
第9卷第2期 智能系统学报 Vol.9 No.2 2014年4月 CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems Apr.2014 D0I:10.3969/j.issn.1673-4785.201307010 网络出版t地址:http:/www.cmki.net/kcms/doi/CNKI:23-1538/TP.20131105.1201.004.html 不完备信息系统中测试代价敏感的 可变精度分类粗糙集 鞠恒荣1,马兴斌,杨习贝12,祁云嵩,杨静宇2 (1.江苏科技大学计算机科学与工程学院,江苏镇江212003:2.南京理工大学计算机科学与技术学院,江苏南京 210094) 摘要:在不完备信息系统中,可变精度分类关系是限制容差关系的改进形式,但其并未考虑数据集中属性的测试 代价。为解决这一问题,提出了基于测试代价敏感的可变精度分类粗糙集模型。进一步地,通过分析传统启发式 算法没有考虑测试代价以及回溯算法的时间消耗等因素,提出一种新的属性重要度测量,并在此基础上设计了一 种新的启发式算法。通过实验对比分析,说明了新提出算法的有效性。 关键词:属性约简:不完备信息系统:测试代价敏感:变精度分类粗糙集 中图分类号:TP18文献标志码:A文章编号:1673-4785(2014)02-0219-05 中文引用格式:鞠恒荣,马兴斌,杨习贝,等.不完备信息系统中测试代价敏感的可变精度分类粗糙集[J].智能系统学报,2014,9 (2):219-223. 英文引用格式:JU Hengrong,MA Xingbin,YANG Xibei,etal.Test-cost-sensitive based variable precision classification rough set in incomplete information system[J].CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems,2014,9(2):219-223. Test-cost-sensitive based variable precision classification rough set in incomplete information system JU Hengrong',MA Xingbin',YANG Xibei2,QI Yunsong',YANG Jingyu2 (1.School of Computer Science and Engineering,Jiangsu University of Science and Technology,Zhenjiang 212003.China;2.School of Computer Science and Technology,Nanjing University of Science and Technology,Nanjing 210094,China) Abstract:In an incomplete information system,the precision-variable classification relation is an improvement of the limited tolerance relation.However,the test costs of the data concentration attributes are not taken into account. To solve this problem,a test-cost-sensitive-based precision-variable precision classification rough set is proposed. Furthermore,the traditional heuristic algorithm does not take the importance of the test costs of the attributes into account,and backtracking algorithm is very time-consuming.Therefore,not only was a new importance of the at- tribute proposed,but a new heuristic algorithm was also presented for obtaining reduction with minor test costs.The experimental results show the effectiveness of the new algorithm by comparing it with the other algorithms. Keywords:attribute reduction;incomplete information system:test cost sensitive;variable precision classification rough set 作为一种处理不精确、不确定性问题的数学工 出后便受到了广泛关注2。然而由于数据测量的误 具,粗糙集理论(rough set)由波兰学者Pawlak提 差、数据获取的限制等原因,导致了所面临的信息系 统往往是不完备的。为处理这类问题,王国胤)提出 收稿日期:2013-07-05.网络出版日期:2013-11-05. 了限制容差关系。进一步,杨习贝[提出了一种新的 基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(61100116,61203024);江苏省 自然科学基金资助项目(BK2011492,BK2012700):江苏省 基于可变精度分类的拓展粗糙集模型,对限制容差 高校自然科学基金资助项目(11KJB520004,13KB520003): 高维信息智能感知与系统教育部重点实验室(南京理工大 关系进行了改进。然而,在实际工程应用中,数据的 学)基金资助项目(30920130122005):江苏省普通高校研究 获取是需要付出一些成本或代价的,称其为测试代 生科研创新计划项目资助项目(CXLX13707). 通信作者:杨习贝.E-mail:yangxibei@hotmail.com 价。针对该问题,Mi等[率先将测试代价引入到
