
Chapter 9 Molecular Structure x§9.1 Valence Bond Theory x§9.2 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR)Theory x§9.3 Molecular Orbital Theory ק9.4 Bond Parameters
Chapter 9 Molecular Structure §9.1 Valence Bond Theory §9.4 Bond Parameters §9.3 Molecular Orbital Theory §9.2 Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion (VSEPR) Theory

§9.1 Valence Bond Theory (VB) -9.1.1 The Essence and Characteristics of Covalent Bond -9.1.2 The Types of Covalent Bond 9.1.3 Hybrid Orbits 返 回
9.1.1 The Essence and Characteristics of Covalent Bond §9.1 Valence Bond Theory (VB) 9.1.3 Hybrid Orbits 9.1.2 The Types of Covalent Bond
9.1.1 The essence and characteristics of covalent bond Chemical bonding: A chemical bonding is an interaction between atoms or molecules and allows the formation of polyatomic chemical compounds. The theory of chemical bonding consists of 1)The ionic bond theory,2)The metallic bond theory and 3)The covalent bond theory Theories development on molecular structure: Lewis theory (1916)->Valence bond theory(1927) >Molecular obital theory(1929)->Hybrid orbit theory (1931)->Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (1940).…
1)The ionic bond theory, 9.1.1 The essence and characteristics of covalent bond Chemical bonding : A chemical bonding is an interaction between atoms or molecules and allows the formation of polyatomic chemical compounds. The theory of chemical bonding consists of : 2) The metallic bond