
第9卷第1期 智能系统学报 Vol.9 No.1 2014年2月 CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems Feb.2014 D0:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4785.201305027 网络出版地址:http://www.cnki.net/kcms/doi/10.3969/j.issn.1673-4785.201305027.html 一种基于模拟退火操作的混合差分进化算法 杨艳霞 (武汉科技大学城市学院信息工程学部,湖北武汉430083) 摘要:为了提高进化算法对大规模欺骗问题和等级问题这类复杂组合优化问题的求解能力,提出了一种将模拟退 火操作引人到差分进化算法的改进方法。该方法对随机产生的初始个体进行模拟退火操作,对新个体进行退温操 作,经过若干次迭代后,选择种群中最优解作为所求问题的解。利用模拟退火算子的突变搜索提高种群多样性,使 差分进化算法能更好地利用群体差异进行全局搜索。在实验中,用各种类型的欺骗函数和具有树状结构的等级函 数对算法进行仿真测试,仿真结果表明该算法在初期保持了种群多样性,在运行的后期能比较好地跳出局部最优 解,收敛到全局最优解附近。 关键词:差分进化:进化算法:模拟退火:欺骗问题:等级问题 中图分类号:TP391.9文献标志码:A文章编号:1673-4785(2014)01-0109-06 中文引用格式:杨艳霞.一种基于模拟退火操作的混合差分进化算法[J].智能系统学报,2014,9(1):109-114. 英文引用格式:YANG Yanxia.A hybrid differential evolutionary algorithm based on the simulated annealing operation[J].CAAl Transactions on Intelligent Systems,2014,9(1):109-114. A hybrid differential evolutionary algorithm based on the simulated annealing operation YANG Yanxia Department of Information Engineering,Wuhan University of Science and Technology City College,Wuhan 430083,China) Abstract:In order to improve the ability of the evolutionary algorithm for solving such complicated combination and optimization problems as the massive deceptive problems and hierarchical problems,this paper proposes an im- proved algorithm,which introduces the simulated annealing operation into the differential evolutionary algorithm.U- sing this method,the simulated annealing operation is carried out for a randomly generated initial individual and the temperature-reducing operation is carried out for a new individual.After several times of iterations,the optimal so- lution in the population is taken as the solution to the question.By utilizing the mutation search of the simulated an- nealing operator to improve the diversity of the population,the differential evolutionary algorithm can better utilize colony differences for an overall search.In the experiment,various types of deceptive functions and the hierarchical functions with a tree-shape structure are applied to simulation testing of the algorithm.In the initial stage,the algo- rithm keeps diversity of the population;in the later stage,a local optimal solution may be generated,the conver- gence scope nears to the overall optimal solution.The simulation results show that the algorithm has advantage for the aspect of searching the overall optimal solution. Keywords:differential evolutionary;evolutionary algorithm;simulated annealing;deceptive problem;hierarchical problem 差分进化算法是一种基于群体差异实现全局优 杂时,差分进化算法和其他进化算法一样,随着进化 化的进化算法,其简单高效,控制参数少,具有快速 代数的增加,个体间的差异会逐渐降低,个体变异的 的全局寻优能力,在工程、管理以及科学领域获得了 多样性逐步减少,从而收敛到局部极值附近,陷入局 广泛的应用山。在实际应用中,当优化问题比较复 部最优解.为了提高差分进化算法的寻优能力,加快 收敛速度,克服一般进化算法常见的局部收敛现象, 收稿日期:2013-05-09.网络出版日期:2014-02-20 基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(70971020) 许多学者对其进行了改进,迄今对差分进化算法的 通信作者:杨艳霞.E-mail:yxy_job@163.com