第 9 卷第 2 期 智 能 系 统 学 报 Vol.9 №.2 2014 年 4 月 CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems Apr. 2014 DOI:10.3969 / j.issn.1673⁃4785.201307010 网络出版地址:http: / / www.cnki.net / kcms/ doi / CNKI:23⁃1538 / TP.20131105.1201.004.html 不完备信息系统中测试代价敏感的 可变精度分类粗糙集 鞠恒荣1 ,马兴斌1 ,杨习贝1,2 ,祁云嵩1 ,杨静宇2 (1.江苏科技大学 计算机科学与工程学院,江苏 镇江 212003; 2. 南京理工大学 计算机科学与技术学院,江苏 南京 210094) 摘 要:在不完备信息系统中, 可变精度分类关系是限制容差关系的改进形式, 但其并未考虑数据集中属性的测试 代价。 为解决这一问题, 提出了基于测试代价敏感的可变精度分类粗糙集模型。 进一步地, 通过分析传统启发式 算法没有考虑测试代价以及回溯算法的时间消耗等因素, 提出一种新的属性重要度测量, 并在此基础上设计了一 种新的启发式算法。 通过实验对比分析,说明了新提出算法的有效性。 关键词:属性约简;不完备信息系统;测试代价敏感;变精度分类粗糙集 中图分类号: TP18 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1673⁃4785(2014)02⁃0219⁃05 中文引用格式:鞠恒荣,马兴斌,杨习贝,等. 不完备信息系统中测试代价敏感的可变精度分类粗糙集[ J]. 智能系统学报, 2014, 9 (2): 219⁃223. 英文引用格式:JU Hengrong,MA Xingbin, YANG Xibei, et al. Test⁃cost⁃sensitive based variable precision classification rough set in incomplete information system[J]. CAAI Transactions on Intelligent Systems, 2014, 9(2): 219⁃223. Test⁃cost⁃sensitive based variable precision classification rough set in incomplete information system JU Hengrong 1 , MA Xingbin 1 , YANG Xibei 1,2 , QI Yunsong 1 , YANG Jingyu 2 (1. School of Computer Science and Engineering, Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, Zhenjiang 212003, China; 2. School of Computer Science and Technology, Nanjing University of Science and Technology, Nanjing 210094, China) Abstract:In an incomplete information system, the precision⁃variable classification relation is an improvement of the limited tolerance relation. However, the test costs of the data concentration attributes are not taken into account. To solve this problem, a test⁃cost⁃sensitive⁃based precision⁃variable precision classification rough set is proposed. Furthermore, the traditional heuristic algorithm does not take the importance of the test costs of the attributes into account, and backtracking algorithm is very time⁃consuming. Therefore, not only was a new importance of the at⁃ tribute proposed, but a new heuristic algorithm was also presented for obtaining reduction with minor test costs. The experimental results show the effectiveness of the new algorithm by comparing it with the other algorithms. Keywords:attribute reduction; incomplete information system; test cost sensitive; variable precision classification rough set 收稿日期:2013⁃07⁃05. 网络出版日期:2013⁃11⁃05. 基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(61100116, 61203024); 江苏省 自然科学基金资助项目(BK2011492, BK2012700);江苏省 高校自然科学基金资助项目(11KJB520004, 13KJB520003); 高维信息智能感知与系统教育部重点实验室(南京理工大 学)基金资助项目(30920130122005);江苏省普通高校研究 生科研创新计划项目资助项目(CXLX13_707). 通信作者:杨习贝. E⁃mail:yangxibei@ hotmail.com. 作为一种处理不精确、不确定性问题的数学工 具, 粗糙集理论[1] (rough set)由波兰学者 Pawlak 提 出后便受到了广泛关注[2⁃4] 。 然而由于数据测量的误 差、数据获取的限制等原因, 导致了所面临的信息系 统往往是不完备的。 为处理这类问题, 王国胤[5]提出 了限制容差关系。 进一步,杨习贝[6]提出了一种新的 基于可变精度分类的拓展粗糙集模型, 对限制容差 关系进行了改进。 然而, 在实际工程应用中, 数据的 获取是需要付出一些成本或代价的, 称其为测试代 价。 针对该问题, Min 等[7⁃11]率先将测试代价引入到