theory and 3) The covalent bond theory Theories development on molecular structure: Lewis theory (1916) → Valence bond theory(1927) →Molecular obital theory(1929) → Hybrid orbit theory (1931) → Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory (1940)……
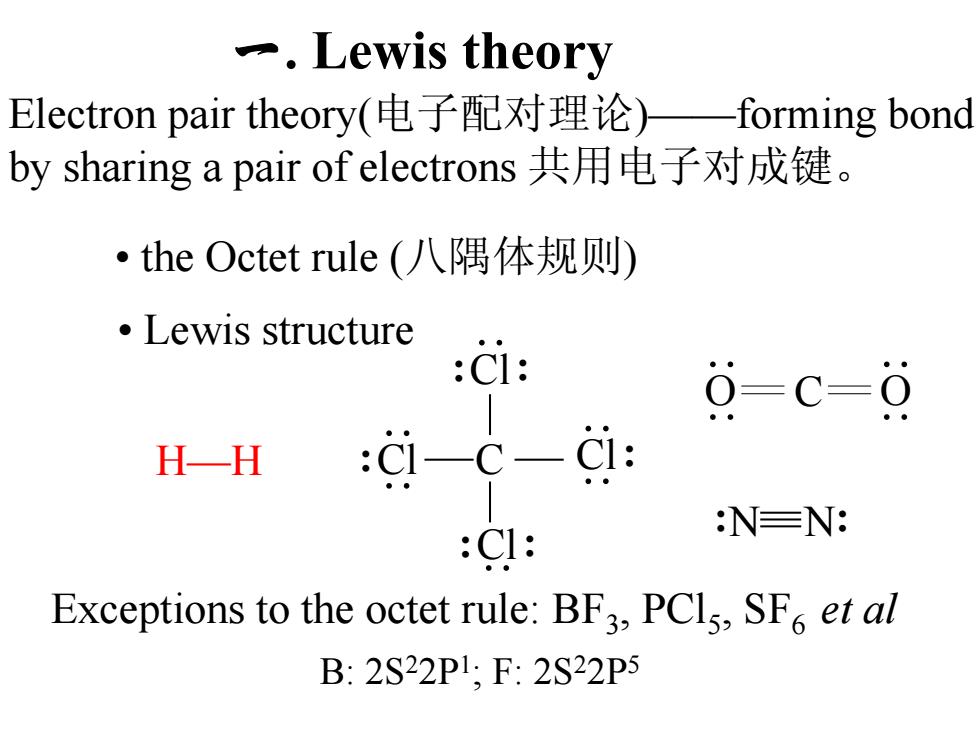
Lewis theory Electron pair theory(电子配对理论)一forming bond by sharing a pair of electrons共用电子对成键。 ·the Octet rule(八隅体规则) ●Lewis structure CI: 0=c=0 H一H :c-c-d: NEN: :CI: Exceptions to the octet rule:BF3,PCls,SF et al B:2S22P1,F:2S22P5
一. Lewis theory Electron pair theory(电子配对理论)——forming bond by sharing a pair of electrons 共用电子对成键。 Exceptions to the octet rule: BF3, PCl5, SF6 et al • Lewis structure • the Octet rule (八隅体规则) H—H :Cl ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ Cl: ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ :Cl: ⋅⋅ :Cl: ⋅⋅ C :N N: O ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ C O ⋅⋅ ⋅⋅ B: 2S22P1; F: 2S22P5
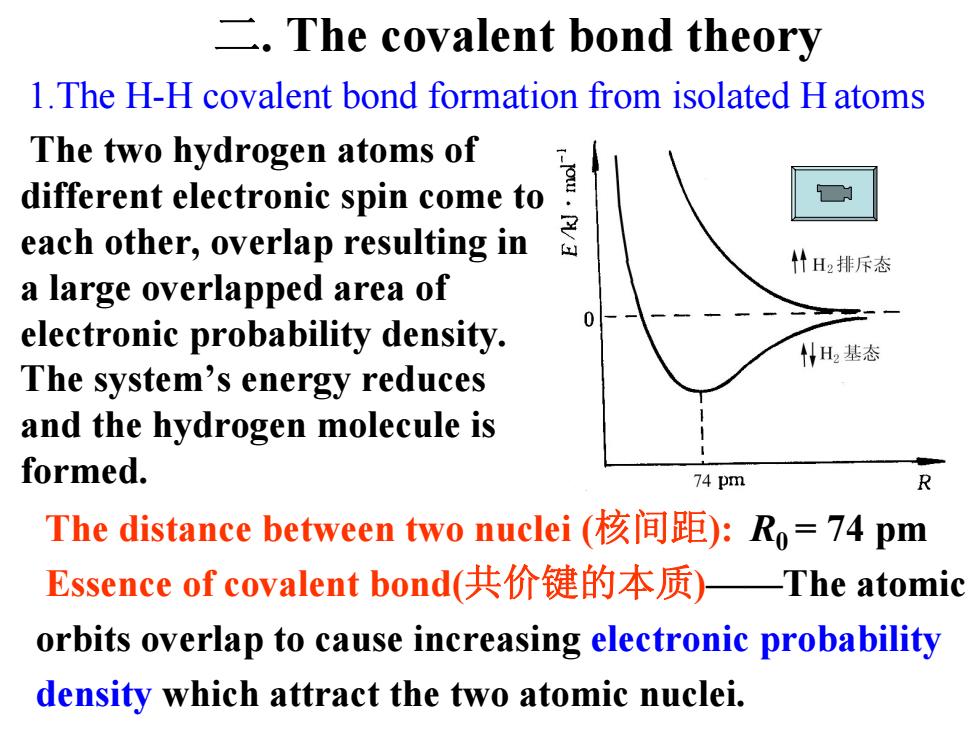
The covalent bond theory 1.The H-H covalent bond formation from isolated H atoms The two hydrogen atoms of each other,.overlap resulting边。 different electronic spin come to 什H2排斥态 a large overlapped area of electronic probability density. 05 WH基态 The system's energy reduces and the hydrogen molecule is formed. 74 pm R The distance between two nuclei(核间距):R,=74pm Essence of covalent bond(共价键的本质)—The atomic orbits overlap to cause increasing electronic probability density which attract the two atomic nuclei