第 9 卷第 1 期 智 能 系 统 学 报 Vol.9 №.1 2014 年 2 月 CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems Feb. 2014 DOI:10.3969 / j.issn.1673-4785.201305027 网络出版地址:http: / / www.cnki.net / kcms/ doi / 10.3969 / j.issn.1673⁃4785.201305027.html 一种基于模拟退火操作的混合差分进化算法 杨艳霞 (武汉科技大学城市学院 信息工程学部,湖北 武汉 430083) 摘 要:为了提高进化算法对大规模欺骗问题和等级问题这类复杂组合优化问题的求解能力,提出了一种将模拟退 火操作引入到差分进化算法的改进方法。 该方法对随机产生的初始个体进行模拟退火操作,对新个体进行退温操 作,经过若干次迭代后,选择种群中最优解作为所求问题的解。 利用模拟退火算子的突变搜索提高种群多样性,使 差分进化算法能更好地利用群体差异进行全局搜索。 在实验中,用各种类型的欺骗函数和具有树状结构的等级函 数对算法进行仿真测试,仿真结果表明该算法在初期保持了种群多样性,在运行的后期能比较好地跳出局部最优 解,收敛到全局最优解附近。 关键词:差分进化;进化算法;模拟退火;欺骗问题;等级问题 中图分类号:TP391.9 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1673⁃4785(2014)01⁃0109⁃06 中文引用格式:杨艳霞.一种基于模拟退火操作的混合差分进化算法[J]. 智能系统学报, 2014, 9(1): 109⁃114. 英文引用格式:YANG Yanxia. A hybrid differential evolutionary algorithm based on the simulated annealing operation[ J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2014, 9(1): 109⁃114. A hybrid differential evolutionary algorithm based on the simulated annealing operation YANG Yanxia (Department of Information Engineering, Wuhan University of Science and Technology City College, Wuhan 430083, China) Abstract:In order to improve the ability of the evolutionary algorithm for solving such complicated combination and optimization problems as the massive deceptive problems and hierarchical problems, this paper proposes an im⁃ proved algorithm, which introduces the simulated annealing operation into the differential evolutionary algorithm. U⁃ sing this method, the simulated annealing operation is carried out for a randomly generated initial individual and the temperature⁃reducing operation is carried out for a new individual. After several times of iterations, the optimal so⁃ lution in the population is taken as the solution to the question. By utilizing the mutation search of the simulated an⁃ nealing operator to improve the diversity of the population, the differential evolutionary algorithm can better utilize colony differences for an overall search. In the experiment, various types of deceptive functions and the hierarchical functions with a tree⁃shape structure are applied to simulation testing of the algorithm. In the initial stage, the algo⁃ rithm keeps diversity of the population; in the later stage, a local optimal solution may be generated, the conver⁃ gence scope nears to the overall optimal solution. The simulation results show that the algorithm has advantage for the aspect of searching the overall optimal solution. Keywords:differential evolutionary; evolutionary algorithm; simulated annealing; deceptive problem; hierarchical problem 收稿日期:2013⁃05⁃09. 网络出版日期:2014⁃02⁃20. 基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(70971020). 通信作者:杨艳霞. E⁃mail: yxy_job@ 163.com. 差分进化算法是一种基于群体差异实现全局优 化的进化算法,其简单高效,控制参数少,具有快速 的全局寻优能力,在工程、管理以及科学领域获得了 广泛的应用[1] 。 在实际应用中,当优化问题比较复 杂时,差分进化算法和其他进化算法一样,随着进化 代数的增加,个体间的差异会逐渐降低,个体变异的 多样性逐步减少,从而收敛到局部极值附近,陷入局 部最优解.为了提高差分进化算法的寻优能力,加快 收敛速度,克服一般进化算法常见的局部收敛现象, 许多学者对其进行了改进,迄今对差分进化算法的

·110· 智能系统学报 第9卷 研究和改进可以归纳为以下几方面:1)操作算子的 1]为交叉概率,i=1,2,…,P,j=1,2,…,no 改进:2)进化参数的自适应调整:3)多种群:4)混合 4)选择操作。 算法[2这些改进的算法虽然起到了一定的效果, 在差分进化算法中,选择操作采取优选策略,在 但在求解一些复杂优化问题时仍显得不够理想.针 变异操作和交叉操作完成后均进行选择操作,即只 对大规模欺骗函数和等级问题这类一般优化算法难 有当新产生的子代个体优于父代个体时才会保留, 以求解的高维复杂优化问题,本文将模拟退火算子 否则父代个体将继续保留在下一代中。 嵌入到差分进化算法的循环中,提出了二者相结合 1.2模拟退火算法原理及操作 的混合差分进化算法,以提高求解精度,新算法既保 模拟退火算法来源于固体退火原理,通过降温 留了差分进化算法具有较强的搜索能力,又克服了 来控制算法的搜索过程。模拟退火算法对当前解重 在复杂优化问题的求解上过早收敛而陷入局部解、 复如下过程:产生新解→计算目标函数差→接受或 进化后期收敛慢及求解精度不高的缺点。 舍弃,并在此过程中逐步衰减温度值,算法终止时, 即得到近似最优解。 1 差分进化算法与模拟退火算法 在模拟退火算法中,对个体L:按式(4)或者式 1.1差分进化算法原理及操作 (5)产生新个体。 本文是对欺骗函数和等级问题进行优化实验, 1)方式1。 根据所求解问题的特点,算法采用二进制编码方式。 