·220 智能系统学报 第9卷 粗糙集的约简问题中,终究未能将测试代价引入到不 策系统,其中AcAr,x,y∈U,Va∈A,定义特征 完备信息系统环境下粗糙集本身的近似模型上。 函数如下所示: 1基本概念 1:P.(x)≠0 8.(x)= 0:P(x)=0 形式化地,信息系统可表示为四元组1、=〈U, 1:P.(x)nP.(y)≠0 A,V,月,其中U={x1,x2,…,xm}为研究对象的 o.(x,y)= 0:P(x)nP.(y)=☑ 有限集合,称为论域;A7={a1,a2,…,an}为描述 式中:P.(x)={aeA:f(x,a)已知}。 对象的全部属性所组成的集合;V=U。'为属性 定义5设TCSIIDS为测试代价敏感不完备决 集合A,的值域,其中Vn为属性a的值域;f:U×A7 策系统,其中AA,由A决定的可变精度分类关 V为信息函数,表示对每一个x∈U,a∈Ar,f(x, 系记为”且 a)∈V,。特别地,当信息系统中属性集A=A,UD且 Va=(x,y)EU:Va EP (x)np(y) A,∩D=⑦(其中A,为条件属性集合,D为决策属性 集合)时,信息系统也被称为决策系统。 ∑e(a)x.x) f(x,a)=f(y,a) ≥aUI 定义1)设S为不完备信息系统,ACA, 三e06 由A决定的可变精度分类关系记为:,且 其中:a∈[0,1]。 a={(x,y)∈U:a∈P4(x)∩P(y), 定义6设TCSIIDS为测试代价敏感不完备决策 P(x)∩Py) f (x,a)=f(y,a)- -≥aUIu 系统,ACA,对于VXcU,X基于可变精度分类关系 I P(x)I ·的下、上近似集分别记为4g`(X)和M(X) (1) 式中:P(x)={a∈A:f(x,a)已知},a∈[0,1], 4g.e`(X)={x∈U:Ve∴(x)cX} IXI表示集合X的基数,Iu为恒等关系且Iu= A(X)={x∈U:.(x)∩X≠0列 {(x,x):x∈U}。 式中:e(x)={y∈U:(x,y)ee}表示在测 定义26)设S为不完备信息系统,A二A7, 试代价敏感不完备决策系统中对象x的可变精度容 对于任意的XU,X基于可变精度分类关系:的 差类。 下、上近似集合分别记为A(X)和A(X): 3属性约简 A(X)={x∈U:(x)cX} 属性约简是粗糙理论的主要研究内容之一。然 A(X)={x∈U:(x)∩X☑} 而,寻找决策表的最小约简已被证明是一个NP-hard 式中:(x)={y∈U:(x,y)∈}表示对象x的 问题,在处理大规模数据时计算时间代价很大,针对 可变精度容差类。 这一问题,许多学者提出了许多高效的约简算法,启 2测试代价与可变精度分类粗糙集 发式搜索方法就是其中的一个典型代表。 定义7设TCSIIDS为测试代价敏感不完备决 不完备信息系统环境下的粗糙集模型未考虑数 据的代价问题,Mi等]将测试代价引入到信息系 策系统,a∈[0,1],U/IND(D)={X1,,Xn}表示 根据决策属性得到的所有决策类的合集,那么U/ 统中,具体的描述见定义3。 定义3[劉一个测试代价敏感的不完备决策系 ND(D)的近似质量可定义为 统TCSIIDS为一个五元组(U,AUD,V,f,c·〉, y(A,a,D)=1U{Ag(X):1≤j≤m}I/1UI U,A,UD,V和f的含义与第1节所示相同, 定理1令TCSIDS为测试代价敏感不完备决 c°:Ar={a1,a2,…,an}→R*U{0}为测试代价函 策系统,AcAT,若00,a:eAro (A,a,D)=y(AT,a,D)且HBCA,y(B,,D)≠ 定义4令TCSIDS为测试代价敏感不完备决 y(A,&,D)
粗糙集的约简问题中,终究未能将测试代价引入到不 完备信息系统环境下粗糙集本身的近似模型上。 1 基本概念 形式化地, 信息系统可表示为四元组 IS = 〈U, AT, V, f〉, 其中 U={x1 , x2 , … , xm }为研究对象的 有限集合, 称为论域; AT = {a1 , a2 , … , an }为描述 对象的全部属性所组成的集合; V = ∪ a Î AT Va为属性 集合 AT 的值域, 其中 Va为属性 a 的值域; f : U ´AT ®V 为信息函数, 表示对每一个 x ÎU, a ÎAT, f(x, a)ÎVa 。 特别地, 当信息系统中属性集 A = AT∪D 且 AT∩D=Æ(其中 AT 为条件属性集合, D 为决策属性 集合)时, 信息系统也被称为决策系统。 定义 1 [6] 设 S 为不完备信息系统, "A ÍAT , 由 A 决定的可变精度分类关系记为 V α A ,且 V α A = {(x, y) ÎU 2 : "a ÎPA(x) ∩ PA(y), f (x, a) = f (y, a) Ù | PA(x) ∩PA(y) | | PA(x) | ≥α} ∪IU (1) 式中:PA(x) = {a ÎA: f (x, a)已知}, α Î[0, 1], | X | 表示集合 X 的基数, IU 为恒等关系且 IU = {(x, x): x ÎU}。 定义 2 [6] 设 S 为不完备信息系统,"A ÍAT , 对于任意的 X ÍU, X 基于可变精度分类关系 V α A 的 下、上近似集合分别记为A- α V(X)和A - α V(X): A- α V(X) = {x ÎU : V α A(x) ÍX} A - α V(X) = {x ÎU :V α A(x) ∩ X ¹Æ} 式中:V α A(x) = {y ÎU : ( x, y)ÎV α A }表示对象 x 的 可变精度容差类。 2 测试代价与可变精度分类粗糙集 不完备信息系统环境下的粗糙集模型未考虑数 据的代价问题, Min 等[8]将测试代价引入到信息系 统中, 具体的描述见定义 3。 定义 3 [8] 一个测试代价敏感的不完备决策系 统 TCSIIDS 为一个五元组〈U, AT∪D, V, f, c ∗ 〉, U, AT ∪ D, V 和 f 的 含 义 与 第 1 节 所 示 相 同, c ∗ : AT = {a1 , a2 ,…,an }®R + ∪{0} 为测试代价函 数(R +表示正整数集), 即 c ∗ ( AT ) = ∑ | AT | i = 1 c ∗ ({ ai }), 其中 c ∗ ({ ai})表示单个属性 ai的测试代价。 本文 假设 所 有 属 性 的 测 试 代 价 均 为 正 整 数, 即 c ∗ ({ai})>0, aiÎAT 。 定义 4 令 TCSIIDS 为测试代价敏感不完备决 策系统, 其中 A ÍAT , "x, y ÎU, "a ÎA, 定义特征 函数如下所示: δ a(x) = 1:Pa(x) ≠ Æ {0:Pa(x) = Æ φa(x,y) = 1:Pa(x) ∩ Pa(y) ≠ Æ {0:Pa(x) ∩ Pa(y) = Æ 式中: Pa(x) = {a ÎA: f (x, a)已知}。 定义 5 设 TCSIIDS 为测试代价敏感不完备决 策系统, 其中 A ÍAT , 由 A 决定的可变精度分类关 系记为 V α,c∗ A 且 V α,c∗ A = {(x,y) ÎU 2 : "a ÎPa(x) ∩ Pa(y) f (x, a)= f (y, a) Ù ∑a∈A (c ∗ (a) × φa(x,y)) ∑a∈A (c ∗ (a) × δa(x)) ≥α} ∪IU 其中:α Î[0, 1 ]。 