1.The H-H covalent bond formation from isolated H atoms The two hydrogen atoms of different electronic spin come to each other, overlap resulting in a large overlapped area of electronic probability density. The system’s energy reduces and the hydrogen molecule is formed. The distance between two nuclei (核间距): R0 = 74 pm Essence of covalent bond(共价键的本质 )——The atomic orbits overlap to cause increasing electronic probability density which attract the two atomic nuclei. 二. The covalent bond theory
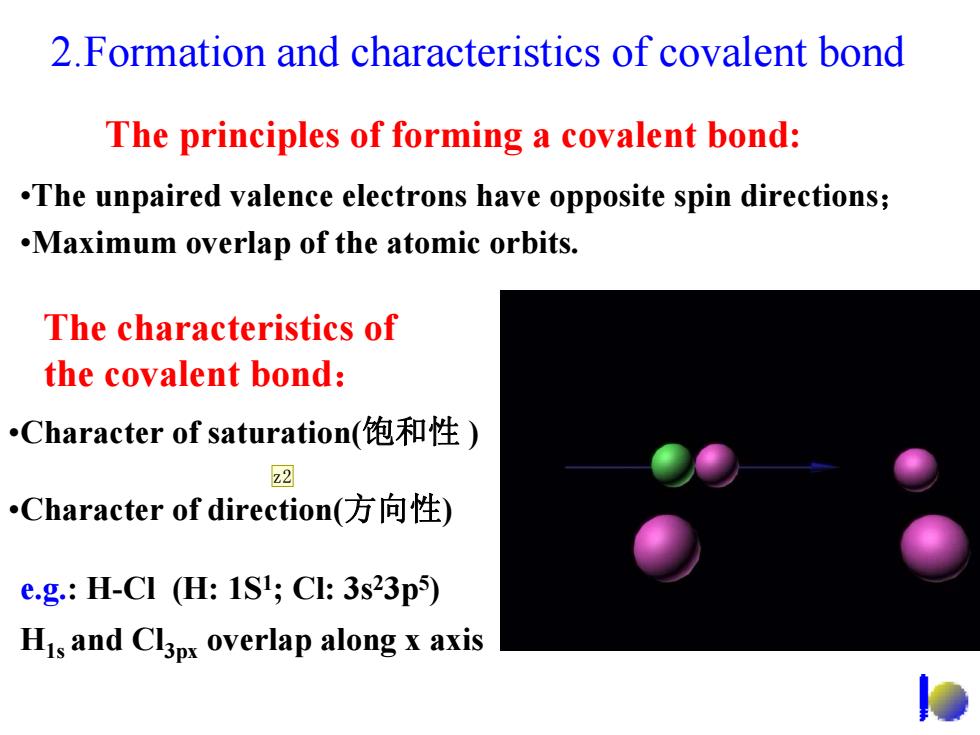
2.Formation and characteristics of covalent bond The principles of forming a covalent bond: .The unpaired valence electrons have opposite spin directions; .Maximum overlap of the atomic orbits. The characteristics of the covalent bond: Character of saturation(饱和性) 22 Character of direction(方向性) e.g.:H-CI (H:1S1;Cl:3s23p5) His and Cl3px overlap along x axis
2.Formation and characteristics of covalent bond The principles of forming a covalent bond: •The unpaired valence electrons have opposite spin directions; •Maximum overlap of the atomic orbits. The characteristics of the covalent bond : •Character of direction(方向性 ) •Character of saturation(饱和性 ) e.g.: H-Cl (H: 1S 1; Cl: 3s 23p 5 ) H1s and Cl3px overlap along x axis z2

幻灯片6 的 子间成键是两个原子的未成对电子的配对,每个原子的未成对电子数是一定的,可提供的成键轨道数也是一定的,所以,最多成键数也是一定 的 ang,.2007-11-16
幻灯片 6 z2 原子间成键是两个原子的未成对电子的配对,每个原子的未成对电子数是一定的,可提供的成键轨道数也是一定的,所以,最多成键数也是一定 的 zhang, 2007-11-16