L=(l1,l2,…,l4,…,lm,…,ln) 差分进化算法的基本原理与遗传算法类似,所不同 (4) L=(l1,h2,…,…,l4,…,ln) 的是,在遗传操作中采用种群个体间的差分向量进 式中:L为当前种群中的个体,L"为新产生的个 行变异,这充分利用了不可行解所携带的重要信息, 体,n为个体的编码长度,1<k<m<n。 减小了陷入局部最优解的机率。 2)方式2。 1)种群初始化。 设原个体L=(l1,l2,…,n),产生的新个体为 设L,=(,5,…,)为一个n维向量,即种群 a=(a1,a2,…,a.),随机数p=rand(0,1)(0和1之 中的一个个体,其中编码长度为n,种群大小为P, 间的随机小数),则产生新个体方式如下: 种群第1代个体按式(1)随机产生: (14-11,pP =rand[0,1],i=1,2,…,P,j=1,2,…,n(1) (5) 其他 式中:rand[0,1]随机产生0或者1,个体为随机产 生的二进制串。初始化种群时产生种群大小为P, 式中:Pm∈[0,1],新个体L"=a,1<j<no 为了对解空间进行充分的搜索,这2种方式都 编码长度为n的个体。 会被使用,在算法运行过程中随机选择其中的一种 2)变异操作。 算法的变异方式是在种群中随机选取2个不同 方式来产生新个体。新个体产生后计算适应度 的个体,将其向量差取绝对值后与待变异的个体进 f(L)和新旧个体间的适应度增量△E=f(L")- 行向量叠加,变异方式如式(2)所示: f八L:),并计算p=ex邓(-△E/T),按概率p选用或者 是舍弃新个体,重复上述过程一定次数后选择新搜 L+1=Lg-|L8-LgI川, 索到的适应度高的个体进入下一代。 i≠a≠b≠c,i=1,2,…,P (2) 式中:L是g+1代种群中第i个要变异的个体, 2混合差分进化算法 L:、L、L是g代种群中的3个互不相同的个体,由 混合差分进化算法是差分进化算法和模拟退火 于是二进制编码,因此差分向量取绝对值。 算法的合理组合,首先由一组随机产生的初始解开 3)交叉操作。 始搜索,通过带有精英保留策略的遗传操作产生新 交叉操作是在种群中随机选择2个不同的个 个体,然后对每一个新个体进行独立的模拟退火操 体,按式(3)产生新一代个体。 作,将操作完成后生成的个体作为混合算法的下一 L&u,rand≥P。 (3) 代个体,并进行退温操作,经过若干次迭代后,最终 (L,其他 选择种群中最优解作为所求问题的解。混合差分进 式中:rand为[0,1]内均匀分布的随机数,P。∈[0, 化算法流程如图1所示
研究和改进可以归纳为以下几方面:1)操作算子的 改进;2)进化参数的自适应调整;3)多种群;4)混合 算法[2⁃11] .这些改进的算法虽然起到了一定的效果, 但在求解一些复杂优化问题时仍显得不够理想.针 对大规模欺骗函数和等级问题这类一般优化算法难 以求解的高维复杂优化问题,本文将模拟退火算子 嵌入到差分进化算法的循环中,提出了二者相结合 的混合差分进化算法,以提高求解精度,新算法既保 留了差分进化算法具有较强的搜索能力,又克服了 在复杂优化问题的求解上过早收敛而陷入局部解、 进化后期收敛慢及求解精度不高的缺点。 1 差分进化算法与模拟退火算法 1.1 差分进化算法原理及操作 本文是对欺骗函数和等级问题进行优化实验, 根据所求解问题的特点,算法采用二进制编码方式。 差分进化算法的基本原理与遗传算法类似,所不同 的是,在遗传操作中采用种群个体间的差分向量进 行变异,这充分利用了不可行解所携带的重要信息, 减小了陷入局部最优解的机率。 1)种群初始化。 设 Li = (l i 1 ,l i 2 ,…,l i n ) 为一个 n 维向量,即种群 中的一个个体,其中编码长度为 n,种群大小为 P, 种群第 1 代个体按式(1)随机产生: l i j = rand[0,1],i = 1,2,…,P,j = 1,2,…,n (1) 式中:rand[0,1]随机产生 0 或者 1,个体为随机产 生的二进制串。 初始化种群时产生种群大小为 P, 编码长度为 n 的个体。 2)变异操作。 算法的变异方式是在种群中随机选取 2 个不同 的个体,将其向量差取绝对值后与待变异的个体进 行向量叠加,变异方式如式(2)所示: L g+1 i =| L g a -| L g b - L g c | | , i ≠ a ≠ b ≠ c, i = 1,2,…,P (2) 式中: L g+1 i 是 g+1 代种群中第 i 个要变异的个体, L g a 、L g b、L g c 是 g 代种群中的 3 个互不相同的个体,由 于是二进制编码,因此差分向量取绝对值。 3)交叉操作。 交叉操作是在种群中随机选择 2 个不同的个 体,按式(3)产生新一代个体。 L g+1 i,j = L g a,j,rand ≥ Pc L g { b,j, 其他 (3) 式中:rand 为[0,1]内均匀分布的随机数,Pc∈[0, 1]为交叉概率,i = 1,2,…,P, j = 1,2,…,n。 4)选择操作。 在差分进化算法中,选择操作采取优选策略,在 变异操作和交叉操作完成后均进行选择操作,即只 有当新产生的子代个体优于父代个体时才会保留, 否则父代个体将继续保留在下一代中。 1.2 模拟退火算法原理及操作 模拟退火算法来源于固体退火原理,通过降温 来控制算法的搜索过程。 模拟退火算法对当前解重 复如下过程:产生新解→计算目标函数差→接受或 舍弃,并在此过程中逐步衰减温度值,算法终止时, 即得到近似最优解。 在模拟退火算法中,对个体 Li按式(4)或者式 (5)产生新个体。 1)方式 1。 Li = (l 1 ,l 2 ,…,l k,…,lm ,…,l n ) L new i = (l 1 ,l 2 ,…,lm ,…,l k,…,l n ) (4) 式中:Li为当前种群中的个体, L new i 为新产生的个 体,n 为个体的编码长度,1<k<m<n。 2)方式 2。 设原个体 L = ( l 1 ,l 2 ,…,l n ),产生的新个体为 a = (a1 ,a2 ,…,an ),随机数 p = rand(0,1) (0 和 1 之 间的随机小数),则产生新个体方式如下: aj = | l j - 1 |, p > Pm l { j, 其他 (5) 式中:Pm∈[0,1],新个体 L new i = a,1<j<n。 为了对解空间进行充分的搜索,这 2 种方式都 会被使用,在算法运行过程中随机选择其中的一种 方式来产生新个体。 新个体产生后计算适应度 f(L new i ) 和新旧个体间的适应度增量△E = f(L new i ) - f(Li),并计算 p = exp( -△E / T),按概率 p 选用或者 是舍弃新个体,重复上述过程一定次数后选择新搜 索到的适应度高的个体进入下一代。 2 混合差分进化算法 混合差分进化算法是差分进化算法和模拟退火 算法的合理组合,首先由一组随机产生的初始解开 始搜索,通过带有精英保留策略的遗传操作产生新 个体,然后对每一个新个体进行独立的模拟退火操 作,将操作完成后生成的个体作为混合算法的下一 代个体,并进行退温操作,经过若干次迭代后,最终 选择种群中最优解作为所求问题的解。 混合差分进 化算法流程如图 1 所示。 ·110· 智 能 系 统 学 报 第 9 卷
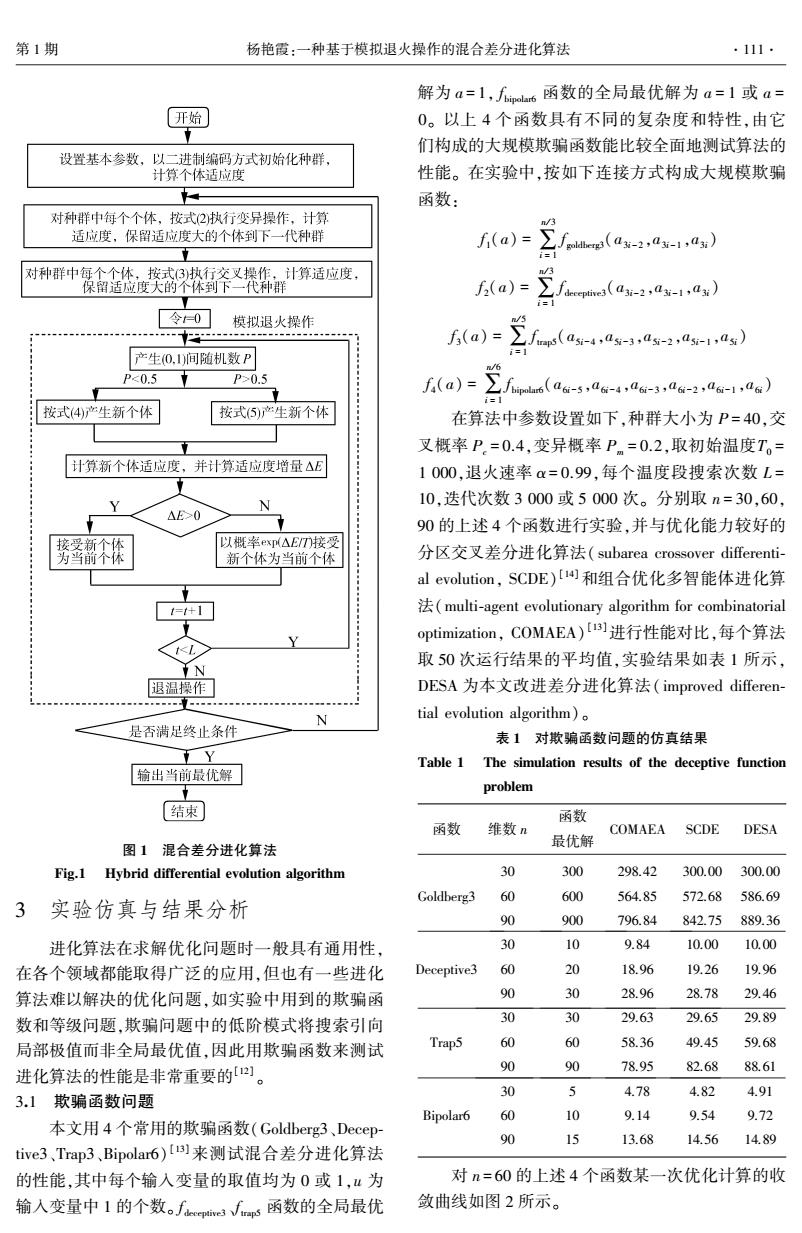
