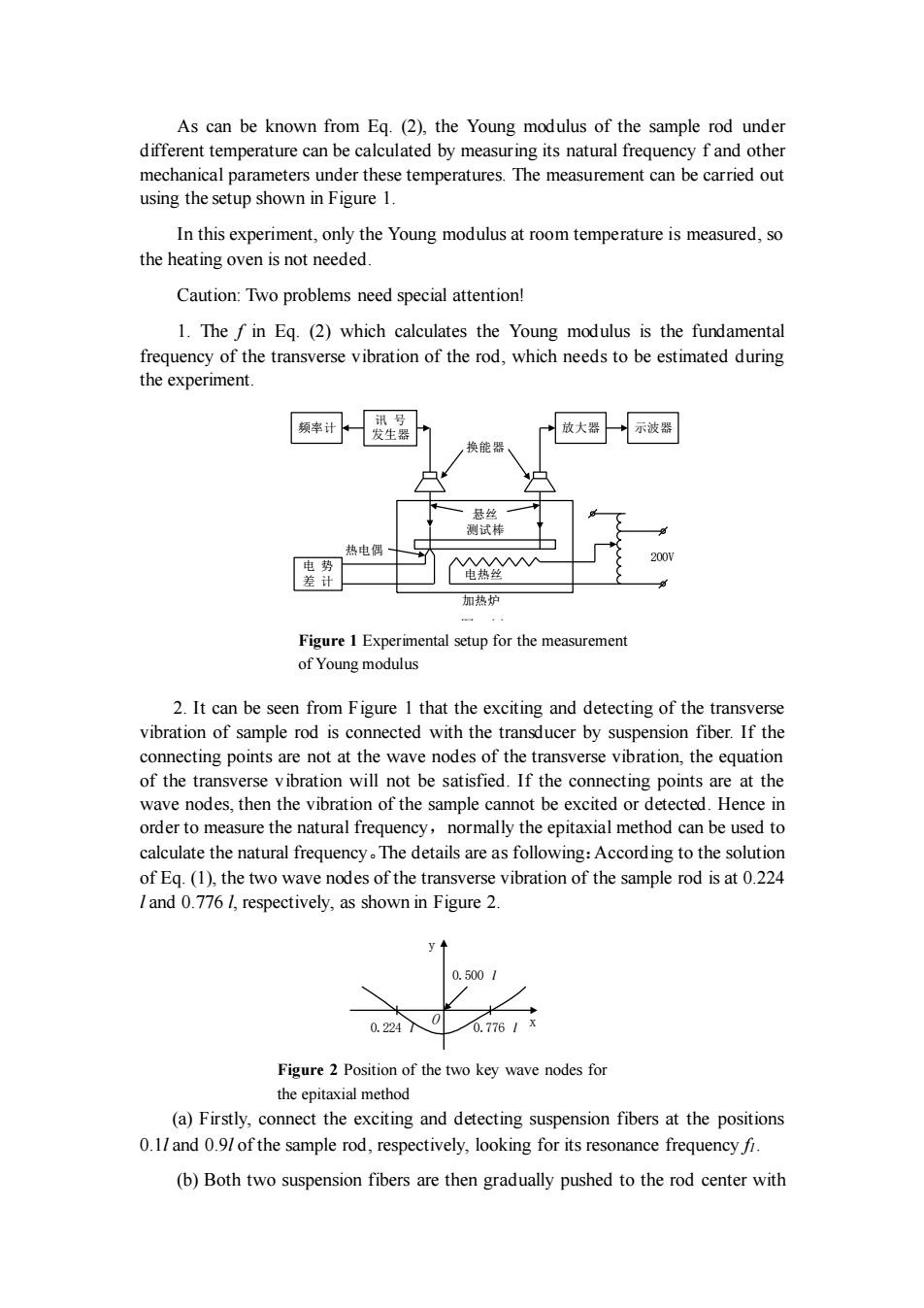
As can be known from Eq.(2),the Young modulus of the sample rod under different temperature can be calculated by measuring its natural frequency f and other mechanical parameters under these temperatures.The measurement can be carried out using the setup shown in Figure 1. In this experiment,only the Young modulus at room temperature is measured,so the heating oven is not needed. Caution:Two problems need special attention! 1.The f in Eg.(2)which calculates the Young modulus is the fundamental frequency of the transverse vibration of the rod,which needs to be estimated during the experiment. 频率计 讯号 发生器 放大器 示波器 换能器 悬丝 测试棒 热电偶 ^ 200 电势 差计 电热丝 加热炉 Figure 1 Experimental setup for the measurement of Young modulus 2.It can be seen from Figure 1 that the exciting and detecting of the transverse vibration of sample rod is connected with the transducer by suspension fiber.If the connecting points are not at the wave nodes of the transverse vibration,the equation of the transverse vibration will not be satisfied.If the connecting points are at the wave nodes,then the vibration of the sample cannot be excited or detected.Hence in order to measure the natural frequency,normally the epitaxial method can be used to calculate the natural frequency.The details are as following:Accord ing to the solution of Eq.(1),the two wave nodes of the transverse vibration of the sample rod is at 0.224 I and 0.776 1,respectively,as shown in Figure 2. y◆ 0.5001 0.2247 0.7761x Figure 2 Position of the two key wave nodes for the epitaxial method (a)Firstly,connect the exciting and detecting suspension fibers at the positions 0.1/and 0.9/of the sample rod,respectively,looking for its resonance frequency fi. (b)Both two suspension fibers are then gradually pushed to the rod center with
As can be known from Eq. (2), the Young modulus of the sample rod under different temperature can be calculated by measuring its natural frequency f and other mechanical parameters under these temperatures. The measurement can be carried out using the setup shown in Figure 1. In this experiment, only the Young modulus at room temperature is measured, so the heating oven is not needed. Caution: Two problems need special attention! 1. The f in Eq. (2) which calculates the Young modulus is the fundamental frequency of the transverse vibration of the rod, which needs to be estimated during the experiment. 频率计 讯 号 发生器 放大器 示波器 电 势 差 计 热电偶 换能器 加热炉 悬丝 测试棒 电热丝 200V 图 (1) 2. It can be seen from Figure 1 that the exciting and detecting of the transverse vibration of sample rod is connected with the transducer by suspension fiber. If the connecting points are not at the wave nodes of the transverse vibration, the equation of the transverse vibration will not be satisfied. If the connecting points are at the wave nodes, then the vibration of the sample cannot be excited or detected. Hence in order to measure the natural frequency,normally the epitaxial method can be used to calculate the natural frequency。