定义 6 设 TCSIIDS 为测试代价敏感不完备决策 系统, A ÍAT, 对于"X ÍU, X 基于可变精度分类关系 V α,c∗ A 的下、上近似集分别记为A- α,c∗ V (X)和A - α,c∗ V (X) A- α,c∗ V (X)= {x ÎU: V α,c∗ A (x)ÍX} A - α,c∗ V (X)= {x ÎU: V α,c∗ A (x)∩X ¹Æ} { 式中:V α,c∗ A (x) = {y ÎU: (x, y) ÎV α,c∗ A }表示在测 试代价敏感不完备决策系统中对象 x 的可变精度容 差类。 3 属性约简 属性约简是粗糙理论的主要研究内容之一。 然 而, 寻找决策表的最小约简已被证明是一个 NP⁃hard 问题, 在处理大规模数据时计算时间代价很大, 针对 这一问题, 许多学者提出了许多高效的约简算法, 启 发式搜索方法就是其中的一个典型代表。 定义 7 设 TCSIIDS 为测试代价敏感不完备决 策系统, α Î[0, 1], U/ IND(D)= {X1 ,¼,Xn }表示 根据决策属性得到的所有决策类的合集, 那么 U/ IND(D)的近似质量可定义为 γ(A, α, D) = | ∪ {A - α,c∗ V (Xj):1 ≤ j ≤ m} | / | U | 定理 1 令 TCSIIDS 为测试代价敏感不完备决 策系统, "A ÍAT, 若 0 <α1<α2<1, 则有 γ(A, α1 , D) ≤ γ(A, α2 , D) 证明 根据定义 6, 定理 1 易证。 定义 8 令 TCSIIDS 为测试代价敏感不完备决 策系统, α Î[0, 1], A ÍAT 为一个约简当且仅当 γ (A, α, D) = γ(AT, α, D)且"B ÌA, γ(B, α, D)¹ γ(A, α, D)。 ·220· 智 能 系 统 学 报 第 9 卷

第2期 鞠恒荣,等:不完备信息系统中测试代价敏感的可变精度分类粗糙集 .221. 令TCSIIDS为测试代价敏感决策系统,ae[0, 2)red←-g 1],VACAT,aeA,a,的重要度为 3)Ha:eA7,计算属性a:的重要度TCSLSigin(a:, LSigin (ai,A,D)=y(A,a,D)-y(A-a;,a,D) ArD); 可以看出,LSign(a,B,D)反映了a,从当前条 4)TCSLSigin (a;,Ar,D)=max TCSISigin (a:, 件属性集A中删除后近似质量的变化,相应地也可 Ar,D):a:eA,},则red←-a,计算y(red,a,D): 定义 5)若y(ed,a,D)y(Az,a,D),则重复以下循 ISig(a;,A,D)=y(A U a;,a,D)-y(A,a,D) 环,否则转6); 式中:a,∈A,-A,LSig(a:,A,D)用以度量向属性集A ①Va,eA,-red,计算TCSLSig(a:,red,D); 增加属性α,后近似质量的变化。根据上述属性的重要 ②若TCSLSig,(a:,B,D)=max{TCSLSigou(a:, 度可以设计启发式属性约简算法。Min等在文献[11] B,D):a,∈A,-red},则red←-a:; 中设计了传统的启发式算法(记为算法1)。其算法复 6)a:∈red,若y(red-a:,a,D)=y(Ar,a,D), 14 杂度为0(1A,IU1+∑1U1(1A,1-i+1)。 red red-a:,tmp =c'(red); 7)c'(red)=minc'(red),tmp Min等从获取约简的测试代价最小出发设计出 8)若0大于给定阈值,则0=0-6(此处8为步 新的约简算法,即回溯算法(记为算法2)。其算法 长,6>0)且重复2)~7),否则转9): 复杂度为0(2r-1)。详细算法见文献[11]。 9)输出red及c·(red)。 3.1考虑属性测试代价的启发式算法 3.2实验分析 由上文可知回溯算法的时间复杂度为O(24- 本节将通过实验,对比算法1、算法2和算法 1)。考虑到现实生活中存在着大量高维属性的数据, 3。表1列出了实验中使用的4组测试数据的基本 这样一种机制将会大大制约属性约简的时间。为解 信息,所有数据集均下载于UCI数据集。由于UCI 决这一问题,本文依然从启发式算法的角度出发,将 数据集中的大部分数据不含有测试代价,所以在本 属性的测试代价考虑到属性重要度定义中。为此,给 组实验中为每个数据集的属性随机增加了取值在 出如下的属性融合重要度定义。 [10,100]之间的测试代价。 TCSLSigin(a:,Ar,D)= 表1实验数据基本信息 0.1×LSigi(a,A7,D)+0.9×(c·(a:))° Table 1 Data sets descriptions TCSLSig (a:,Ar,D)= Decision 0.1 xLSig.(a,A7,D)+0.9×(c(a))° Data ID Data sets Samples Attributes Classes 式中:0≤0。可以看出,TCSLSig..(a:,A7,D)是LSig 1 Bridges 108 12 1 2 Credit Approval 263 3 (a:,A,D)与(c(a:)”之和。当9=0时,无论属性 3 Heart-Disease 303 14 的测试代价取何值,都有TCSLSigin(a:,Ar,D)=0.1× 4 Hepatitis 155 19 2 LSig(a:,A,D)+1,这说明TCSLSig.(a:,A7,D)的大 由于基于测试代价敏感的可变精度分类粗糙集 小与属性测试代价的大小无关,仅与LSig.(a:,Ar, 模型的下、上近似集由阈值α控制,因此,在实验 D)的值有关。随着0值的不断减小,(c(a:))°的值 中选取了10组不同的α值分别对比3个算法的测 也不断减小(本文随机产生测试代价在[10,100]), 试代价,在算法3的第8步中,给定阈值设为-5, 此时(c(a:)°在TCSLSig.(a:,A7,D)中所占的比重 步长δ为0.5,即重复求得10次约简,取其中的最 也越来越小,表明属性测试代价在属性的重要度中 小测试代价作为输出。具体的实验结果见图1。 的影响作用越来越小。根据新的属性融合重要度, ×109 7 不难设计出综合考虑了测试代价的启发式算法,具 算法1 6 算法2 体算法流程见算法1。 ★ 24 算法3 算法1基于测试代价敏感不完备决策系统 TCSIIDS综合考虑测试代价的启发式算法 输入:测试代价敏感不完备决策系统TCSIIDS,a; 0 0.10.20.30.40.50.60.70.80.91.0 输出:约简red及约简的测试代价c·(red)。 1)计算y(4,a,D):令=0,c(d)=c(4): (a)Bridges