第1期 杨艳霞:一种基于模拟退火操作的混合差分进化算法 .111. 解为a=1,人b6函数的全局最优解为a=1或a= 开始 0。以上4个函数具有不同的复杂度和特性,由它 们构成的大规模欺骗函数能比较全面地测试算法的 设置基本参数,以二进制编码方式初始化种群, 计算个体适应度 性能。在实验中,按如下连接方式构成大规模欺骗 阳 函数: 对种群中每个个体,按式(2执行变异操作,计算 /3 适应度,保留适应度大的个体到下一代种群 f(a)=∑f(as-2,a-a) 对种群中每个个体,按式3)执行交叉操作,计算适应度, 保留适应度大的个体到下一代种群 f(a)= [令0 模拟退火操作 f5(a)= f(a5-4,05-3,4-2,4-1,ax) 产生(0,1)间随机数P i=1 0.5 a=芝人 按式4产生新个体 按式(5)产生新个体 在算法中参数设置如下,种群大小为P=40,交 叉概率P.=0.4,变异概率Pm=0.2,取初始温度T。= 计算新个体适应度,并计算适应度增量△E 1000,退火速率a=0.99,每个温度段搜索次数L= 10,迭代次数3000或5000次。分别取n=30,60, △E>0 N 90的上述4个函数进行实验,并与优化能力较好的 接受新个体 以概率exp(△E/T接受 为当箭个体 新个体为当前个体 分区交叉差分进化算法(subarea crossover differenti- al evolution,SCDE)[和组合优化多智能体进化算 f+ multi-agent evolutionary algorithm for combinatorial optimization,COMAEA)[u)进行性能对比,每个算法 KL 取50次运行结果的平均值,实验结果如表1所示, IN 退温操作☐ DESA为本文改进差分进化算法(improved differen- tial evolution algorithm). 是否满足终止条件 表1对欺骗函数问题的仿真结果 Y Table 1 The simulation results of the deceptive function 输出当前最优解 problem 结束 函数 函数 维数n COMAEA SCDE DESA 图1混合差分进化算法 最优解 Fig.1 Hybrid differential evolution algorithm 30 300 298.42 300.00 300.00 Goldberg3 60 600 564.85 572.68 586.69 3实验仿真与结果分析 90 900 796.84 842.75889.36 进化算法在求解优化问题时一般具有通用性, 30 10 9.84 10.00 10.00 在各个领域都能取得广泛的应用,但也有一些进化 Deceptive3 60 20 18.96 19.26 19.96 算法难以解决的优化问题,如实验中用到的欺骗函 90 30 28.96 28.78 29.46 数和等级问题,欺骗问题中的低阶模式将搜索引向 30 30 29.63 29.65 29.89 局部极值而非全局最优值,因此用欺骗函数来测试 Trap5 60 60 58.36 49.45 59.68 进化算法的性能是非常重要的)。 90 90 78.95 82.68 88.61 30 J 4.78 4.82 4.91 3.1欺骗函数问题 Bipolar6 60 10 9.14 9.54 9.72 本文用4个常用的欺骗函数(Goldberg3.、Decep- 90 15 13.68 14.56 14.89 tive3、Trap3,Bipolare6)【B来测试混合差分进化算法 的性能,其中每个输入变量的取值均为0或1,“为 对n=60的上述4个函数某一次优化计算的收 输入变量中I的个数。fii3ps函数的全局最优 敛曲线如图2所示
图 1 混合差分进化算法 Fig.1 Hybrid differential evolution algorithm 3 实验仿真与结果分析 进化算法在求解优化问题时一般具有通用性, 在各个领域都能取得广泛的应用,但也有一些进化 算法难以解决的优化问题,如实验中用到的欺骗函 数和等级问题,欺骗问题中的低阶模式将搜索引向 局部极值而非全局最优值,因此用欺骗函数来测试 进化算法的性能是非常重要的[12] 。 3.1 欺骗函数问题 本文用 4 个常用的欺骗函数(Goldberg3、Decep⁃ tive3、Trap3、Bipolar6) [13]来测试混合差分进化算法 的性能,其中每个输入变量的取值均为 0 或 1,u 为 输入变量中 1 的个数。 f deceptive3 、f trap5 函数的全局最优 解为 a = 1, f bipolar6 函数的全局最优解为 a = 1 或 a = 0。 以上 4 个函数具有不同的复杂度和特性,由它 们构成的大规模欺骗函数能比较全面地测试算法的 性能。 在实验中,按如下连接方式构成大规模欺骗 函数: f 1(a) = ∑ n/ 3 i = 1 f goldberg3(a3i-2 ,a3i-1 ,a3i) f 2(a) = ∑ n/ 3 i = 1 f deceptive3(a3i-2 ,a3i-1 ,a3i) f 3(a) = ∑ n/ 5 i = 1 f trap5(a5i-4 ,a5i-3 ,a5i-2 ,a5i-1 ,a5i) f 4(a) = ∑ n/ 6 i = 1 f bipolar6(a6i-5 ,a6i-4 ,a6i-3 ,a6i-2 ,a6i-1 ,a6i) 在算法中参数设置如下,种群大小为 P = 40,交 叉概率 Pc = 0.4,变异概率 Pm = 0.2,取初始温度T0 = 1 000,退火速率 α= 0.99,每个温度段搜索次数 L = 10,迭代次数 3 000 或 5 000 次。 分别取 n = 30,60, 90 的上述 4 个函数进行实验,并与优化能力较好的 分区交叉差分进化算法( subarea crossover differenti⁃ al evolution, SCDE) [14]和组合优化多智能体进化算 法(multi⁃agent evolutionary algorithm for combinatorial optimization, COMAEA) [13]进行性能对比,每个算法 取 50 次运行结果的平均值,实验结果如表 1 所示, DESA 为本文改进差分进化算法( improved differen⁃ tial evolution algorithm)。 表 1 对欺骗函数问题的仿真结果 Table 1 The simulation results of the deceptive function problem 函数 维数 n 函数 最优解 COMAEA SCDE DESA Goldberg3 Deceptive3 Trap5 Bipolar6 30 60 90 30 60 90 30 60 90 30 60 90 300 600 900 10 20 30 30 60 90 5 10 15 298.42 564.85 796.84 9.84 18.96 28.96 29.63 58.36 78.95 4.78 9.14 13.68 300.00 572.68 842.75 10.00 19.26 28.78 29.65 49.45 82.68 4.82 9.54 14.56 300.00 586.69 889.36 10.00 19.96 29.46 29.89 59.68 88.61 4.91 9.72 14.89 对 n = 60 的上述 4 个函数某一次优化计算的收 敛曲线如图 2 所示。 第 1 期 杨艳霞:一种基于模拟退火操作的混合差分进化算法 ·111·