9.1.2 The types of covalmd 1.o bonds: o bonds arise from the overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis..(头碰头重叠). s·s轨道形成键 Symmetry of o bond:o symmetry,i.e., rotation of any angle around the x axis, both shape and symbols are unchanged 8-p,轨道形成。键 o bonds have much overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis
1.σ bonds: σ bonds arise from the overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis. (头碰头重叠). Symmetry of σ bond:σ symmetry, i.e., rotation of any angle around the x axis, both shape and symbols are unchanged σ bonds have much overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis. 9.1.2 The types of covalent bond
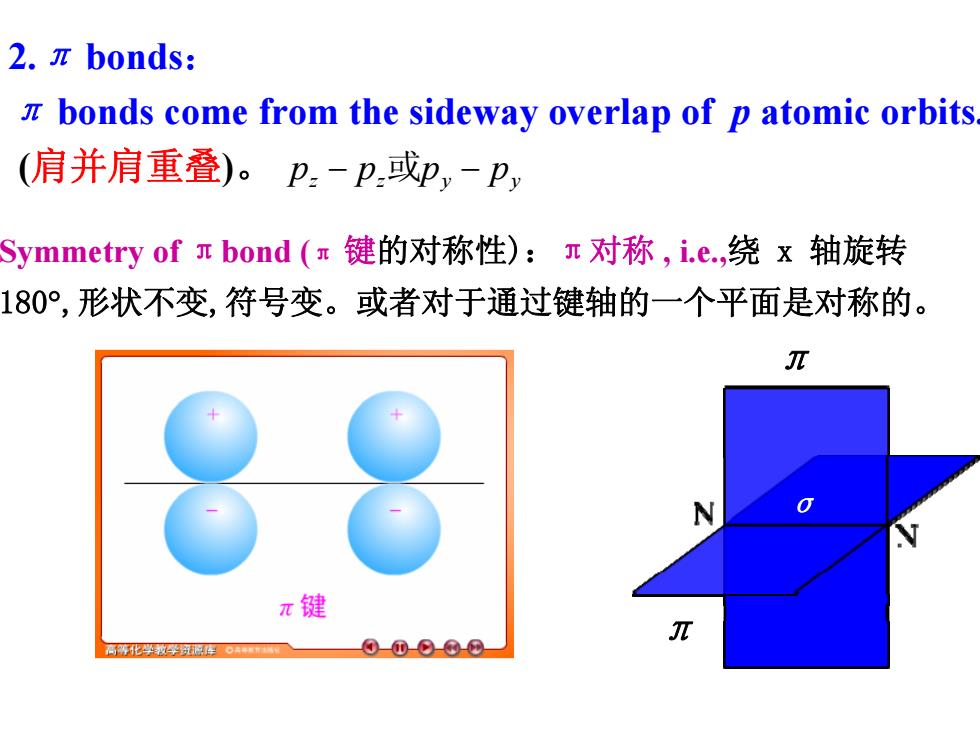
2.πbonds: z bonds come from the sideway overlap of p atomic orbits (肩并肩重叠)。p-p或p,-P, Symmetry of n bond(π键的对称性):r对称,i.e.,绕x轴旋转 180°,形状不变,符号变。或者对于通过键轴的一个平面是对称的。 π N π键 π 高鸦化学被学别形库。+ 0-①-9-©-@
2.π bonds: π bonds come from the sideway overlap of p atomic orbits. (肩并肩重叠)。 z z y y p − p 或p − p Symmetry of πbond (π 键的对称性):π对称 , i.e.,绕 x 轴旋转 180°,形状不变,符号变。或者对于通过键轴的一个平面是对称的。 σ π π

o bonds have much overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis,while n bonds have less overlap, resulting in that o bonds are relatively stronger than x bonds
σ bonds have much overlap of atomic orbits along the internuclear axis, while π bonds have less overlap, resulting in that σ bonds are relatively stronger than π bonds