令 TCSIIDS 为测试代价敏感决策系统, α Î[0, 1], "A ÍAT, "aiÎA, ai的重要度为 LSigin(ai, A, D) = γ(A, α, D) -γ(A -ai, α, D) 可以看出, LSigin(ai, B, D)反映了 ai从当前条 件属性集 A 中删除后近似质量的变化, 相应地也可 定义 LSigout(ai, A, D) = γ(A ∪ ai, α, D) -γ(A, α, D) 式中:aiÎAT -A, LSigout(ai,A, D)用以度量向属性集 A 增加属性 ai后近似质量的变化。 根据上述属性的重要 度可以设计启发式属性约简算法。 Min 等在文献[11] 中设计了传统的启发式算法(记为算法 1)。 其算法复 杂度为 O( |AT | |U| +∑ | AT | i = 1 |U|( |AT | -i+1))。 Min 等从获取约简的测试代价最小出发设计出 新的约简算法, 即回溯算法(记为算法 2)。 其算法 复杂度为 O(2 | AT | -1)。 详细算法见文献[11]。 3.1 考虑属性测试代价的启发式算法 由上文可知回溯算法的时间复杂度为 O(2 | AT | - 1)。 考虑到现实生活中存在着大量高维属性的数据, 这样一种机制将会大大制约属性约简的时间。 为解 决这一问题, 本文依然从启发式算法的角度出发, 将 属性的测试代价考虑到属性重要度定义中。 为此, 给 出如下的属性融合重要度定义。 TCSLSigin(ai, AT , D) = 0.1 ´LSigin(ai, AT , D) + 0.9 ´(c ∗ (ai)) θ TCSLSigout(ai, AT , D) = 0.1 ´LSigout(ai, AT , D) + 0.9 ´(c ∗ (ai)) θ 式中:θ≤ 0。 可以看出, TCSLSigin(ai,AT,D)是 LSigin (ai, AT, D)与(c ∗ (ai)) θ 之和。 当 θ= 0 时, 无论属性 的测试代价取何值, 都有 TCSLSigin(ai,AT,D)= 0.1 ´ LSigin (ai,AT,D)+1, 这说明 TCSLSigin(ai,AT,D)的大 小与属性测试代价的大小无关, 仅与 LSigin (ai,AT, D)的值有关。 随着 θ 值的不断减小, (c ∗ (ai)) θ 的值 也不断减小(本文随机产生测试代价在[10, 100]), 此时(c ∗ (ai)) θ 在 TCSLSigin(ai,AT,D)中所占的比重 也越来越小, 表明属性测试代价在属性的重要度中 的影响作用越来越小。 根据新的属性融合重要度, 不难设计出综合考虑了测试代价的启发式算法, 具 体算法流程见算法 1。 算法 1 基于测试代价敏感不完备决策系统 TCSIIDS 综合考虑测试代价的启发式算法 输入:测试代价敏感不完备决策系统 TCSIIDS, α; 输出:约简 red 及约简的测试代价 c ∗ (red)。 1)计算 γ(AT, α, D); 令θ=0, c ∗ (red)= c ∗ (AT); 2) red ¬Æ; 3)"aiÎAT , 计算属性 ai的重要度 TCSLSigin(ai, AT ,D); 4)若 TCSLSigin(aj,AT,D) = max{TCSLSigin(ai, AT,D): aiÎAT}, 则 red ¬aj,计算 γ(red,α,D); 5)若 γ(red,α,D)¹γ(AT ,α,D), 则重复以下循 环, 否则转 6); ①"aiÎAT -red,计算 TCSLSigout(ai,red,D); ②若 TCSLSigout(ai,B,D) = max{TCSLSigout( ai, B,D): aiÎAT -red},则 red ¬ai; 6)"aiÎred, 若 γ(red -ai,α,D)= γ(AT ,α,D), 则 red = red -ai, tmp = c ∗ (red); 7)c ∗ (red)= min{c ∗ (red), tmp}; 8)若 θ 大于给定阈值, 则 θ = θ -δ(此处 δ 为步 长,δ>0)且重复 2) ~7),否则转 9); 9)输出 red 及 c ∗ (red)。 3.2 实验分析 本节将通过实验, 对比算法 1、算法 2 和算法 3。 表 1 列出了实验中使用的 4 组测试数据的基本 信息, 所有数据集均下载于 UCI 数据集。 由于 UCI 数据集中的大部分数据不含有测试代价, 所以在本 组实验中为每个数据集的属性随机增加了取值在 [10, 100]之间的测试代价。 表 1 实验数据基本信息 Table 1 Data sets descriptions Data ID Data sets Samples Attributes Decision Classes 1 Bridges 108 12 7 2 Credit Approval 263 15 3 3 Heart⁃Disease 303 14 5 4 Hepatitis 155 19 2 由于基于测试代价敏感的可变精度分类粗糙集 模型的下、上近似集由阈值 α 控制, 因此, 在实验 中选取了 10 组不同的 α 值分别对比 3 个算法的测 试代价, 在算法 3 的第 8 步中, 给定阈值设为-5, 步长 δ 为 0.5, 即重复求得 10 次约简, 取其中的最 小测试代价作为输出。 具体的实验结果见图 1。 (a)Bridges 第 2 期 鞠恒荣,等:不完备信息系统中测试代价敏感的可变精度分类粗糙集 ·221·
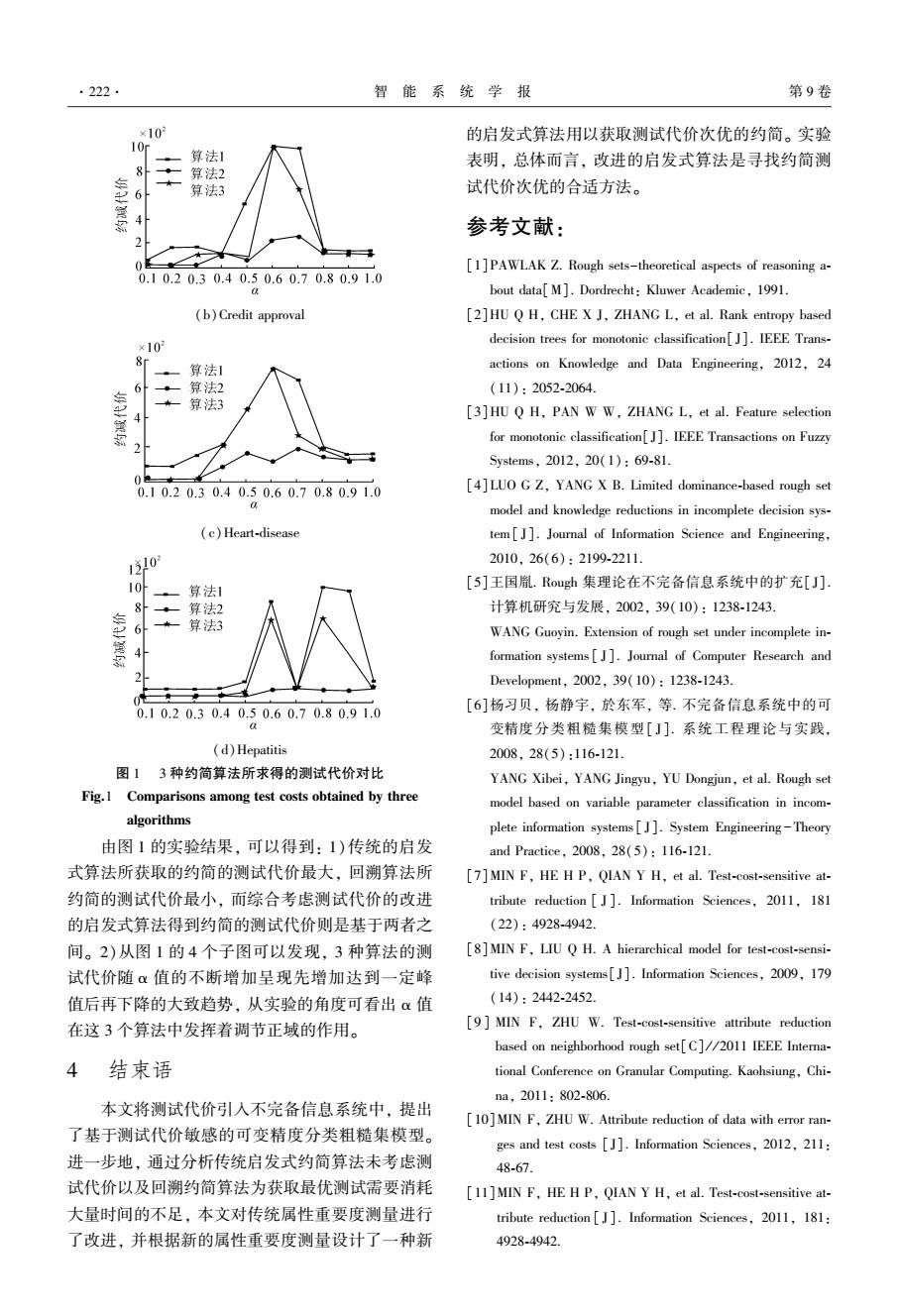
.222. 智能系统学报 第9卷 ×10 的启发式算法用以获取测试代价次优的约简。实验 10r 算法1 表明,总体而言,改进的启发式算法是寻找约简测 ·一算法2 ★一 6 算法3 试代价次优的合适方法。 参考文献: 0 [1]PAWLAK Z.Rough sets-theoretical aspects of reasoning a- 0.10.20.30.40.50.60.70.80.91.0 bout data[M].Dordrecht:Kluwer Academic,1991 (b)Credit approval [2]HU Q H,CHE X J,ZHANG L,et al.Rank entropy based ×10 decision trees for monotonic classification[J].IEEE Trans- 算法1 actions on Knowledge and Data Engineering,2012,24 6 算法2 (11):2052-2064. ★一 算法3 4 [3]HU Q H,PAN WW,ZHANG L,et al.Feature selection for monotonic classification[.IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems.2012,20(1):69-81. 