·112. 智能系统学报 第9卷 ×10 3.2等级问题 0.60 等级问题由等级结构、映射函数、函数值3部分 0.55 组成,输入变量作为最底层,按照映射函数将下一层 SCDE ▣0.50 COMAEA 映射到上一层,便构成了树状结构,每一层的函数值 之和即为最终的函数值。本文用HIFF(hierarchical DESA if-and-omly-if function)函数和HtrapI(hierarchical 0.40 tapI)函数[这2个比较典型的等级函数来测试 ×10 算法的性能。 0.35 0 0.51.01.52.02.53.0 1)HIFF函数。 迭代次数 (a)Goldberg函数 按式(6)由下层向上层映射: 20r 0, a=0且a鸣=0 19 SCDE fr(d)=1, a=1且ag=1 18 其他 17 COMAEA i=2,3,…,L,j=1,2,…,2 (6) 16 DESA 式中:L为层数,每一层的函数值由式(7)计算: 15 fi(a)=2-∑f, 14B 13 ×10 1,a=0或a=1 0.5 1.01.52.02.53.0 = 迭代次数 0, 其他 (b)Deceptive函数 i=1,2,…,L (7) 60 COMAEA 总函数值由式(8)计算: 50 fr(a)= ∑fr(a)+ SCDE 2, a=a5=0或a1=a5=1 40 (8) DESA 0, 其他 35 2)HtrapI函数。 30 HtrapI函数和HIFF函数映射过程类似,将下一 25 ,×103 0 2 3 层的3个变量映射为上一层的1个变量,问题规模 迭代次数 满足n=3L,映射函数如式(9)所示: (c)Trap5函数 10.0 0, a2=0且a=0且写=0 SCDE DESA- fhap(ad)= 1, a2=1且a1=1且ag=1, 9.6 -1, 其他 9.2 i=2,3,…,L,j=1,2,…,3 (9) 各层的函数值由式(10)计算: 8.8 COMAEA fap(a)=3 8.4 =1 1, u=0或u=3 8.0 ×10 0, u=2 2 3 5 f(a-2,-1,a)= 迭代次数 0.5 u=1 (d)Bipolare6函数 (10) 图260维函数收敛曲线对比图 Fig.2 Comparison of 60-dimensional function conver- 式中:u表示424-1、a中1的个数,最终的函数 gence curve 值由式(11)计算:
(a) Goldberg 函数 (b) Deceptive 函数 (c) Trap5 函数 (d) Bipolar6 函数 图 2 60 维函数收敛曲线对比图 Fig. 2 Comparison of 60⁃dimensional function conver⁃ gence curve 3.2 等级问题 等级问题由等级结构、映射函数、函数值 3 部分 组成,输入变量作为最底层,按照映射函数将下一层 映射到上一层,便构成了树状结构,每一层的函数值 之和即为最终的函数值。 本文用 HIFF (hierarchical if⁃and⁃only⁃if function) 函 数 和 HtrapI ( hierarchical trap I)函数[13] 这 2 个比较典型的等级函数来测试 算法的性能。 1)HIFF 函数。 按式(6)由下层向上层映射: fHIFF(a j i) = 0, a i-1 2j-1 = 0 且 a i-1 2j = 0 1, a i-1 2j-1 = 1 且 a i-1 2j = 1 - 1, 其他 ì î í ï ï ï ï i = 2,3,…,L,j = 1,2,…,2 i (6) 式中:L 为层数,每一层的函数值由式(7)计算: f i HIFF( a i ) = 2 i- 1∑ 2 i j = 1 f i j , f i j = 1, a i j = 0 或 a i j = 1 0, 其他 { i = 1,2,…,L (7) 总函数值由式(8)计算: fHIFF(a) = ∑ L i = 1 f i HIFF(a i ) + 2 L , a L 1 = a L 2 = 0 或 a L 1 = a L 2 = 1 0, 其他 { (8) 2)HtrapI 函数。 HtrapI 函数和 HIFF 函数映射过程类似,将下一 层的 3 个变量映射为上一层的 1 个变量,问题规模 满足 n = 3L,映射函数如式(9)所示: fHtrapI(a j i) = 0, a i-1 3j-2 = 0 且 a i-1 3j-1 = 0 且 a i-1 3j = 0 1, a i-1 3j-2 = 1 且 a i-1 3j-1 = 1 且 a i-1 3j = 1 - 1, 其他 ì î í ï ï ï ï , i = 2,3,…,L,j = 1,2,…,3 i (9) 各层的函数值由式(10)计算: f i HtrapI(a i ) = 3 i∑ 3 i / 3 j = 1 f i j (a i 3j-2 ,a i 3j-1 ,a i 3j) , f i j (a i 3j-2 ,a i 3j-1 ,a i 3j) = 1, u = 0 或 u = 3 0, u = 2 0.5, u = 1 ì î í ïï ï (10) 式中:u 表示 a i 3j-2 、a i 3j-1 、a i 3j 中 1 的个数,最终的函数 值由式(11)计算: ·112· 智 能 系 统 学 报 第 9 卷

第1期 杨艳霞:一种基于模拟退火操作的混合差分进化算法 ·113 u=3 从以上的实验结果可以看出,对于复杂的、具 fpi(a)= h(d)+3x u=2 有欺骗引导的优化问题,COMAEA算法和SCDE算 i=1 0.45, =1 法比较快地收敛到局部极值附近,出现早熟收敛现 0.9, u=0 象,而改进的差分进化算法DESA随着迭代的进行, (11) 在算法运行的后期,能比较好地跳出局部最优解,收 在对这2个函数进行优化实验时,算法参数同 敛到全局最优解附近。 上,每个算法取30次实验结果的平均值,实验结果 分析其原因在于:在算法运行的初期,利用模拟 如表2所示。 退火算子的突变搜索来减少陷入局部最优的个体, 表2对等级问题的仿真结果 提高种群多样性,使差分进化算法能更好地利用群 Table 2 The simulation results of the hierarchical function 体差异进行全局搜索:在算法运行末期,模拟退火算 problem 子以更大的机率接受好解,使种群朝着最优解的方 函数 函数维数n COMAEA SCDE DESA 向进化,从而保证收敛的稳定性。因此通过模拟退 最优解 火算子和差分进化算法的有机结合,进一步增强了 32 192 148.42 153.24 189.78 算法的求解能力。 HIFF 64 448 372.69 312.33 424.62 128 1024 836.54 821.35 989.36 4 结束语 27 135 129.94 121.26134.82 Htrapl 81 1134 1083.16 1041.741131.43 对于复杂的优化问题,一般进化算法在选择算 243 9963 9228.769128.139927.31 子的作用下,优良个体的迅速增多使得种群失去多 对于n=64的HIFF函数和n=81的HtrapI函 样性,从而陷入局部最优解。本文提出的混合差分 数,某一次优化计算的收敛曲线如图3所示。 进化算法在模拟退火操作的作用下,能较好地保持 种群多样性,使差分变异更好地发挥作用,同时利用 ×10 4.5 模拟操作的局部搜索功能,更有利地搜索到全局最 优解。对欺骗函数问题和等级问题的仿真实验表明 4.0 SCDE 了混合差分进化算法的有效性和实用性。如何进一 3.5 DESA 步改进该算法,使之适用于其他问题是本课题下一 提 3.0 步工作的研究重点。 