The details are as following:According to the solution of Eq. (1), the two wave nodes of the transverse vibration of the sample rod is at 0.224 l and 0.776 l, respectively, as shown in Figure 2. 0.500 l 0.224 l 0.776 l y O x 图 (2) (a) Firstly, connect the exciting and detecting suspension fibers at the positions 0.1l and 0.9l of the sample rod, respectively, looking for its resonance frequency f1. (b) Both two suspension fibers are then gradually pushed to the rod center with Figure 1 Experimental setup for the measurement of Young modulus Figure 2 Position of the two key wave nodes for the epitaxial method

the step 0.02 I,looking for corresponding frequency f33...until the suspension points are at 0.22 and 0.78 1. (c)Set as the independent variable and fas the dependent variable and draw the curve of f-I.Extend the curve to 0.2241,then the corresponding f at that position is the natural frequency of the rod. Content: 1.Connect the experimental device according to Figure 1 and connect the suspension fibers at the 0.1/and 0.9 of the sample rod. 2.Adjust the frequency of the signal generator from low to high value and observe the change of oscilloscope signal.If the oscilloscope display of the detected vibration signal (AC signal)reaches a maximum at a certain frequency,then the resonance between the excitation frequency of the signal generator and test rod can be considered to occur,write down the frequency fi. 3.push the two suspension fibers gradually at the interval of 0.02 to the center, write down the frequency、…。 4.Measure the mechanical quantities 1,m,d of the sample rod (each six times). 5.Draw the graphics and calculate the natural frequency fof the rod. 6.Substitute f into Eq.(2)to calculate the Young modulus. 7.You can repeat the steps 1~6 by changing test samples and calculate the Young modulus E of different samples
the step 0.02 l, looking for corresponding frequency f2、f3…until the suspension points are at 0.22 l and 0.78 l. (c) Set l as the independent variable and f as the dependent variable and draw the curve of f-l. Extend the curve to 0.224l, then the corresponding f at that position is the natural frequency of the rod. Content: 1. Connect the experimental device according to Figure 1 and connect the suspension fibers at the 0.1l and 0.9 l of the sample rod。 2. Adjust the frequency of the signal generator from low to high value and observe the change of oscilloscope signal. If the oscilloscope display of the detected vibration signal (AC signal) reaches a maximum at a certain frequency, then the resonance between the excitation frequency of the signal generator and test rod can be considered to occur, write down the frequency f1。 3. push the two suspension fibers gradually at the interval of 0.02 l to the center, write down the frequency f2、f3……。 4. Measure the mechanical quantities l, m, d of the sample rod (each six times)。 5. Draw the graphics and calculate the natural frequency f of the rod. 6. Substitute f into Eq. (2) to calculate the Young modulus. 7. You can repeat the steps 1~6 by changing test samples and calculate the Young modulus E of different samples