0.10.20.30.40.50.60.70.80.91.0 [4]LUO G Z,YANG X B.Limited dominance-based rough set 以 model and knowledge reductions in incomplete decision sys- (c)Heart-disease tem[].Journal of Information Science and Engineering, 110 2010,26(6):2199-2211. 10 算法1 [5]王国胤.Rough集理论在不完备信息系统中的扩充[J]. 算法2 计算机研究与发展,2002,39(10):1238-1243。 42 6 算法3 WANG Guoyin.Extension of rough set under incomplete in- formation systems[J].Journal of Computer Research and Development,.2002,39(10):1238-1243. 0 0.10.20.30.40.50.60.70.80.91.0 [6]杨习贝,杨静宇,於东军,等.不完备信息系统中的可 变精度分类粗糙集模型[J].系统工程理论与实践, (d)Hepatitis 2008,28(5):116-121 图13种约简算法所求得的测试代价对比 YANG Xibei,YANG Jingyu,YU Dongjun,et al.Rough set Fig.1 Comparisons among test costs obtained by three model based on variable parameter classification in incom- algorithms plete information systems[J].System Engineering-Theory 由图1的实验结果,可以得到:1)传统的启发 and Practice,2008,28(5):116-121. 式算法所获取的约简的测试代价最大,回溯算法所 [7]MIN F,HE H P,QIAN Y H,et al.Test-cost-sensitive at- 约简的测试代价最小,而综合考虑测试代价的改进 tribute reduction J].Information Sciences,2011,181 的启发式算法得到约简的测试代价则是基于两者之 (22):4928-4942. 间。2)从图1的4个子图可以发现,3种算法的测 [8]MIN F,LIU Q H.A hierarchical model for test-cost-sensi- 试代价随α值的不断增加呈现先增加达到一定峰 tive decision systems[J].Information Sciences,2009,179 值后再下降的大致趋势,从实验的角度可看出α值 (14):2442-2452. 在这3个算法中发挥着调节正域的作用。 [9]MIN F,ZHU W.Test-cost-sensitive attribute reduction based on neighborhood rough set[C]//2011 IEEE Interna- 4结束语 tional Conference on Granular Computing.Kaohsiung,Chi- na,2011:802-806. 本文将测试代价引入不完备信息系统中,提出 [10]MIN F,ZHU W.Attribute reduction of data with error ran- 了基于测试代价敏感的可变精度分类粗糙集模型。 ges and test costs [J].Information Sciences,2012,211: 进一步地,通过分析传统启发式约简算法未考虑测 48-67. 试代价以及回溯约简算法为获取最优测试需要消耗 [11]MIN F,HE H P,QIAN Y H,et al.Test-cost-sensitive at- 大量时间的不足,本文对传统属性重要度测量进行 tribute reduction[J].Information Sciences,2011,181: 了改进,并根据新的属性重要度测量设计了一种新 4928.4942
(b)Credit approval (c)Heart⁃disease (d)Hepatitis 图 1 3 种约简算法所求得的测试代价对比 Fig.1 Comparisons among test costs obtained by three algorithms 由图 1 的实验结果, 可以得到: 1)传统的启发 式算法所获取的约简的测试代价最大, 回溯算法所 约简的测试代价最小, 而综合考虑测试代价的改进 的启发式算法得到约简的测试代价则是基于两者之 间。 2)从图 1 的 4 个子图可以发现, 3 种算法的测 试代价随 α 值的不断增加呈现先增加达到一定峰 值后再下降的大致趋势, 从实验的角度可看出 α 值 在这 3 个算法中发挥着调节正域的作用。 4 结束语 本文将测试代价引入不完备信息系统中, 提出 了基于测试代价敏感的可变精度分类粗糙集模型。 进一步地, 通过分析传统启发式约简算法未考虑测 试代价以及回溯约简算法为获取最优测试需要消耗 大量时间的不足, 本文对传统属性重要度测量进行 了改进, 并根据新的属性重要度测量设计了一种新 的启发式算法用以获取测试代价次优的约简。 实验 表明, 总体而言, 改进的启发式算法是寻找约简测 试代价次优的合适方法。 参考文献: [1]PAWLAK Z. Rough sets-theoretical aspects of reasoning a⁃ bout data[M]. Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic, 1991. [2]HU Q H, CHE X J, ZHANG L, et al. Rank entropy based decision trees for monotonic classification[ J]. IEEE Trans⁃ actions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2012, 24 (11): 2052⁃2064. [3]HU Q H, PAN W W, ZHANG L, et al. Feature selection for monotonic classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2012, 20(1): 69⁃81. [4]LUO G Z, YANG X B. Limited dominance⁃based rough set model and knowledge reductions in incomplete decision sys⁃ tem[ J]. Journal of Information Science and Engineering, 2010, 26(6): 2199⁃2211. [5]王国胤. Rough 集理论在不完备信息系统中的扩充[ J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2002, 39(10): 1238⁃1243. WANG Guoyin. Extension of rough set under incomplete in⁃ formation systems [ J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2002, 39(10): 1238⁃1243. [6]杨习贝, 杨静宇, 於东军, 等. 不完备信息系统中的可 变精度分类粗糙集模型[ J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2008, 28(5):116⁃121. YANG Xibei, YANG Jingyu, YU Dongjun, et al. Rough set model based on variable parameter classification in incom⁃ plete information systems [ J]. System Engineering - Theory and Practice, 2008, 28(5): 116⁃121. [7]MIN F, HE H P, QIAN Y H, et al. Test⁃cost⁃sensitive at⁃ tribute reduction [ J ]. Information Sciences, 2011, 181 (22): 4928⁃4942. [8]MIN F, LIU Q H. A hierarchical model for test⁃cost⁃sensi⁃ tive decision systems[ J]. Information Sciences, 2009, 179 (14): 2442⁃2452. [9 ] MIN F, ZHU W. Test⁃cost⁃sensitive attribute reduction based on neighborhood rough set[C] / / 2011 IEEE Interna⁃ tional Conference on Granular Computing. Kaohsiung, Chi⁃ na, 2011: 802⁃806. [10]MIN F, ZHU W. Attribute reduction of data with error ran⁃ ges and test costs [ J]. Information Sciences, 2012, 211: 48⁃67. [11]MIN F, HE H P, QIAN Y H, et al. Test⁃cost⁃sensitive at⁃ tribute reduction [ J]. Information Sciences, 2011, 181: 4928⁃4942. ·222· 智 能 系 统 学 报 第 9 卷

第2期 鞠恒荣,等:不完备信息系统中测试代价敏感的可变精度分类粗糙集 .223, 作者简介: 杨习贝,男,1980年生,副教授, 鞠恒荣,男,1989年生,硕士研究 博士(后),江苏省青蓝工程优秀青年 生,主要研究方向为粗糙集,主持江苏 骨干教师。主要研究方向为粗糙集、粒 省普通高校研究生科研创新计划项目 计算、知识工程、人工智能等。近年来, 一项。 发表学术论文60余篇,出版英文学术 专著一部。现主持国家自然科学基金、 江苏省自然科学基金等多项科研项目。 马兴斌,男,1992年生,硕士研究 生,主要研究方向为粗糙集。 第11届全球智能控制与自动化大会(WCICA2014) The 11th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation(WCICA2014) The 11th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation (WCICA 2014)will be held in Shenyang,China, from June 27 to 30,2014.WCICA 2014 is technically sponsored by IEEE Robotics and Automation Society,IEEE Control Systems Society,National Natural Science Foundation of China,the Chinese Association of Automation,and the Chinese Association of Artificial Intelligence. WCICA 2014 features plenary keynotes and plenary panel discussion sessions by the world leading researchers as well as awards to honor outstanding papers presented at this Congress.The awards include Best Paper on Theory,Best Paper on Applications,Best Student Paper,Best Poster Paper,Best Paper on Biomedical Biosystem Related Areas,SUPCON Best Paper on Industrial Automation,and AIAG Best Paper on Supply Chain Related Topics. Moreover,we are in the process to arrange post-conference publication of a selected group of accepted papers at WCI- CA 2014 in more than ten leading international