2.5 参考文献: 2.0 COMAEA [1]刘建平.基于混沌和差分进化的混合粒子群优化算法 [J].计算机仿真,2012,29(2):208-212 ×10 2 3 4 5 LIU Jianping.Hybrid particle swarm optimization algorithm 迭代次数 based on chaos and differential evolution[]].Computer (a)HIFF函数 Simulation,2012,29(2):208-212. [2]刘波,王凌,金以慧差分进化算法研究进展[J]控制与 ×10 1.15 决策,2007,22(7):721-729. LIU Bo,WANG Ling,JIN Yihui.Advances in differential 1.05 COMAEA evolution[J].Control and Decision,2007,22(7):721- 729. 0.95 SCDE [3]徐斌,祁荣宾,钱锋.基于混合差分进化和alpha约束支配 处理的多目标优化算法[J].控制理论与应用,2012,29 (3):353-360. DESA 0.75 XU Bin,QI Rongbin,QIAN Feng.Constrained multi-objec- tive optimization with hybrid differential evolution and alpha 0.65 ×10 constrained domination technique[J].Control Theory Ap- 23 4 迭代次数 plications,2012,29(3):353-360. [4]刘若辰,焦李成,雷七峰,等.一种新的差分进化约束优化 (b)HtrapI函数 算法[刀.西安电子科技大学学报:自然科学版,2011, 图3HFF函数和HtrapI函数收敛曲线对比 38(1):47-53. Fig.3 Comparison of HIFF function and Htrapl func- LIU Ruochen,JIAO Licheng,LEI Qifeng,et al.New dif- tion convergence curve ferential evolution constrained optimization algorithm[J]
fHtrapI(a) = ∑ L-1 i = 1 f i HtrapI(a i ) + 3 L × 1, u = 3 0, u = 2 0.45, u = 1 0.9, u = 0 ì î í ï ï ï ï (11) 在对这 2 个函数进行优化实验时,算法参数同 上,每个算法取 30 次实验结果的平均值,实验结果 如表 2 所示。 表 2 对等级问题的仿真结果 Table 2 The simulation results of the hierarchical function problem 函数 维数 n 函数 最优解 COMAEA SCDE DESA HIFF HtrapI 32 64 128 27 81 243 192 448 1 024 135 1 134 9 963 148.42 372.69 836.54 129.94 1 083.16 9 228.76 153.24 312.33 821.35 121.26 1 041.74 9 128.13 189.78 424.62 989.36 134.82 1 131.43 9 927.31 对于 n = 64 的 HIFF 函数和 n = 81 的 HtrapI 函 数,某一次优化计算的收敛曲线如图 3 所示。 (a) HIFF 函数 (b) HtrapI 函数 图 3 HIFF 函数和 HtrapI 函数收敛曲线对比 Fig.3 Comparison of HIFF function and HtrapI func⁃ tion convergence curve 从以上的实验结果可以看出,对于复杂的、具 有欺骗引导的优化问题,COMAEA 算法和 SCDE 算 法比较快地收敛到局部极值附近,出现早熟收敛现 象,而改进的差分进化算法 DESA 随着迭代的进行, 在算法运行的后期,能比较好地跳出局部最优解,收 敛到全局最优解附近。 分析其原因在于:在算法运行的初期,利用模拟 退火算子的突变搜索来减少陷入局部最优的个体, 提高种群多样性,使差分进化算法能更好地利用群 体差异进行全局搜索;在算法运行末期,模拟退火算 子以更大的机率接受好解,使种群朝着最优解的方 向进化,从而保证收敛的稳定性。 因此通过模拟退 火算子和差分进化算法的有机结合,进一步增强了 算法的求解能力。 4 结束语 对于复杂的优化问题,一般进化算法在选择算 子的作用下,优良个体的迅速增多使得种群失去多 样性,从而陷入局部最优解。 本文提出的混合差分 进化算法在模拟退火操作的作用下,能较好地保持 种群多样性,使差分变异更好地发挥作用,同时利用 模拟操作的局部搜索功能,更有利地搜索到全局最 优解。 对欺骗函数问题和等级问题的仿真实验表明 了混合差分进化算法的有效性和实用性。 如何进一 步改进该算法,使之适用于其他问题是本课题下一 步工作的研究重点。 参考文献: [1]刘建平.基于混沌和差分进化的混合粒子群优化算法 [J].计算机仿真, 2012, 29(2): 208⁃212. LIU Jianping. Hybrid particle swarm optimization algorithm based on chaos and differential evolution[J]. Computer Simulation, 2012, 29(2): 208⁃212. [2]刘波,王凌,金以慧.差分进化算法研究进展[ J].控制与 决策, 2007, 22(7): 721⁃729. LIU Bo, WANG Ling, JIN Yihui. Advances in differential evolution[ J]. Control and Decision, 2007, 22 ( 7): 721⁃ 729. [3]徐斌,祁荣宾,钱锋.基于混合差分进化和 alpha 约束支配 处理的多目标优化算法[ J].控制理论与应用, 2012, 29 (3): 353⁃360. XU Bin, QI Rongbin, QIAN Feng. Constrained multi⁃objec⁃ tive optimization with hybrid differential evolution and alpha constrained domination technique[J]. Control Theory & Ap⁃ plications, 2012, 29(3): 353⁃360. [4]刘若辰,焦李成,雷七峰,等.一种新的差分进化约束优化 算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2011, 38(1): 47⁃53. LIU Ruochen, JIAO Licheng, LEI Qifeng, et al. New dif⁃ ferential evolution constrained optimization algorithm[J]. 第 1 期 杨艳霞:一种基于模拟退火操作的混合差分进化算法 ·113·