journals and top Chinese journals as special issues,among them are IEEE/ ASME Transactions on Mechatronics,IEEE Transactions on Robotics,IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,IEEE Transactions on Systems,Man,and Cybernetics,Part B,and Acta Automation Sinica. It is our great pleasure to invite you to submit your original research papers to the Congress.WCICA 2014 also wel- comes proposals for organizing Focused Theme Sessions on the conference topics,Tutorials and Workshops on emerging topics.You are invited to submit focused theme session proposals to Prof.Simon X.Yang (syang@uoguelph.ca)before Dec.1,2013.Please refer to the Congress website for details. Website:http://2014.wcica.info/index.shtml. Tel:02483681047-8013. E-mail:wcica2014@gmail.com
作者简介: 鞠恒荣, 男, 1989 年生,硕士研究 生,主要研究方向为粗糙集, 主持江苏 省普通高校研究生科研创新计划项目 一项。 马兴斌, 男, 1992 年生, 硕士研究 生, 主要研究方向为粗糙集。 杨习贝, 男, 1980 年生, 副教授, 博士(后), 江苏省青蓝工程优秀青年 骨干教师。 主要研究方向为粗糙集、粒 计算、知识工程、人工智能等。 近年来, 发表学术论文 60 余篇, 出版英文学术 专著一部。 现主持国家自然科学基金、 江苏省自然科学基金等多项科研项目。 第 11 届全球智能控制与自动化大会(WCICA2014) The 11th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation(WCICA2014) The 11th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation (WCICA 2014) will be held in Shenyang, China, from June 27 to 30, 2014. WCICA 2014 is technically sponsored by IEEE Robotics and Automation Society, IEEE Control Systems Society, National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Chinese Association of Automation, and the Chinese Association of Artificial Intelligence. WCICA 2014 features plenary keynotes and plenary panel discussion sessions by the world leading researchers as well as awards to honor outstanding papers presented at this Congress. The awards include Best Paper on Theory, Best Paper on Applications, Best Student Paper, Best Poster Paper, Best Paper on Biomedical & Biosystem Related Areas, SUPCON Best Paper on Industrial Automation, and AIAG Best Paper on Supply Chain Related Topics. Moreover, we are in the process to arrange post⁃conference publication of a selected group of accepted papers at WCI⁃ CA 2014 in more than ten leading international journals and top Chinese journals as special issues, among them are IEEE/ ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, IEEE Transactions on Robotics, IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B, and Acta Automation Sinica. It is our great pleasure to invite you to submit your original research papers to the Congress. WCICA 2014 also wel⁃ comes proposals for organizing Focused Theme Sessions on the conference topics, Tutorials and Workshops on emerging topics. You are invited to submit focused theme session proposals to Prof. Simon X. Yang ( syang@ uoguelph.ca) before Dec. 1, 2013. Please refer to the Congress website for details. Website: http: / / 2014.wcica.info / index.shtml. Tel: 02483681047⁃8013. E⁃mail: wcica2014@ gmail.com. 第 2 期 鞠恒荣,等:不完备信息系统中测试代价敏感的可变精度分类粗糙集 ·223·