·114. 智能系统学报 第9卷 Journal of Xidian University:Natural Science,2011,38 [11]阳春华,钱晓山,桂卫华.一种混沌差分进化和粒子群优 (1):47-53. 化混合算法[J].计算机应用研究,2011,28(2):439 [5]张伟丰.引入模拟退火算子的差分进化算法性能研究 441. [J刀数值计算与计算机应用,2011,32(4):301-304. YANG Chunhua,QIAN Xiaoshan,GUI Weihua.Hybrid ZHANG Weifeng.The performance research of differential e- volution algorithm which introduced the simulated and an- algorithm of chaotic differential evolution and particle nealing operator [J].Joumal on Numerical Methods and swarm optimization[J].Application Research of Comput- Computer Applications,2011,32(4):301-304. ers,2011,28(2):439-441. [6]郑建国,王翔,刘荣辉.求解约束优化问题的8-DE算法 [12]GOLDBERG D E,DEB K,KORB B.Messy genetic algo- [J]软件学报,2012,23(9):2374-2387. rithms revisited:studies in mixed size and scale[J].Com- ZHENG Jianguo,WANG Xiang,LIU Ronghui.s-differenti- plex Systems,1990,4(4):415-444. al evolution algorithm for constrained optimization problems [13]钟伟才,刘静,刘芳,等.组合优化多智能体进化算法 [J].Journal of Software,2012,23(9):2374-2387. [7]ZOU Dexuan,GAO Liqun.An efficient improved differential [J].计算机学报,2004,27(10):1341-1353. evolution algorithm[C]//The 31st Chinese Control Confer- ZHONG Weicai,LIU Jing,LIU Fang,et al.Combinatorial ence.Hefei,China,2012:2385-2390. optimization using multi-agent evolutionary algorithm[J]. [8]LI Yinghai.Optimal scheduling of cascade hydropower sys- Chinese Journal of Computers,2004,27(10):1341- tem using grouping differential evolution algorithm [C]/ 1353. 2012 International Conference on Computer Science and E- [14]刘荣辉,郑建国.分区交叉差分进化算法及其约束优化 lectronic Engineering.Hangzhou,China,2012:625-629. [9]陶新明,徐鹏,刘福荣,等组合分布估计和差分进化的多 [J].计算机科学,2012,39(2):283-287. 目标优化算法[J].智能系统学报,2013,8(1):39-45. LIU Ronghui,ZHENG Jianguo.Subarea crossover differen- TAO Xinmin,XU Peng,LIU Furong,et al.Multi-objective tial evolution algorithm and its constrained optimization optimization algorithm composed of estimation of distribution [J].Computer Science,2012,39(2):283-287. and differential evolution[J].CAAI Transactions on Intelli- 作者简介: gent Systems,2013,8(1):39-45. 杨艳霞,女,1979年生,讲师,主要 [10]杨振宇,唐珂差分进化算法参数控制与适应策略综述 研究方向为数据挖掘与智能计算,发表 [J].智能系统学报,2011,6(5):415-423. YANG Zhengyu,TANG Ke.An overview of parameter con- 学术论文20余篇。 trol and adaptation strategies in differential evolution algo- rithm [J].CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2011,6(5):415-423. 2014年IFIP智能信息处理国际会议 8th International Conference on Intelligent Information Processing The IIP conference series provides a forum for engineers and scientists in academia,university and industry to pres- ent their latest research findings in any aspects of intelligent information processing.IIP2014 attempts to meet the needs of a large and diverse community. The proceedings will be published by the Springer.Please click here to get the detailed paper format.All papers should be sent electronically preferably in PDF)to the Easychair paper management system http://www. easychair.org/conferences/?conf=iip2014 or through the IIP2014 Website http://www.intsci.ac.cn/iip2014/). All accepted papers will be indexed by EI and Inspec. Important Dates Submission Deadline:1 April,2014 Author Notification:1 May,2014 Camera-ready Due:1 June,2014 Website:http://www.intsci.ac.cn/iip2014/
Journal of Xidian University: Natural Science, 2011, 38 (1): 47⁃53. [5]张伟丰.引入模拟退火算子的差分进化算法性能研究 [J].数值计算与计算机应用, 2011, 32(4): 301⁃304. ZHANG Weifeng. The performance research of differential e⁃ volution algorithm which introduced the simulated and an⁃ nealing operator [ J]. Journal on Numerical Methods and Computer Applications, 2011, 32(4): 301⁃304. [6]郑建国,王翔,刘荣辉.求解约束优化问题的 ε⁃DE 算法 [J].软件学报, 2012, 23(9): 2374⁃2387. ZHENG Jianguo, WANG Xiang, LIU Ronghui. ε⁃differenti⁃ al evolution algorithm for constrained optimization problems [J]. Journal of Software, 2012, 23(9): 2374⁃2387. [7]ZOU Dexuan, GAO Liqun. An efficient improved differential evolution algorithm[C] / / The 31st Chinese Control Confer⁃ ence. Hefei, China, 2012: 2385⁃2390. [8]LI Yinghai. Optimal scheduling of cascade hydropower sys⁃ tem using grouping differential evolution algorithm [ C] / / 2012 International Conference on Computer Science and E⁃ lectronic Engineering. Hangzhou, China, 2012: 625⁃629. [9]陶新明,徐鹏,刘福荣,等.组合分布估计和差分进化的多 目标优化算法[J].智能系统学报, 2013, 8(1): 39⁃45. TAO Xinmin, XU Peng, LIU Furong, et al. Multi⁃objective optimization algorithm composed of estimation of distribution and differential evolution[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelli⁃ gent Systems, 2013, 8(1): 39⁃45. [10]杨振宇,唐珂.差分进化算法参数控制与适应策略综述 [J].智能系统学报, 2011, 6(5): 415⁃423. YANG Zhengyu, TANG Ke. An overview of parameter con⁃ trol and adaptation strategies in differential evolution algo⁃ rithm [ J ]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2011, 6(5): 415⁃423. [11]阳春华,钱晓山,桂卫华.一种混沌差分进化和粒子群优 化混合算法[ J].计算机应用研究, 2011, 28(2): 439⁃ 441. YANG Chunhua, QIAN Xiaoshan, GUI Weihua. Hybrid algorithm of chaotic differential evolution and particle swarm optimization[ J]. Application Research of Comput⁃ ers, 2011, 28(2):439⁃441. [12]GOLDBERG D E, DEB K, KORB B. Messy genetic algo⁃ rithms revisited: studies in mixed size and scale[J]. Com⁃ plex Systems, 1990, 4(4): 415⁃444. [13]钟伟才,刘静,刘芳,等. 组合优化多智能体进化算法 [J].计算机学报, 2004, 27(10): 1341⁃1353. ZHONG Weicai, LIU Jing, LIU Fang, et al. Combinatorial optimization using multi⁃agent evolutionary algorithm[ J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2004, 27 ( 10 ): 1341⁃ 1353. [14]刘荣辉,郑建国.分区交叉差分进化算法及其约束优化 [J].计算机科学, 2012, 39(2): 283⁃287. LIU Ronghui, ZHENG Jianguo. Subarea crossover differen⁃ tial evolution algorithm and its constrained optimization [J]. Computer Science, 2012, 39(2): 283⁃287. 作者简介: 杨艳霞,女,1979 年生,讲师,主要 研究方向为数据挖掘与智能计算,发表 学术论文 20 余篇。 2014 年 IFIP 智能信息处理国际会议 8th International Conference on Intelligent Information Processing The IIP conference series provides a forum for engineers and scientists in academia, university and industry to pres⁃ ent their latest research findings in any aspects of intelligent information processing. IIP2014 attempts to meet the needs of a large and diverse community. The proceedings will be published by the Springer. Please click here to get the detailed paper format. All papers should be sent electronically ( preferably in PDF) to the Easychair paper management system http: / / www. easychair.org / conferences/ ? conf = iip2014 or through the IIP2014 Website (http: / / www.intsci.ac.cn / iip2014 / ). All accepted papers will be indexed by EI and Inspec. Important Dates Submission Deadline: 1 April, 2014 Author Notification: 1 May, 2014 Camera⁃ready Due: 1 June, 2014 Website: http: / / www.intsci.ac.cn / iip2014 / ·114· 智 能 系 统 学 报 第 9 卷